Future Trends in LDPE Consumption and Production
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Market Overview and Objectives
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone of the plastics industry since its commercial introduction in the 1930s. This versatile material has found widespread applications across various sectors, including packaging, construction, and agriculture. As we look towards the future, understanding the trends in LDPE consumption and production becomes crucial for industry stakeholders and policymakers alike.
The global LDPE market has experienced steady growth over the past decades, driven by increasing demand in emerging economies and the material's adaptability to diverse applications. However, the landscape is evolving rapidly, influenced by factors such as environmental concerns, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. This dynamic environment necessitates a comprehensive analysis of the market's trajectory and the objectives that will shape its future.
One of the primary drivers of LDPE consumption has been the packaging industry, particularly in food and beverage sectors. The material's excellent barrier properties, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness have made it a preferred choice for manufacturers. However, the growing emphasis on sustainability and recycling has begun to challenge LDPE's dominance in certain applications, prompting the industry to innovate and adapt.
In terms of production, technological advancements have led to more efficient manufacturing processes, reducing costs and environmental impact. The development of metallocene catalysts, for instance, has allowed for the production of LDPE with enhanced properties, opening up new application possibilities. Additionally, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies in LDPE production facilities is expected to further optimize operations and improve product quality.
Looking ahead, the LDPE market faces both opportunities and challenges. The push towards a circular economy is driving research into more recyclable and biodegradable alternatives, which could potentially impact LDPE's market share. Conversely, the material's versatility and established supply chains provide a strong foundation for continued growth, particularly in developing regions where plastic consumption is on the rise.
The objectives for the LDPE industry moving forward are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a pressing need to improve the material's environmental profile through enhanced recycling capabilities and the development of bio-based alternatives. Secondly, manufacturers are focusing on product innovation to maintain LDPE's competitiveness against other polymers and materials. Lastly, the industry aims to expand into new application areas, leveraging LDPE's unique properties to solve emerging challenges in sectors such as renewable energy and healthcare.
The global LDPE market has experienced steady growth over the past decades, driven by increasing demand in emerging economies and the material's adaptability to diverse applications. However, the landscape is evolving rapidly, influenced by factors such as environmental concerns, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. This dynamic environment necessitates a comprehensive analysis of the market's trajectory and the objectives that will shape its future.
One of the primary drivers of LDPE consumption has been the packaging industry, particularly in food and beverage sectors. The material's excellent barrier properties, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness have made it a preferred choice for manufacturers. However, the growing emphasis on sustainability and recycling has begun to challenge LDPE's dominance in certain applications, prompting the industry to innovate and adapt.
In terms of production, technological advancements have led to more efficient manufacturing processes, reducing costs and environmental impact. The development of metallocene catalysts, for instance, has allowed for the production of LDPE with enhanced properties, opening up new application possibilities. Additionally, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies in LDPE production facilities is expected to further optimize operations and improve product quality.
Looking ahead, the LDPE market faces both opportunities and challenges. The push towards a circular economy is driving research into more recyclable and biodegradable alternatives, which could potentially impact LDPE's market share. Conversely, the material's versatility and established supply chains provide a strong foundation for continued growth, particularly in developing regions where plastic consumption is on the rise.
The objectives for the LDPE industry moving forward are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a pressing need to improve the material's environmental profile through enhanced recycling capabilities and the development of bio-based alternatives. Secondly, manufacturers are focusing on product innovation to maintain LDPE's competitiveness against other polymers and materials. Lastly, the industry aims to expand into new application areas, leveraging LDPE's unique properties to solve emerging challenges in sectors such as renewable energy and healthcare.
LDPE Demand Analysis
The global demand for Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) continues to grow steadily, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. LDPE's unique properties, including flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance, make it a preferred choice in packaging, agriculture, and construction sectors. The packaging industry remains the largest consumer of LDPE, accounting for a significant portion of the total demand. This is primarily due to the increasing use of flexible packaging solutions in food, beverage, and consumer goods industries.
In recent years, the e-commerce boom has further accelerated the demand for LDPE in packaging applications. The need for protective packaging materials for online shipments has created a new growth avenue for LDPE producers. Additionally, the agricultural sector has shown increased adoption of LDPE films for greenhouse coverings and mulching, contributing to the overall demand growth.
However, the LDPE market faces challenges from environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The growing awareness of plastic pollution has led to increased scrutiny of single-use plastics, many of which are made from LDPE. This has prompted some regions to implement restrictions on certain plastic products, potentially impacting LDPE demand in the long term.
Despite these challenges, innovations in recycling technologies and the development of bio-based LDPE alternatives are opening up new opportunities. The circular economy initiatives are driving the demand for recycled LDPE, creating a parallel market that complements virgin LDPE production. Furthermore, the automotive and healthcare industries are exploring new applications for LDPE, which could offset potential losses in traditional markets.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains the largest consumer and producer of LDPE, with China leading the market. The region's rapid industrialization and growing middle-class population continue to drive demand. North America and Europe, while mature markets, are seeing steady demand, particularly in high-value applications such as medical packaging and specialty films.
Looking ahead, the LDPE market is expected to navigate a complex landscape of environmental regulations, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. The industry's ability to innovate and adapt to these changes will be crucial in shaping future demand patterns. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, the focus on developing more environmentally friendly LDPE products and improving recycling infrastructure will likely intensify, potentially reshaping the market dynamics in the coming years.
In recent years, the e-commerce boom has further accelerated the demand for LDPE in packaging applications. The need for protective packaging materials for online shipments has created a new growth avenue for LDPE producers. Additionally, the agricultural sector has shown increased adoption of LDPE films for greenhouse coverings and mulching, contributing to the overall demand growth.
However, the LDPE market faces challenges from environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The growing awareness of plastic pollution has led to increased scrutiny of single-use plastics, many of which are made from LDPE. This has prompted some regions to implement restrictions on certain plastic products, potentially impacting LDPE demand in the long term.
Despite these challenges, innovations in recycling technologies and the development of bio-based LDPE alternatives are opening up new opportunities. The circular economy initiatives are driving the demand for recycled LDPE, creating a parallel market that complements virgin LDPE production. Furthermore, the automotive and healthcare industries are exploring new applications for LDPE, which could offset potential losses in traditional markets.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains the largest consumer and producer of LDPE, with China leading the market. The region's rapid industrialization and growing middle-class population continue to drive demand. North America and Europe, while mature markets, are seeing steady demand, particularly in high-value applications such as medical packaging and specialty films.
Looking ahead, the LDPE market is expected to navigate a complex landscape of environmental regulations, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. The industry's ability to innovate and adapt to these changes will be crucial in shaping future demand patterns. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, the focus on developing more environmentally friendly LDPE products and improving recycling infrastructure will likely intensify, potentially reshaping the market dynamics in the coming years.
LDPE Production Challenges
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) production faces several significant challenges that impact its future trends in consumption and production. One of the primary issues is the increasing pressure to reduce the environmental impact of plastic production. LDPE, being a petroleum-based product, contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and plastic waste pollution. This has led to growing regulatory scrutiny and consumer demand for more sustainable alternatives, forcing manufacturers to explore eco-friendly production methods and materials.
Energy consumption is another major challenge in LDPE production. The process is energy-intensive, requiring high temperatures and pressures to polymerize ethylene. As energy costs continue to rise and environmental regulations become stricter, producers are compelled to invest in more efficient technologies and processes to reduce energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. This drive for efficiency is pushing the industry towards advanced catalysts and process optimizations.
Raw material availability and price volatility present ongoing challenges for LDPE producers. The primary feedstock, ethylene, is derived from petroleum or natural gas, making LDPE production susceptible to fluctuations in oil and gas prices. This volatility can significantly impact production costs and, consequently, market competitiveness. Producers are thus exploring alternative feedstock sources and diversifying their supply chains to mitigate these risks.
The increasing demand for higher performance plastics is also challenging traditional LDPE production. End-users in various industries are seeking materials with enhanced properties such as improved strength, barrier characteristics, and processability. This trend is driving producers to innovate and develop new grades of LDPE or hybrid materials that can meet these evolving requirements while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Capacity management and market oversupply are persistent issues in the LDPE industry. The cyclical nature of the petrochemical industry, coupled with the long lead times for new plant construction, often results in periods of overcapacity. This can lead to price pressures and reduced profitability for producers, necessitating careful strategic planning and market forecasting to align production capacity with demand.
Technological obsolescence is an emerging challenge as newer polyethylene technologies, such as metallocene LLDPE, gain market share. LDPE producers must continually invest in research and development to improve their processes and products to remain competitive. This includes exploring new catalyst systems, process control technologies, and product formulations to enhance efficiency and product quality.
Lastly, the global shift towards a circular economy model is reshaping the LDPE production landscape. There is growing pressure to incorporate recycled content into LDPE products and to design materials that are more easily recyclable. This transition requires significant investments in recycling infrastructure, technologies for chemical recycling, and the development of new product designs that facilitate end-of-life recovery and reuse.
Energy consumption is another major challenge in LDPE production. The process is energy-intensive, requiring high temperatures and pressures to polymerize ethylene. As energy costs continue to rise and environmental regulations become stricter, producers are compelled to invest in more efficient technologies and processes to reduce energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. This drive for efficiency is pushing the industry towards advanced catalysts and process optimizations.
Raw material availability and price volatility present ongoing challenges for LDPE producers. The primary feedstock, ethylene, is derived from petroleum or natural gas, making LDPE production susceptible to fluctuations in oil and gas prices. This volatility can significantly impact production costs and, consequently, market competitiveness. Producers are thus exploring alternative feedstock sources and diversifying their supply chains to mitigate these risks.
The increasing demand for higher performance plastics is also challenging traditional LDPE production. End-users in various industries are seeking materials with enhanced properties such as improved strength, barrier characteristics, and processability. This trend is driving producers to innovate and develop new grades of LDPE or hybrid materials that can meet these evolving requirements while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Capacity management and market oversupply are persistent issues in the LDPE industry. The cyclical nature of the petrochemical industry, coupled with the long lead times for new plant construction, often results in periods of overcapacity. This can lead to price pressures and reduced profitability for producers, necessitating careful strategic planning and market forecasting to align production capacity with demand.
Technological obsolescence is an emerging challenge as newer polyethylene technologies, such as metallocene LLDPE, gain market share. LDPE producers must continually invest in research and development to improve their processes and products to remain competitive. This includes exploring new catalyst systems, process control technologies, and product formulations to enhance efficiency and product quality.
Lastly, the global shift towards a circular economy model is reshaping the LDPE production landscape. There is growing pressure to incorporate recycled content into LDPE products and to design materials that are more easily recyclable. This transition requires significant investments in recycling infrastructure, technologies for chemical recycling, and the development of new product designs that facilitate end-of-life recovery and reuse.
Current LDPE Production Methods
01 LDPE production methods
Various methods for producing Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) are described, including high-pressure polymerization processes and the use of specific catalysts. These methods aim to improve production efficiency and control the properties of the resulting LDPE.- LDPE production methods: Various methods for producing Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) are described, including high-pressure polymerization processes and the use of specific catalysts. These methods aim to improve production efficiency and control the properties of the resulting LDPE.
- LDPE applications and consumption: LDPE finds widespread use in various industries, including packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods. The consumption patterns and market demand for LDPE products are analyzed, highlighting the material's versatility and economic importance.
- LDPE recycling and sustainability: Innovations in LDPE recycling processes and sustainable production methods are presented. These advancements aim to reduce environmental impact and promote circular economy principles in the plastics industry.
- LDPE blends and composites: Research on LDPE blends and composites with other materials to enhance properties such as strength, durability, and functionality. These developments expand the potential applications of LDPE in various sectors.
- LDPE processing technologies: Advancements in LDPE processing technologies, including extrusion, molding, and film production techniques. These innovations aim to improve product quality, reduce production costs, and increase manufacturing efficiency.
02 LDPE applications and consumption
LDPE finds widespread use in various industries, including packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods. The consumption patterns and market demand for LDPE products are analyzed, highlighting its versatility and importance in different sectors.Expand Specific Solutions03 LDPE recycling and sustainability
Efforts to improve the recyclability and sustainability of LDPE are discussed. This includes developing new recycling technologies, enhancing the biodegradability of LDPE products, and exploring eco-friendly alternatives to reduce environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions04 LDPE blends and composites
Research on LDPE blends and composites is presented, focusing on enhancing the material properties by combining LDPE with other polymers or additives. These innovations aim to improve the performance and expand the application range of LDPE-based materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 LDPE processing and manufacturing equipment
Advancements in LDPE processing techniques and manufacturing equipment are explored. This includes innovations in extrusion, molding, and film production technologies to enhance production efficiency and product quality.Expand Specific Solutions
Key LDPE Manufacturers
The future trends in LDPE consumption and production are shaped by a competitive landscape involving major players across the petrochemical industry. The market is in a mature stage but continues to grow, driven by increasing demand in packaging and construction sectors. The global LDPE market size is expected to expand, with key companies like Dow, ExxonMobil, and Sinopec leading technological advancements. These firms, along with others such as LG Chem and SABIC, are investing in research and development to improve LDPE properties and production efficiency. The technology's maturity is evident in the involvement of established petrochemical giants, yet ongoing innovation in catalysts and processes by companies and research institutions indicates potential for further market evolution.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow is pioneering advanced LDPE production technologies to meet future consumption trends. They are developing catalysts and processes for more efficient LDPE production, including hybrid metallocene catalysts that allow for precise control of polymer properties[1]. Dow is also investing in circular economy solutions, such as mechanical and advanced recycling technologies, to address the growing demand for sustainable LDPE products[2]. Their focus on digitalization and automation in LDPE production aims to improve efficiency and reduce energy consumption, aligning with future sustainability requirements[3].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, global market presence, and leadership in sustainable solutions. Weaknesses: High capital investment required for new technologies and potential regulatory challenges in some markets.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil is advancing LDPE production through innovative technologies like their proprietary tubular process, which allows for the production of high-quality LDPE with improved optical and mechanical properties[4]. They are also developing new catalyst systems that enable the production of LDPE with enhanced performance characteristics, such as increased strength and better processability[5]. ExxonMobil is investing in research to reduce the carbon footprint of LDPE production, including the use of renewable feedstocks and more energy-efficient processes[6].
Strengths: Extensive research capabilities, proprietary technologies, and global supply chain. Weaknesses: Dependence on fossil fuel-based feedstocks and potential challenges in transitioning to more sustainable production methods.
LDPE Innovation Breakthroughs
Blends of virgin LDPE with post-consumer recycled low density and/or linear low density polyethylene and methods thereof
PatentPendingCN119816547A
Innovation
- Compound LDPE polymers with a density of 0.915-0.928 g/cm3 and a melt index of 3.0-20 g/10 min were prepared by mixing native LDPE with a high shear index of LDPE with a lower melt index in a twin-screw extruder.
Process to control output and quality of ethylene-based polymer formed by high pressure free radical polymerization
PatentInactiveUS20180346613A1
Innovation
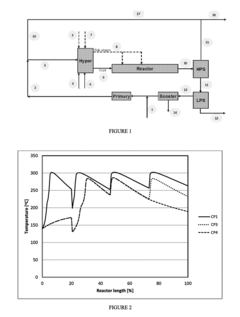
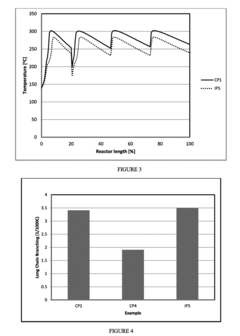
- A process that involves polymerizing ethylene in the presence of specific initiator systems at varying inlet pressures and throughputs, with a hyper compressor and reactor configuration that allows for controlled reduction of reactor inlet pressure by at least 200 Bar, while maintaining the ratio of total reactor consumption of the highest temperature class initiator system within specific bounds, to control polymer output and quality.
Environmental Impact of LDPE
The environmental impact of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a critical concern as global consumption and production trends continue to evolve. LDPE, widely used in packaging and various consumer products, poses significant challenges to ecosystems and waste management systems worldwide.
One of the primary environmental issues associated with LDPE is its persistence in nature. As a non-biodegradable material, LDPE can remain in the environment for hundreds of years, contributing to long-term pollution of land and water bodies. This persistence leads to the accumulation of plastic waste in oceans, forming large garbage patches and posing threats to marine life through ingestion and entanglement.
The production process of LDPE also contributes to environmental degradation. The manufacturing of LDPE relies heavily on fossil fuels, both as raw materials and energy sources. This dependence results in significant greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change and air pollution. Additionally, the extraction and processing of these fossil fuels can lead to habitat destruction and ecosystem disruption.
Improper disposal of LDPE products exacerbates its environmental impact. When incinerated, LDPE releases toxic chemicals into the atmosphere, including dioxins and furans, which are harmful to human health and the environment. Landfilling of LDPE waste occupies valuable land space and can lead to soil and groundwater contamination through leaching of additives and microplastics.
The issue of microplastics, tiny plastic particles less than 5mm in size, is another significant concern related to LDPE. As LDPE products break down in the environment, they form microplastics that can enter food chains and ecosystems, potentially causing harm to wildlife and human health. These particles have been found in various environments, from deep ocean sediments to Arctic ice, highlighting the global scale of plastic pollution.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of LDPE include improved recycling technologies and waste management practices. However, the low recycling rates of LDPE, due to contamination and mixed plastic types, remain a challenge. Innovations in biodegradable and compostable alternatives to LDPE are being explored, but these solutions often come with their own set of environmental trade-offs and implementation challenges.
As future trends in LDPE consumption and production are considered, addressing its environmental impact becomes increasingly crucial. Sustainable alternatives, improved recycling technologies, and more effective waste management strategies will be essential in mitigating the long-term environmental consequences of LDPE use.
One of the primary environmental issues associated with LDPE is its persistence in nature. As a non-biodegradable material, LDPE can remain in the environment for hundreds of years, contributing to long-term pollution of land and water bodies. This persistence leads to the accumulation of plastic waste in oceans, forming large garbage patches and posing threats to marine life through ingestion and entanglement.
The production process of LDPE also contributes to environmental degradation. The manufacturing of LDPE relies heavily on fossil fuels, both as raw materials and energy sources. This dependence results in significant greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change and air pollution. Additionally, the extraction and processing of these fossil fuels can lead to habitat destruction and ecosystem disruption.
Improper disposal of LDPE products exacerbates its environmental impact. When incinerated, LDPE releases toxic chemicals into the atmosphere, including dioxins and furans, which are harmful to human health and the environment. Landfilling of LDPE waste occupies valuable land space and can lead to soil and groundwater contamination through leaching of additives and microplastics.
The issue of microplastics, tiny plastic particles less than 5mm in size, is another significant concern related to LDPE. As LDPE products break down in the environment, they form microplastics that can enter food chains and ecosystems, potentially causing harm to wildlife and human health. These particles have been found in various environments, from deep ocean sediments to Arctic ice, highlighting the global scale of plastic pollution.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of LDPE include improved recycling technologies and waste management practices. However, the low recycling rates of LDPE, due to contamination and mixed plastic types, remain a challenge. Innovations in biodegradable and compostable alternatives to LDPE are being explored, but these solutions often come with their own set of environmental trade-offs and implementation challenges.
As future trends in LDPE consumption and production are considered, addressing its environmental impact becomes increasingly crucial. Sustainable alternatives, improved recycling technologies, and more effective waste management strategies will be essential in mitigating the long-term environmental consequences of LDPE use.
Circular Economy for LDPE
The circular economy for LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) represents a paradigm shift in how we approach the production, consumption, and disposal of this widely used plastic material. As global concerns over plastic waste and environmental sustainability grow, the circular economy model offers a promising solution to mitigate the negative impacts of LDPE while maximizing its value throughout its lifecycle.
At the core of the circular economy for LDPE is the principle of reducing waste and pollution by keeping materials in use for as long as possible. This approach involves several key strategies, including design for recyclability, efficient collection and sorting systems, and advanced recycling technologies. By implementing these strategies, the LDPE industry can significantly reduce its reliance on virgin materials and minimize the amount of plastic waste entering the environment.
One of the primary challenges in establishing a circular economy for LDPE is improving the recyclability of LDPE products. This involves redesigning packaging and other LDPE applications to facilitate easier separation and recycling. For instance, manufacturers are increasingly adopting mono-material designs that eliminate the need for complex separation processes during recycling.
Collection and sorting systems play a crucial role in the circular economy for LDPE. Improved infrastructure for collecting post-consumer LDPE waste, coupled with advanced sorting technologies such as near-infrared spectroscopy, can significantly increase the quantity and quality of recycled LDPE. This, in turn, enhances the economic viability of LDPE recycling and encourages further investment in recycling facilities.
Advanced recycling technologies are emerging as a game-changer in the circular economy for LDPE. Chemical recycling processes, such as pyrolysis and depolymerization, offer the potential to break down LDPE into its chemical building blocks, which can then be used to produce new, high-quality plastics. These technologies complement mechanical recycling and can handle contaminated or mixed plastic waste that is typically difficult to recycle through conventional methods.
The transition to a circular economy for LDPE also presents opportunities for innovation in business models. Companies are exploring new ways to deliver products and services that reduce LDPE consumption, such as refill and reuse systems for packaging. Additionally, the development of LDPE alternatives from renewable sources, such as bio-based plastics, is gaining traction as part of the broader circular economy strategy.
As the circular economy for LDPE gains momentum, collaboration across the value chain becomes increasingly important. Manufacturers, retailers, waste management companies, and policymakers must work together to create an ecosystem that supports the circular flow of LDPE materials. This collaboration can lead to the development of industry-wide standards for recyclability, improved recycling infrastructure, and policies that incentivize the use of recycled LDPE.
At the core of the circular economy for LDPE is the principle of reducing waste and pollution by keeping materials in use for as long as possible. This approach involves several key strategies, including design for recyclability, efficient collection and sorting systems, and advanced recycling technologies. By implementing these strategies, the LDPE industry can significantly reduce its reliance on virgin materials and minimize the amount of plastic waste entering the environment.
One of the primary challenges in establishing a circular economy for LDPE is improving the recyclability of LDPE products. This involves redesigning packaging and other LDPE applications to facilitate easier separation and recycling. For instance, manufacturers are increasingly adopting mono-material designs that eliminate the need for complex separation processes during recycling.
Collection and sorting systems play a crucial role in the circular economy for LDPE. Improved infrastructure for collecting post-consumer LDPE waste, coupled with advanced sorting technologies such as near-infrared spectroscopy, can significantly increase the quantity and quality of recycled LDPE. This, in turn, enhances the economic viability of LDPE recycling and encourages further investment in recycling facilities.
Advanced recycling technologies are emerging as a game-changer in the circular economy for LDPE. Chemical recycling processes, such as pyrolysis and depolymerization, offer the potential to break down LDPE into its chemical building blocks, which can then be used to produce new, high-quality plastics. These technologies complement mechanical recycling and can handle contaminated or mixed plastic waste that is typically difficult to recycle through conventional methods.
The transition to a circular economy for LDPE also presents opportunities for innovation in business models. Companies are exploring new ways to deliver products and services that reduce LDPE consumption, such as refill and reuse systems for packaging. Additionally, the development of LDPE alternatives from renewable sources, such as bio-based plastics, is gaining traction as part of the broader circular economy strategy.
As the circular economy for LDPE gains momentum, collaboration across the value chain becomes increasingly important. Manufacturers, retailers, waste management companies, and policymakers must work together to create an ecosystem that supports the circular flow of LDPE materials. This collaboration can lead to the development of industry-wide standards for recyclability, improved recycling infrastructure, and policies that incentivize the use of recycled LDPE.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!