QLED Displays: Breaking Barriers in Visual Communication
QLED Technology Evolution and Objectives
Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode (QLED) technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation in the field of visual communication, revolutionizing display technology. The evolution of QLED displays can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers first began exploring the potential of quantum dots in light-emitting applications. Since then, QLED technology has undergone significant advancements, driven by the pursuit of superior image quality, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
The primary objective of QLED technology is to overcome the limitations of traditional display technologies, such as LCD and OLED, by offering enhanced color accuracy, brightness, and longevity. QLED displays aim to provide a wider color gamut, higher peak brightness, and improved contrast ratios, ultimately delivering a more immersive and lifelike visual experience. Additionally, QLED technology seeks to address the challenges of manufacturing scalability and production costs, making high-quality displays more accessible to a broader consumer base.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, several key trends have emerged. One notable trend is the development of cadmium-free quantum dots, addressing environmental concerns and regulatory requirements. Another significant focus has been on improving the efficiency of quantum dot light conversion, leading to reduced power consumption and enhanced display performance. Furthermore, researchers are exploring novel quantum dot materials and structures to expand the capabilities of QLED displays, including flexible and transparent display applications.
The evolution of QLED technology has been marked by several milestones. In 2013, the first commercially available QLED TV was introduced, showcasing the technology's potential in consumer electronics. Subsequent years saw rapid improvements in color volume, peak brightness, and black levels, narrowing the gap with OLED technology. More recently, advancements in quantum dot synthesis and integration techniques have led to the development of self-emissive QLED displays, promising even greater improvements in picture quality and energy efficiency.
Looking ahead, the objectives for QLED technology include further enhancing color accuracy and brightness while reducing power consumption. Researchers are also focusing on improving the stability and longevity of quantum dots to ensure consistent performance over extended periods. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on developing QLED displays for diverse applications beyond traditional televisions and monitors, such as automotive displays, augmented reality devices, and large-scale outdoor signage.
In conclusion, the evolution of QLED technology represents a significant leap forward in visual communication, with ongoing research and development aimed at pushing the boundaries of display performance. As the technology continues to mature, it is poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of digital displays across various industries and applications.
QLED Display Market Analysis
The QLED display market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for high-quality visual experiences across various sectors. This technology, which utilizes quantum dot light-emitting diodes, offers superior color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays.
Market research indicates that the global QLED display market is poised for substantial expansion. The consumer electronics segment, particularly televisions and smartphones, remains the primary driver of QLED adoption. Major manufacturers have been aggressively promoting QLED technology in their premium product lines, contributing to increased consumer awareness and market penetration.
The automotive industry has emerged as a promising growth sector for QLED displays. As vehicles become more technologically advanced, there is a growing demand for high-quality, durable displays for infotainment systems and digital dashboards. QLED technology's ability to deliver vibrant colors and high contrast ratios in various lighting conditions makes it particularly suitable for in-vehicle applications.
Commercial and industrial sectors are also showing increased interest in QLED displays. Digital signage, control room monitors, and large-format displays for public spaces are adopting QLED technology to enhance visual impact and improve energy efficiency. The technology's long lifespan and resistance to image retention make it an attractive option for applications requiring continuous operation.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific leads the QLED display market, with South Korea and China being major manufacturing hubs. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by high consumer spending on premium electronics and rapid adoption of new display technologies in various industries.
Despite its growth, the QLED market faces competition from other emerging display technologies, such as OLED and MicroLED. Each technology has its strengths and limitations, and the market dynamics are influenced by factors such as production costs, technological advancements, and intellectual property considerations.
Looking ahead, the QLED display market is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Technological improvements are likely to focus on enhancing color gamut, increasing energy efficiency, and reducing production costs. As manufacturing processes become more refined, QLED displays are anticipated to become more accessible across different price points, potentially expanding their market reach.
QLED Technical Challenges
QLED displays, while offering significant advancements in visual communication, face several technical challenges that researchers and manufacturers are actively working to overcome. One of the primary hurdles is the optimization of quantum dot efficiency and stability. Despite their superior color performance, quantum dots can degrade over time, especially when exposed to high temperatures or intense light. This degradation can lead to color shifts and reduced display longevity, necessitating the development of more robust quantum dot materials and protective encapsulation techniques.
Another significant challenge lies in the blue light emission. While red and green quantum dots have achieved high efficiency, blue quantum dots still lag behind in terms of both efficiency and stability. This imbalance affects the overall color gamut and power consumption of QLED displays. Researchers are exploring various approaches, including novel quantum dot compositions and structures, to enhance blue light emission without compromising stability.
The manufacturing process for QLED displays also presents technical difficulties. Achieving uniform quantum dot deposition across large display areas while maintaining precise control over quantum dot size and distribution is crucial for consistent color performance. Current manufacturing techniques often struggle to meet these requirements at scale, leading to yield issues and increased production costs.
Heat management is another critical challenge in QLED technology. The high current densities required for bright displays can generate significant heat, potentially accelerating quantum dot degradation and affecting display performance. Developing effective thermal management solutions that can dissipate heat without compromising display thinness or flexibility is an ongoing area of research.
Furthermore, the integration of quantum dots with other display components, such as color filters and light management films, presents its own set of challenges. Optimizing the interplay between these elements to maximize color purity, brightness, and viewing angles while minimizing optical losses requires sophisticated optical engineering and materials science.
Lastly, environmental concerns and regulatory compliance pose additional challenges. The use of heavy metals in some quantum dot compositions has raised questions about the environmental impact and long-term sustainability of QLED technology. Developing cadmium-free quantum dots that can match or exceed the performance of cadmium-based alternatives remains a significant focus of research and development efforts in the field.
Current QLED Solutions
01 QLED display technology advancements
Recent developments in Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode (QLED) display technology have led to improved visual communication capabilities. These advancements include enhanced color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency, making QLED displays suitable for various applications in visual communication, from digital signage to high-end consumer electronics.- QLED display technology advancements: Recent developments in Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode (QLED) display technology have led to improved visual communication capabilities. These advancements include enhanced color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency, making QLED displays suitable for various applications in visual communication, from digital signage to high-end consumer electronics.
- Integration of QLED displays in communication systems: QLED displays are being integrated into various communication systems to enhance visual information delivery. This integration allows for improved user interfaces, more immersive video conferencing experiences, and better data visualization in fields such as healthcare, education, and business communications.
- QLED display driver innovations: Advancements in display driver technology specifically designed for QLED displays have led to improved performance and functionality. These innovations include better power management, faster refresh rates, and enhanced image processing capabilities, contributing to superior visual communication experiences.
- QLED display manufacturing techniques: Novel manufacturing techniques for QLED displays have been developed to improve production efficiency and display quality. These methods focus on enhancing quantum dot deposition, improving color conversion layers, and optimizing the overall display structure to achieve better visual communication performance.
- QLED display applications in visual communication: QLED displays are finding new applications in various visual communication scenarios. These include large-scale digital signage, interactive information kiosks, high-fidelity medical imaging displays, and advanced automotive infotainment systems, all of which benefit from the superior color reproduction and brightness of QLED technology.
02 Integration of QLED displays in communication systems
QLED displays are being integrated into various communication systems to enhance visual information delivery. This integration allows for improved user interfaces, more immersive video conferencing experiences, and better data visualization in fields such as healthcare, education, and business communications.Expand Specific Solutions03 QLED display driver and control mechanisms
Innovative driver circuits and control mechanisms have been developed to optimize the performance of QLED displays in visual communication applications. These advancements include improved refresh rates, reduced latency, and enhanced power management, resulting in smoother and more responsive visual experiences.Expand Specific Solutions04 QLED display manufacturing techniques
New manufacturing techniques for QLED displays have been introduced to improve production efficiency and display quality. These methods focus on enhancing the uniformity of quantum dot deposition, increasing yield rates, and reducing production costs, making QLED technology more accessible for various visual communication applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 QLED display applications in augmented and virtual reality
QLED display technology is being applied to augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) systems, enhancing visual communication in immersive environments. These applications leverage the high color gamut, brightness, and resolution of QLED displays to create more realistic and engaging virtual experiences for education, training, and entertainment purposes.Expand Specific Solutions
QLED Industry Leaders
The QLED display market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across various sectors due to superior visual quality and energy efficiency. The market size is expanding rapidly, driven by demand in consumer electronics and commercial applications. Technologically, QLED displays are maturing, with key players like Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE Technology Group leading innovation. These companies, along with others like Sharp and TCL, are investing heavily in R&D to enhance color accuracy, brightness, and longevity. The competitive landscape is intense, with established electronics giants competing against specialized display manufacturers. Emerging players from China, such as BOE and TCL China Star Optoelectronics, are challenging traditional market leaders, driving innovation and price competition in the QLED sector.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
LG Display Co., Ltd.
QLED Core Innovations
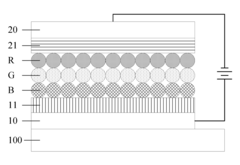
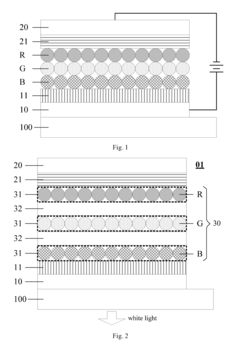
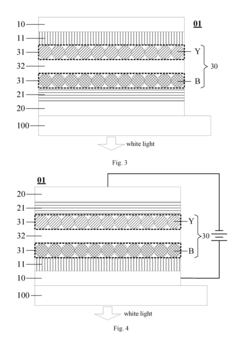
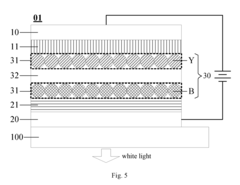
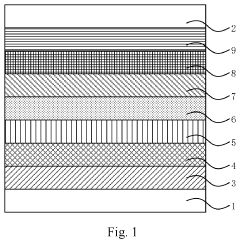
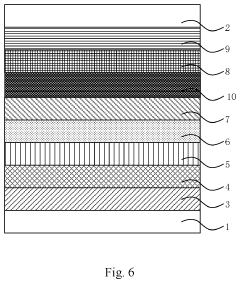
- Incorporating a transparent insulating layer between neighboring QD light-emitting layers of different colors in a light-emitting device, which blocks high-energy exciton transfer and acts as a buffer to maintain light balance and prevent electric leakage.
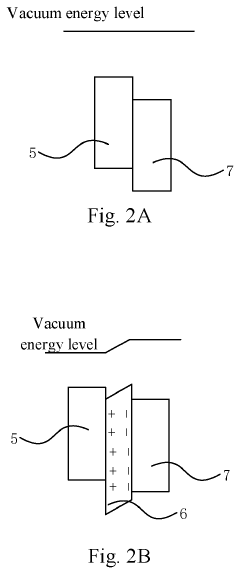
- Incorporating ionic coordination compound layers with built-in electric fields between the hole transport layer and quantum dot luminescent layer, and between the electron transport layer and quantum dot luminescent layer, to alter vacuum energy levels and reduce potential barriers, thereby improving hole injection efficiency and balancing carriers.
QLED Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) displays is a crucial consideration in the ongoing development and adoption of this technology. As QLED displays continue to gain prominence in the visual communication landscape, it is essential to assess their ecological footprint throughout their lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental advantages of QLED technology is its energy efficiency. Compared to traditional LCD displays, QLED screens consume less power while delivering superior brightness and color accuracy. This reduced energy consumption translates to lower carbon emissions during the operational phase of the displays, contributing to a more sustainable visual communication ecosystem.
The manufacturing process of QLED displays also presents some environmental challenges. The production of quantum dots, the key component in QLED technology, involves the use of heavy metals such as cadmium. While efforts are being made to develop cadmium-free quantum dots, the current reliance on these materials raises concerns about potential environmental contamination during production and disposal.
In terms of lifespan, QLED displays generally offer longer operational durability compared to OLED alternatives. This extended lifespan reduces the frequency of replacements, potentially decreasing electronic waste generation. However, the complex nature of QLED panels can make recycling more challenging, necessitating the development of specialized recycling processes to effectively recover and reuse materials.
The packaging and transportation of QLED displays also contribute to their overall environmental impact. As these displays become increasingly popular in various sizes and applications, optimizing packaging materials and logistics can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with their distribution.
Research and development efforts are ongoing to further improve the environmental profile of QLED technology. This includes exploring more sustainable quantum dot materials, enhancing energy efficiency, and developing eco-friendly manufacturing processes. Additionally, initiatives to establish comprehensive recycling programs for QLED displays are crucial for minimizing their end-of-life environmental impact.
As the visual communication industry continues to evolve, balancing the technological advancements of QLED displays with environmental responsibility remains a key challenge. Manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers must collaborate to ensure that the benefits of QLED technology are realized without compromising ecological sustainability.
QLED Standards and Regulations
The development and widespread adoption of QLED display technology have necessitated the establishment of comprehensive standards and regulations to ensure product quality, safety, and performance consistency across the industry. These standards play a crucial role in fostering innovation, promoting fair competition, and protecting consumer interests.
Several international organizations are at the forefront of developing and maintaining QLED standards. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has been instrumental in creating specifications for QLED displays, focusing on aspects such as color gamut, brightness, and power efficiency. Their standards provide a common framework for manufacturers and consumers to evaluate and compare QLED products.
The Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) has also contributed significantly to QLED regulations, particularly in the realm of HDR performance. Their DisplayHDR certification program includes specific tiers for QLED displays, setting benchmarks for peak brightness, black levels, and color accuracy.
In terms of environmental regulations, QLED displays must adhere to strict guidelines regarding the use of hazardous substances. The European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive and the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation have direct implications for QLED manufacturing processes and material selection.
Energy efficiency standards have become increasingly important in the QLED industry. The ENERGY STAR program, administered by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, has established specific criteria for QLED televisions and monitors. These standards encourage manufacturers to develop more energy-efficient products, benefiting both consumers and the environment.
Safety regulations for QLED displays are primarily governed by international standards such as IEC 62368-1, which covers audio/video, information, and communication technology equipment. These safety standards address potential hazards related to electrical shock, fire, and mechanical instability.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, standards and regulations are regularly updated to keep pace with innovations. Industry consortiums and regulatory bodies work closely with manufacturers to ensure that new developments in QLED technology are reflected in updated standards. This ongoing collaboration helps maintain a balance between technological advancement and consumer protection.
The implementation of these standards and regulations has had a significant impact on the QLED market. They have helped establish a level playing field for manufacturers, driving competition based on quality and innovation rather than marketing claims. For consumers, these standards provide assurance of product performance and safety, simplifying the decision-making process when purchasing QLED displays.