QLED in Smart Homes: The Next Evolution
JUN 19, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
QLED Smart Home Evolution
QLED technology has rapidly evolved from its inception in the early 2010s to become a significant player in the display market. Initially developed as an alternative to OLED, QLED has made substantial strides in picture quality, energy efficiency, and durability. The evolution of QLED in smart homes represents a convergence of advanced display technology with the growing demand for interconnected, intelligent living spaces.
The trajectory of QLED development has been marked by continuous improvements in color accuracy, brightness, and contrast ratios. Early iterations focused on enhancing the basic quantum dot technology, while recent advancements have centered on refining the backlight systems and expanding the color gamut. The integration of QLED displays into smart home ecosystems has opened up new possibilities for ambient computing and immersive experiences.
As QLED technology progresses, we anticipate several key developments that will shape its role in smart homes. Enhanced AI integration is expected to enable QLED displays to adapt dynamically to environmental conditions and user preferences. This could include automatic brightness and color temperature adjustments based on time of day and ambient light levels, as well as personalized content recommendations.
Improved energy efficiency is another critical area of focus. Future QLED displays are likely to incorporate more sophisticated power management systems, potentially leveraging machine learning algorithms to optimize energy consumption without compromising visual quality. This aligns well with the growing emphasis on sustainability in smart home design.
Connectivity and interoperability will play a crucial role in the evolution of QLED in smart homes. We expect to see tighter integration with other smart home devices, allowing QLED displays to serve as central hubs for controlling various aspects of the home environment. This could include seamless interaction with smart lighting systems, security cameras, and voice assistants.
The form factor of QLED displays is also likely to evolve. Flexible and modular QLED panels may become more prevalent, allowing for customizable display configurations that can adapt to different spaces and use cases within the smart home. This could lead to innovative applications such as QLED-enhanced smart windows or interactive wall displays.
As QLED technology continues to mature, we anticipate its increasing adoption in various smart home applications beyond traditional TV screens. This may include integration into smart mirrors, kitchen appliances, and even furniture, further blurring the lines between technology and home decor.
The trajectory of QLED development has been marked by continuous improvements in color accuracy, brightness, and contrast ratios. Early iterations focused on enhancing the basic quantum dot technology, while recent advancements have centered on refining the backlight systems and expanding the color gamut. The integration of QLED displays into smart home ecosystems has opened up new possibilities for ambient computing and immersive experiences.
As QLED technology progresses, we anticipate several key developments that will shape its role in smart homes. Enhanced AI integration is expected to enable QLED displays to adapt dynamically to environmental conditions and user preferences. This could include automatic brightness and color temperature adjustments based on time of day and ambient light levels, as well as personalized content recommendations.
Improved energy efficiency is another critical area of focus. Future QLED displays are likely to incorporate more sophisticated power management systems, potentially leveraging machine learning algorithms to optimize energy consumption without compromising visual quality. This aligns well with the growing emphasis on sustainability in smart home design.
Connectivity and interoperability will play a crucial role in the evolution of QLED in smart homes. We expect to see tighter integration with other smart home devices, allowing QLED displays to serve as central hubs for controlling various aspects of the home environment. This could include seamless interaction with smart lighting systems, security cameras, and voice assistants.
The form factor of QLED displays is also likely to evolve. Flexible and modular QLED panels may become more prevalent, allowing for customizable display configurations that can adapt to different spaces and use cases within the smart home. This could lead to innovative applications such as QLED-enhanced smart windows or interactive wall displays.
As QLED technology continues to mature, we anticipate its increasing adoption in various smart home applications beyond traditional TV screens. This may include integration into smart mirrors, kitchen appliances, and even furniture, further blurring the lines between technology and home decor.
Smart Home Market Analysis
The smart home market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for convenience, energy efficiency, and enhanced home security. As QLED technology enters this space, it is poised to revolutionize the way we interact with our living environments. The global smart home market was valued at $78.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $182.4 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 18.4% during the forecast period.
One of the key drivers of this market growth is the rising adoption of IoT devices and the increasing penetration of smartphones and other smart devices. These technologies serve as control hubs for smart home systems, making it easier for consumers to manage their homes remotely. The integration of QLED displays into smart home ecosystems is expected to further accelerate this trend, offering superior visual experiences and new possibilities for home automation.
In terms of regional distribution, North America currently holds the largest share of the smart home market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable income, and growing awareness of smart home technologies.
The smart home market can be segmented into various categories, including lighting control, security and access control, HVAC control, entertainment systems, and home healthcare. With the introduction of QLED technology, the entertainment and display segment is likely to see significant growth and innovation. QLED displays offer superior color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LED and OLED technologies, making them ideal for smart home applications.
Consumer preferences in the smart home market are shifting towards more integrated and seamless experiences. There is a growing demand for devices that not only perform their primary functions but also contribute to the overall aesthetics of the home. QLED displays, with their slim profiles and vibrant picture quality, are well-positioned to meet this demand, potentially serving as both functional devices and design elements in smart homes.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also had a notable impact on the smart home market. With more people spending time at home, there has been an increased focus on home improvement and the adoption of technologies that enhance comfort, productivity, and entertainment. This trend is expected to continue even as pandemic restrictions ease, providing a favorable environment for the integration of advanced display technologies like QLED into smart home systems.
One of the key drivers of this market growth is the rising adoption of IoT devices and the increasing penetration of smartphones and other smart devices. These technologies serve as control hubs for smart home systems, making it easier for consumers to manage their homes remotely. The integration of QLED displays into smart home ecosystems is expected to further accelerate this trend, offering superior visual experiences and new possibilities for home automation.
In terms of regional distribution, North America currently holds the largest share of the smart home market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable income, and growing awareness of smart home technologies.
The smart home market can be segmented into various categories, including lighting control, security and access control, HVAC control, entertainment systems, and home healthcare. With the introduction of QLED technology, the entertainment and display segment is likely to see significant growth and innovation. QLED displays offer superior color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LED and OLED technologies, making them ideal for smart home applications.
Consumer preferences in the smart home market are shifting towards more integrated and seamless experiences. There is a growing demand for devices that not only perform their primary functions but also contribute to the overall aesthetics of the home. QLED displays, with their slim profiles and vibrant picture quality, are well-positioned to meet this demand, potentially serving as both functional devices and design elements in smart homes.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also had a notable impact on the smart home market. With more people spending time at home, there has been an increased focus on home improvement and the adoption of technologies that enhance comfort, productivity, and entertainment. This trend is expected to continue even as pandemic restrictions ease, providing a favorable environment for the integration of advanced display technologies like QLED into smart home systems.
QLED Technology Challenges
While QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology has made significant strides in recent years, its integration into smart homes faces several key challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
One of the primary obstacles is the high production cost of QLED displays. The manufacturing process for quantum dots remains complex and expensive, making QLED devices less accessible for average consumers. This cost barrier limits the technology's penetration into various smart home applications beyond high-end televisions and monitors.
Energy efficiency is another critical challenge for QLED in smart homes. Although QLEDs offer improved power consumption compared to traditional LED displays, they still consume more energy than some competing technologies like OLED. In a smart home context, where energy management is crucial, this higher power draw could be a significant drawback.
Durability and lifespan concerns also pose challenges for QLED integration. Quantum dots can degrade over time, especially when exposed to heat and moisture. This vulnerability raises questions about the long-term reliability of QLED devices in diverse smart home environments, where conditions may vary significantly.
Color accuracy and consistency present ongoing technical hurdles. While QLEDs excel in producing vibrant colors, maintaining precise color reproduction across different lighting conditions and viewing angles remains challenging. This is particularly important in smart home applications where ambient light levels can fluctuate dramatically.
Integration with existing smart home ecosystems is another significant challenge. QLED devices need to seamlessly communicate and interact with other smart home components, requiring robust connectivity solutions and standardized protocols. Ensuring compatibility across various platforms and manufacturers adds complexity to the development process.
Heat management is a persistent issue for QLED technology. The quantum dots' performance can be affected by temperature fluctuations, necessitating advanced cooling systems. This requirement adds to the complexity and cost of QLED devices, potentially limiting their application in compact or heat-sensitive smart home products.
Lastly, the environmental impact of quantum dot production and disposal remains a concern. Some quantum dots contain heavy metals, raising questions about sustainability and potential health risks. Addressing these environmental challenges is crucial for the long-term viability of QLED technology in eco-conscious smart homes.
One of the primary obstacles is the high production cost of QLED displays. The manufacturing process for quantum dots remains complex and expensive, making QLED devices less accessible for average consumers. This cost barrier limits the technology's penetration into various smart home applications beyond high-end televisions and monitors.
Energy efficiency is another critical challenge for QLED in smart homes. Although QLEDs offer improved power consumption compared to traditional LED displays, they still consume more energy than some competing technologies like OLED. In a smart home context, where energy management is crucial, this higher power draw could be a significant drawback.
Durability and lifespan concerns also pose challenges for QLED integration. Quantum dots can degrade over time, especially when exposed to heat and moisture. This vulnerability raises questions about the long-term reliability of QLED devices in diverse smart home environments, where conditions may vary significantly.
Color accuracy and consistency present ongoing technical hurdles. While QLEDs excel in producing vibrant colors, maintaining precise color reproduction across different lighting conditions and viewing angles remains challenging. This is particularly important in smart home applications where ambient light levels can fluctuate dramatically.
Integration with existing smart home ecosystems is another significant challenge. QLED devices need to seamlessly communicate and interact with other smart home components, requiring robust connectivity solutions and standardized protocols. Ensuring compatibility across various platforms and manufacturers adds complexity to the development process.
Heat management is a persistent issue for QLED technology. The quantum dots' performance can be affected by temperature fluctuations, necessitating advanced cooling systems. This requirement adds to the complexity and cost of QLED devices, potentially limiting their application in compact or heat-sensitive smart home products.
Lastly, the environmental impact of quantum dot production and disposal remains a concern. Some quantum dots contain heavy metals, raising questions about sustainability and potential health risks. Addressing these environmental challenges is crucial for the long-term viability of QLED technology in eco-conscious smart homes.
Current QLED Solutions
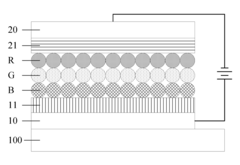
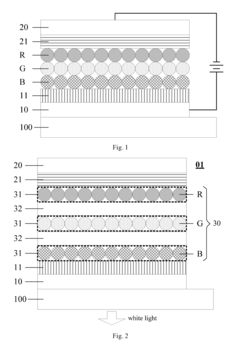
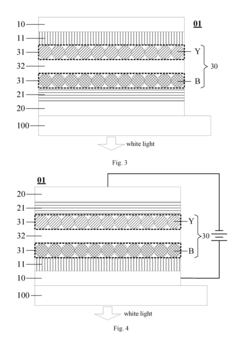
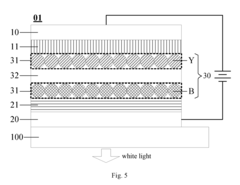
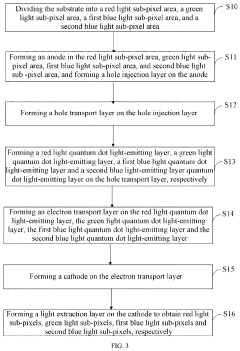
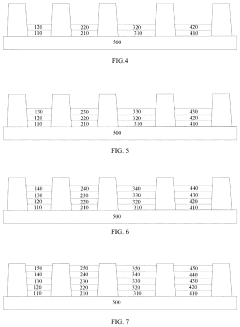
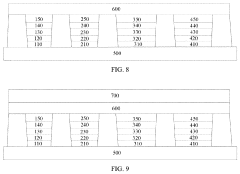
01 QLED structure and composition
QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology involves the use of quantum dots as light-emitting materials. The structure typically includes layers of quantum dots sandwiched between electron and hole transport layers. The composition and arrangement of these layers are crucial for optimizing the device's performance, including color purity, brightness, and efficiency.- QLED structure and composition: QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology involves the use of quantum dots as light-emitting materials. The structure typically includes layers of quantum dots sandwiched between electron and hole transport layers. The composition and arrangement of these layers are crucial for optimizing the device's performance, including color purity, brightness, and efficiency.
- Quantum dot synthesis and modification: The synthesis and modification of quantum dots play a vital role in QLED performance. This includes developing methods to control the size, shape, and surface properties of quantum dots. Techniques such as core-shell structures and surface ligand engineering are employed to enhance the optical and electrical properties of the quantum dots, leading to improved QLED devices.
- QLED manufacturing processes: Advancements in QLED manufacturing processes focus on improving scalability, yield, and cost-effectiveness. This includes developing novel deposition techniques for quantum dot layers, such as inkjet printing or transfer printing methods. Additionally, innovations in encapsulation and packaging technologies are crucial for enhancing device stability and longevity.
- Color tuning and light management: Techniques for precise color tuning and light management in QLED displays are essential for achieving high color gamut and display performance. This involves optimizing the quantum dot emission spectra, developing color conversion layers, and implementing advanced optical designs to enhance light extraction and reduce optical losses within the device structure.
- QLED device stability and lifetime improvement: Enhancing the stability and operational lifetime of QLED devices is a critical area of research. This includes developing strategies to mitigate degradation mechanisms, such as photo-oxidation and thermal quenching of quantum dots. Innovations in materials selection, device architecture, and encapsulation techniques are explored to improve the long-term performance and reliability of QLED displays and lighting applications.
02 Quantum dot synthesis and modification
The synthesis and modification of quantum dots play a vital role in QLED performance. This includes developing methods to control the size, shape, and surface properties of quantum dots. Surface modification techniques are employed to enhance stability, improve charge transfer, and prevent aggregation of quantum dots in the emissive layer.Expand Specific Solutions03 Charge transport layer optimization
Optimizing the charge transport layers in QLEDs is crucial for efficient device operation. This involves developing novel materials and structures for both electron and hole transport layers. The focus is on improving charge injection, transport, and balance within the device to enhance overall performance and longevity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Color tuning and light management
Techniques for precise color tuning and light management in QLEDs are essential for display applications. This includes developing methods to control the emission spectrum of quantum dots, implementing color conversion layers, and optimizing light extraction from the device. Advanced optical designs are employed to enhance color gamut and viewing angles.Expand Specific Solutions05 QLED manufacturing and scaling
Developing efficient and scalable manufacturing processes for QLEDs is crucial for commercialization. This includes improving deposition techniques for quantum dot and charge transport layers, developing patterning methods for display applications, and addressing challenges related to large-scale production and yield improvement.Expand Specific Solutions
Key QLED Manufacturers
The QLED technology in smart homes is entering a mature phase, with significant market growth potential. The industry is transitioning from early adoption to mainstream integration, driven by increasing consumer demand for high-quality displays in connected living spaces. Major players like BOE Technology Group, TCL China Star Optoelectronics, and Sharp Corp. are leading the technological advancements, while companies such as Huawei Technologies and Google LLC are integrating QLED into their smart home ecosystems. The market is characterized by intense competition and rapid innovation, with companies like Nanosys, Inc. focusing on quantum dot technology improvements. As the technology matures, we're seeing increased collaboration between display manufacturers and smart home solution providers, indicating a convergence of display technology and IoT capabilities in the smart home sector.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed advanced QLED technology for smart home applications, focusing on high color gamut, energy efficiency, and longevity. Their QLED displays utilize quantum dot technology to enhance color accuracy and brightness. BOE's smart home QLED solutions incorporate AI-driven local dimming for improved contrast and reduced power consumption. They have also integrated voice control and IoT connectivity features to enhance user interaction within smart home ecosystems.
Strengths: Wide color gamut, energy efficiency, and seamless integration with smart home systems. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional LED displays, and potential for image retention in static content scenarios.
Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Semicon Display Tech Co.
Technical Solution: China Star Optoelectronics has developed a proprietary QLED technology for smart home applications, focusing on ultra-thin display panels with high brightness and wide color gamut. Their QLED solution incorporates advanced quantum dot materials and precise light management techniques to achieve superior picture quality. The company has also integrated smart sensors and AI algorithms to automatically adjust display settings based on ambient light conditions and user preferences, enhancing the overall smart home experience.
Strengths: Ultra-thin design, high brightness, and adaptive display technology. Weaknesses: Limited experience in smart home ecosystem integration compared to some competitors.
QLED Patents and Research
Light emitting device and fabricating method thereof, display device
PatentActiveUS20180054872A1
Innovation
- Incorporating a transparent insulating layer between neighboring QD light-emitting layers of different colors in a light-emitting device, which blocks high-energy exciton transfer and acts as a buffer to maintain light balance and prevent electric leakage.
Display device and pixel lighting control method therefor
PatentPendingUS20240013710A1
Innovation
- A display device comprising a plurality of pixels, each including a red light sub-pixel, a green light sub-pixel, a first blue light sub-pixel, and a second blue light sub-pixel, where the first blue light sub-pixel is configured to emit light at high brightness and the second blue light sub-pixel is configured to emit light at low brightness, with the first blue light sub-pixel having high efficiency and the second blue light sub-pixel having a long lifetime, allowing for independent control based on brightness requirements.
Energy Efficiency Impact
The integration of QLED technology in smart homes represents a significant leap forward in energy efficiency for residential lighting and display systems. QLED, or Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode, offers several advantages over traditional LED and OLED technologies in terms of power consumption and overall energy performance.
QLED displays consume less power compared to conventional LED and LCD screens, particularly when displaying bright and vibrant colors. This is due to the quantum dots' ability to produce more precise wavelengths of light, resulting in less energy waste. In smart home applications, where displays are often used for extended periods, this translates to substantial energy savings over time.
Moreover, QLED technology allows for better light management and local dimming capabilities. This means that in smart home control panels or ambient displays, only the necessary parts of the screen need to be illuminated, further reducing power consumption. The improved contrast ratio and peak brightness of QLED displays also contribute to energy efficiency, as they can deliver the same visual impact at lower power levels compared to other display technologies.
In the context of smart lighting systems, QLED-based bulbs and fixtures offer superior color accuracy and brightness while consuming less energy. This is particularly beneficial in creating dynamic lighting environments that adapt to user preferences and daily routines, optimizing both comfort and energy use.
The longevity of QLED technology also plays a role in its energy efficiency impact. With a longer lifespan compared to traditional LEDs, QLED-based devices in smart homes require less frequent replacement, reducing the overall energy footprint associated with manufacturing and disposal of electronic components.
Furthermore, the integration of QLED technology with smart home energy management systems can lead to more sophisticated and efficient control of display and lighting elements. For instance, QLED displays can automatically adjust their brightness and color temperature based on ambient light conditions or user presence, ensuring optimal energy use without compromising on visual quality or user experience.
As smart homes become increasingly interconnected, the energy-efficient properties of QLED technology contribute to the overall reduction of household energy consumption. This aligns with the growing trend towards sustainable living and the development of net-zero energy homes, where every component's energy efficiency is crucial.
QLED displays consume less power compared to conventional LED and LCD screens, particularly when displaying bright and vibrant colors. This is due to the quantum dots' ability to produce more precise wavelengths of light, resulting in less energy waste. In smart home applications, where displays are often used for extended periods, this translates to substantial energy savings over time.
Moreover, QLED technology allows for better light management and local dimming capabilities. This means that in smart home control panels or ambient displays, only the necessary parts of the screen need to be illuminated, further reducing power consumption. The improved contrast ratio and peak brightness of QLED displays also contribute to energy efficiency, as they can deliver the same visual impact at lower power levels compared to other display technologies.
In the context of smart lighting systems, QLED-based bulbs and fixtures offer superior color accuracy and brightness while consuming less energy. This is particularly beneficial in creating dynamic lighting environments that adapt to user preferences and daily routines, optimizing both comfort and energy use.
The longevity of QLED technology also plays a role in its energy efficiency impact. With a longer lifespan compared to traditional LEDs, QLED-based devices in smart homes require less frequent replacement, reducing the overall energy footprint associated with manufacturing and disposal of electronic components.
Furthermore, the integration of QLED technology with smart home energy management systems can lead to more sophisticated and efficient control of display and lighting elements. For instance, QLED displays can automatically adjust their brightness and color temperature based on ambient light conditions or user presence, ensuring optimal energy use without compromising on visual quality or user experience.
As smart homes become increasingly interconnected, the energy-efficient properties of QLED technology contribute to the overall reduction of household energy consumption. This aligns with the growing trend towards sustainable living and the development of net-zero energy homes, where every component's energy efficiency is crucial.
QLED Integration Standards
The integration of QLED technology into smart homes requires standardized protocols and interfaces to ensure seamless connectivity and interoperability. These standards are crucial for the widespread adoption and efficient functioning of QLED devices within the smart home ecosystem.
One of the primary standards for QLED integration is the HDMI 2.1 specification. This standard supports higher resolutions and refresh rates, making it ideal for QLED displays in smart homes. It also includes features like Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) and Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM), which enhance the viewing experience for both entertainment and gaming applications.
Another important standard is the HDR10+ format, which is specifically designed to optimize the performance of QLED displays. This dynamic metadata standard allows for frame-by-frame adjustment of brightness and color, resulting in more accurate and vibrant images. Many smart home devices and streaming services are adopting HDR10+ to ensure compatibility with QLED screens.
The Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) protocol is also essential for QLED integration in smart homes. It allows users to control multiple devices with a single remote, simplifying the user experience. CEC enables QLED displays to communicate with other smart home devices, such as sound systems and media players, creating a more cohesive entertainment setup.
For wireless connectivity, Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) and Bluetooth 5.0 standards are becoming increasingly important. These protocols provide faster data transfer rates and improved range, allowing QLED devices to communicate more efficiently with other smart home components. This is particularly crucial for streaming high-quality content and controlling QLED displays through mobile devices or voice assistants.
The Matter standard, developed by the Connectivity Standards Alliance, is set to play a significant role in QLED integration. This open-source protocol aims to unify smart home devices across different brands and ecosystems, potentially simplifying the integration of QLED displays with various smart home platforms.
Energy efficiency standards are also critical for QLED integration. The ENERGY STAR certification program provides guidelines for energy-efficient electronics, including QLED displays. Compliance with these standards ensures that QLED devices in smart homes contribute to overall energy savings and sustainability efforts.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, new standards are likely to emerge. These may include advanced color management protocols, improved content protection standards, and enhanced interoperability specifications. Staying abreast of these developments will be crucial for manufacturers and consumers alike to fully leverage the potential of QLED technology in smart homes.
One of the primary standards for QLED integration is the HDMI 2.1 specification. This standard supports higher resolutions and refresh rates, making it ideal for QLED displays in smart homes. It also includes features like Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) and Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM), which enhance the viewing experience for both entertainment and gaming applications.
Another important standard is the HDR10+ format, which is specifically designed to optimize the performance of QLED displays. This dynamic metadata standard allows for frame-by-frame adjustment of brightness and color, resulting in more accurate and vibrant images. Many smart home devices and streaming services are adopting HDR10+ to ensure compatibility with QLED screens.
The Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) protocol is also essential for QLED integration in smart homes. It allows users to control multiple devices with a single remote, simplifying the user experience. CEC enables QLED displays to communicate with other smart home devices, such as sound systems and media players, creating a more cohesive entertainment setup.
For wireless connectivity, Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) and Bluetooth 5.0 standards are becoming increasingly important. These protocols provide faster data transfer rates and improved range, allowing QLED devices to communicate more efficiently with other smart home components. This is particularly crucial for streaming high-quality content and controlling QLED displays through mobile devices or voice assistants.
The Matter standard, developed by the Connectivity Standards Alliance, is set to play a significant role in QLED integration. This open-source protocol aims to unify smart home devices across different brands and ecosystems, potentially simplifying the integration of QLED displays with various smart home platforms.
Energy efficiency standards are also critical for QLED integration. The ENERGY STAR certification program provides guidelines for energy-efficient electronics, including QLED displays. Compliance with these standards ensures that QLED devices in smart homes contribute to overall energy savings and sustainability efforts.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, new standards are likely to emerge. These may include advanced color management protocols, improved content protection standards, and enhanced interoperability specifications. Staying abreast of these developments will be crucial for manufacturers and consumers alike to fully leverage the potential of QLED technology in smart homes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!