Exploring QLED in Augmented Reality Applications
JUN 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
QLED AR Tech Evolution
The evolution of QLED technology in augmented reality (AR) applications represents a significant advancement in display technology. QLED, or Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode, has emerged as a promising solution for AR devices due to its superior color reproduction, brightness, and energy efficiency.
The journey of QLED in AR began with the development of quantum dot technology in the early 2000s. Initially used in LCD displays, quantum dots were recognized for their potential to enhance color accuracy and brightness. As AR technology gained traction, researchers began exploring ways to integrate QLED into compact, wearable devices.
A key milestone in this evolution was the miniaturization of QLED displays. Early prototypes were bulky and impractical for AR applications. However, advancements in manufacturing processes and materials science led to the creation of micro-LED displays, which paved the way for QLED integration in AR headsets.
The mid-2010s saw the first successful demonstrations of QLED-based AR displays. These early models showcased improved color gamut and contrast ratios compared to traditional OLED or LCD displays. However, challenges remained in areas such as power consumption and heat dissipation.
From 2018 to 2020, significant progress was made in addressing these challenges. Researchers developed more efficient quantum dot materials and improved the overall system architecture of QLED displays. This resulted in AR prototypes with higher brightness levels and lower power requirements, making them more suitable for extended use.
The most recent phase of QLED AR evolution, from 2021 onwards, has focused on enhancing the user experience. Developments in this period include improved refresh rates, reduced latency, and wider field of view. These advancements have been crucial in creating more immersive and realistic AR experiences.
Currently, QLED AR technology is on the cusp of commercial viability. Major tech companies are investing heavily in research and development, with several announcing plans to release QLED-based AR devices in the near future. The technology is expected to revolutionize various sectors, including gaming, education, and industrial applications.
Looking ahead, the evolution of QLED in AR is likely to continue at a rapid pace. Future developments may include further miniaturization, integration with advanced optics for improved depth perception, and the incorporation of AI for enhanced image processing. As the technology matures, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of QLED-based AR devices across various industries and consumer applications.
The journey of QLED in AR began with the development of quantum dot technology in the early 2000s. Initially used in LCD displays, quantum dots were recognized for their potential to enhance color accuracy and brightness. As AR technology gained traction, researchers began exploring ways to integrate QLED into compact, wearable devices.
A key milestone in this evolution was the miniaturization of QLED displays. Early prototypes were bulky and impractical for AR applications. However, advancements in manufacturing processes and materials science led to the creation of micro-LED displays, which paved the way for QLED integration in AR headsets.
The mid-2010s saw the first successful demonstrations of QLED-based AR displays. These early models showcased improved color gamut and contrast ratios compared to traditional OLED or LCD displays. However, challenges remained in areas such as power consumption and heat dissipation.
From 2018 to 2020, significant progress was made in addressing these challenges. Researchers developed more efficient quantum dot materials and improved the overall system architecture of QLED displays. This resulted in AR prototypes with higher brightness levels and lower power requirements, making them more suitable for extended use.
The most recent phase of QLED AR evolution, from 2021 onwards, has focused on enhancing the user experience. Developments in this period include improved refresh rates, reduced latency, and wider field of view. These advancements have been crucial in creating more immersive and realistic AR experiences.
Currently, QLED AR technology is on the cusp of commercial viability. Major tech companies are investing heavily in research and development, with several announcing plans to release QLED-based AR devices in the near future. The technology is expected to revolutionize various sectors, including gaming, education, and industrial applications.
Looking ahead, the evolution of QLED in AR is likely to continue at a rapid pace. Future developments may include further miniaturization, integration with advanced optics for improved depth perception, and the incorporation of AI for enhanced image processing. As the technology matures, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of QLED-based AR devices across various industries and consumer applications.
AR Market Demand Analysis
The augmented reality (AR) market has been experiencing significant growth and transformation, driven by advancements in display technologies such as QLED. The demand for AR applications is rapidly expanding across various sectors, including gaming, education, healthcare, and industrial manufacturing.
In the consumer market, AR-enabled devices are gaining traction, with a particular focus on enhancing user experiences in gaming and entertainment. The integration of QLED technology in AR displays promises to deliver more vibrant colors, higher contrast ratios, and improved energy efficiency, addressing key consumer demands for immersive and visually stunning AR experiences.
The enterprise sector is also showing increased interest in AR solutions, particularly in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. These industries are leveraging AR for training, maintenance, and complex assembly tasks. The potential of QLED in AR applications is particularly appealing in these sectors, as it can provide clearer and more detailed visual information, crucial for precision work and reducing errors.
Education and e-learning platforms are another area where AR market demand is surging. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote learning solutions, and AR technologies are being explored to create more engaging and interactive educational experiences. QLED's superior color reproduction and brightness could significantly enhance the quality of educational content delivered through AR platforms.
In the retail sector, AR is revolutionizing the shopping experience, allowing customers to virtually try on products or visualize items in their homes before purchase. The integration of QLED technology in AR displays could provide more accurate color representation and improved visual fidelity, potentially increasing consumer confidence in making purchasing decisions based on AR previews.
The healthcare industry is also showing a growing interest in AR applications, particularly for surgical planning, medical training, and patient education. QLED's potential to deliver high-resolution, color-accurate displays could be particularly valuable in medical imaging and visualization applications, where precise color reproduction is critical.
As 5G networks continue to roll out globally, the demand for AR applications is expected to surge further. The low latency and high bandwidth of 5G networks will enable more sophisticated and responsive AR experiences, creating new opportunities for QLED-enhanced AR displays in both consumer and enterprise markets.
In the consumer market, AR-enabled devices are gaining traction, with a particular focus on enhancing user experiences in gaming and entertainment. The integration of QLED technology in AR displays promises to deliver more vibrant colors, higher contrast ratios, and improved energy efficiency, addressing key consumer demands for immersive and visually stunning AR experiences.
The enterprise sector is also showing increased interest in AR solutions, particularly in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. These industries are leveraging AR for training, maintenance, and complex assembly tasks. The potential of QLED in AR applications is particularly appealing in these sectors, as it can provide clearer and more detailed visual information, crucial for precision work and reducing errors.
Education and e-learning platforms are another area where AR market demand is surging. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote learning solutions, and AR technologies are being explored to create more engaging and interactive educational experiences. QLED's superior color reproduction and brightness could significantly enhance the quality of educational content delivered through AR platforms.
In the retail sector, AR is revolutionizing the shopping experience, allowing customers to virtually try on products or visualize items in their homes before purchase. The integration of QLED technology in AR displays could provide more accurate color representation and improved visual fidelity, potentially increasing consumer confidence in making purchasing decisions based on AR previews.
The healthcare industry is also showing a growing interest in AR applications, particularly for surgical planning, medical training, and patient education. QLED's potential to deliver high-resolution, color-accurate displays could be particularly valuable in medical imaging and visualization applications, where precise color reproduction is critical.
As 5G networks continue to roll out globally, the demand for AR applications is expected to surge further. The low latency and high bandwidth of 5G networks will enable more sophisticated and responsive AR experiences, creating new opportunities for QLED-enhanced AR displays in both consumer and enterprise markets.
QLED AR Tech Challenges
The integration of QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology into Augmented Reality (AR) applications presents several significant technical challenges that researchers and developers must overcome. These challenges span various aspects of the technology, from hardware limitations to software complexities.
One of the primary obstacles is the miniaturization of QLED displays for AR devices. Current QLED panels, while offering superior color performance and energy efficiency, are typically designed for larger screens. Scaling down these displays to fit into compact AR glasses or headsets without compromising image quality or increasing power consumption is a formidable task.
Another critical challenge lies in achieving sufficient brightness and contrast for outdoor use. AR applications often require displays that can compete with ambient light, especially in bright sunlight. While QLEDs excel in color reproduction, pushing their brightness levels to match outdoor conditions without overheating or reducing lifespan remains problematic.
The issue of power efficiency also looms large in QLED AR development. AR devices, particularly wearables, have strict power constraints. Balancing the high-performance display capabilities of QLEDs with the need for all-day battery life in AR glasses is a complex engineering problem that demands innovative power management solutions.
Latency is another crucial factor in AR applications. The delay between user movement and display update must be minimal to maintain immersion and prevent motion sickness. Developing QLED displays with ultra-fast response times and integrating them with low-latency sensors and processing systems is essential for a seamless AR experience.
Color accuracy and consistency across different viewing angles present additional hurdles. AR applications require displays that maintain color fidelity regardless of the user's head position or environmental lighting conditions. Achieving this level of consistency with QLED technology in a wearable form factor is challenging.
Furthermore, the integration of QLED displays with other AR components, such as waveguides or holographic elements, introduces new complexities. Ensuring compatibility and optimal performance when combining these technologies requires extensive research and development.
Lastly, manufacturing scalability remains a significant challenge. Producing QLED displays for AR at scale, with high yield rates and consistent quality, is crucial for widespread adoption. Developing cost-effective production methods that can meet the demand for millions of high-quality, miniaturized QLED displays is a major hurdle for the industry.
One of the primary obstacles is the miniaturization of QLED displays for AR devices. Current QLED panels, while offering superior color performance and energy efficiency, are typically designed for larger screens. Scaling down these displays to fit into compact AR glasses or headsets without compromising image quality or increasing power consumption is a formidable task.
Another critical challenge lies in achieving sufficient brightness and contrast for outdoor use. AR applications often require displays that can compete with ambient light, especially in bright sunlight. While QLEDs excel in color reproduction, pushing their brightness levels to match outdoor conditions without overheating or reducing lifespan remains problematic.
The issue of power efficiency also looms large in QLED AR development. AR devices, particularly wearables, have strict power constraints. Balancing the high-performance display capabilities of QLEDs with the need for all-day battery life in AR glasses is a complex engineering problem that demands innovative power management solutions.
Latency is another crucial factor in AR applications. The delay between user movement and display update must be minimal to maintain immersion and prevent motion sickness. Developing QLED displays with ultra-fast response times and integrating them with low-latency sensors and processing systems is essential for a seamless AR experience.
Color accuracy and consistency across different viewing angles present additional hurdles. AR applications require displays that maintain color fidelity regardless of the user's head position or environmental lighting conditions. Achieving this level of consistency with QLED technology in a wearable form factor is challenging.
Furthermore, the integration of QLED displays with other AR components, such as waveguides or holographic elements, introduces new complexities. Ensuring compatibility and optimal performance when combining these technologies requires extensive research and development.
Lastly, manufacturing scalability remains a significant challenge. Producing QLED displays for AR at scale, with high yield rates and consistent quality, is crucial for widespread adoption. Developing cost-effective production methods that can meet the demand for millions of high-quality, miniaturized QLED displays is a major hurdle for the industry.
Current QLED AR Solutions
01 Quantum dot structure and composition
QLED technology utilizes quantum dots, which are semiconductor nanocrystals. The structure and composition of these quantum dots are crucial for the performance of QLEDs. Various materials and fabrication methods are employed to optimize the quantum dot properties, such as emission wavelength, efficiency, and stability.- Quantum dot structure and composition: QLED technology utilizes quantum dots, which are semiconductor nanocrystals. The structure and composition of these quantum dots are crucial for the performance of QLEDs. Various materials and fabrication methods are employed to optimize the quantum dot properties, such as emission wavelength, efficiency, and stability.
- QLED device architecture: The design and architecture of QLED devices play a significant role in their performance. This includes the arrangement of layers such as the electron transport layer, hole transport layer, and emissive layer. Innovations in device structure aim to improve efficiency, color purity, and longevity of QLED displays.
- Quantum dot synthesis and processing: The synthesis and processing of quantum dots are critical for QLED manufacturing. Various methods are employed to produce quantum dots with desired properties, including solution-based synthesis, vapor deposition, and surface modification techniques. These processes aim to enhance quantum yield, stability, and uniformity of the quantum dots.
- Color conversion and light management: QLEDs utilize quantum dots for color conversion and light management. This involves optimizing the interaction between blue LEDs and quantum dots to produce a wide color gamut. Techniques such as patterning, light extraction, and color filtering are employed to enhance display performance and energy efficiency.
- QLED manufacturing and integration: The manufacturing and integration of QLEDs into display panels present unique challenges. Innovations in this area focus on scalable production methods, such as inkjet printing and photolithography, as well as techniques for integrating quantum dots with existing display technologies. This includes addressing issues related to encapsulation, thermal management, and device lifetime.
02 QLED device architecture
The design and architecture of QLED devices play a significant role in their performance. This includes the arrangement of layers, such as the electron transport layer, hole transport layer, and emissive layer. Innovations in device structure aim to improve efficiency, color purity, and longevity of QLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quantum dot synthesis and processing
The synthesis and processing of quantum dots are critical for QLED manufacturing. Various methods are employed to produce quantum dots with desired properties, including solution-based synthesis, vapor deposition, and surface modification techniques. These processes aim to enhance the quantum yield and stability of the quantum dots.Expand Specific Solutions04 Color conversion and light management
QLED technology utilizes quantum dots for color conversion and light management. This involves optimizing the emission spectrum, improving color gamut, and enhancing the overall display performance. Techniques such as down-conversion and optical tuning are employed to achieve better color reproduction and energy efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration with other display technologies
QLED technology can be integrated with other display technologies to create hybrid solutions. This includes combining quantum dots with OLED, LCD, or micro-LED technologies to leverage the strengths of each approach. Such integrations aim to achieve improved performance, energy efficiency, and manufacturing scalability.Expand Specific Solutions
Key AR QLED Players
The QLED technology in Augmented Reality (AR) applications is in an early growth stage, with significant potential for market expansion. The global AR market is projected to reach substantial size in the coming years, driven by increasing adoption across various industries. QLED technology for AR is still evolving, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology Group, and OSRAM Opto Semiconductors are at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in display technologies. Tech giants such as Apple, Google, and Microsoft are also investing heavily in AR-related QLED research, while specialized AR companies like Magic Leap and Meta Platforms Technologies are exploring innovative applications. The competitive landscape is dynamic, with both established display manufacturers and emerging AR-focused firms vying for market share and technological breakthroughs.
Google LLC
Technical Solution: Google is researching QLED applications for AR, particularly focusing on integrating the technology into future versions of Google Glass and other AR devices. Their approach involves developing high-brightness, low-latency QLED displays suitable for outdoor use in AR glasses. Google's solution includes advanced color processing algorithms to enhance visibility and readability of AR content in various lighting conditions. They are also exploring the use of QLED in combination with waveguide optics to create compact, lightweight AR displays. Additionally, Google is working on software optimizations to leverage QLED's capabilities in rendering AR content more efficiently, potentially improving battery life and overall performance of AR devices.
Strengths: Strong software ecosystem and AI capabilities to enhance QLED performance in AR. Weaknesses: Previous challenges with consumer AR adoption (Google Glass), potential privacy concerns.
Magic Leap, Inc.
Technical Solution: Magic Leap is exploring QLED technology for their next-generation AR headsets. Their approach involves using QLED displays to create a wider field of view and improve color accuracy in AR environments. Magic Leap's solution incorporates advanced optics and light field technology to blend QLED-generated digital content seamlessly with the real world. They are developing custom algorithms to optimize QLED performance for AR-specific use cases, such as outdoor visibility and reduced latency. Magic Leap is also working on integrating eye-tracking technology with QLED displays to enable foveated rendering, which could significantly reduce power consumption and improve overall performance.
Strengths: Expertise in AR optics and integration, potential for wide field of view. Weaknesses: Previous challenges in market adoption, competition from larger tech companies.
QLED AR Core Innovations
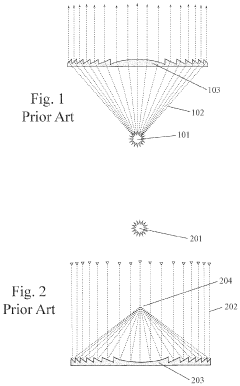
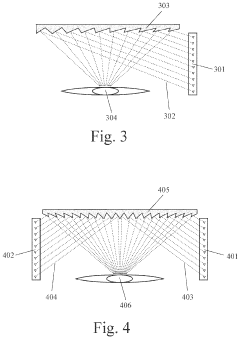
Augmented Reality (AR) Eyewear with at Least One Quasi Fresnel Reflector (QFR)
PatentActiveUS20200089004A1
Innovation
- The use of a Quasi Fresnel Reflector (QFR) in AR eyewear, which reflects light rays from a lateral Light Emitter Array toward the user's eye to create virtual images, allowing for a compact design with improved image quality and field of view without significant loss of real-world three-dimensionality.
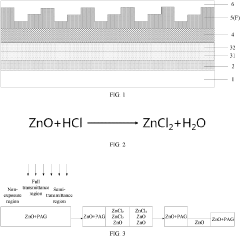
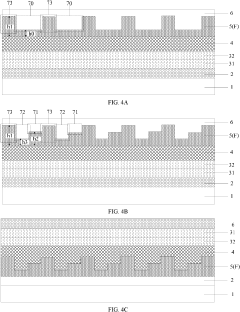
Display substrate, display device, and manufacturing method for display substrate
PatentPendingUS20230145503A1
Innovation
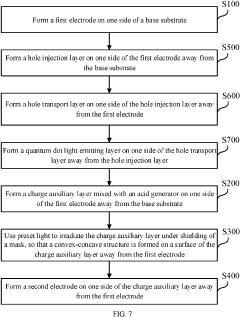
- A display substrate with a base substrate, a first electrode, a charge auxiliary layer featuring concave-convex structures and varying acid generator content, and a quantum dot light emitting layer, where the charge auxiliary layer is formed using a mask with different light transmittance regions to create periodic convex-concave structures that enhance light extraction by total reflection.
QLED AR Integration
The integration of QLED (Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diode) technology into Augmented Reality (AR) applications represents a significant advancement in display technology for wearable devices. QLED offers several advantages that make it particularly suitable for AR implementations, including high brightness, wide color gamut, and energy efficiency.
QLED displays utilize quantum dots, which are semiconductor nanocrystals that emit light when excited by an electric current. These quantum dots can be precisely tuned to emit specific colors, resulting in more vibrant and accurate color reproduction compared to traditional LED displays. This characteristic is crucial for AR applications, where the seamless blending of virtual content with the real world requires high-fidelity color representation.
One of the primary challenges in AR display technology is achieving sufficient brightness to ensure visibility in various lighting conditions, especially in outdoor environments. QLED technology excels in this aspect, as it can produce significantly higher brightness levels than conventional OLED displays while maintaining energy efficiency. This capability is essential for AR headsets and smart glasses, where power consumption is a critical factor due to the limited battery capacity of wearable devices.
The integration process of QLED into AR systems involves several key components. First, the QLED display panel must be miniaturized to fit within the form factor of AR devices without compromising performance. This requires advanced manufacturing techniques and materials science innovations to maintain the quantum dot structure at smaller scales.
Additionally, the optical system of AR devices must be optimized to work in conjunction with QLED displays. This includes the development of specialized lenses and waveguides that can effectively project the QLED-generated images onto the user's field of view while maintaining clarity and minimizing distortions.
Another crucial aspect of QLED AR integration is the development of driver electronics and software that can fully leverage the capabilities of QLED technology. This includes implementing advanced color management systems and dynamic brightness control to adapt to changing ambient light conditions and user preferences.
Furthermore, the integration of QLED technology in AR applications opens up new possibilities for enhanced user experiences. The wider color gamut and higher contrast ratios offered by QLED displays enable more realistic and immersive AR content, potentially expanding the applications of AR technology in fields such as industrial design, medical visualization, and entertainment.
As QLED AR integration continues to evolve, researchers and engineers are focusing on addressing remaining challenges, such as further reducing power consumption, improving the lifespan of quantum dot materials in wearable device conditions, and enhancing the overall durability of QLED displays for everyday use in AR applications.
QLED displays utilize quantum dots, which are semiconductor nanocrystals that emit light when excited by an electric current. These quantum dots can be precisely tuned to emit specific colors, resulting in more vibrant and accurate color reproduction compared to traditional LED displays. This characteristic is crucial for AR applications, where the seamless blending of virtual content with the real world requires high-fidelity color representation.
One of the primary challenges in AR display technology is achieving sufficient brightness to ensure visibility in various lighting conditions, especially in outdoor environments. QLED technology excels in this aspect, as it can produce significantly higher brightness levels than conventional OLED displays while maintaining energy efficiency. This capability is essential for AR headsets and smart glasses, where power consumption is a critical factor due to the limited battery capacity of wearable devices.
The integration process of QLED into AR systems involves several key components. First, the QLED display panel must be miniaturized to fit within the form factor of AR devices without compromising performance. This requires advanced manufacturing techniques and materials science innovations to maintain the quantum dot structure at smaller scales.
Additionally, the optical system of AR devices must be optimized to work in conjunction with QLED displays. This includes the development of specialized lenses and waveguides that can effectively project the QLED-generated images onto the user's field of view while maintaining clarity and minimizing distortions.
Another crucial aspect of QLED AR integration is the development of driver electronics and software that can fully leverage the capabilities of QLED technology. This includes implementing advanced color management systems and dynamic brightness control to adapt to changing ambient light conditions and user preferences.
Furthermore, the integration of QLED technology in AR applications opens up new possibilities for enhanced user experiences. The wider color gamut and higher contrast ratios offered by QLED displays enable more realistic and immersive AR content, potentially expanding the applications of AR technology in fields such as industrial design, medical visualization, and entertainment.
As QLED AR integration continues to evolve, researchers and engineers are focusing on addressing remaining challenges, such as further reducing power consumption, improving the lifespan of quantum dot materials in wearable device conditions, and enhancing the overall durability of QLED displays for everyday use in AR applications.
QLED AR Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a critical factor in the development and adoption of QLED technology for augmented reality (AR) applications. As AR devices become more prevalent, the need for power-efficient display solutions becomes increasingly important. QLED technology offers several advantages in this regard, making it a promising candidate for future AR implementations.
QLED displays utilize quantum dots, which are semiconductor nanocrystals that emit light when excited by an electric current. This unique property allows for highly efficient light emission, resulting in improved energy consumption compared to traditional display technologies. In the context of AR applications, where battery life is a crucial consideration, the energy efficiency of QLED displays can significantly extend device usage time.
One of the key factors contributing to QLED's energy efficiency in AR is its ability to produce high brightness levels with lower power consumption. This is particularly important for outdoor use, where AR displays need to compete with ambient light. QLED technology can achieve higher peak brightness levels while maintaining lower overall power draw, ensuring clear visibility in various lighting conditions without draining the battery excessively.
Color accuracy and wide color gamut are essential for immersive AR experiences. QLED displays excel in this area, producing vibrant and accurate colors with minimal energy expenditure. The quantum dots' narrow emission spectra allow for precise color control, reducing the need for additional power-hungry color filters or backlighting adjustments.
Another aspect of QLED's energy efficiency in AR applications is its potential for implementing local dimming techniques. By selectively dimming or turning off individual pixels or zones, QLED displays can achieve high contrast ratios while conserving energy in darker areas of the image. This feature is particularly beneficial for AR overlays, where only specific portions of the display may need to be active at any given time.
The thermal management advantages of QLED technology also contribute to its overall energy efficiency. Quantum dots operate at lower temperatures compared to some other display technologies, reducing the need for active cooling systems in AR devices. This not only saves energy but also allows for more compact and lightweight designs, which are crucial for wearable AR applications.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, researchers are exploring ways to further enhance its energy efficiency for AR use cases. This includes developing new quantum dot materials with improved light emission properties, optimizing driving circuits to reduce power consumption, and implementing advanced power management algorithms tailored for AR content.
In conclusion, QLED technology's energy efficiency characteristics make it a compelling option for augmented reality applications. Its ability to deliver high brightness, accurate colors, and contrast while maintaining low power consumption addresses many of the key challenges faced in AR display development. As the technology matures, we can expect to see even greater improvements in energy efficiency, further solidifying QLED's position as a leading display solution for next-generation AR devices.
QLED displays utilize quantum dots, which are semiconductor nanocrystals that emit light when excited by an electric current. This unique property allows for highly efficient light emission, resulting in improved energy consumption compared to traditional display technologies. In the context of AR applications, where battery life is a crucial consideration, the energy efficiency of QLED displays can significantly extend device usage time.
One of the key factors contributing to QLED's energy efficiency in AR is its ability to produce high brightness levels with lower power consumption. This is particularly important for outdoor use, where AR displays need to compete with ambient light. QLED technology can achieve higher peak brightness levels while maintaining lower overall power draw, ensuring clear visibility in various lighting conditions without draining the battery excessively.
Color accuracy and wide color gamut are essential for immersive AR experiences. QLED displays excel in this area, producing vibrant and accurate colors with minimal energy expenditure. The quantum dots' narrow emission spectra allow for precise color control, reducing the need for additional power-hungry color filters or backlighting adjustments.
Another aspect of QLED's energy efficiency in AR applications is its potential for implementing local dimming techniques. By selectively dimming or turning off individual pixels or zones, QLED displays can achieve high contrast ratios while conserving energy in darker areas of the image. This feature is particularly beneficial for AR overlays, where only specific portions of the display may need to be active at any given time.
The thermal management advantages of QLED technology also contribute to its overall energy efficiency. Quantum dots operate at lower temperatures compared to some other display technologies, reducing the need for active cooling systems in AR devices. This not only saves energy but also allows for more compact and lightweight designs, which are crucial for wearable AR applications.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, researchers are exploring ways to further enhance its energy efficiency for AR use cases. This includes developing new quantum dot materials with improved light emission properties, optimizing driving circuits to reduce power consumption, and implementing advanced power management algorithms tailored for AR content.
In conclusion, QLED technology's energy efficiency characteristics make it a compelling option for augmented reality applications. Its ability to deliver high brightness, accurate colors, and contrast while maintaining low power consumption addresses many of the key challenges faced in AR display development. As the technology matures, we can expect to see even greater improvements in energy efficiency, further solidifying QLED's position as a leading display solution for next-generation AR devices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!