QLED Visual Experiences: A Look at Emerging Trends
JUN 19, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
QLED Evolution and Objectives
Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diode (QLED) technology has emerged as a revolutionary force in the display industry, offering enhanced visual experiences through superior color reproduction and brightness. The evolution of QLED technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers first began exploring the potential of quantum dots in display applications. Since then, QLED has undergone significant advancements, driven by the pursuit of more immersive and lifelike visual experiences.
The primary objective of QLED technology is to deliver unparalleled picture quality by leveraging the unique properties of quantum dots. These nanoscale semiconductor particles emit light at specific wavelengths when excited, allowing for precise color control and enhanced color gamut. As the technology has progressed, manufacturers have focused on improving key performance metrics such as color accuracy, brightness, contrast ratio, and energy efficiency.
One of the most notable trends in QLED evolution has been the continuous refinement of quantum dot synthesis and implementation. Early QLED displays used cadmium-based quantum dots, which raised environmental concerns. This led to the development of cadmium-free alternatives, marking a significant milestone in the technology's progression towards sustainability and wider market acceptance.
Another crucial aspect of QLED evolution has been the integration of quantum dots with existing display technologies. Initially, quantum dots were primarily used in LCD backlight systems to enhance color performance. However, recent advancements have paved the way for electroluminescent QLED displays, where quantum dots themselves emit light, potentially rivaling OLED technology in terms of picture quality and energy efficiency.
The objectives for future QLED development are multifaceted. Researchers and manufacturers are striving to further improve color volume and accuracy, aiming to reproduce an even wider range of colors with greater precision. Enhancing brightness capabilities while maintaining energy efficiency remains a key goal, particularly for HDR content display. Additionally, there is a strong focus on increasing the lifespan of QLED displays and reducing production costs to make the technology more accessible to a broader consumer base.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, emerging trends point towards its application in flexible and transparent displays, opening up new possibilities for innovative product designs. The integration of QLED with other cutting-edge technologies, such as micro-LED and AI-driven picture processing, is also being explored to create next-generation visual experiences. These advancements aim to push the boundaries of what is possible in display technology, promising even more immersive and realistic visual content in the future.
The primary objective of QLED technology is to deliver unparalleled picture quality by leveraging the unique properties of quantum dots. These nanoscale semiconductor particles emit light at specific wavelengths when excited, allowing for precise color control and enhanced color gamut. As the technology has progressed, manufacturers have focused on improving key performance metrics such as color accuracy, brightness, contrast ratio, and energy efficiency.
One of the most notable trends in QLED evolution has been the continuous refinement of quantum dot synthesis and implementation. Early QLED displays used cadmium-based quantum dots, which raised environmental concerns. This led to the development of cadmium-free alternatives, marking a significant milestone in the technology's progression towards sustainability and wider market acceptance.
Another crucial aspect of QLED evolution has been the integration of quantum dots with existing display technologies. Initially, quantum dots were primarily used in LCD backlight systems to enhance color performance. However, recent advancements have paved the way for electroluminescent QLED displays, where quantum dots themselves emit light, potentially rivaling OLED technology in terms of picture quality and energy efficiency.
The objectives for future QLED development are multifaceted. Researchers and manufacturers are striving to further improve color volume and accuracy, aiming to reproduce an even wider range of colors with greater precision. Enhancing brightness capabilities while maintaining energy efficiency remains a key goal, particularly for HDR content display. Additionally, there is a strong focus on increasing the lifespan of QLED displays and reducing production costs to make the technology more accessible to a broader consumer base.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, emerging trends point towards its application in flexible and transparent displays, opening up new possibilities for innovative product designs. The integration of QLED with other cutting-edge technologies, such as micro-LED and AI-driven picture processing, is also being explored to create next-generation visual experiences. These advancements aim to push the boundaries of what is possible in display technology, promising even more immersive and realistic visual content in the future.
QLED Market Demand Analysis
The QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) display market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for high-quality visual experiences. This technology offers superior color reproduction, brightness, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays, making it particularly attractive for premium televisions and monitors.
Market research indicates that the global QLED TV market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% from 2021 to 2026. This robust growth is attributed to several factors, including the rising popularity of 4K and 8K resolution content, increasing disposable income in emerging economies, and growing consumer preference for larger screen sizes.
The demand for QLED displays is not limited to the consumer electronics sector. There is a growing interest in QLED technology for commercial applications, such as digital signage, control rooms, and high-end presentation displays. This diversification of market segments is contributing to the overall expansion of the QLED market.
In terms of regional demand, North America and Asia-Pacific are the leading markets for QLED displays. The North American market is driven by early technology adoption and high consumer spending on premium electronics. In contrast, the Asia-Pacific region's growth is fueled by the presence of major manufacturers, increasing urbanization, and rising middle-class populations in countries like China and India.
The gaming industry is emerging as a significant driver of QLED demand. Gamers are increasingly seeking displays with high refresh rates, low input lag, and vibrant colors – all attributes that QLED technology can deliver. This has led to the development of QLED gaming monitors and TVs specifically tailored to meet the needs of this growing market segment.
Environmental concerns and energy efficiency regulations are also influencing market demand. QLED displays are more energy-efficient than traditional LED-LCD displays, aligning with global efforts to reduce energy consumption. This factor is becoming increasingly important for both consumers and businesses looking to minimize their environmental impact and reduce operating costs.
Despite the positive outlook, the QLED market faces competition from other emerging display technologies, such as OLED and MicroLED. However, ongoing improvements in QLED technology, including advancements in quantum dot materials and manufacturing processes, are expected to maintain its competitive edge and drive continued market growth.
Market research indicates that the global QLED TV market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% from 2021 to 2026. This robust growth is attributed to several factors, including the rising popularity of 4K and 8K resolution content, increasing disposable income in emerging economies, and growing consumer preference for larger screen sizes.
The demand for QLED displays is not limited to the consumer electronics sector. There is a growing interest in QLED technology for commercial applications, such as digital signage, control rooms, and high-end presentation displays. This diversification of market segments is contributing to the overall expansion of the QLED market.
In terms of regional demand, North America and Asia-Pacific are the leading markets for QLED displays. The North American market is driven by early technology adoption and high consumer spending on premium electronics. In contrast, the Asia-Pacific region's growth is fueled by the presence of major manufacturers, increasing urbanization, and rising middle-class populations in countries like China and India.
The gaming industry is emerging as a significant driver of QLED demand. Gamers are increasingly seeking displays with high refresh rates, low input lag, and vibrant colors – all attributes that QLED technology can deliver. This has led to the development of QLED gaming monitors and TVs specifically tailored to meet the needs of this growing market segment.
Environmental concerns and energy efficiency regulations are also influencing market demand. QLED displays are more energy-efficient than traditional LED-LCD displays, aligning with global efforts to reduce energy consumption. This factor is becoming increasingly important for both consumers and businesses looking to minimize their environmental impact and reduce operating costs.
Despite the positive outlook, the QLED market faces competition from other emerging display technologies, such as OLED and MicroLED. However, ongoing improvements in QLED technology, including advancements in quantum dot materials and manufacturing processes, are expected to maintain its competitive edge and drive continued market growth.
QLED Technology Landscape
QLED (Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diode) technology has emerged as a significant player in the display industry, offering enhanced color reproduction, brightness, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays. The QLED technology landscape is characterized by rapid advancements and fierce competition among major manufacturers.
At the core of QLED technology are quantum dots, nanoscale semiconductor particles that emit light of specific wavelengths when excited by an energy source. These quantum dots are typically made of materials such as cadmium selenide or indium phosphide, and their size determines the color of light they emit. This precise control over color output allows QLED displays to achieve a wider color gamut and more accurate color reproduction than conventional LCD displays.
The current QLED market is dominated by a few key players, with Samsung leading the pack in terms of market share and technological innovation. Other significant contributors include TCL, Hisense, and Vizio. These companies are continuously pushing the boundaries of QLED technology, focusing on improving color accuracy, contrast ratios, and overall picture quality.
Recent advancements in QLED technology have focused on enhancing the quantum dot layer's efficiency and stability. Researchers are exploring new materials and manufacturing processes to improve the longevity of quantum dots and reduce the reliance on rare or toxic elements. Additionally, there is a growing interest in developing self-emissive QLED displays, which would eliminate the need for a backlight and potentially rival OLED technology in terms of picture quality and energy efficiency.
The QLED technology landscape is also witnessing a shift towards larger display sizes and higher resolutions. 8K QLED TVs are becoming more prevalent, offering unprecedented levels of detail and clarity. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms is enhancing the picture processing capabilities of QLED displays, allowing for real-time optimization of image quality based on content and viewing conditions.
As the demand for high-quality visual experiences continues to grow across various sectors, including home entertainment, professional content creation, and digital signage, the QLED technology landscape is expected to evolve rapidly. Future developments may include the incorporation of quantum dot technology into flexible and transparent displays, opening up new possibilities for innovative product designs and applications.
At the core of QLED technology are quantum dots, nanoscale semiconductor particles that emit light of specific wavelengths when excited by an energy source. These quantum dots are typically made of materials such as cadmium selenide or indium phosphide, and their size determines the color of light they emit. This precise control over color output allows QLED displays to achieve a wider color gamut and more accurate color reproduction than conventional LCD displays.
The current QLED market is dominated by a few key players, with Samsung leading the pack in terms of market share and technological innovation. Other significant contributors include TCL, Hisense, and Vizio. These companies are continuously pushing the boundaries of QLED technology, focusing on improving color accuracy, contrast ratios, and overall picture quality.
Recent advancements in QLED technology have focused on enhancing the quantum dot layer's efficiency and stability. Researchers are exploring new materials and manufacturing processes to improve the longevity of quantum dots and reduce the reliance on rare or toxic elements. Additionally, there is a growing interest in developing self-emissive QLED displays, which would eliminate the need for a backlight and potentially rival OLED technology in terms of picture quality and energy efficiency.
The QLED technology landscape is also witnessing a shift towards larger display sizes and higher resolutions. 8K QLED TVs are becoming more prevalent, offering unprecedented levels of detail and clarity. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms is enhancing the picture processing capabilities of QLED displays, allowing for real-time optimization of image quality based on content and viewing conditions.
As the demand for high-quality visual experiences continues to grow across various sectors, including home entertainment, professional content creation, and digital signage, the QLED technology landscape is expected to evolve rapidly. Future developments may include the incorporation of quantum dot technology into flexible and transparent displays, opening up new possibilities for innovative product designs and applications.
Current QLED Solutions
01 QLED display technology advancements
QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology has made significant advancements in display quality and visual experiences. These improvements include enhanced color accuracy, brightness, and contrast ratios, resulting in more vibrant and lifelike images. QLED displays utilize quantum dots to produce pure and precise colors, offering a wider color gamut compared to traditional LED displays.- QLED display technology advancements: QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology has made significant advancements in display quality and visual experiences. These improvements include enhanced color accuracy, brightness, and contrast ratios, resulting in more vibrant and lifelike images. QLED displays utilize quantum dots to produce pure and precise colors, offering a wider color gamut compared to traditional LED displays.
- Visual processing and enhancement techniques: Various visual processing and enhancement techniques are employed in QLED technology to improve the overall viewing experience. These include advanced algorithms for image upscaling, motion smoothing, and HDR (High Dynamic Range) processing. Such techniques help in reducing motion blur, enhancing detail in both bright and dark scenes, and optimizing content for QLED displays.
- User interface and interaction improvements: QLED technology incorporates innovative user interface and interaction features to enhance the visual experience. This includes gesture control, voice commands, and adaptive display settings that adjust based on ambient lighting conditions. These improvements aim to make the interaction with QLED displays more intuitive and user-friendly.
- Integration with smart home and IoT devices: QLED displays are being integrated with smart home and Internet of Things (IoT) devices to create more immersive and connected visual experiences. This integration allows for seamless content sharing, synchronized lighting effects, and personalized viewing experiences based on user preferences and habits.
- Energy efficiency and sustainability: Advancements in QLED technology focus on improving energy efficiency and sustainability. This includes the development of more power-efficient quantum dot materials, optimized backlight systems, and intelligent power management features. These improvements not only reduce energy consumption but also contribute to longer display lifespans and reduced environmental impact.
02 Visual processing and enhancement techniques
Various visual processing and enhancement techniques are employed in QLED technology to improve the overall viewing experience. These include advanced image processing algorithms, HDR (High Dynamic Range) support, and local dimming technologies. Such techniques help in optimizing picture quality, reducing motion blur, and enhancing contrast in different lighting conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 User interface and interaction improvements
QLED technology incorporates innovative user interface designs and interaction methods to enhance the overall user experience. This includes touch-sensitive displays, gesture recognition, and voice control features. These advancements allow for more intuitive and seamless interaction with QLED devices, improving usability and accessibility.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration with smart home and IoT systems
QLED displays are increasingly being integrated with smart home and Internet of Things (IoT) systems. This integration allows for enhanced connectivity, remote control capabilities, and seamless interaction with other smart devices. Users can control their QLED displays through mobile apps, voice assistants, or other connected devices, creating a more immersive and interconnected visual experience.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy efficiency and sustainability features
QLED technology incorporates energy-efficient designs and sustainability features to reduce power consumption and environmental impact. This includes the use of low-power components, adaptive brightness controls, and eco-friendly materials in the manufacturing process. These advancements contribute to longer device lifespan and reduced energy costs while maintaining high-quality visual experiences.Expand Specific Solutions
QLED Industry Leaders
The QLED visual experiences market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand for high-quality displays across various sectors. The market size is expanding rapidly, driven by advancements in display technology and consumer preferences for immersive viewing experiences. Technologically, QLED is maturing, with key players like Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, and BOE Technology Group leading innovation. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to enhance color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency. Emerging players such as TCL China Star Optoelectronics and Sharp Corp. are also making significant strides, intensifying competition. The industry is seeing a trend towards larger screens, higher resolutions, and integration with smart technologies, indicating a dynamic and evolving competitive landscape.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed its own QLED technology, focusing on large-scale production of high-quality quantum dot displays. Their QLED panels utilize a unique quantum dot film structure that enhances color gamut and brightness while reducing power consumption. BOE has also integrated advanced local dimming techniques to improve contrast ratios in their QLED displays. They are working on flexible QLED displays for curved and foldable applications.
Strengths: Cost-effective large-scale production, wide color gamut, and flexibility for various form factors. Weaknesses: Less brand recognition in consumer markets compared to some competitors.
LG Electronics, Inc.
Technical Solution: LG has developed NanoCell technology, which is their version of quantum dot technology for enhanced color reproduction in LCD displays. Their QNED (Quantum Dot NanoCell) technology combines quantum dots with NanoCell and mini-LED backlighting for improved contrast and color accuracy. LG is also exploring the integration of AI-driven picture processing to optimize QLED visual experiences in real-time based on content and ambient lighting conditions.
Strengths: Innovative combination of quantum dot and NanoCell technologies, strong brand presence in the TV market. Weaknesses: QLED offerings are less prominent in their product lineup compared to OLED technology.
QLED Core Innovations
Photoelectric devices
PatentPendingUS20240040816A1
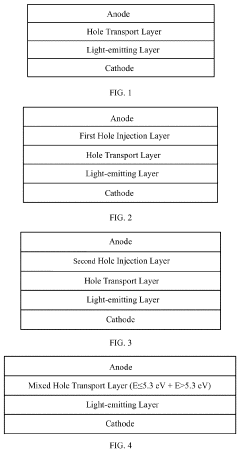
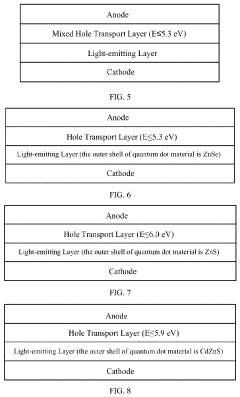
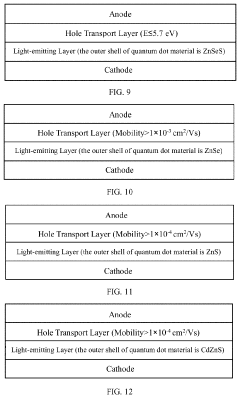
Innovation
- A photoelectric device structure is designed with specific energy level differences between hole transport and hole injection layers, such as |ΔEHTL-HIL| ≤ 0.2 eV, to reduce energy barriers and prevent charge accumulation, and a core-shell quantum dot structure with ΔEEML-HTL ≥ 0.5 eV to balance hole and electron injection.
Light-emitting element and display device
PatentPendingUS20240414975A1
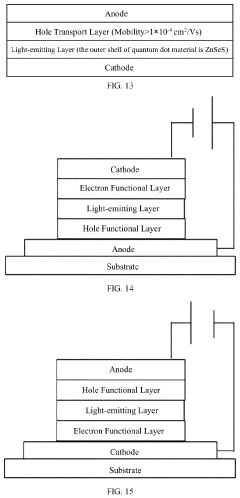
Innovation
- A light-emitting element design featuring a first conductive layer with a flat surface for reflecting visible light, a second conductive layer with varying thickness regions, a functional light-emitting layer, and a second electrode that transmits visible light, along with an edge cover containing scattering or light-blocking materials to reduce optical path variations.
QLED Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing processes for QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) displays are complex and highly specialized, involving several key stages that contribute to the creation of these advanced visual technologies. At the core of QLED manufacturing is the production of quantum dots, which are nanoscale semiconductor particles that emit light when excited by an electric current.
The process begins with the synthesis of quantum dots, typically using colloidal chemistry methods. Precise control over temperature, reaction time, and precursor concentrations is crucial to produce quantum dots with uniform size and composition. These factors directly influence the color purity and efficiency of the final display.
Once synthesized, the quantum dots undergo a purification process to remove any impurities that could affect their performance. This is followed by a surface treatment stage, where the quantum dots are coated with protective layers to enhance their stability and prevent degradation when exposed to air and moisture.
The next critical step is the integration of quantum dots into the display structure. This is often achieved through a printing or deposition process, where a thin film of quantum dots is applied to a substrate. Advanced techniques such as photolithography or inkjet printing are employed to ensure precise placement and uniform distribution of the quantum dots.
The quantum dot layer is then combined with other essential components of the display, including the backlight unit, color filters, and TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) array. This integration process requires extreme precision to maintain the alignment and integrity of each layer.
Quality control is a crucial aspect of QLED manufacturing. Rigorous testing is conducted at various stages to ensure color accuracy, brightness uniformity, and overall display performance. Advanced imaging and spectroscopic techniques are used to detect any defects or inconsistencies in the quantum dot layer.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, manufacturers are constantly refining their processes to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Recent trends include the development of cadmium-free quantum dots to address environmental concerns, and the exploration of new deposition methods to enhance the quantum dot film's uniformity and durability.
The manufacturing of QLED displays also involves significant challenges, particularly in scaling up production while maintaining consistent quality. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research and development in materials science, process engineering, and quality control methodologies.
The process begins with the synthesis of quantum dots, typically using colloidal chemistry methods. Precise control over temperature, reaction time, and precursor concentrations is crucial to produce quantum dots with uniform size and composition. These factors directly influence the color purity and efficiency of the final display.
Once synthesized, the quantum dots undergo a purification process to remove any impurities that could affect their performance. This is followed by a surface treatment stage, where the quantum dots are coated with protective layers to enhance their stability and prevent degradation when exposed to air and moisture.
The next critical step is the integration of quantum dots into the display structure. This is often achieved through a printing or deposition process, where a thin film of quantum dots is applied to a substrate. Advanced techniques such as photolithography or inkjet printing are employed to ensure precise placement and uniform distribution of the quantum dots.
The quantum dot layer is then combined with other essential components of the display, including the backlight unit, color filters, and TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) array. This integration process requires extreme precision to maintain the alignment and integrity of each layer.
Quality control is a crucial aspect of QLED manufacturing. Rigorous testing is conducted at various stages to ensure color accuracy, brightness uniformity, and overall display performance. Advanced imaging and spectroscopic techniques are used to detect any defects or inconsistencies in the quantum dot layer.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, manufacturers are constantly refining their processes to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Recent trends include the development of cadmium-free quantum dots to address environmental concerns, and the exploration of new deposition methods to enhance the quantum dot film's uniformity and durability.
The manufacturing of QLED displays also involves significant challenges, particularly in scaling up production while maintaining consistent quality. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research and development in materials science, process engineering, and quality control methodologies.
QLED Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology is an increasingly important consideration as these displays become more prevalent in the consumer electronics market. QLED displays offer significant advantages in terms of visual quality and energy efficiency, but their production and disposal processes raise certain environmental concerns.
One of the primary environmental benefits of QLED technology is its improved energy efficiency compared to traditional LED and LCD displays. QLED screens typically consume less power while delivering higher brightness and color accuracy, potentially reducing the overall energy consumption of display devices. This efficiency can contribute to lower carbon emissions over the lifetime of the product.
However, the production of quantum dots, the key component in QLED displays, involves the use of heavy metals such as cadmium. While manufacturers have made efforts to reduce or eliminate cadmium content, concerns remain about the potential environmental and health impacts of these materials. The extraction and processing of rare earth elements used in QLED production also have environmental implications, including habitat disruption and water pollution.
The manufacturing process for QLED displays requires sophisticated clean room environments and energy-intensive procedures. This results in a significant carbon footprint during production, which must be balanced against the energy savings achieved during the product's use phase. Efforts are ongoing to optimize manufacturing processes and reduce their environmental impact.
End-of-life considerations for QLED displays present both challenges and opportunities. The complex nature of these devices makes recycling more difficult than for traditional displays. However, the valuable materials used in QLEDs, including quantum dots and rare earth elements, provide an incentive for developing more effective recycling processes. Proper recycling can help recover these materials and reduce the need for new resource extraction.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, manufacturers are exploring more sustainable production methods and materials. This includes research into quantum dots made from non-toxic, abundant materials and the development of more easily recyclable display components. Additionally, improvements in manufacturing efficiency and the use of renewable energy in production facilities are helping to mitigate the environmental impact of QLED displays.
The long lifespan of QLED displays compared to some other technologies can also contribute to reduced electronic waste. By lasting longer and maintaining better performance over time, these displays may need to be replaced less frequently, potentially decreasing the overall environmental impact of consumer electronics.
One of the primary environmental benefits of QLED technology is its improved energy efficiency compared to traditional LED and LCD displays. QLED screens typically consume less power while delivering higher brightness and color accuracy, potentially reducing the overall energy consumption of display devices. This efficiency can contribute to lower carbon emissions over the lifetime of the product.
However, the production of quantum dots, the key component in QLED displays, involves the use of heavy metals such as cadmium. While manufacturers have made efforts to reduce or eliminate cadmium content, concerns remain about the potential environmental and health impacts of these materials. The extraction and processing of rare earth elements used in QLED production also have environmental implications, including habitat disruption and water pollution.
The manufacturing process for QLED displays requires sophisticated clean room environments and energy-intensive procedures. This results in a significant carbon footprint during production, which must be balanced against the energy savings achieved during the product's use phase. Efforts are ongoing to optimize manufacturing processes and reduce their environmental impact.
End-of-life considerations for QLED displays present both challenges and opportunities. The complex nature of these devices makes recycling more difficult than for traditional displays. However, the valuable materials used in QLEDs, including quantum dots and rare earth elements, provide an incentive for developing more effective recycling processes. Proper recycling can help recover these materials and reduce the need for new resource extraction.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, manufacturers are exploring more sustainable production methods and materials. This includes research into quantum dots made from non-toxic, abundant materials and the development of more easily recyclable display components. Additionally, improvements in manufacturing efficiency and the use of renewable energy in production facilities are helping to mitigate the environmental impact of QLED displays.
The long lifespan of QLED displays compared to some other technologies can also contribute to reduced electronic waste. By lasting longer and maintaining better performance over time, these displays may need to be replaced less frequently, potentially decreasing the overall environmental impact of consumer electronics.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!