LDPE's Role in Modern Packaging: Challenges & Solutions
JUN 30, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Packaging Evolution
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has played a pivotal role in the evolution of modern packaging since its introduction in the 1930s. Initially developed as a flexible and durable material, LDPE quickly gained popularity in the packaging industry due to its unique properties. The evolution of LDPE packaging can be traced through several key phases, each marked by technological advancements and changing market demands.
In the early stages, LDPE was primarily used for simple applications such as plastic bags and food wraps. Its flexibility, moisture resistance, and low cost made it an ideal choice for these basic packaging needs. As manufacturing processes improved, LDPE found its way into more complex packaging solutions, including bottles, containers, and industrial packaging materials.
The 1960s and 1970s saw a significant expansion in LDPE usage, driven by the growth of the consumer goods industry and the increasing demand for convenient, disposable packaging. During this period, LDPE packaging became ubiquitous in supermarkets and households, revolutionizing food storage and transportation.
The late 20th century brought about increased awareness of environmental issues, prompting the packaging industry to explore ways to make LDPE more sustainable. This led to the development of thinner LDPE films and improved recycling techniques, aiming to reduce the material's environmental footprint while maintaining its functional benefits.
In recent years, the evolution of LDPE packaging has focused on enhancing its performance characteristics. Advanced manufacturing techniques have allowed for the production of LDPE with improved barrier properties, making it suitable for a wider range of applications, including sensitive food products and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, the integration of LDPE with other materials in multi-layer packaging has further expanded its versatility.
The digital age has also influenced LDPE packaging evolution, with smart packaging solutions incorporating LDPE as a base material. These innovations include QR codes printed on LDPE films for product tracking and interactive consumer experiences, as well as the development of LDPE packaging with embedded sensors for monitoring product freshness and integrity.
Looking ahead, the evolution of LDPE packaging continues to be driven by sustainability concerns and technological advancements. Research is ongoing into biodegradable LDPE alternatives and more efficient recycling methods. The industry is also exploring ways to reduce the overall use of LDPE through innovative packaging designs and the adoption of reusable packaging systems.
In the early stages, LDPE was primarily used for simple applications such as plastic bags and food wraps. Its flexibility, moisture resistance, and low cost made it an ideal choice for these basic packaging needs. As manufacturing processes improved, LDPE found its way into more complex packaging solutions, including bottles, containers, and industrial packaging materials.
The 1960s and 1970s saw a significant expansion in LDPE usage, driven by the growth of the consumer goods industry and the increasing demand for convenient, disposable packaging. During this period, LDPE packaging became ubiquitous in supermarkets and households, revolutionizing food storage and transportation.
The late 20th century brought about increased awareness of environmental issues, prompting the packaging industry to explore ways to make LDPE more sustainable. This led to the development of thinner LDPE films and improved recycling techniques, aiming to reduce the material's environmental footprint while maintaining its functional benefits.
In recent years, the evolution of LDPE packaging has focused on enhancing its performance characteristics. Advanced manufacturing techniques have allowed for the production of LDPE with improved barrier properties, making it suitable for a wider range of applications, including sensitive food products and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, the integration of LDPE with other materials in multi-layer packaging has further expanded its versatility.
The digital age has also influenced LDPE packaging evolution, with smart packaging solutions incorporating LDPE as a base material. These innovations include QR codes printed on LDPE films for product tracking and interactive consumer experiences, as well as the development of LDPE packaging with embedded sensors for monitoring product freshness and integrity.
Looking ahead, the evolution of LDPE packaging continues to be driven by sustainability concerns and technological advancements. Research is ongoing into biodegradable LDPE alternatives and more efficient recycling methods. The industry is also exploring ways to reduce the overall use of LDPE through innovative packaging designs and the adoption of reusable packaging systems.
Market Demand Analysis
The global market for LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) in packaging has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the material's versatility, cost-effectiveness, and performance characteristics. The packaging industry, particularly in food and beverage sectors, has been the primary driver of LDPE demand. This material's excellent moisture barrier properties, flexibility, and durability make it ideal for various packaging applications, including films, bags, and containers.
Consumer trends towards convenience and on-the-go consumption have further boosted the demand for LDPE packaging solutions. The rise of e-commerce has also contributed to increased usage of LDPE in protective packaging and shipping materials. Additionally, the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries have shown growing interest in LDPE packaging due to its ability to maintain product integrity and meet stringent regulatory requirements.
However, the market demand for LDPE packaging faces challenges from environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. Increasing awareness of plastic pollution has led to calls for more sustainable packaging alternatives. This has resulted in a shift towards recyclable and biodegradable materials, potentially impacting LDPE's market share in certain applications.
Despite these challenges, innovations in LDPE technology are opening up new market opportunities. The development of bio-based LDPE and improved recycling techniques are addressing some of the environmental concerns associated with traditional LDPE. These advancements are likely to sustain market demand in the face of growing sustainability pressures.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key growth market for LDPE packaging, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and changing consumer lifestyles. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and specialized LDPE packaging solutions.
Looking ahead, the market demand for LDPE in packaging is expected to continue growing, albeit at a more moderate pace. The material's cost-effectiveness and performance advantages will likely sustain its position in many packaging applications. However, the industry must address environmental concerns and adapt to changing regulatory landscapes to maintain long-term growth prospects.
Technological advancements in LDPE production and processing are anticipated to open up new application areas, potentially expanding market demand. The development of thinner, stronger LDPE films and improved barrier properties could lead to increased adoption in high-performance packaging applications.
Consumer trends towards convenience and on-the-go consumption have further boosted the demand for LDPE packaging solutions. The rise of e-commerce has also contributed to increased usage of LDPE in protective packaging and shipping materials. Additionally, the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries have shown growing interest in LDPE packaging due to its ability to maintain product integrity and meet stringent regulatory requirements.
However, the market demand for LDPE packaging faces challenges from environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. Increasing awareness of plastic pollution has led to calls for more sustainable packaging alternatives. This has resulted in a shift towards recyclable and biodegradable materials, potentially impacting LDPE's market share in certain applications.
Despite these challenges, innovations in LDPE technology are opening up new market opportunities. The development of bio-based LDPE and improved recycling techniques are addressing some of the environmental concerns associated with traditional LDPE. These advancements are likely to sustain market demand in the face of growing sustainability pressures.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key growth market for LDPE packaging, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and changing consumer lifestyles. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and specialized LDPE packaging solutions.
Looking ahead, the market demand for LDPE in packaging is expected to continue growing, albeit at a more moderate pace. The material's cost-effectiveness and performance advantages will likely sustain its position in many packaging applications. However, the industry must address environmental concerns and adapt to changing regulatory landscapes to maintain long-term growth prospects.
Technological advancements in LDPE production and processing are anticipated to open up new application areas, potentially expanding market demand. The development of thinner, stronger LDPE films and improved barrier properties could lead to increased adoption in high-performance packaging applications.
Technical Challenges
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone in modern packaging due to its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and desirable physical properties. However, its widespread use has led to significant environmental concerns, presenting several technical challenges that the industry must address.
One of the primary challenges is the recyclability of LDPE packaging. While LDPE is theoretically recyclable, the process is often complicated by contamination from food residues, labels, and mixed materials in multi-layer packaging. This contamination can significantly reduce the quality of recycled LDPE, limiting its potential applications and creating a bottleneck in the circular economy of plastics.
Another technical hurdle is the development of bio-based alternatives that can match LDPE's performance characteristics. Current bio-based plastics often fall short in terms of barrier properties, tensile strength, and heat resistance, making them less suitable for many packaging applications. Bridging this performance gap while maintaining cost-effectiveness remains a significant challenge for researchers and manufacturers.
The persistence of LDPE in the environment poses another set of technical challenges. Traditional LDPE does not biodegrade in natural conditions, leading to long-term accumulation in landfills and oceans. Developing LDPE variants that can degrade in various environmental conditions without compromising the material's performance during its intended use is a complex task that requires innovative approaches in polymer science.
Furthermore, the industry faces challenges in reducing the carbon footprint associated with LDPE production. The current manufacturing process is energy-intensive and relies heavily on fossil fuels. Developing more energy-efficient production methods and transitioning to renewable energy sources without affecting product quality or increasing costs is a significant technical challenge.
Lastly, there is the challenge of improving LDPE's barrier properties to extend the shelf life of packaged products while reducing material usage. This involves developing advanced LDPE formulations or incorporating nanotechnology to enhance gas and moisture barrier properties without compromising recyclability or increasing environmental impact.
Addressing these technical challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in materials science, chemical engineering, and environmental technology. The solutions developed will play a crucial role in shaping the future of sustainable packaging and the circular economy of plastics.
One of the primary challenges is the recyclability of LDPE packaging. While LDPE is theoretically recyclable, the process is often complicated by contamination from food residues, labels, and mixed materials in multi-layer packaging. This contamination can significantly reduce the quality of recycled LDPE, limiting its potential applications and creating a bottleneck in the circular economy of plastics.
Another technical hurdle is the development of bio-based alternatives that can match LDPE's performance characteristics. Current bio-based plastics often fall short in terms of barrier properties, tensile strength, and heat resistance, making them less suitable for many packaging applications. Bridging this performance gap while maintaining cost-effectiveness remains a significant challenge for researchers and manufacturers.
The persistence of LDPE in the environment poses another set of technical challenges. Traditional LDPE does not biodegrade in natural conditions, leading to long-term accumulation in landfills and oceans. Developing LDPE variants that can degrade in various environmental conditions without compromising the material's performance during its intended use is a complex task that requires innovative approaches in polymer science.
Furthermore, the industry faces challenges in reducing the carbon footprint associated with LDPE production. The current manufacturing process is energy-intensive and relies heavily on fossil fuels. Developing more energy-efficient production methods and transitioning to renewable energy sources without affecting product quality or increasing costs is a significant technical challenge.
Lastly, there is the challenge of improving LDPE's barrier properties to extend the shelf life of packaged products while reducing material usage. This involves developing advanced LDPE formulations or incorporating nanotechnology to enhance gas and moisture barrier properties without compromising recyclability or increasing environmental impact.
Addressing these technical challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in materials science, chemical engineering, and environmental technology. The solutions developed will play a crucial role in shaping the future of sustainable packaging and the circular economy of plastics.
Current LDPE Solutions
01 Composition and properties of LDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a low density and high flexibility. It is characterized by its branched structure, which results in lower crystallinity and density compared to other polyethylene types. LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance, low water absorption, and excellent electrical insulation properties.- Composition and properties of LDPE: Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a low density and high flexibility. It is characterized by its branched structure, which results in lower crystallinity and density compared to other polyethylene types. LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance, low water absorption, and excellent electrical insulation properties.
- Manufacturing processes for LDPE: LDPE is typically produced through high-pressure polymerization of ethylene using free-radical initiators. Various manufacturing techniques have been developed to improve the production efficiency and control the properties of LDPE, including the use of different catalysts, reactor designs, and process conditions.
- Applications of LDPE: LDPE finds widespread use in various industries due to its unique properties. Common applications include packaging materials, such as plastic bags and films, agricultural films, wire and cable insulation, and disposable containers. It is also used in the production of toys, laboratory equipment, and certain medical devices.
- Modifications and blends of LDPE: To enhance its properties and expand its applications, LDPE is often modified or blended with other materials. This includes the incorporation of additives, crosslinking, and blending with other polymers to improve strength, heat resistance, or biodegradability. Such modifications can result in specialized grades of LDPE for specific applications.
- Recycling and environmental considerations of LDPE: As a widely used plastic, the recycling and environmental impact of LDPE are important considerations. Research and development efforts focus on improving LDPE recycling processes, developing biodegradable variants, and finding sustainable alternatives. This includes the exploration of bio-based sources for LDPE production and the development of more efficient recycling technologies.
02 Manufacturing processes for LDPE
LDPE is typically produced through high-pressure polymerization of ethylene using free-radical initiators. Various manufacturing techniques have been developed to improve the production efficiency and control the properties of LDPE, including the use of different catalysts, reactor designs, and process conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of LDPE
LDPE finds widespread use in various industries due to its unique properties. Common applications include packaging materials, such as plastic bags and films, agricultural films, wire and cable insulation, and disposable containers. It is also used in the production of toys, laboratory equipment, and certain medical devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modifications and blends of LDPE
To enhance its properties and expand its applications, LDPE is often modified or blended with other materials. This includes the incorporation of additives, crosslinking agents, or blending with other polymers to improve mechanical strength, thermal stability, or specific functional properties. Such modifications can result in materials with tailored characteristics for specific end-uses.Expand Specific Solutions05 Recycling and environmental considerations of LDPE
As a widely used plastic, the recycling and environmental impact of LDPE have become important considerations. Research and development efforts focus on improving LDPE recycling processes, developing biodegradable alternatives, and exploring sustainable production methods to reduce its environmental footprint.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The LDPE packaging market is in a mature stage, characterized by steady growth and widespread adoption across various industries. The global market size for LDPE packaging is substantial, estimated to be in the billions of dollars, driven by increasing demand in food, beverage, and consumer goods sectors. Technologically, LDPE is well-established, with ongoing innovations focused on improving sustainability and performance. Key players like Dow Global Technologies, Saudi Basic Industries Corp., and DuPont de Nemours are leading the market with advanced R&D capabilities. Emerging companies such as Abu Dhabi Polymers Co. Ltd. (Borouge) and Borealis AG are also making significant contributions, particularly in developing eco-friendly solutions to address environmental concerns in the packaging industry.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed advanced LDPE resins with enhanced properties for modern packaging applications. Their AGILITY™ CE LDPE resins offer improved processability and optical properties[1]. These resins are designed for high-speed extrusion coating and lamination processes, providing excellent adhesion to various substrates. Dow's LDPE solutions also incorporate additives for enhanced barrier properties and seal strength, addressing key challenges in food packaging and industrial applications[2]. The company has invested in sustainable LDPE production, focusing on circular economy principles and recycling technologies to address environmental concerns[3].
Strengths: Wide range of specialized LDPE grades, strong R&D capabilities, focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: Dependence on petrochemical feedstocks, potential regulatory challenges related to plastic packaging.
Saudi Basic Industries Corp.
Technical Solution: SABIC has developed a range of LDPE resins tailored for modern packaging needs. Their LDPE portfolio includes grades with enhanced clarity, toughness, and processability[4]. SABIC's LDPE resins are designed for various packaging applications, including food packaging, shrink film, and agricultural films. The company has invested in advanced catalyst technologies to improve LDPE production efficiency and product quality[5]. SABIC is also focusing on developing sustainable LDPE solutions, including bio-based and recyclable options, to address environmental concerns in the packaging industry[6].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, diverse product portfolio, strong presence in emerging markets. Weaknesses: Reliance on fossil fuel-based feedstocks, potential impact of oil price fluctuations on profitability.
Breakthrough Patents
High pressure LDPE for medical applications
PatentActiveUS20120220738A1
Innovation
- Development of a new LDPE with higher density and crystallinity, achieved through radical polymerization, allowing for higher melting and softening temperatures while maintaining a high melt flow rate, enabling faster and more effective sterilization processes.
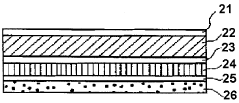
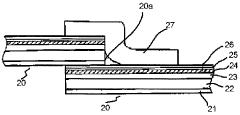
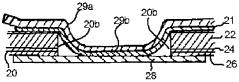
Laminated packaging material for paper container
PatentWO2000044632A1
Innovation
- A packaging material comprising a thermoplastic layer, a paper layer, and a barrier layer, with an innermost thermoplastic layer made of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) having specific molecular weight distribution and melting properties, enhancing sealability and preventing leakage while maintaining quality.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) in modern packaging is a critical concern that has garnered significant attention in recent years. As a widely used plastic material, LDPE has contributed to the global plastic pollution crisis, with packaging being one of its primary applications.
LDPE's durability, which makes it valuable for packaging, also poses a significant environmental challenge. The material can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, leading to long-term ecological consequences. When improperly disposed of, LDPE packaging often ends up in landfills, oceans, and other natural habitats, causing harm to wildlife and ecosystems.
Marine pollution is a particularly pressing issue associated with LDPE packaging. As the material breaks down into smaller particles, it forms microplastics that can be ingested by marine life, leading to potential health issues for animals and humans through the food chain. The accumulation of LDPE in ocean gyres has resulted in vast "plastic islands," highlighting the global scale of the problem.
The production of LDPE also contributes to environmental concerns. The manufacturing process relies heavily on fossil fuels, both as a raw material and energy source, leading to significant greenhouse gas emissions. This carbon footprint adds to the overall environmental impact of LDPE packaging throughout its lifecycle.
Recycling challenges further compound the environmental issues associated with LDPE. While technically recyclable, the material often ends up in mixed waste streams, making it difficult to separate and process effectively. Additionally, the quality of recycled LDPE is often lower than virgin material, limiting its applications and creating a demand for new production.
In response to these environmental challenges, there has been a push for more sustainable alternatives and improved waste management strategies. Biodegradable and compostable materials are being explored as potential replacements for LDPE in certain packaging applications. Additionally, efforts to enhance recycling infrastructure and promote circular economy principles aim to reduce the environmental impact of LDPE packaging.
Innovations in LDPE formulations are also being pursued to address environmental concerns. These include the development of additives that enhance biodegradability and the creation of LDPE blends that incorporate recycled content or renewable resources. Such advancements seek to mitigate the environmental impact while maintaining the material's desirable properties for packaging applications.
LDPE's durability, which makes it valuable for packaging, also poses a significant environmental challenge. The material can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, leading to long-term ecological consequences. When improperly disposed of, LDPE packaging often ends up in landfills, oceans, and other natural habitats, causing harm to wildlife and ecosystems.
Marine pollution is a particularly pressing issue associated with LDPE packaging. As the material breaks down into smaller particles, it forms microplastics that can be ingested by marine life, leading to potential health issues for animals and humans through the food chain. The accumulation of LDPE in ocean gyres has resulted in vast "plastic islands," highlighting the global scale of the problem.
The production of LDPE also contributes to environmental concerns. The manufacturing process relies heavily on fossil fuels, both as a raw material and energy source, leading to significant greenhouse gas emissions. This carbon footprint adds to the overall environmental impact of LDPE packaging throughout its lifecycle.
Recycling challenges further compound the environmental issues associated with LDPE. While technically recyclable, the material often ends up in mixed waste streams, making it difficult to separate and process effectively. Additionally, the quality of recycled LDPE is often lower than virgin material, limiting its applications and creating a demand for new production.
In response to these environmental challenges, there has been a push for more sustainable alternatives and improved waste management strategies. Biodegradable and compostable materials are being explored as potential replacements for LDPE in certain packaging applications. Additionally, efforts to enhance recycling infrastructure and promote circular economy principles aim to reduce the environmental impact of LDPE packaging.
Innovations in LDPE formulations are also being pursued to address environmental concerns. These include the development of additives that enhance biodegradability and the creation of LDPE blends that incorporate recycled content or renewable resources. Such advancements seek to mitigate the environmental impact while maintaining the material's desirable properties for packaging applications.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding LDPE in modern packaging is complex and evolving, reflecting growing environmental concerns and the push for sustainable practices. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations to address the environmental impact of plastic packaging, particularly single-use plastics.
In the European Union, the Single-Use Plastics Directive, implemented in 2021, aims to reduce plastic waste by banning certain single-use plastic items and setting targets for recycling and reuse. This directive has significant implications for LDPE packaging, as it encourages the development of more sustainable alternatives and improved recycling infrastructure.
The United States has a patchwork of state and local regulations concerning plastic packaging. Several states, including California and New York, have implemented bans on single-use plastic bags, many of which are made from LDPE. These regulations are driving innovation in packaging materials and design, pushing manufacturers to explore biodegradable or easily recyclable alternatives.
In Asia, countries like China and India have also introduced regulations to curb plastic waste. China's ban on importing plastic waste has forced many countries to reassess their recycling strategies, including those for LDPE packaging. This has led to increased pressure on domestic recycling capabilities and a push for more circular economy approaches.
Global initiatives, such as the New Plastics Economy Global Commitment led by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, are also shaping the regulatory landscape. These initiatives promote collaboration between governments, businesses, and NGOs to create a circular economy for plastics, including LDPE packaging.
The regulatory focus is increasingly shifting towards Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes, which make manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. This approach is being adopted in various forms across Europe, Canada, and parts of the United States, significantly impacting the LDPE packaging industry.
As regulations tighten, the LDPE packaging industry faces challenges in compliance and adaptation. However, these challenges also drive innovation in materials science, recycling technologies, and packaging design. Companies are investing in research and development to create LDPE alternatives that meet regulatory requirements while maintaining the material's desirable properties for packaging applications.
The regulatory landscape is expected to continue evolving, with a trend towards more stringent environmental standards and increased emphasis on circular economy principles. This dynamic environment necessitates ongoing adaptation and innovation in the LDPE packaging industry to ensure compliance and maintain market competitiveness.
In the European Union, the Single-Use Plastics Directive, implemented in 2021, aims to reduce plastic waste by banning certain single-use plastic items and setting targets for recycling and reuse. This directive has significant implications for LDPE packaging, as it encourages the development of more sustainable alternatives and improved recycling infrastructure.
The United States has a patchwork of state and local regulations concerning plastic packaging. Several states, including California and New York, have implemented bans on single-use plastic bags, many of which are made from LDPE. These regulations are driving innovation in packaging materials and design, pushing manufacturers to explore biodegradable or easily recyclable alternatives.
In Asia, countries like China and India have also introduced regulations to curb plastic waste. China's ban on importing plastic waste has forced many countries to reassess their recycling strategies, including those for LDPE packaging. This has led to increased pressure on domestic recycling capabilities and a push for more circular economy approaches.
Global initiatives, such as the New Plastics Economy Global Commitment led by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, are also shaping the regulatory landscape. These initiatives promote collaboration between governments, businesses, and NGOs to create a circular economy for plastics, including LDPE packaging.
The regulatory focus is increasingly shifting towards Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes, which make manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. This approach is being adopted in various forms across Europe, Canada, and parts of the United States, significantly impacting the LDPE packaging industry.
As regulations tighten, the LDPE packaging industry faces challenges in compliance and adaptation. However, these challenges also drive innovation in materials science, recycling technologies, and packaging design. Companies are investing in research and development to create LDPE alternatives that meet regulatory requirements while maintaining the material's desirable properties for packaging applications.
The regulatory landscape is expected to continue evolving, with a trend towards more stringent environmental standards and increased emphasis on circular economy principles. This dynamic environment necessitates ongoing adaptation and innovation in the LDPE packaging industry to ensure compliance and maintain market competitiveness.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!