Innovations in QLED for Cinematic Quality Displays
QLED Evolution and Objectives
Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diode (QLED) technology has emerged as a revolutionary advancement in display technology, offering unprecedented color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency. The evolution of QLED displays can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers first began exploring the potential of quantum dots in light-emitting applications. Since then, QLED technology has undergone significant improvements, driven by the increasing demand for high-quality, immersive visual experiences in both consumer and professional markets.
The primary objective of QLED innovation for cinematic quality displays is to achieve a level of visual fidelity that rivals or surpasses traditional cinema projection systems. This involves enhancing several key aspects of display performance, including color gamut, contrast ratio, peak brightness, and motion handling. By leveraging the unique properties of quantum dots, researchers and manufacturers aim to create displays that can reproduce the full spectrum of colors visible to the human eye, with particular emphasis on achieving deep blacks and vibrant, saturated colors.
One of the most significant trends in QLED evolution is the pursuit of ever-smaller quantum dot sizes, which allows for more precise control over the emitted light wavelengths. This trend has led to the development of quantum dots with narrower emission spectra, resulting in purer and more vivid colors. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve the stability and longevity of quantum dots, addressing concerns about color shift and degradation over time.
Another critical objective in QLED development is the enhancement of energy efficiency. As displays grow larger and resolutions increase, power consumption becomes a significant concern. QLED technology offers a promising solution, as quantum dots can theoretically convert nearly 100% of input energy into light, minimizing waste heat generation. Researchers are working on optimizing the quantum yield of these nanoparticles and developing more efficient excitation methods to further improve energy efficiency.
The integration of QLED technology with other display innovations is also a key focus area. For instance, the combination of QLED with Mini-LED backlighting systems aims to achieve superior local dimming capabilities, enhancing contrast and black levels. Furthermore, efforts are being made to develop self-emissive QLED displays, which would eliminate the need for a separate backlight altogether, potentially rivaling OLED technology in terms of picture quality and form factor flexibility.
As the technology continues to mature, the objectives for QLED in cinematic displays extend beyond mere picture quality improvements. Researchers are exploring ways to reduce production costs, simplify manufacturing processes, and enhance the environmental sustainability of QLED displays. These efforts are crucial for widespread adoption and long-term viability of the technology in both consumer and professional markets.
Cinematic Display Market Analysis
The cinematic display market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for high-quality visual experiences in both home entertainment and commercial settings. This market segment encompasses a wide range of display technologies, including OLED, QLED, and other advanced LCD variants, all competing to deliver the most immersive and lifelike viewing experience.
The global cinematic display market size was valued at approximately $15 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $25 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 8.9% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising consumer preference for premium viewing experiences, technological advancements in display technologies, and the increasing adoption of 4K and 8K resolution displays.
QLED technology, in particular, has gained significant traction in the cinematic display market. As a key player in this space, Samsung has reported a substantial increase in QLED TV sales, with over 5 million units sold in 2020 alone. This represents a year-over-year growth of 35%, highlighting the growing consumer interest in QLED technology for high-quality displays.
The market is segmented based on display technology, resolution, screen size, and end-user applications. In terms of resolution, 4K displays currently dominate the market, accounting for over 60% of the total market share. However, 8K displays are expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by increasing content availability and declining prices.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for cinematic displays, collectively accounting for over 50% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, with countries like China and India driving demand due to rising disposable incomes and increasing adoption of advanced display technologies.
Key market players in the cinematic display segment include Samsung, LG, Sony, and TCL, among others. These companies are continuously investing in research and development to enhance their product offerings and gain a competitive edge. For instance, Samsung has recently introduced its Neo QLED technology, which combines QLED with Mini-LED backlighting to deliver improved contrast and brightness levels.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the cinematic display market. While it initially disrupted supply chains and manufacturing processes, the increased time spent at home has led to a surge in demand for high-quality home entertainment systems, benefiting the cinematic display market in the long run.
QLED Technology Challenges
QLED technology, while promising for cinematic quality displays, faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and optimal performance. One of the primary obstacles is the issue of color accuracy and consistency. While QLEDs offer a wider color gamut compared to traditional LED displays, achieving precise color reproduction across the entire spectrum remains a complex task. This challenge is particularly evident in maintaining color accuracy at different brightness levels and viewing angles.
Another critical challenge lies in the longevity and stability of quantum dots. These nanocrystals are susceptible to degradation over time, especially when exposed to heat and oxygen. This degradation can lead to a shift in color output and overall display performance, potentially reducing the lifespan of QLED displays. Developing more robust quantum dot materials and effective encapsulation techniques to protect them from environmental factors is an ongoing area of research.
The manufacturing process for QLED displays presents its own set of challenges. Achieving uniform deposition of quantum dots across large display areas while maintaining consistent performance is technically demanding. This challenge becomes more pronounced as manufacturers aim to produce larger screen sizes for cinematic experiences. Additionally, the integration of quantum dots with existing display technologies requires precise engineering to ensure optimal light emission and color conversion.
Power efficiency remains a concern for QLED technology. While QLEDs are generally more energy-efficient than traditional LED-LCD displays, there is still room for improvement, especially when competing with OLED technology in terms of energy consumption. Enhancing the quantum yield of quantum dots and optimizing the overall display architecture to reduce power loss are key areas of focus.
The cost of production is another significant hurdle. The materials and processes involved in manufacturing QLED displays are currently more expensive compared to conventional display technologies. This higher cost can limit the market penetration of QLED displays, particularly in price-sensitive segments. Developing more cost-effective production methods and materials is crucial for wider adoption.
Lastly, the challenge of achieving true black levels and high contrast ratios comparable to OLED technology persists. While QLED displays have made significant strides in this area, particularly with the introduction of mini-LED backlighting, further improvements are needed to match the deep blacks and infinite contrast ratios offered by OLED displays. This aspect is particularly important for cinematic quality, where deep blacks and high contrast are essential for an immersive viewing experience.
Current QLED Display Solutions
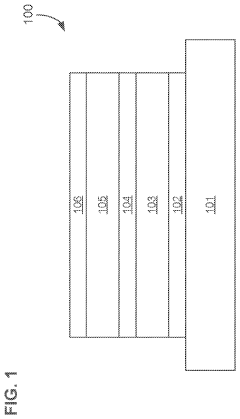
01 Quantum dot light-emitting diode structure
QLED devices utilize a structure incorporating quantum dots as the light-emitting material. This structure typically includes layers such as electron transport layers, hole transport layers, and quantum dot emissive layers. The precise arrangement and composition of these layers can significantly impact the device's performance and cinematic quality.- Quantum dot composition and structure: QLED technology utilizes quantum dots with specific compositions and structures to enhance color performance and efficiency. These quantum dots are typically made of semiconductor materials and can be engineered to emit precise wavelengths of light, resulting in improved color gamut and brightness for cinematic quality displays.
- Light-emitting layer design: The design of the light-emitting layer in QLED displays is crucial for achieving cinematic quality. This includes optimizing the quantum dot arrangement, incorporating light-enhancing structures, and developing novel materials to improve light extraction and color purity.
- Color conversion and enhancement: QLED technology employs various color conversion and enhancement techniques to achieve superior cinematic quality. This includes the use of color filters, phosphors, and advanced quantum dot materials to optimize color reproduction and expand the color gamut for more vivid and accurate images.
- Backlight and display panel integration: The integration of quantum dot technology with backlight systems and display panels is essential for achieving cinematic quality in QLED displays. This involves optimizing the placement of quantum dots, developing advanced optical films, and improving light distribution for enhanced contrast and brightness.
- Driving and control methods: Advanced driving and control methods are employed in QLED displays to optimize performance and achieve cinematic quality. This includes developing sophisticated algorithms for color management, implementing dynamic contrast enhancement techniques, and utilizing adaptive brightness control to improve overall image quality.
02 Color enhancement and gamut expansion
QLED technology offers superior color reproduction capabilities, enabling a wider color gamut and more vibrant, accurate colors. This is achieved through the precise control of quantum dot size and composition, allowing for fine-tuning of the emitted light wavelengths. The result is enhanced cinematic quality with more lifelike and immersive visuals.Expand Specific Solutions03 Brightness and contrast improvement
QLED displays can achieve higher brightness levels and improved contrast ratios compared to traditional LED displays. This is due to the efficient light emission properties of quantum dots and advanced backlight technologies. The enhanced brightness and contrast contribute to a more dynamic and cinematic viewing experience, especially in HDR content.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum dot synthesis and application methods
The quality of QLED displays is heavily dependent on the synthesis and application methods of quantum dots. Advanced techniques for producing uniform, stable quantum dots and efficiently incorporating them into display devices are crucial for achieving high cinematic quality. This includes methods for quantum dot deposition, encapsulation, and integration with other display components.Expand Specific Solutions05 Display driver and image processing technologies
To fully leverage the capabilities of QLED technology for cinematic quality, advanced display drivers and image processing algorithms are essential. These technologies optimize the rendering of content on QLED displays, enhancing features such as local dimming, color mapping, and motion handling to deliver a more refined and immersive viewing experience.Expand Specific Solutions
Key QLED Display Manufacturers
The QLED display technology market for cinematic quality displays is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. Major players like BOE Technology Group, TCL China Star Optoelectronics, and Sharp Corp. are driving innovation in this field. The technology is maturing rapidly, with companies such as Huawei Technologies and Hisense Visual Technology contributing to its development. Research institutions like MIT and The Hong Kong University of Science & Technology are also playing crucial roles in advancing QLED technology. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established electronics manufacturers and specialized display technology firms, indicating a dynamic and evolving market with significant potential for further growth and innovation.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
TCL China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd.
QLED Quantum Dot Innovations
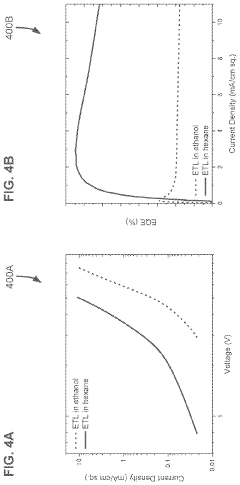
- Incorporating a metal-oxide nanoparticle-based electron transport layer with specific solvent polarity and size characteristics, which improves charge balance and injection efficiency by depositing nanoparticles in a multi-layer structure with varying sizes and polarities, potentially matching or exceeding the size of quantum dots.
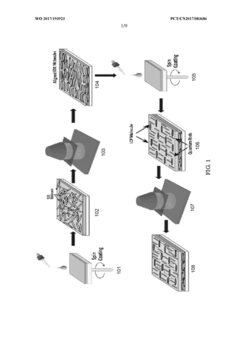
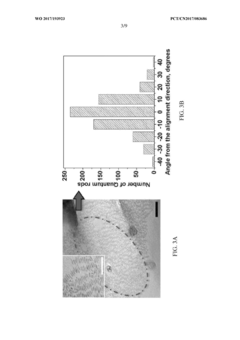
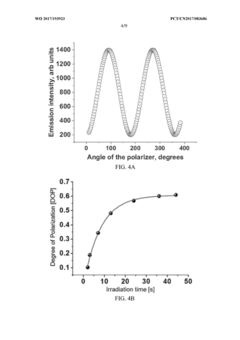
- Utilization of photoaligned quantum rod enhancement films (QREFs) to improve optical efficiency and color gamut of LCDs.
- Integration of quantum rods that emit polarized light, potentially reducing the need for traditional polarizers and improving overall display efficiency.
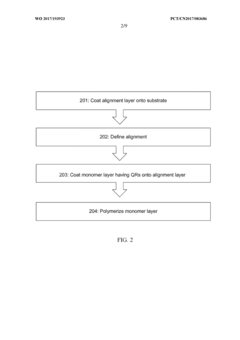
- Development of a scalable production method for QREFs involving photoalignment and polymerization steps.
Environmental Impact of QLED
The environmental impact of QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology is an important consideration in the development and adoption of cinematic quality displays. As QLED technology continues to advance, it is crucial to assess its ecological footprint and potential sustainability benefits compared to other display technologies.
One of the primary environmental advantages of QLED displays is their energy efficiency. QLED screens typically consume less power than traditional LED-LCD displays, particularly when displaying bright and colorful content. This reduced energy consumption translates to lower electricity usage and, consequently, decreased carbon emissions over the lifetime of the display.
The manufacturing process of QLED displays also presents some environmental considerations. Quantum dots, the key component of QLED technology, are typically made from semiconductor nanocrystals. While these materials are produced in small quantities, their synthesis often involves the use of toxic precursors and solvents. However, ongoing research is focused on developing more environmentally friendly production methods, including the use of non-toxic, abundant materials and green synthesis techniques.
In terms of lifespan, QLED displays generally offer longer operational lives compared to OLED alternatives. This extended durability reduces the frequency of replacements, potentially decreasing electronic waste generation. Additionally, the absence of organic compounds in QLED technology mitigates the risk of screen burn-in, further extending the usable life of these displays.
The disposal and recycling of QLED displays present both challenges and opportunities. While the quantum dot layer itself is thin and uses minimal materials, the overall display structure still contains various electronic components and materials common to other display technologies. Proper recycling processes need to be developed and implemented to recover valuable materials and minimize environmental impact at the end of the product's life cycle.
It is worth noting that the production of QLED displays does not require the use of rare earth elements, which are often associated with environmentally damaging mining practices. This aspect gives QLED technology an advantage over some other display technologies in terms of resource sustainability.
As the technology matures, there is a growing focus on incorporating eco-friendly materials into QLED displays. Research is underway to develop quantum dots from sustainable sources and to improve the overall recyclability of display components. These efforts aim to further reduce the environmental footprint of QLED technology throughout its lifecycle.
In conclusion, while QLED technology offers several environmental benefits, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and durability, there is still room for improvement in manufacturing processes and end-of-life management. As innovations in QLED continue to advance, it is crucial for manufacturers and researchers to prioritize environmental considerations alongside performance enhancements to ensure the technology's long-term sustainability in the cinematic display market.
QLED vs. OLED Comparison
QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) and OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) are two leading display technologies competing for dominance in the high-end television and cinematic display market. Both offer significant improvements over traditional LED-LCD displays, but they achieve their results through different means.
QLED technology, pioneered by Samsung, utilizes quantum dots to enhance color and brightness. These nano-scale semiconductors emit light of specific wavelengths when excited by electricity, resulting in highly saturated and precise colors. QLED displays typically offer higher peak brightness levels, making them ideal for well-lit environments and HDR content.
OLED, on the other hand, uses organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. Each pixel in an OLED display is self-emissive, allowing for perfect blacks and infinite contrast ratios. This technology excels in dark room viewing conditions and offers wider viewing angles compared to QLED.
In terms of color reproduction, both technologies can deliver impressive results. QLED displays often boast a wider color gamut, particularly in the brighter parts of the image. OLED, while capable of excellent color accuracy, may struggle to maintain color volume at higher brightness levels.
Longevity and burn-in resistance are areas where QLED currently holds an advantage. Quantum dots are inorganic and more stable over time, whereas OLED's organic compounds can degrade, potentially leading to image retention or burn-in with static content.
Power efficiency is another point of comparison. OLED displays are generally more energy-efficient, especially when displaying darker content, as they can turn off individual pixels completely. QLED displays, which rely on a backlight, consume more power but have been improving in this aspect.
Manufacturing costs and scalability also differ between the two technologies. QLED displays are easier and less expensive to produce in larger sizes, which has contributed to their popularity in the big-screen TV market. OLED production is more complex and costly, particularly for larger panels.
As both technologies continue to evolve, the gap in performance is narrowing. QLED is improving its black levels and viewing angles, while OLED is addressing brightness limitations and burn-in concerns. The choice between QLED and OLED often comes down to specific viewing preferences and environmental conditions, with each technology offering unique strengths for cinematic quality displays.