Innovations in LDPE Film Technologies for Improved Usability
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Film Tech Evolution
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) film technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the 1930s. The journey of LDPE film development can be traced through several key phases, each marked by technological advancements and improved usability.
In the early stages, LDPE films were primarily used for basic packaging applications. The focus was on creating a flexible, waterproof material that could protect goods during transportation and storage. However, these early films had limitations in terms of strength, clarity, and barrier properties.
The 1960s and 1970s saw a shift towards enhancing the mechanical properties of LDPE films. Innovations in polymer science led to the development of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), which offered improved tensile strength and puncture resistance. This advancement expanded the use of polyethylene films in more demanding applications, such as industrial packaging and agricultural films.
The 1980s and 1990s marked a period of significant progress in film processing technologies. The introduction of multi-layer extrusion techniques allowed for the creation of films with tailored properties. By combining different types of polyethylene and other materials, manufacturers could produce films with enhanced barrier properties, improved printability, and better sealing characteristics.
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, the focus shifted towards sustainability and environmental concerns. This led to the development of thinner films that maintained the same performance characteristics as their thicker counterparts, reducing material usage and waste. Additionally, research into biodegradable and compostable alternatives gained momentum, although LDPE remained the dominant material due to its cost-effectiveness and versatile properties.
The most recent phase of LDPE film technology evolution, spanning from the 2010s to the present, has been characterized by a drive towards smart and functional films. Innovations in this area include the incorporation of active ingredients for extended shelf life in food packaging, the development of films with improved recyclability, and the integration of nanotechnology to enhance film properties at the molecular level.
Throughout this evolution, the overarching trend has been towards creating LDPE films that offer improved usability across various applications. This has involved enhancing mechanical properties, optimizing barrier characteristics, improving processability, and addressing environmental concerns. The continuous innovation in LDPE film technology has enabled its widespread use in diverse sectors, from food packaging to construction materials, solidifying its position as a versatile and indispensable material in modern industry.
In the early stages, LDPE films were primarily used for basic packaging applications. The focus was on creating a flexible, waterproof material that could protect goods during transportation and storage. However, these early films had limitations in terms of strength, clarity, and barrier properties.
The 1960s and 1970s saw a shift towards enhancing the mechanical properties of LDPE films. Innovations in polymer science led to the development of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), which offered improved tensile strength and puncture resistance. This advancement expanded the use of polyethylene films in more demanding applications, such as industrial packaging and agricultural films.
The 1980s and 1990s marked a period of significant progress in film processing technologies. The introduction of multi-layer extrusion techniques allowed for the creation of films with tailored properties. By combining different types of polyethylene and other materials, manufacturers could produce films with enhanced barrier properties, improved printability, and better sealing characteristics.
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, the focus shifted towards sustainability and environmental concerns. This led to the development of thinner films that maintained the same performance characteristics as their thicker counterparts, reducing material usage and waste. Additionally, research into biodegradable and compostable alternatives gained momentum, although LDPE remained the dominant material due to its cost-effectiveness and versatile properties.
The most recent phase of LDPE film technology evolution, spanning from the 2010s to the present, has been characterized by a drive towards smart and functional films. Innovations in this area include the incorporation of active ingredients for extended shelf life in food packaging, the development of films with improved recyclability, and the integration of nanotechnology to enhance film properties at the molecular level.
Throughout this evolution, the overarching trend has been towards creating LDPE films that offer improved usability across various applications. This has involved enhancing mechanical properties, optimizing barrier characteristics, improving processability, and addressing environmental concerns. The continuous innovation in LDPE film technology has enabled its widespread use in diverse sectors, from food packaging to construction materials, solidifying its position as a versatile and indispensable material in modern industry.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for innovations in LDPE film technologies has been steadily increasing, driven by the growing need for improved usability across various industries. The packaging sector, in particular, has shown a significant appetite for enhanced LDPE films, as manufacturers seek to meet consumer demands for more convenient, durable, and sustainable packaging solutions.
In the food industry, there is a rising demand for LDPE films with improved barrier properties to extend shelf life and maintain product freshness. This trend is particularly evident in the ready-to-eat meals and snack food segments, where consumers expect packaging that preserves flavor and texture while offering easy opening and resealing features.
The agricultural sector has also emerged as a key market for advanced LDPE film technologies. Farmers and growers are increasingly adopting mulch films and greenhouse covers made from improved LDPE materials, which offer better light transmission, temperature control, and durability. This demand is further fueled by the global push towards sustainable farming practices and increased crop yields.
In the construction industry, there is a growing need for LDPE films with enhanced mechanical properties and weather resistance. These films are used in applications such as vapor barriers, temporary protective coverings, and insulation materials. The booming construction sector in developing countries is expected to drive significant growth in this market segment.
The healthcare and medical device industries have shown increasing interest in LDPE films with improved sterilization compatibility and barrier properties. This demand is driven by the need for more effective packaging solutions for medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and diagnostic equipment, especially in light of recent global health challenges.
E-commerce and retail sectors are seeking LDPE film innovations that can withstand the rigors of shipping and handling while maintaining product integrity. This has led to a demand for films with enhanced puncture resistance, tear strength, and sealability, as well as those that incorporate smart packaging technologies for improved traceability and consumer engagement.
The push for sustainability has also significantly influenced market demand. Consumers and regulatory bodies are calling for LDPE films that are recyclable, biodegradable, or made from renewable sources. This has created opportunities for innovations in bio-based LDPE films and technologies that facilitate easier recycling of existing LDPE products.
Overall, the market for innovative LDPE film technologies is expected to experience robust growth in the coming years. This growth will be driven by the increasing demand for packaging solutions that offer improved functionality, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness across a wide range of industries.
In the food industry, there is a rising demand for LDPE films with improved barrier properties to extend shelf life and maintain product freshness. This trend is particularly evident in the ready-to-eat meals and snack food segments, where consumers expect packaging that preserves flavor and texture while offering easy opening and resealing features.
The agricultural sector has also emerged as a key market for advanced LDPE film technologies. Farmers and growers are increasingly adopting mulch films and greenhouse covers made from improved LDPE materials, which offer better light transmission, temperature control, and durability. This demand is further fueled by the global push towards sustainable farming practices and increased crop yields.
In the construction industry, there is a growing need for LDPE films with enhanced mechanical properties and weather resistance. These films are used in applications such as vapor barriers, temporary protective coverings, and insulation materials. The booming construction sector in developing countries is expected to drive significant growth in this market segment.
The healthcare and medical device industries have shown increasing interest in LDPE films with improved sterilization compatibility and barrier properties. This demand is driven by the need for more effective packaging solutions for medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and diagnostic equipment, especially in light of recent global health challenges.
E-commerce and retail sectors are seeking LDPE film innovations that can withstand the rigors of shipping and handling while maintaining product integrity. This has led to a demand for films with enhanced puncture resistance, tear strength, and sealability, as well as those that incorporate smart packaging technologies for improved traceability and consumer engagement.
The push for sustainability has also significantly influenced market demand. Consumers and regulatory bodies are calling for LDPE films that are recyclable, biodegradable, or made from renewable sources. This has created opportunities for innovations in bio-based LDPE films and technologies that facilitate easier recycling of existing LDPE products.
Overall, the market for innovative LDPE film technologies is expected to experience robust growth in the coming years. This growth will be driven by the increasing demand for packaging solutions that offer improved functionality, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness across a wide range of industries.
Current Tech Challenges
The current technological landscape of LDPE film production faces several significant challenges that hinder the advancement of improved usability. One of the primary obstacles is the trade-off between film strength and flexibility. As manufacturers strive to enhance the durability of LDPE films, they often compromise on flexibility, which can negatively impact user experience in various applications.
Another pressing challenge is the limited recyclability of LDPE films. While LDPE is theoretically recyclable, the presence of additives, coatings, and contaminants often complicates the recycling process. This issue is particularly pronounced in multi-layer films, where separating different polymer layers remains a technical hurdle.
The industry also grapples with the challenge of reducing film thickness without sacrificing performance. Thinner films are desirable for both economic and environmental reasons, but maintaining strength, barrier properties, and processability at reduced thicknesses presents significant technical difficulties.
Improving the barrier properties of LDPE films, especially against oxygen and moisture, continues to be a major focus area. Enhanced barrier performance is crucial for extending shelf life in packaging applications, but achieving this without resorting to multi-layer structures or expensive additives remains challenging.
The demand for more sustainable LDPE film solutions has intensified, pushing the industry to explore bio-based alternatives and biodegradable options. However, matching the performance and cost-effectiveness of traditional LDPE with these eco-friendly alternatives is proving to be a complex undertaking.
Addressing the issue of film clarity and optical properties while maintaining other desirable characteristics is another ongoing challenge. Many applications require high transparency and low haze, which can be difficult to achieve without compromising other functional properties.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in scaling up new technologies from laboratory to industrial production. Innovations in LDPE film technologies often struggle to transition from promising research results to commercially viable manufacturing processes, due to issues such as process stability, equipment compatibility, and cost-effectiveness at scale.
These technological challenges collectively represent the current hurdles that researchers and manufacturers must overcome to drive innovations in LDPE film technologies for improved usability. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach, combining advances in polymer science, processing technologies, and sustainable practices.
Another pressing challenge is the limited recyclability of LDPE films. While LDPE is theoretically recyclable, the presence of additives, coatings, and contaminants often complicates the recycling process. This issue is particularly pronounced in multi-layer films, where separating different polymer layers remains a technical hurdle.
The industry also grapples with the challenge of reducing film thickness without sacrificing performance. Thinner films are desirable for both economic and environmental reasons, but maintaining strength, barrier properties, and processability at reduced thicknesses presents significant technical difficulties.
Improving the barrier properties of LDPE films, especially against oxygen and moisture, continues to be a major focus area. Enhanced barrier performance is crucial for extending shelf life in packaging applications, but achieving this without resorting to multi-layer structures or expensive additives remains challenging.
The demand for more sustainable LDPE film solutions has intensified, pushing the industry to explore bio-based alternatives and biodegradable options. However, matching the performance and cost-effectiveness of traditional LDPE with these eco-friendly alternatives is proving to be a complex undertaking.
Addressing the issue of film clarity and optical properties while maintaining other desirable characteristics is another ongoing challenge. Many applications require high transparency and low haze, which can be difficult to achieve without compromising other functional properties.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in scaling up new technologies from laboratory to industrial production. Innovations in LDPE film technologies often struggle to transition from promising research results to commercially viable manufacturing processes, due to issues such as process stability, equipment compatibility, and cost-effectiveness at scale.
These technological challenges collectively represent the current hurdles that researchers and manufacturers must overcome to drive innovations in LDPE film technologies for improved usability. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach, combining advances in polymer science, processing technologies, and sustainable practices.
Existing LDPE Solutions
01 LDPE film composition and properties
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) films are widely used due to their unique properties. These films can be modified with various additives to enhance their performance characteristics such as strength, flexibility, and barrier properties. The composition of LDPE films can be tailored to meet specific application requirements.- LDPE film composition and properties: Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) films are widely used due to their unique properties. These films can be modified with various additives to enhance their performance characteristics such as strength, flexibility, and barrier properties. The composition of LDPE films can be tailored to meet specific application requirements in packaging, agriculture, and other industries.
- LDPE film manufacturing processes: Various manufacturing processes are employed to produce LDPE films with desired characteristics. These processes may include extrusion, blown film extrusion, and cast film extrusion. Advanced manufacturing techniques can be used to control film thickness, uniformity, and surface properties, which are crucial for the film's performance in different applications.
- Applications of LDPE films: LDPE films find applications in diverse fields due to their versatility. They are commonly used in packaging for food and non-food products, agricultural mulch films, greenhouse covers, and industrial applications. The films can be designed to provide specific functionalities such as moisture resistance, UV protection, or enhanced printability, making them suitable for a wide range of uses.
- Recycling and environmental considerations of LDPE films: As environmental concerns grow, the recycling and sustainable use of LDPE films have become important considerations. Efforts are being made to develop more eco-friendly LDPE film formulations, improve recycling processes, and explore biodegradable alternatives. The industry is focusing on reducing the environmental impact of LDPE films while maintaining their performance benefits.
- LDPE film testing and quality control: To ensure the usability and performance of LDPE films, various testing and quality control measures are implemented. These may include mechanical strength tests, barrier property assessments, and durability evaluations. Advanced testing methods and equipment are used to verify the film's compliance with industry standards and specific application requirements.
02 LDPE film applications in packaging
LDPE films find extensive use in packaging applications due to their excellent moisture barrier properties and flexibility. They are commonly used for food packaging, industrial packaging, and consumer goods packaging. The films can be customized for specific packaging needs, such as shrink wrap or stretch film applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 LDPE film processing techniques
Various processing techniques are employed in the manufacture of LDPE films, including extrusion, blown film extrusion, and cast film extrusion. These techniques allow for the production of films with different thicknesses, widths, and surface characteristics. Advanced processing methods can improve film uniformity and enhance overall quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 LDPE film recycling and sustainability
As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on the recyclability and sustainability of LDPE films. Efforts are being made to develop more eco-friendly LDPE film formulations and improve recycling processes. This includes the use of recycled LDPE in film production and the development of biodegradable additives.Expand Specific Solutions05 LDPE film testing and quality control
To ensure the usability and performance of LDPE films, various testing and quality control measures are implemented. These include tests for mechanical properties, optical properties, and barrier performance. Advanced testing methods and equipment are used to assess film quality and consistency throughout the production process.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for LDPE film technologies is in a mature stage, with ongoing innovations focused on improving usability. The global LDPE film market size is substantial, estimated to be in the billions of dollars, driven by demand in packaging, agriculture, and construction sectors. Technologically, the field is well-established but continues to evolve, with companies like ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Dow Global Technologies, and SABIC Global Technologies leading in R&D. These industry giants, along with regional players such as PetroChina and Sinopec, are pushing boundaries in film performance, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of multinational corporations and specialized firms, each contributing to incremental advancements in LDPE film technologies.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed innovative ELITE™ Enhanced Polyethylene (EPE) resins for LDPE film applications. This technology combines the processability of LDPE with the strength and toughness of LLDPE. The ELITE™ EPE resins offer improved film strength, puncture resistance, and optical properties[1]. Dow's INNATE™ Precision Packaging Resins provide enhanced toughness, stiffness, and processing stability for LDPE films[2]. These resins enable the production of thinner, stronger films with better seal integrity and improved sustainability profiles[3].
Strengths: Superior film strength, improved optical properties, and enhanced processability. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for optimal performance, potentially higher production costs.
SABIC Global Technologies BV
Technical Solution: SABIC has introduced SUPEER™ polyethylene resins for LDPE film applications. These resins offer improved processability, enhanced optical properties, and superior mechanical performance[7]. SABIC's COHERE™ adhesive resins provide excellent adhesion and compatibility in multi-layer film structures, enhancing overall film performance[8]. The company's FLOWPACT™ FPC5480 resin offers high melt strength and excellent bubble stability for blown film extrusion, enabling improved productivity and film quality[9].
Strengths: Enhanced processability, superior optical properties, and improved multi-layer film performance. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for optimal results, potential higher initial investment.
Core LDPE Innovations
Polyolefin composition and film thereof
PatentWO2011022033A1
Innovation
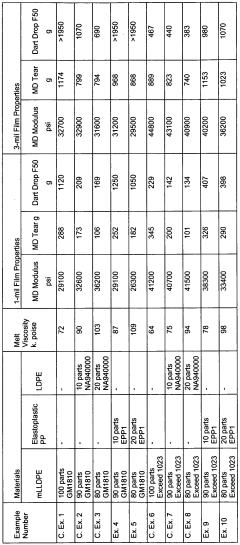
- A polyolefin composition comprising 70-99 wt% mLLDPE and 1-30 wt% elastoplastic polypropylene, with specific properties such as density, crystallinity, and molecular weight distribution, to enhance processability and physical properties, including improved bubble stability and film properties like impact strength and tear strength.
Linear low density polyethylenes with high melt strength and high melt index ratio
PatentInactiveEP1448632A1
Innovation
- A gas phase polymerization process using a blend of supported metallocene catalysts, specifically zirconocenes with tetrahydroindenyl and indenyl rings, to produce LLDPE with high melt index, high melt index ratio, and high melt strength, maintaining mechanical properties without the need for blending with branched polymers.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of LDPE film technologies has become a critical concern in recent years, driving innovations towards more sustainable solutions. Traditional LDPE films, while versatile and widely used, have faced scrutiny due to their environmental footprint throughout their lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental challenges associated with LDPE films is their persistence in the environment. These films, when improperly disposed of, can take hundreds of years to decompose, contributing to plastic pollution in terrestrial and marine ecosystems. This has led to increased efforts in developing biodegradable and compostable alternatives that maintain the desirable properties of LDPE while reducing environmental persistence.
The production process of LDPE films also contributes to environmental concerns. The manufacturing of these films typically involves the use of fossil fuels, resulting in greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. Innovations in this area have focused on improving energy efficiency in production processes and exploring the use of renewable energy sources to power manufacturing facilities.
Recycling presents another significant challenge for LDPE films. While technically recyclable, the thin and often contaminated nature of these films makes them difficult to process in conventional recycling streams. This has spurred research into advanced recycling technologies and the development of more easily recyclable film formulations.
Recent innovations have targeted the reduction of material usage through the development of thinner, yet equally effective films. This approach not only conserves raw materials but also reduces the overall carbon footprint associated with production and transportation. Additionally, there has been a growing interest in incorporating recycled content into LDPE films, creating a circular economy approach to film production.
The use of bio-based materials as alternatives or additives to traditional LDPE has gained traction. These materials, derived from renewable resources, aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and potentially offer improved end-of-life options. However, challenges remain in ensuring that these bio-based alternatives do not compete with food production or lead to unintended environmental consequences.
Advancements in additive technologies have also played a role in addressing environmental concerns. Oxo-biodegradable additives, for instance, have been developed to accelerate the breakdown of LDPE films in the environment. However, the effectiveness and potential microplastic generation from these additives remain subjects of ongoing research and debate.
As regulations and consumer preferences continue to evolve, the LDPE film industry is increasingly focusing on life cycle assessments to comprehensively evaluate the environmental impact of their products. This holistic approach considers factors such as raw material sourcing, production processes, use phase, and end-of-life scenarios, driving innovations that address environmental concerns at every stage of the product lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental challenges associated with LDPE films is their persistence in the environment. These films, when improperly disposed of, can take hundreds of years to decompose, contributing to plastic pollution in terrestrial and marine ecosystems. This has led to increased efforts in developing biodegradable and compostable alternatives that maintain the desirable properties of LDPE while reducing environmental persistence.
The production process of LDPE films also contributes to environmental concerns. The manufacturing of these films typically involves the use of fossil fuels, resulting in greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. Innovations in this area have focused on improving energy efficiency in production processes and exploring the use of renewable energy sources to power manufacturing facilities.
Recycling presents another significant challenge for LDPE films. While technically recyclable, the thin and often contaminated nature of these films makes them difficult to process in conventional recycling streams. This has spurred research into advanced recycling technologies and the development of more easily recyclable film formulations.
Recent innovations have targeted the reduction of material usage through the development of thinner, yet equally effective films. This approach not only conserves raw materials but also reduces the overall carbon footprint associated with production and transportation. Additionally, there has been a growing interest in incorporating recycled content into LDPE films, creating a circular economy approach to film production.
The use of bio-based materials as alternatives or additives to traditional LDPE has gained traction. These materials, derived from renewable resources, aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and potentially offer improved end-of-life options. However, challenges remain in ensuring that these bio-based alternatives do not compete with food production or lead to unintended environmental consequences.
Advancements in additive technologies have also played a role in addressing environmental concerns. Oxo-biodegradable additives, for instance, have been developed to accelerate the breakdown of LDPE films in the environment. However, the effectiveness and potential microplastic generation from these additives remain subjects of ongoing research and debate.
As regulations and consumer preferences continue to evolve, the LDPE film industry is increasingly focusing on life cycle assessments to comprehensively evaluate the environmental impact of their products. This holistic approach considers factors such as raw material sourcing, production processes, use phase, and end-of-life scenarios, driving innovations that address environmental concerns at every stage of the product lifecycle.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in the development and implementation of innovations in LDPE film technologies for improved usability. As the industry continues to evolve, manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of regulations and standards to ensure their products meet safety, environmental, and performance requirements.
One of the primary regulatory considerations for LDPE film technologies is food contact compliance. Many LDPE films are used in food packaging applications, necessitating adherence to strict guidelines set by regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). These regulations govern the materials and additives that can be used in food contact films, as well as migration limits for various substances.
Environmental regulations also significantly impact LDPE film innovations. With increasing global focus on sustainability and waste reduction, many jurisdictions have implemented regulations aimed at reducing plastic waste and promoting recycling. For instance, the European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan sets targets for plastic recycling and mandates the use of recycled content in packaging materials. This has driven innovations in LDPE film technologies to improve recyclability and incorporate recycled content while maintaining performance characteristics.
Product safety regulations are another critical aspect of compliance for LDPE film technologies. Depending on the application, films may need to meet specific safety standards, such as flame retardancy for construction applications or biocompatibility for medical uses. Manufacturers must ensure their innovations comply with relevant safety standards and obtain necessary certifications.
Labeling and packaging regulations also influence LDPE film innovations. Many countries require specific information to be displayed on packaging, including material composition, recycling instructions, and environmental claims. As LDPE film technologies evolve, manufacturers must ensure their products can accommodate these labeling requirements while maintaining desired performance characteristics.
Compliance with chemical regulations, such as the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, is essential for LDPE film innovations. These regulations may restrict the use of certain substances or require extensive testing and documentation for new materials or additives used in film production.
As innovations in LDPE film technologies continue to emerge, manufacturers must stay abreast of evolving regulatory landscapes across different markets. This includes monitoring changes in existing regulations and anticipating new requirements that may impact product development and commercialization. Proactive engagement with regulatory bodies and industry associations can help manufacturers navigate compliance challenges and ensure their innovations meet all necessary requirements.
One of the primary regulatory considerations for LDPE film technologies is food contact compliance. Many LDPE films are used in food packaging applications, necessitating adherence to strict guidelines set by regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). These regulations govern the materials and additives that can be used in food contact films, as well as migration limits for various substances.
Environmental regulations also significantly impact LDPE film innovations. With increasing global focus on sustainability and waste reduction, many jurisdictions have implemented regulations aimed at reducing plastic waste and promoting recycling. For instance, the European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan sets targets for plastic recycling and mandates the use of recycled content in packaging materials. This has driven innovations in LDPE film technologies to improve recyclability and incorporate recycled content while maintaining performance characteristics.
Product safety regulations are another critical aspect of compliance for LDPE film technologies. Depending on the application, films may need to meet specific safety standards, such as flame retardancy for construction applications or biocompatibility for medical uses. Manufacturers must ensure their innovations comply with relevant safety standards and obtain necessary certifications.
Labeling and packaging regulations also influence LDPE film innovations. Many countries require specific information to be displayed on packaging, including material composition, recycling instructions, and environmental claims. As LDPE film technologies evolve, manufacturers must ensure their products can accommodate these labeling requirements while maintaining desired performance characteristics.
Compliance with chemical regulations, such as the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, is essential for LDPE film innovations. These regulations may restrict the use of certain substances or require extensive testing and documentation for new materials or additives used in film production.
As innovations in LDPE film technologies continue to emerge, manufacturers must stay abreast of evolving regulatory landscapes across different markets. This includes monitoring changes in existing regulations and anticipating new requirements that may impact product development and commercialization. Proactive engagement with regulatory bodies and industry associations can help manufacturers navigate compliance challenges and ensure their innovations meet all necessary requirements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!