The Impact of QLED on Digital Consumer Experiences
QLED Technology Evolution
QLED technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception, revolutionizing digital consumer experiences. The journey began with the development of quantum dots, nanoscale semiconductor particles that emit light when excited. These quantum dots were initially used to enhance the color gamut of traditional LCD displays.
The first generation of QLED displays, introduced in the mid-2010s, utilized a film of quantum dots placed in front of an LED backlight. This configuration improved color accuracy and brightness compared to conventional LCD screens. However, these early QLEDs still relied on LCD technology for image formation, limiting their potential for true blacks and high contrast ratios.
As research progressed, manufacturers developed methods to integrate quantum dots directly into the display's color filters. This advancement led to the second generation of QLED displays, offering improved efficiency and color purity. The integration of quantum dots into the display structure allowed for better light management and reduced energy consumption.
The third generation of QLED technology marked a significant leap forward with the introduction of self-emissive quantum dot displays. These displays eliminated the need for a separate backlight, as each quantum dot could emit light independently. This breakthrough enabled QLED displays to achieve deeper blacks, higher contrast ratios, and improved viewing angles, rivaling the performance of OLED technology.
Recent advancements in QLED technology have focused on enhancing color volume and peak brightness. Manufacturers have developed quantum dots capable of producing a wider range of colors, resulting in more vibrant and lifelike images. Additionally, improvements in quantum dot efficiency have led to displays with higher peak brightness levels, enhancing HDR performance and visibility in bright environments.
The evolution of QLED technology has also seen advancements in manufacturing processes, leading to more cost-effective production and increased adoption in consumer electronics. This has resulted in a wider range of QLED-equipped devices, from high-end televisions to smartphones and tablets, making the technology more accessible to consumers.
Looking ahead, ongoing research in quantum dot materials and display architectures promises further improvements in QLED technology. Areas of focus include developing quantum dots with even higher efficiency and stability, as well as exploring new methods of quantum dot integration to enhance display performance and reduce power consumption.
Consumer Demand Analysis
The demand for QLED (Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diode) technology in digital consumer experiences has been growing rapidly in recent years. This surge in interest is primarily driven by the technology's ability to deliver superior color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays. Consumers are increasingly seeking immersive and high-quality visual experiences across various devices, from smartphones and tablets to large-screen televisions and gaming monitors.
In the television market, QLED has gained significant traction, with major manufacturers like Samsung, TCL, and Vizio incorporating the technology into their premium product lines. The enhanced color gamut and HDR capabilities of QLED displays have resonated well with consumers who prioritize picture quality for their home entertainment systems. This has led to a steady increase in QLED TV sales, particularly in the high-end segment of the market.
The gaming industry has also shown a strong appetite for QLED technology. Gamers are particularly drawn to the fast response times, high refresh rates, and vibrant colors that QLED monitors can offer. This has resulted in a growing number of QLED gaming monitors being introduced to the market, catering to both casual and professional gamers who demand top-tier visual performance.
Mobile devices represent another area where QLED technology is making inroads. As consumers increasingly use smartphones and tablets for content consumption, there is a rising demand for displays that can deliver vivid colors and high contrast ratios while maintaining energy efficiency. QLED's ability to meet these requirements has led to its adoption in premium mobile devices, albeit at a slower pace compared to the television and monitor markets.
The automotive industry is also showing interest in QLED technology for in-vehicle displays. As cars become more connected and feature-rich, there is a growing need for high-quality displays that can provide clear information and entertainment in various lighting conditions. QLED's superior brightness and color performance make it an attractive option for next-generation automotive displays.
Looking at market trends, the global QLED market is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors contributing to this growth include increasing disposable income in emerging markets, the ongoing transition to 4K and 8K resolution displays, and the expanding ecosystem of HDR content. Additionally, as manufacturing processes improve and economies of scale are realized, the cost of QLED technology is likely to decrease, making it more accessible to a broader range of consumers.
However, it's important to note that QLED faces competition from other display technologies, particularly OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode). While QLED excels in brightness and color volume, OLED offers advantages in terms of contrast ratio and viewing angles. The ongoing competition between these technologies is likely to drive further innovation and improvements in both, ultimately benefiting consumers with a wider range of high-quality display options.
QLED Technical Challenges
QLED technology, while revolutionary in many aspects, faces several significant technical challenges that impact its widespread adoption and performance optimization. One of the primary hurdles is the stability and longevity of quantum dots. These nanocrystals are prone to degradation when exposed to air, moisture, and high temperatures, which can lead to a decrease in display performance over time. Manufacturers are actively researching ways to enhance the encapsulation of quantum dots to protect them from environmental factors and extend their lifespan.
Another critical challenge lies in the color purity and efficiency of blue quantum dots. While red and green quantum dots have achieved high levels of efficiency, blue quantum dots lag behind in terms of both color saturation and energy efficiency. This imbalance affects the overall color gamut and power consumption of QLED displays. Researchers are exploring alternative materials and structures to improve blue quantum dot performance without compromising stability.
The manufacturing process of QLED displays presents its own set of challenges. Achieving uniform deposition of quantum dots across large display areas while maintaining precise control over their size and distribution is technically demanding. Any inconsistencies in this process can lead to color variations and reduced display quality. Additionally, scaling up production to meet market demands while maintaining high yields and cost-effectiveness remains a significant hurdle for manufacturers.
Heat management is another crucial technical challenge for QLED displays. The high current densities required to excite quantum dots can generate substantial heat, potentially leading to thermal quenching and reduced efficiency. Developing effective heat dissipation mechanisms without increasing the overall thickness of the display is an ongoing area of research and development.
Lastly, the integration of QLED technology with flexible and foldable display substrates presents unique challenges. Ensuring the integrity and performance of quantum dots under mechanical stress and repeated folding cycles requires innovative materials and manufacturing techniques. As consumer demand for flexible display devices grows, overcoming these technical barriers becomes increasingly important for the future of QLED technology in digital consumer experiences.
Current QLED Solutions
01 QLED display technology for enhanced consumer experiences
QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology is used to create displays with improved color accuracy, brightness, and contrast. This technology enhances digital consumer experiences by providing more vibrant and lifelike images, making it ideal for various applications such as televisions, monitors, and mobile devices.- QLED display technology for enhanced consumer experiences: QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology is utilized to create vibrant, high-contrast displays for digital consumer devices. This technology offers improved color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays, enhancing the overall viewing experience for consumers.
- Interactive digital consumer interfaces: Advanced user interfaces are developed to improve digital consumer experiences with QLED devices. These interfaces may include touch-sensitive displays, gesture recognition, and voice control, allowing for more intuitive and engaging interactions with digital content and services.
- Personalized content delivery systems: AI-driven algorithms and data analytics are employed to deliver personalized content recommendations and targeted advertisements to consumers using QLED devices. This tailored approach enhances user engagement and satisfaction with digital services.
- Integration of QLED technology with smart home systems: QLED displays are integrated with smart home ecosystems, allowing consumers to control various household devices and access information through a central interface. This integration enhances the overall digital experience by providing seamless connectivity and control.
- Enhanced digital shopping experiences using QLED displays: QLED technology is utilized to create immersive and interactive digital shopping experiences. This includes virtual try-on features, 3D product visualizations, and augmented reality applications, allowing consumers to make more informed purchasing decisions.
02 Interactive digital consumer experiences with QLED displays
QLED displays are integrated with interactive features to create immersive consumer experiences. This includes touch-sensitive screens, gesture recognition, and voice control, allowing users to interact with digital content in more intuitive and engaging ways. These interactive experiences can be applied to retail environments, educational settings, and entertainment venues.Expand Specific Solutions03 Personalized content delivery on QLED devices
QLED devices are equipped with AI and machine learning algorithms to analyze user preferences and behavior, enabling personalized content delivery. This technology allows for tailored recommendations, targeted advertising, and customized user interfaces, enhancing the overall digital consumer experience across various platforms and applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of QLED technology with IoT and smart home systems
QLED displays are integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) devices and smart home systems to create seamless digital experiences for consumers. This integration allows for centralized control of various home devices, real-time information display, and enhanced connectivity between different smart appliances, improving overall user convenience and functionality.Expand Specific Solutions05 QLED-based augmented and virtual reality experiences
QLED technology is utilized in the development of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) devices to create more immersive and realistic digital experiences. The improved color accuracy and contrast of QLED displays enhance the visual quality of AR and VR content, making these technologies more engaging and applicable to various industries such as gaming, education, and professional training.Expand Specific Solutions
Key QLED Industry Players
The QLED technology market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption in consumer electronics. The market size is expanding rapidly, driven by demand for high-quality displays in TVs, smartphones, and other devices. Technologically, QLED is maturing but still evolving, with key players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology Group, and TCL China Star Optoelectronics leading innovation. Companies such as Sharp, Huawei, and Corning are also contributing to advancements. Research institutions like The Hong Kong University of Science & Technology and Zhejiang University are pushing boundaries in QLED development. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established electronics giants and specialized display technology firms, all vying to enhance digital consumer experiences through QLED innovations.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Sharp Corp.
QLED Core Innovations
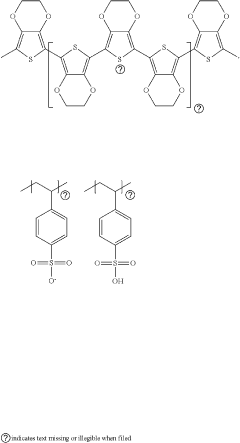
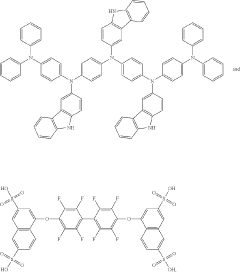
- Incorporating a metal-oxide nanoparticle-based electron transport layer with specific solvent polarity and size characteristics, which improves charge balance and injection efficiency by depositing nanoparticles in a multi-layer structure with varying sizes and polarities, potentially matching or exceeding the size of quantum dots.
- An optoelectronic device with a quantum dot light-emitting layer in a core-shell structure, where the valence band top energy level difference between the shell layer material and the hole transport material is greater than or equal to 0.5 eV, and the electron transport layer comprises zinc oxide nanomaterials bound with amine/carboxyl ligands of 3-8 carbon atoms, optimizing hole and electron injection balance and reducing charge accumulation.
QLED Energy Efficiency
QLED technology has made significant strides in energy efficiency, positioning itself as a competitive option in the display market. The energy consumption of QLED displays has been steadily decreasing over the years, thanks to advancements in quantum dot technology and improved backlight systems.
One of the key factors contributing to QLED's energy efficiency is the use of quantum dots, which can produce highly saturated colors with less power input compared to traditional LED-LCD displays. This allows QLED TVs to achieve higher brightness levels while consuming less energy, resulting in improved overall efficiency.
The implementation of local dimming technology in QLED displays has further enhanced their energy efficiency. By selectively dimming or turning off individual LED zones in darker areas of the screen, power consumption is reduced without compromising picture quality. This feature is particularly beneficial for HDR content, where high contrast ratios are essential.
Recent advancements in QLED technology have also focused on optimizing the backlight system. The introduction of mini-LED backlights has allowed for more precise control over local dimming, resulting in improved energy efficiency and better contrast. Some manufacturers have even begun exploring the use of micro-LED technology in conjunction with quantum dots, which promises even greater energy savings in the future.
Energy-saving modes and intelligent brightness adjustment features have become standard in many QLED displays. These features automatically adjust the screen's brightness based on ambient light conditions and content being displayed, further reducing power consumption without sacrificing the viewing experience.
The energy efficiency of QLED technology has a direct impact on digital consumer experiences. Lower power consumption translates to reduced electricity costs for consumers, making QLED displays more attractive for long-term use. Additionally, the improved energy efficiency allows for the development of larger screens and higher resolutions without excessive power requirements, enabling consumers to enjoy more immersive viewing experiences.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements in energy efficiency. Research is ongoing to develop more efficient quantum dot materials and optimize their integration with display panels. These advancements will likely lead to even lower power consumption in future QLED displays, enhancing their appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and potentially reducing the overall carbon footprint of digital display technologies.
QLED Content Ecosystem
The QLED content ecosystem plays a crucial role in shaping the digital consumer experience. As QLED technology continues to advance, it has sparked a revolution in content creation, distribution, and consumption. This ecosystem encompasses a wide range of stakeholders, including content creators, streaming platforms, and device manufacturers.
One of the primary drivers of the QLED content ecosystem is the demand for high-quality, visually stunning content. QLED displays offer superior color accuracy, brightness, and contrast ratios compared to traditional LED screens. This has led to a surge in the production of HDR (High Dynamic Range) content, which takes full advantage of QLED's capabilities. Major streaming platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ have invested heavily in creating and acquiring HDR content to cater to QLED users.
The gaming industry has also embraced QLED technology, with game developers optimizing their titles to leverage the enhanced visual fidelity offered by these displays. This has resulted in more immersive gaming experiences, with richer colors and improved contrast in both bright and dark scenes. Console manufacturers have responded by ensuring their latest hardware can output content that fully utilizes QLED's potential.
In the realm of digital art and photography, QLED displays have become a preferred choice for professionals and enthusiasts alike. The technology's ability to reproduce a wider color gamut has led to the development of new tools and workflows in digital content creation. Software companies have updated their applications to support the extended color spaces that QLED can display, enabling artists to work with a broader palette of colors.
The QLED content ecosystem has also influenced the way content is distributed. Streaming services have implemented adaptive bitrate technologies that can deliver higher quality streams to QLED-equipped devices, ensuring that viewers can fully appreciate the enhanced visual experience. This has, in turn, driven improvements in broadband infrastructure to support the increased bandwidth requirements of high-quality QLED content.
As the QLED ecosystem continues to evolve, we are seeing the emergence of new content formats and experiences. Virtual and augmented reality applications are being developed with QLED displays in mind, promising even more immersive and lifelike experiences. The technology's impact extends beyond entertainment, influencing fields such as education, where high-fidelity visual content can enhance learning experiences, and in professional sectors like medical imaging, where accurate color reproduction is critical.