The Growing Popularity of QLED in Global Markets
JUN 19, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
QLED Technology Evolution
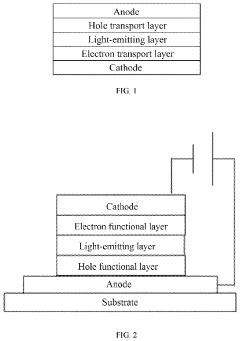
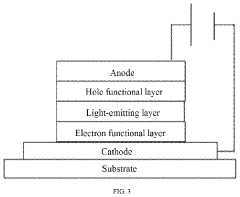
QLED technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception, marking key milestones in display technology advancement. The journey began with the development of quantum dots, nano-sized semiconductor particles that emit light when excited by electricity. These quantum dots were initially used to enhance the color performance of traditional LCD displays.
The first generation of QLED displays, introduced in the mid-2010s, utilized quantum dots in a film layer placed over an LED backlight. This configuration improved color accuracy and brightness compared to conventional LED-LCD screens. However, these early QLEDs still relied on LCD technology for image formation.
A major breakthrough came with the development of electroluminescent quantum dots, which could emit light directly when stimulated by an electric current. This paved the way for true QLED displays, where each pixel is composed of quantum dots that produce their own light, similar to OLED technology but with distinct advantages in brightness and color volume.
The evolution continued with improvements in quantum dot synthesis and manufacturing processes. Enhanced quantum yield and stability of quantum dots led to better energy efficiency and longer lifespan of QLED displays. Researchers also made progress in developing cadmium-free quantum dots, addressing environmental concerns associated with earlier formulations.
Recent advancements have focused on refining the quantum dot layer structure and improving light management within displays. This has resulted in QLEDs with deeper blacks, wider viewing angles, and reduced power consumption. The integration of quantum dots with micro-LED technology is another promising direction, potentially combining the color performance of quantum dots with the high contrast and fast response times of micro-LEDs.
The latest generation of QLED displays incorporates advanced local dimming techniques, utilizing mini-LED backlights with thousands of individually controllable zones. This innovation significantly enhances contrast ratios and HDR performance, bringing QLED picture quality closer to that of OLED displays while maintaining advantages in brightness and color volume.
Looking ahead, researchers are exploring the potential of perovskite quantum dots, which offer improved efficiency and color purity. Additionally, work is underway to develop blue quantum dots with improved stability, which could lead to all-quantum dot displays without the need for color filters, further enhancing energy efficiency and color accuracy.
The first generation of QLED displays, introduced in the mid-2010s, utilized quantum dots in a film layer placed over an LED backlight. This configuration improved color accuracy and brightness compared to conventional LED-LCD screens. However, these early QLEDs still relied on LCD technology for image formation.
A major breakthrough came with the development of electroluminescent quantum dots, which could emit light directly when stimulated by an electric current. This paved the way for true QLED displays, where each pixel is composed of quantum dots that produce their own light, similar to OLED technology but with distinct advantages in brightness and color volume.
The evolution continued with improvements in quantum dot synthesis and manufacturing processes. Enhanced quantum yield and stability of quantum dots led to better energy efficiency and longer lifespan of QLED displays. Researchers also made progress in developing cadmium-free quantum dots, addressing environmental concerns associated with earlier formulations.
Recent advancements have focused on refining the quantum dot layer structure and improving light management within displays. This has resulted in QLEDs with deeper blacks, wider viewing angles, and reduced power consumption. The integration of quantum dots with micro-LED technology is another promising direction, potentially combining the color performance of quantum dots with the high contrast and fast response times of micro-LEDs.
The latest generation of QLED displays incorporates advanced local dimming techniques, utilizing mini-LED backlights with thousands of individually controllable zones. This innovation significantly enhances contrast ratios and HDR performance, bringing QLED picture quality closer to that of OLED displays while maintaining advantages in brightness and color volume.
Looking ahead, researchers are exploring the potential of perovskite quantum dots, which offer improved efficiency and color purity. Additionally, work is underway to develop blue quantum dots with improved stability, which could lead to all-quantum dot displays without the need for color filters, further enhancing energy efficiency and color accuracy.
QLED Market Dynamics
The QLED market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for high-quality display technologies. This surge in popularity can be attributed to several key factors that have shaped the market dynamics of QLED technology.
Firstly, the superior picture quality offered by QLED displays has been a major driving force behind its market expansion. QLED technology provides enhanced color accuracy, brightness, and contrast ratios compared to traditional LED and OLED displays. This improvement in visual performance has resonated strongly with consumers seeking immersive viewing experiences, particularly in the high-end television segment.
The competitive pricing strategy adopted by QLED manufacturers has also played a crucial role in market penetration. While initially positioned as a premium product, QLED displays have gradually become more affordable, bridging the gap between conventional LED TVs and the more expensive OLED options. This pricing approach has made QLED technology accessible to a broader consumer base, contributing to its widespread adoption.
Furthermore, the versatility of QLED technology has allowed for its integration into various product categories beyond televisions. The expansion into monitors, digital signage, and other display applications has opened up new market segments and revenue streams for manufacturers. This diversification has strengthened the overall market position of QLED technology and contributed to its growing popularity.
The global QLED market has also benefited from strategic partnerships and collaborations between display manufacturers and content providers. These alliances have focused on optimizing content for QLED displays, ensuring that consumers can fully appreciate the technology's capabilities. Such partnerships have not only enhanced the perceived value of QLED products but have also created a more cohesive ecosystem for users.
Geographically, the QLED market has seen varying rates of adoption across different regions. North America and Europe have been at the forefront of QLED adoption, driven by high consumer spending power and a strong appetite for cutting-edge display technologies. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly countries like China and South Korea, has emerged as both a significant market and a major manufacturing hub for QLED displays.
Looking ahead, the QLED market is poised for continued growth, with several trends shaping its future dynamics. The increasing demand for larger screen sizes in home entertainment systems is expected to favor QLED technology, which can maintain picture quality across expansive displays. Additionally, the growing focus on energy efficiency and sustainability in consumer electronics aligns well with the ongoing improvements in QLED power consumption and manufacturing processes.
Firstly, the superior picture quality offered by QLED displays has been a major driving force behind its market expansion. QLED technology provides enhanced color accuracy, brightness, and contrast ratios compared to traditional LED and OLED displays. This improvement in visual performance has resonated strongly with consumers seeking immersive viewing experiences, particularly in the high-end television segment.
The competitive pricing strategy adopted by QLED manufacturers has also played a crucial role in market penetration. While initially positioned as a premium product, QLED displays have gradually become more affordable, bridging the gap between conventional LED TVs and the more expensive OLED options. This pricing approach has made QLED technology accessible to a broader consumer base, contributing to its widespread adoption.
Furthermore, the versatility of QLED technology has allowed for its integration into various product categories beyond televisions. The expansion into monitors, digital signage, and other display applications has opened up new market segments and revenue streams for manufacturers. This diversification has strengthened the overall market position of QLED technology and contributed to its growing popularity.
The global QLED market has also benefited from strategic partnerships and collaborations between display manufacturers and content providers. These alliances have focused on optimizing content for QLED displays, ensuring that consumers can fully appreciate the technology's capabilities. Such partnerships have not only enhanced the perceived value of QLED products but have also created a more cohesive ecosystem for users.
Geographically, the QLED market has seen varying rates of adoption across different regions. North America and Europe have been at the forefront of QLED adoption, driven by high consumer spending power and a strong appetite for cutting-edge display technologies. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly countries like China and South Korea, has emerged as both a significant market and a major manufacturing hub for QLED displays.
Looking ahead, the QLED market is poised for continued growth, with several trends shaping its future dynamics. The increasing demand for larger screen sizes in home entertainment systems is expected to favor QLED technology, which can maintain picture quality across expansive displays. Additionally, the growing focus on energy efficiency and sustainability in consumer electronics aligns well with the ongoing improvements in QLED power consumption and manufacturing processes.
Technical Hurdles in QLED
Despite the growing popularity of QLED technology in global markets, several technical hurdles still need to be addressed to fully realize its potential. One of the primary challenges is the stability and longevity of quantum dots, particularly blue quantum dots. These nanocrystals tend to degrade faster than their red and green counterparts, leading to color shift and reduced display lifespan. Researchers are actively working on improving the chemical composition and structure of blue quantum dots to enhance their durability.
Another significant hurdle is the efficiency of quantum dot light emission. While QLED displays offer superior color gamut and brightness compared to traditional LED-LCD screens, there is still room for improvement in terms of energy efficiency. The quantum yield of quantum dots, especially when integrated into display panels, needs to be optimized to reduce power consumption and heat generation.
The manufacturing process for QLED displays also presents challenges. Achieving uniform deposition of quantum dots across large-scale panels while maintaining precise control over their size and distribution is technically demanding. This affects the consistency of color reproduction and overall display quality. Additionally, the integration of quantum dots with existing display technologies requires careful engineering to prevent degradation caused by exposure to oxygen, moisture, and heat.
Color purity and spectral characteristics of quantum dots remain areas of ongoing research. While QLEDs offer excellent color saturation, further refinement is needed to achieve even narrower emission spectra for each primary color. This would result in more accurate color reproduction and an expanded color gamut, pushing the boundaries of display technology.
The cost of production is another hurdle that needs to be overcome for wider adoption of QLED technology. Currently, the synthesis of high-quality quantum dots and their integration into display panels is relatively expensive compared to conventional display technologies. Developing more cost-effective production methods and scaling up manufacturing processes are crucial for making QLED displays more accessible to consumers.
Lastly, environmental concerns and regulatory compliance pose challenges for QLED technology. Many quantum dots contain heavy metals like cadmium, which are subject to strict regulations in various countries. Developing cadmium-free quantum dots that maintain the same level of performance is an ongoing area of research, aimed at ensuring the long-term sustainability and global acceptance of QLED technology.
Another significant hurdle is the efficiency of quantum dot light emission. While QLED displays offer superior color gamut and brightness compared to traditional LED-LCD screens, there is still room for improvement in terms of energy efficiency. The quantum yield of quantum dots, especially when integrated into display panels, needs to be optimized to reduce power consumption and heat generation.
The manufacturing process for QLED displays also presents challenges. Achieving uniform deposition of quantum dots across large-scale panels while maintaining precise control over their size and distribution is technically demanding. This affects the consistency of color reproduction and overall display quality. Additionally, the integration of quantum dots with existing display technologies requires careful engineering to prevent degradation caused by exposure to oxygen, moisture, and heat.
Color purity and spectral characteristics of quantum dots remain areas of ongoing research. While QLEDs offer excellent color saturation, further refinement is needed to achieve even narrower emission spectra for each primary color. This would result in more accurate color reproduction and an expanded color gamut, pushing the boundaries of display technology.
The cost of production is another hurdle that needs to be overcome for wider adoption of QLED technology. Currently, the synthesis of high-quality quantum dots and their integration into display panels is relatively expensive compared to conventional display technologies. Developing more cost-effective production methods and scaling up manufacturing processes are crucial for making QLED displays more accessible to consumers.
Lastly, environmental concerns and regulatory compliance pose challenges for QLED technology. Many quantum dots contain heavy metals like cadmium, which are subject to strict regulations in various countries. Developing cadmium-free quantum dots that maintain the same level of performance is an ongoing area of research, aimed at ensuring the long-term sustainability and global acceptance of QLED technology.
Current QLED Solutions
01 QLED display technology advancements
Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode (QLED) technology has seen significant advancements, improving display quality and efficiency. These improvements include enhanced color reproduction, brightness, and energy efficiency, contributing to the increasing popularity of QLED displays in various applications such as televisions, monitors, and mobile devices.- QLED display technology advancements: Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode (QLED) technology has seen significant advancements, improving display quality and efficiency. These improvements include enhanced color gamut, brightness, and energy efficiency, contributing to the increasing popularity of QLED displays in various applications such as televisions, monitors, and mobile devices.
- Market trends and consumer adoption: The popularity of QLED technology is reflected in market trends and consumer adoption rates. Factors such as competitive pricing, improved performance, and marketing strategies have contributed to the increased demand for QLED products. This trend is observed across various regions and market segments.
- Comparison with other display technologies: QLED popularity is often analyzed in comparison to other display technologies such as OLED, LED, and LCD. The unique advantages of QLED, including better brightness, longer lifespan, and reduced risk of burn-in, have contributed to its growing popularity in certain market segments.
- Manufacturing and production innovations: Innovations in manufacturing processes and production techniques have played a crucial role in increasing QLED popularity. These advancements have led to improved yield rates, reduced production costs, and enhanced product quality, making QLED displays more accessible and attractive to consumers.
- Integration with smart technologies: The integration of QLED displays with smart technologies and IoT devices has contributed to their popularity. This includes features such as voice control, AI-enhanced picture quality, and seamless connectivity with other smart home devices, making QLED displays more appealing to tech-savvy consumers.
02 Manufacturing processes for QLED devices
Innovations in manufacturing processes have made QLED production more cost-effective and scalable. These advancements include improved quantum dot synthesis methods, enhanced deposition techniques, and optimized device structures, leading to higher yields and better performance of QLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions03 QLED market growth and consumer adoption
The QLED market has experienced significant growth due to increasing consumer demand for high-quality displays. Factors contributing to this growth include competitive pricing, improved product offerings, and effective marketing strategies. The popularity of QLED technology has led to its adoption in various consumer electronics segments.Expand Specific Solutions04 QLED integration with other technologies
QLED technology has been successfully integrated with other display and electronic technologies, enhancing its versatility and appeal. This integration includes combinations with OLED, mini-LED backlighting, and smart TV platforms, expanding the range of applications and improving overall user experience.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and sustainability aspects of QLED
The popularity of QLED technology has been influenced by its environmental and sustainability benefits. These include lower energy consumption compared to some other display technologies, potential for longer device lifespan, and ongoing research into more eco-friendly quantum dot materials and manufacturing processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key QLED Manufacturers
The QLED market is experiencing rapid growth globally, driven by increasing demand for high-quality displays in consumer electronics and commercial applications. The industry is in a phase of technological maturation and market expansion, with key players like BOE Technology Group, Sharp Corp., and Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. leading innovation. The market size is projected to grow significantly, fueled by advancements in quantum dot technology and improved manufacturing processes. Companies such as Chengdu BOE Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd. and Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Semicon Display Tech Co. are contributing to the technology's maturity through research and development efforts, while academic institutions like Zhejiang University and The Hong Kong University of Science & Technology are pushing the boundaries of QLED capabilities.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
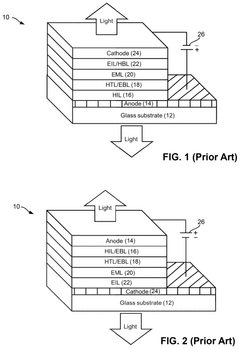
Technical Solution: BOE has developed advanced QLED technology using quantum dot materials to enhance color performance and brightness. Their QLED displays feature a quantum dot layer that converts blue light from LEDs into pure red and green light, resulting in a wider color gamut and higher peak brightness compared to traditional LCD displays. BOE's QLED panels also incorporate local dimming technology to improve contrast ratios and HDR performance.
Strengths: Wide color gamut, high brightness, improved energy efficiency. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional LCD, potential for burn-in with static images.
Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Semicon Display Tech Co.
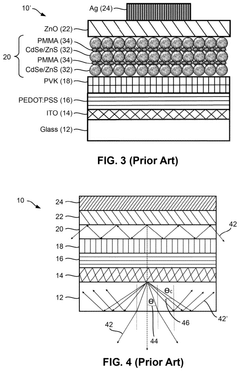
Technical Solution: China Star Optoelectronics has developed a proprietary QLED technology called "Q-Light" that utilizes quantum dot enhancement film (QDEF) to improve color performance and energy efficiency. Their QLED displays feature a special optical design that maximizes light output while minimizing color crosstalk. The company has also implemented advanced local dimming algorithms to enhance contrast and HDR capabilities in their QLED panels.
Strengths: Excellent color accuracy, high energy efficiency, competitive pricing. Weaknesses: Limited production capacity compared to larger competitors, potential for color shift over time.
QLED Core Innovations
Optoelectronic device
PatentPendingUS20240107791A1
Innovation
- An optoelectronic device with a quantum dot light-emitting layer in a core-shell structure, where the valence band top energy level difference between the shell layer material and the hole transport material is greater than or equal to 0.5 eV, and the electron transport layer comprises zinc oxide nanomaterials bound with amine/carboxyl ligands of 3-8 carbon atoms, optimizing hole and electron injection balance and reducing charge accumulation.
Integrated optoelectronic devices for lighting and display applications
PatentPendingUS20240341118A1
Innovation
- Incorporation of metasurfaces with two-dimensional arrays of nanostructures into the light-emitting devices to reduce photon reflection, control light direction, and manipulate emission profiles, combined with machine-learning methods for optimizing light patterns and using flexible substrates like hybrid silver nanowires and carbon nanotubes for improved conductivity and stability.
QLED vs. OLED Comparison
QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) and OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) are two leading display technologies competing for dominance in the global market. Both offer superior picture quality compared to traditional LED-LCD displays, but they achieve this through different mechanisms.
QLED technology, pioneered by Samsung, utilizes quantum dots to enhance color and brightness. These nano-sized semiconductor particles emit light when excited by electricity, producing vibrant and accurate colors. QLED displays typically offer higher peak brightness levels, making them ideal for well-lit environments and HDR content.
OLED, on the other hand, uses organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. Each pixel in an OLED display is self-illuminating, allowing for perfect blacks and infinite contrast ratios. This technology excels in dark room viewing conditions and offers wider viewing angles compared to QLED.
In terms of lifespan, QLED displays generally have an advantage. The inorganic nature of quantum dots makes them more resistant to degradation over time, whereas OLED panels may experience burn-in or image retention issues with prolonged static image display.
Energy efficiency is another point of comparison. OLED displays tend to be more energy-efficient overall, especially when displaying darker content, as individual pixels can be turned off completely. QLED displays, while improving in efficiency, still rely on a backlight system that consumes more power.
Manufacturing costs and scalability also differ between the two technologies. QLED displays are generally less expensive to produce and easier to manufacture in larger sizes, contributing to their growing popularity in the TV market. OLED production, while becoming more efficient, still faces challenges in scaling up to very large sizes cost-effectively.
As the display market evolves, both QLED and OLED continue to improve. QLED technology is advancing with innovations like Mini-LED backlighting, which offers better local dimming capabilities. OLED is progressing with developments such as QLED-OLED hybrid technologies, aiming to combine the strengths of both approaches.
The choice between QLED and OLED often comes down to specific use cases and personal preferences. QLED's brightness advantage makes it popular for daytime viewing and in bright rooms, while OLED's superior contrast and black levels are preferred for cinema-like experiences in darker environments. As both technologies continue to evolve, consumers benefit from a wider range of high-quality display options across various price points and applications.
QLED technology, pioneered by Samsung, utilizes quantum dots to enhance color and brightness. These nano-sized semiconductor particles emit light when excited by electricity, producing vibrant and accurate colors. QLED displays typically offer higher peak brightness levels, making them ideal for well-lit environments and HDR content.
OLED, on the other hand, uses organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. Each pixel in an OLED display is self-illuminating, allowing for perfect blacks and infinite contrast ratios. This technology excels in dark room viewing conditions and offers wider viewing angles compared to QLED.
In terms of lifespan, QLED displays generally have an advantage. The inorganic nature of quantum dots makes them more resistant to degradation over time, whereas OLED panels may experience burn-in or image retention issues with prolonged static image display.
Energy efficiency is another point of comparison. OLED displays tend to be more energy-efficient overall, especially when displaying darker content, as individual pixels can be turned off completely. QLED displays, while improving in efficiency, still rely on a backlight system that consumes more power.
Manufacturing costs and scalability also differ between the two technologies. QLED displays are generally less expensive to produce and easier to manufacture in larger sizes, contributing to their growing popularity in the TV market. OLED production, while becoming more efficient, still faces challenges in scaling up to very large sizes cost-effectively.
As the display market evolves, both QLED and OLED continue to improve. QLED technology is advancing with innovations like Mini-LED backlighting, which offers better local dimming capabilities. OLED is progressing with developments such as QLED-OLED hybrid technologies, aiming to combine the strengths of both approaches.
The choice between QLED and OLED often comes down to specific use cases and personal preferences. QLED's brightness advantage makes it popular for daytime viewing and in bright rooms, while OLED's superior contrast and black levels are preferred for cinema-like experiences in darker environments. As both technologies continue to evolve, consumers benefit from a wider range of high-quality display options across various price points and applications.
QLED Energy Efficiency
QLED technology has made significant strides in energy efficiency, positioning itself as a competitive option in the global display market. The energy efficiency of QLED displays is primarily attributed to their unique quantum dot structure, which allows for more precise light emission and reduced power consumption compared to traditional LED displays.
One of the key factors contributing to QLED's energy efficiency is its ability to produce a wider color gamut with less energy input. Quantum dots can emit specific wavelengths of light with high precision, resulting in more vibrant and accurate colors while consuming less power. This efficiency is particularly noticeable in high dynamic range (HDR) content, where QLED displays can achieve higher peak brightness levels without significantly increasing power consumption.
Furthermore, QLED technology incorporates advanced local dimming techniques, which allow for more granular control over backlight zones. This feature enables the display to selectively dim or turn off areas of the screen that don't require illumination, thereby reducing overall power consumption. The combination of quantum dot efficiency and sophisticated backlight control systems results in impressive energy savings, especially in larger screen sizes.
Recent advancements in QLED manufacturing processes have also contributed to improved energy efficiency. Refinements in quantum dot synthesis and application methods have led to higher quantum yields, meaning more of the input energy is converted into visible light rather than being lost as heat. This not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to the longevity of the display by reducing thermal stress on components.
In comparison to OLED technology, QLED displays often demonstrate superior energy efficiency in bright room conditions and when displaying content with large areas of white or light colors. This is due to the fact that QLED screens use a backlight, which can be more energy-efficient than individually lit pixels in OLED displays when producing bright images.
As global energy regulations become more stringent, the energy efficiency of QLED technology has become a significant selling point for manufacturers. Many QLED displays now boast energy ratings that meet or exceed international standards, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint and energy costs.
One of the key factors contributing to QLED's energy efficiency is its ability to produce a wider color gamut with less energy input. Quantum dots can emit specific wavelengths of light with high precision, resulting in more vibrant and accurate colors while consuming less power. This efficiency is particularly noticeable in high dynamic range (HDR) content, where QLED displays can achieve higher peak brightness levels without significantly increasing power consumption.
Furthermore, QLED technology incorporates advanced local dimming techniques, which allow for more granular control over backlight zones. This feature enables the display to selectively dim or turn off areas of the screen that don't require illumination, thereby reducing overall power consumption. The combination of quantum dot efficiency and sophisticated backlight control systems results in impressive energy savings, especially in larger screen sizes.
Recent advancements in QLED manufacturing processes have also contributed to improved energy efficiency. Refinements in quantum dot synthesis and application methods have led to higher quantum yields, meaning more of the input energy is converted into visible light rather than being lost as heat. This not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to the longevity of the display by reducing thermal stress on components.
In comparison to OLED technology, QLED displays often demonstrate superior energy efficiency in bright room conditions and when displaying content with large areas of white or light colors. This is due to the fact that QLED screens use a backlight, which can be more energy-efficient than individually lit pixels in OLED displays when producing bright images.
As global energy regulations become more stringent, the energy efficiency of QLED technology has become a significant selling point for manufacturers. Many QLED displays now boast energy ratings that meet or exceed international standards, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint and energy costs.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!