Investigating LDPE's Role in Food Preservation
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE in Food Packaging: Evolution and Objectives
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has played a pivotal role in food packaging since its introduction in the 1930s. The evolution of LDPE in food preservation has been marked by continuous advancements in material science and packaging technology. Initially developed as a flexible and durable plastic, LDPE quickly found its niche in food packaging due to its excellent moisture barrier properties and chemical resistance.
The journey of LDPE in food packaging began with simple applications such as bread bags and produce wraps. As manufacturing techniques improved, LDPE films became thinner and more versatile, leading to their widespread use in various food packaging formats. The 1960s and 1970s saw significant developments in LDPE formulations, enhancing its performance characteristics and expanding its applicability across different food types.
The objectives of LDPE in food preservation have evolved alongside technological progress. Early goals focused primarily on extending shelf life by creating a barrier against moisture and oxygen. As consumer demands and regulatory requirements changed, the objectives expanded to include improved food safety, reduced food waste, and enhanced product presentation. The industry also began to prioritize the development of LDPE variants with better mechanical properties and increased recyclability.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and environmental concerns. The food packaging industry is now exploring ways to make LDPE more eco-friendly without compromising its preservation capabilities. This includes research into biodegradable additives, the development of thinner films that use less material, and improved recycling technologies for LDPE packaging.
The current objectives for LDPE in food preservation encompass a wide range of factors. These include further enhancing barrier properties to extend shelf life, developing active packaging solutions that interact with food to maintain quality, and creating intelligent packaging systems that can monitor and indicate food freshness. Additionally, there is a strong emphasis on reducing the environmental impact of LDPE packaging through improved recyclability and the exploration of bio-based alternatives.
As we look to the future, the evolution of LDPE in food packaging continues to be driven by the dual goals of superior food preservation and environmental sustainability. Researchers and industry professionals are working on next-generation LDPE materials that can offer enhanced functionality while addressing ecological concerns. This includes the development of nanocomposite LDPE films with improved barrier properties and the integration of smart technologies for real-time food quality monitoring.
The journey of LDPE in food packaging began with simple applications such as bread bags and produce wraps. As manufacturing techniques improved, LDPE films became thinner and more versatile, leading to their widespread use in various food packaging formats. The 1960s and 1970s saw significant developments in LDPE formulations, enhancing its performance characteristics and expanding its applicability across different food types.
The objectives of LDPE in food preservation have evolved alongside technological progress. Early goals focused primarily on extending shelf life by creating a barrier against moisture and oxygen. As consumer demands and regulatory requirements changed, the objectives expanded to include improved food safety, reduced food waste, and enhanced product presentation. The industry also began to prioritize the development of LDPE variants with better mechanical properties and increased recyclability.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and environmental concerns. The food packaging industry is now exploring ways to make LDPE more eco-friendly without compromising its preservation capabilities. This includes research into biodegradable additives, the development of thinner films that use less material, and improved recycling technologies for LDPE packaging.
The current objectives for LDPE in food preservation encompass a wide range of factors. These include further enhancing barrier properties to extend shelf life, developing active packaging solutions that interact with food to maintain quality, and creating intelligent packaging systems that can monitor and indicate food freshness. Additionally, there is a strong emphasis on reducing the environmental impact of LDPE packaging through improved recyclability and the exploration of bio-based alternatives.
As we look to the future, the evolution of LDPE in food packaging continues to be driven by the dual goals of superior food preservation and environmental sustainability. Researchers and industry professionals are working on next-generation LDPE materials that can offer enhanced functionality while addressing ecological concerns. This includes the development of nanocomposite LDPE films with improved barrier properties and the integration of smart technologies for real-time food quality monitoring.
Market Analysis of LDPE Food Packaging
The global market for LDPE food packaging has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for convenient and safe food storage solutions. LDPE, or Low-Density Polyethylene, has emerged as a preferred material for food packaging due to its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases.
The food packaging industry has witnessed a shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly materials, which has impacted the LDPE market. While LDPE remains a popular choice, there is growing pressure to develop more recyclable and biodegradable alternatives. This trend has led to innovations in LDPE formulations and manufacturing processes to enhance its environmental profile.
Consumer preferences for extended shelf life and food safety have been key drivers in the LDPE food packaging market. The material's ability to preserve food quality by preventing contamination and spoilage has made it indispensable in various food sectors, including fresh produce, dairy, and processed foods. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for hygienic and tamper-evident packaging solutions, benefiting the LDPE market.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as the largest and fastest-growing market for LDPE food packaging, fueled by rapid urbanization, changing lifestyles, and increasing disposable incomes. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on technological advancements and sustainable packaging solutions.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, including Dow Chemical Company, LyondellBasell Industries, and ExxonMobil Corporation. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve LDPE properties and manufacturing efficiency. Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships have become common strategies to expand market presence and technological capabilities.
Regulatory landscape plays a crucial role in shaping the LDPE food packaging market. Stringent food safety regulations and increasing environmental concerns have led to the development of new standards and certifications for food-grade LDPE. Manufacturers are adapting to these regulations by improving their production processes and product formulations.
The future of the LDPE food packaging market is expected to be influenced by advancements in nanotechnology and smart packaging solutions. Integration of nanotechnology in LDPE production could enhance its barrier properties and extend food shelf life. Additionally, the development of active and intelligent packaging using LDPE as a base material presents new opportunities for market growth and differentiation.
The food packaging industry has witnessed a shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly materials, which has impacted the LDPE market. While LDPE remains a popular choice, there is growing pressure to develop more recyclable and biodegradable alternatives. This trend has led to innovations in LDPE formulations and manufacturing processes to enhance its environmental profile.
Consumer preferences for extended shelf life and food safety have been key drivers in the LDPE food packaging market. The material's ability to preserve food quality by preventing contamination and spoilage has made it indispensable in various food sectors, including fresh produce, dairy, and processed foods. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for hygienic and tamper-evident packaging solutions, benefiting the LDPE market.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as the largest and fastest-growing market for LDPE food packaging, fueled by rapid urbanization, changing lifestyles, and increasing disposable incomes. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on technological advancements and sustainable packaging solutions.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, including Dow Chemical Company, LyondellBasell Industries, and ExxonMobil Corporation. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve LDPE properties and manufacturing efficiency. Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships have become common strategies to expand market presence and technological capabilities.
Regulatory landscape plays a crucial role in shaping the LDPE food packaging market. Stringent food safety regulations and increasing environmental concerns have led to the development of new standards and certifications for food-grade LDPE. Manufacturers are adapting to these regulations by improving their production processes and product formulations.
The future of the LDPE food packaging market is expected to be influenced by advancements in nanotechnology and smart packaging solutions. Integration of nanotechnology in LDPE production could enhance its barrier properties and extend food shelf life. Additionally, the development of active and intelligent packaging using LDPE as a base material presents new opportunities for market growth and differentiation.
Current LDPE Technology and Challenges
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone in food packaging and preservation for decades. Its widespread use stems from its excellent barrier properties, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, the current LDPE technology faces several challenges in meeting evolving consumer demands and environmental concerns.
One of the primary technological challenges is improving LDPE's oxygen barrier properties. While LDPE provides a good moisture barrier, its oxygen permeability is relatively high compared to other packaging materials. This limitation can lead to reduced shelf life for oxygen-sensitive foods. Researchers are exploring various methods to enhance oxygen barrier properties, including the incorporation of nanoparticles and the development of multilayer structures.
Another significant challenge is the need for enhanced mechanical properties. LDPE films can be prone to tearing and puncturing, which compromises food safety and preservation. Current research focuses on improving the tensile strength and puncture resistance of LDPE films without sacrificing their flexibility and sealability. This includes the development of new LDPE grades with improved molecular structures and the use of reinforcing additives.
The recyclability of LDPE packaging is a growing concern in the face of increasing environmental awareness. While LDPE is technically recyclable, contamination from food residues and the presence of multi-material laminates often hinder effective recycling. The industry is working on developing more easily recyclable LDPE packaging solutions, including mono-material structures and compatibilizers for mixed plastic waste streams.
Antimicrobial properties are becoming increasingly important in food packaging. Current LDPE technology lacks inherent antimicrobial activity, which limits its ability to prevent microbial growth and extend food shelf life. Researchers are exploring various approaches to impart antimicrobial properties to LDPE, such as incorporating antimicrobial agents into the polymer matrix or developing surface treatments.
The migration of low molecular weight compounds from LDPE into food remains a challenge, particularly for fatty foods. While LDPE is generally considered safe for food contact, there are ongoing efforts to minimize migration and develop more inert LDPE formulations. This includes the use of higher molecular weight polymers and the optimization of processing conditions to reduce the formation of potential migrants.
Lastly, the industry faces the challenge of balancing performance improvements with cost-effectiveness. Many advanced LDPE technologies, such as nanocomposites or plasma treatments, can significantly enhance performance but often at a higher cost. Finding economically viable solutions that maintain LDPE's cost advantage while addressing its limitations is a key focus of current research and development efforts.
One of the primary technological challenges is improving LDPE's oxygen barrier properties. While LDPE provides a good moisture barrier, its oxygen permeability is relatively high compared to other packaging materials. This limitation can lead to reduced shelf life for oxygen-sensitive foods. Researchers are exploring various methods to enhance oxygen barrier properties, including the incorporation of nanoparticles and the development of multilayer structures.
Another significant challenge is the need for enhanced mechanical properties. LDPE films can be prone to tearing and puncturing, which compromises food safety and preservation. Current research focuses on improving the tensile strength and puncture resistance of LDPE films without sacrificing their flexibility and sealability. This includes the development of new LDPE grades with improved molecular structures and the use of reinforcing additives.
The recyclability of LDPE packaging is a growing concern in the face of increasing environmental awareness. While LDPE is technically recyclable, contamination from food residues and the presence of multi-material laminates often hinder effective recycling. The industry is working on developing more easily recyclable LDPE packaging solutions, including mono-material structures and compatibilizers for mixed plastic waste streams.
Antimicrobial properties are becoming increasingly important in food packaging. Current LDPE technology lacks inherent antimicrobial activity, which limits its ability to prevent microbial growth and extend food shelf life. Researchers are exploring various approaches to impart antimicrobial properties to LDPE, such as incorporating antimicrobial agents into the polymer matrix or developing surface treatments.
The migration of low molecular weight compounds from LDPE into food remains a challenge, particularly for fatty foods. While LDPE is generally considered safe for food contact, there are ongoing efforts to minimize migration and develop more inert LDPE formulations. This includes the use of higher molecular weight polymers and the optimization of processing conditions to reduce the formation of potential migrants.
Lastly, the industry faces the challenge of balancing performance improvements with cost-effectiveness. Many advanced LDPE technologies, such as nanocomposites or plasma treatments, can significantly enhance performance but often at a higher cost. Finding economically viable solutions that maintain LDPE's cost advantage while addressing its limitations is a key focus of current research and development efforts.
Existing LDPE Food Preservation Solutions
01 Composition and properties of LDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a low density and high flexibility. It is characterized by its branched structure, which results in lower crystallinity and density compared to other polyethylene types. LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance, electrical insulation properties, and processability, making it suitable for various applications.- Composition and properties of LDPE: Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a low density and high flexibility. It is characterized by its branched structure, which results in lower crystallinity and density compared to other polyethylene types. LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance, electrical insulation properties, and processability, making it suitable for various applications.
- Manufacturing processes for LDPE: LDPE is primarily produced through high-pressure polymerization of ethylene using free-radical initiators. Various manufacturing techniques have been developed to improve the efficiency and quality of LDPE production, including the use of different catalysts, reactor designs, and process conditions to control the polymer's molecular weight and branching.
- Applications of LDPE: LDPE finds widespread use in numerous applications due to its unique properties. It is commonly used in packaging materials, such as plastic bags, films, and containers. LDPE is also utilized in the production of wire and cable insulation, toys, and various household items. Its flexibility and chemical resistance make it suitable for agricultural applications and as a coating material.
- Modifications and blends of LDPE: To enhance its properties and expand its applications, LDPE is often modified or blended with other materials. This includes the incorporation of additives, such as antioxidants or UV stabilizers, to improve its performance. LDPE can also be blended with other polymers or fillers to create composites with tailored properties for specific applications.
- Recycling and sustainability of LDPE: As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on the recycling and sustainability of LDPE. Various recycling methods have been developed to process post-consumer LDPE waste into reusable materials. Research is also being conducted on biodegradable alternatives and the development of more sustainable production processes for LDPE to reduce its environmental impact.
02 Manufacturing processes for LDPE
LDPE is typically produced through high-pressure polymerization of ethylene using free-radical initiators. Various manufacturing techniques have been developed to improve the production efficiency and control the properties of LDPE. These processes may involve different reactor designs, catalysts, and process conditions to achieve desired molecular weight distributions and branching characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of LDPE
LDPE finds widespread use in numerous applications due to its unique properties. It is commonly used in packaging materials, such as plastic bags, films, and containers. LDPE is also utilized in the production of wire and cable insulation, toys, and various household items. Its flexibility and chemical resistance make it suitable for agricultural applications and as a component in composite materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modifications and blends of LDPE
To enhance the performance of LDPE, various modifications and blending techniques have been developed. These include the incorporation of additives, crosslinking, and blending with other polymers. Such modifications can improve mechanical properties, thermal stability, and barrier characteristics of LDPE, expanding its range of applications and addressing specific performance requirements.Expand Specific Solutions05 Recycling and sustainability of LDPE
As environmental concerns grow, efforts have been made to improve the recyclability and sustainability of LDPE. This includes developing more efficient recycling processes, incorporating recycled LDPE into new products, and exploring bio-based alternatives. Research is ongoing to address the environmental impact of LDPE and promote circular economy principles in its lifecycle.Expand Specific Solutions
Key LDPE Manufacturers and Market Dynamics
The investigation into LDPE's role in food preservation is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market demand and technological advancements. The global market for food packaging, including LDPE applications, is expanding rapidly due to changing consumer preferences and food safety concerns. While the technology is relatively mature, ongoing research by companies like Dow Global Technologies, Equistar Chemicals, and Basell Polyolefine GmbH is driving innovation in LDPE formulations and applications. Academic institutions such as Northwestern University and Jiangnan University are also contributing to the field, focusing on enhancing LDPE's properties for food preservation. This collaborative ecosystem of industry leaders and research institutions is propelling the sector forward, with a focus on improving sustainability and performance.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
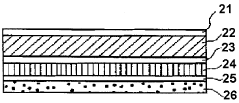
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies LLC has developed advanced LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) formulations specifically designed for food preservation applications. Their technology focuses on enhancing the barrier properties of LDPE films to extend shelf life. They have implemented a multi-layer film structure that combines LDPE with other materials to create a synergistic effect, improving oxygen and moisture barrier properties[1]. The company has also developed a proprietary additive package that enhances the film's resistance to puncture and tear, crucial for maintaining package integrity during transportation and storage[2]. Additionally, Dow has introduced a novel crosslinking technology that improves the thermal stability of LDPE films, allowing for better performance in hot-fill applications and microwaveable packaging[3].
Strengths: Superior barrier properties, enhanced durability, and improved thermal stability. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and more complex recycling processes due to multi-layer structures.
Performance Materials NA, Inc.
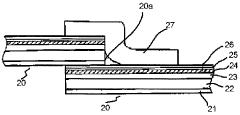
Technical Solution: Performance Materials NA, Inc. has focused on developing specialized LDPE blends for food preservation. Their approach involves incorporating nanoparticles into the LDPE matrix to enhance its barrier properties[4]. This nano-enhanced LDPE demonstrates significantly reduced oxygen transmission rates, effectively extending the shelf life of packaged foods. The company has also developed a proprietary surface treatment technology that improves the adhesion of LDPE films to other materials, enabling the creation of more effective multi-layer packaging solutions[5]. Furthermore, they have introduced a novel antifog additive for LDPE films, which prevents condensation on the inner surface of the packaging, maintaining product visibility and reducing the risk of microbial growth[6].
Strengths: Enhanced barrier properties through nanotechnology, improved multi-layer compatibility, and advanced antifog properties. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges related to nanoparticle use in food packaging and increased production complexity.
Innovative LDPE Technologies for Food Packaging
Laminated packaging material for paper container
PatentWO2000044632A1
Innovation
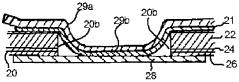
- A packaging material comprising a thermoplastic layer, a paper layer, and a barrier layer, with an innermost thermoplastic layer made of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) having specific molecular weight distribution and melting properties, enhancing sealability and preventing leakage while maintaining quality.
Food biopreservative composition and uses thereof
PatentInactiveUS20230329287A1
Innovation
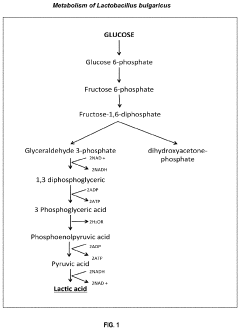
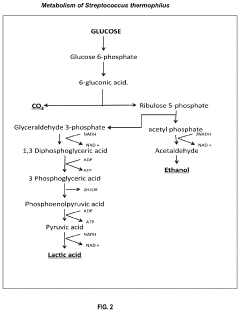
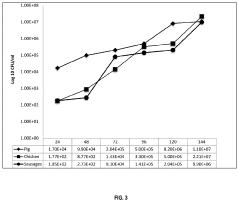
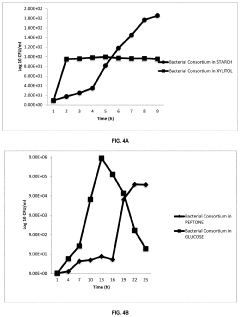
- A biopreservative composition comprising a consortium of lactic acid bacteria, including homofermentative and heterofermentative strains, combined with an activating agent such as starch or plantain peels extract, which effectively inhibits pathogenic microorganisms and extends food shelf life without altering food quality.
Environmental Impact of LDPE in Food Packaging
The environmental impact of LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) in food packaging is a critical concern in the context of sustainable development and ecological preservation. LDPE, while effective in food preservation, poses significant challenges to the environment throughout its lifecycle.
Production of LDPE involves the use of non-renewable fossil fuels, contributing to resource depletion and greenhouse gas emissions. The manufacturing process requires substantial energy inputs and often results in the release of harmful pollutants, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter, which can negatively affect air quality and human health.
Once in use, LDPE food packaging effectively extends the shelf life of products, potentially reducing food waste. However, this benefit is offset by the material's persistence in the environment. LDPE is not biodegradable and can take hundreds of years to decompose naturally. This longevity leads to accumulation in landfills, where it occupies valuable space and can leach harmful chemicals into soil and groundwater.
Marine pollution is another significant concern associated with LDPE food packaging. Improper disposal and inadequate waste management systems result in large quantities of plastic waste entering oceans and waterways. In marine environments, LDPE breaks down into microplastics, which can be ingested by marine life, causing physical harm and potentially entering the food chain.
Recycling LDPE presents challenges due to contamination from food residues and the presence of additives and colorants. While technically recyclable, the economic viability of recycling LDPE is often low, leading to low recycling rates globally. This results in a large portion of LDPE packaging being incinerated or sent to landfills, further contributing to environmental degradation.
The production and disposal of LDPE food packaging also contribute to climate change. The carbon footprint associated with its lifecycle, from raw material extraction to end-of-life management, is substantial. Incineration of LDPE releases greenhouse gases and toxic substances, exacerbating air pollution and global warming.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, various strategies are being explored. These include the development of biodegradable alternatives, improvements in recycling technologies, and the implementation of circular economy principles in packaging design. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on reducing overall packaging use through innovative product designs and consumer education.
Production of LDPE involves the use of non-renewable fossil fuels, contributing to resource depletion and greenhouse gas emissions. The manufacturing process requires substantial energy inputs and often results in the release of harmful pollutants, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter, which can negatively affect air quality and human health.
Once in use, LDPE food packaging effectively extends the shelf life of products, potentially reducing food waste. However, this benefit is offset by the material's persistence in the environment. LDPE is not biodegradable and can take hundreds of years to decompose naturally. This longevity leads to accumulation in landfills, where it occupies valuable space and can leach harmful chemicals into soil and groundwater.
Marine pollution is another significant concern associated with LDPE food packaging. Improper disposal and inadequate waste management systems result in large quantities of plastic waste entering oceans and waterways. In marine environments, LDPE breaks down into microplastics, which can be ingested by marine life, causing physical harm and potentially entering the food chain.
Recycling LDPE presents challenges due to contamination from food residues and the presence of additives and colorants. While technically recyclable, the economic viability of recycling LDPE is often low, leading to low recycling rates globally. This results in a large portion of LDPE packaging being incinerated or sent to landfills, further contributing to environmental degradation.
The production and disposal of LDPE food packaging also contribute to climate change. The carbon footprint associated with its lifecycle, from raw material extraction to end-of-life management, is substantial. Incineration of LDPE releases greenhouse gases and toxic substances, exacerbating air pollution and global warming.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, various strategies are being explored. These include the development of biodegradable alternatives, improvements in recycling technologies, and the implementation of circular economy principles in packaging design. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on reducing overall packaging use through innovative product designs and consumer education.
Food Safety Regulations for LDPE Packaging
Food safety regulations for LDPE packaging play a crucial role in ensuring the protection of consumers and maintaining the integrity of food products. These regulations are established and enforced by various governmental bodies and international organizations to address potential risks associated with the use of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) in food packaging applications.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for regulating food contact materials, including LDPE packaging. The FDA's Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21, Part 177, Subpart B, Section 177.1520 specifically addresses olefin polymers, including LDPE, and outlines the requirements for their use in food contact applications. This regulation specifies the permissible raw materials, additives, and processing aids that can be used in LDPE production for food packaging.
The European Union has established comprehensive regulations for food contact materials through Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004. This framework regulation sets out general principles for all food contact materials, including LDPE packaging. Additionally, Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 provides specific requirements for plastic materials intended to come into contact with food, including migration limits for various substances used in LDPE production.
One of the key aspects of food safety regulations for LDPE packaging is the concept of migration limits. These limits define the maximum amount of substances that can transfer from the packaging material to the food under specified conditions. For LDPE, migration limits are set for various additives, monomers, and other components used in its production. Manufacturers must conduct migration testing to ensure compliance with these limits and demonstrate the safety of their packaging materials.
Regulations also address the use of recycled LDPE in food packaging. The FDA has established guidelines for the use of recycled plastics in food contact applications, requiring manufacturers to demonstrate that the recycling process effectively removes contaminants and produces a material suitable for food contact. In the EU, Regulation (EC) No 282/2008 specifically addresses recycled plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with foods.
Food safety regulations for LDPE packaging also extend to labeling requirements. Manufacturers must provide accurate information about the composition and intended use of their packaging materials. This includes proper identification of the material as LDPE and any specific instructions for use or limitations related to food contact applications.
As the understanding of potential health risks associated with food packaging materials evolves, regulations are periodically updated to reflect new scientific findings. For instance, concerns about endocrine disruptors and nanomaterials have led to increased scrutiny and potential regulatory changes in recent years. Manufacturers and users of LDPE packaging must stay informed about these regulatory developments and adapt their practices accordingly to ensure ongoing compliance and food safety.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for regulating food contact materials, including LDPE packaging. The FDA's Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21, Part 177, Subpart B, Section 177.1520 specifically addresses olefin polymers, including LDPE, and outlines the requirements for their use in food contact applications. This regulation specifies the permissible raw materials, additives, and processing aids that can be used in LDPE production for food packaging.
The European Union has established comprehensive regulations for food contact materials through Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004. This framework regulation sets out general principles for all food contact materials, including LDPE packaging. Additionally, Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 provides specific requirements for plastic materials intended to come into contact with food, including migration limits for various substances used in LDPE production.
One of the key aspects of food safety regulations for LDPE packaging is the concept of migration limits. These limits define the maximum amount of substances that can transfer from the packaging material to the food under specified conditions. For LDPE, migration limits are set for various additives, monomers, and other components used in its production. Manufacturers must conduct migration testing to ensure compliance with these limits and demonstrate the safety of their packaging materials.
Regulations also address the use of recycled LDPE in food packaging. The FDA has established guidelines for the use of recycled plastics in food contact applications, requiring manufacturers to demonstrate that the recycling process effectively removes contaminants and produces a material suitable for food contact. In the EU, Regulation (EC) No 282/2008 specifically addresses recycled plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with foods.
Food safety regulations for LDPE packaging also extend to labeling requirements. Manufacturers must provide accurate information about the composition and intended use of their packaging materials. This includes proper identification of the material as LDPE and any specific instructions for use or limitations related to food contact applications.
As the understanding of potential health risks associated with food packaging materials evolves, regulations are periodically updated to reflect new scientific findings. For instance, concerns about endocrine disruptors and nanomaterials have led to increased scrutiny and potential regulatory changes in recent years. Manufacturers and users of LDPE packaging must stay informed about these regulatory developments and adapt their practices accordingly to ensure ongoing compliance and food safety.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!