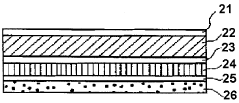
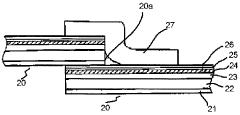
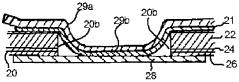
Impact of LDPE on the Future of Flexible Packaging
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE in Packaging: Evolution and Objectives
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone in the packaging industry since its introduction in the 1930s. The evolution of LDPE in packaging has been driven by its unique properties, including flexibility, transparency, and moisture resistance. Initially used for simple applications like plastic bags, LDPE has undergone significant advancements to meet the growing demands of the packaging sector.
The development of LDPE technology has been marked by continuous improvements in polymer structure and processing techniques. Early iterations focused on enhancing basic properties, while recent advancements have targeted specific performance characteristics such as improved barrier properties, reduced thickness, and enhanced recyclability. These developments have expanded LDPE's applications from basic packaging to more sophisticated uses in food preservation and industrial packaging.
In the context of flexible packaging, LDPE has played a pivotal role in shaping industry trends. Its versatility has allowed for the creation of lightweight, durable, and cost-effective packaging solutions. The material's ability to be easily modified and combined with other polymers has led to the development of multi-layer films, which offer superior protection and extended shelf life for packaged products.
The objectives for LDPE in packaging have evolved alongside technological advancements and changing market demands. Current goals include improving sustainability, enhancing recyclability, and reducing material usage while maintaining or improving performance. There is a growing focus on developing LDPE formulations that are more compatible with recycling processes and exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived LDPE.
Looking ahead, the future objectives for LDPE in packaging are likely to center around circular economy principles. This includes designing LDPE packaging for easier recycling, increasing the use of recycled content in LDPE products, and developing new end-of-life solutions for LDPE packaging waste. Additionally, there is a push towards improving the overall environmental footprint of LDPE production and use in packaging applications.
The impact of LDPE on the future of flexible packaging is expected to be significant, with ongoing research aimed at addressing current limitations and exploring new possibilities. Innovations in LDPE technology are likely to focus on enhancing barrier properties to extend product shelf life, improving heat resistance for broader application ranges, and developing smart packaging solutions that incorporate LDPE with advanced functionalities.
As environmental concerns continue to shape industry priorities, the evolution of LDPE in packaging will likely be guided by sustainability goals. This may include the development of fully recyclable LDPE packaging systems, the integration of LDPE into compostable packaging solutions, and the exploration of chemical recycling technologies specifically tailored for LDPE materials.
The development of LDPE technology has been marked by continuous improvements in polymer structure and processing techniques. Early iterations focused on enhancing basic properties, while recent advancements have targeted specific performance characteristics such as improved barrier properties, reduced thickness, and enhanced recyclability. These developments have expanded LDPE's applications from basic packaging to more sophisticated uses in food preservation and industrial packaging.
In the context of flexible packaging, LDPE has played a pivotal role in shaping industry trends. Its versatility has allowed for the creation of lightweight, durable, and cost-effective packaging solutions. The material's ability to be easily modified and combined with other polymers has led to the development of multi-layer films, which offer superior protection and extended shelf life for packaged products.
The objectives for LDPE in packaging have evolved alongside technological advancements and changing market demands. Current goals include improving sustainability, enhancing recyclability, and reducing material usage while maintaining or improving performance. There is a growing focus on developing LDPE formulations that are more compatible with recycling processes and exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived LDPE.
Looking ahead, the future objectives for LDPE in packaging are likely to center around circular economy principles. This includes designing LDPE packaging for easier recycling, increasing the use of recycled content in LDPE products, and developing new end-of-life solutions for LDPE packaging waste. Additionally, there is a push towards improving the overall environmental footprint of LDPE production and use in packaging applications.
The impact of LDPE on the future of flexible packaging is expected to be significant, with ongoing research aimed at addressing current limitations and exploring new possibilities. Innovations in LDPE technology are likely to focus on enhancing barrier properties to extend product shelf life, improving heat resistance for broader application ranges, and developing smart packaging solutions that incorporate LDPE with advanced functionalities.
As environmental concerns continue to shape industry priorities, the evolution of LDPE in packaging will likely be guided by sustainability goals. This may include the development of fully recyclable LDPE packaging systems, the integration of LDPE into compostable packaging solutions, and the exploration of chemical recycling technologies specifically tailored for LDPE materials.
Flexible Packaging Market Dynamics
The flexible packaging market has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and sustainability concerns. This dynamic landscape is characterized by several key factors that are shaping the future of the industry.
One of the primary drivers of market growth is the increasing demand for convenient and portable packaging solutions. As consumers lead busier lifestyles, there is a growing preference for on-the-go products that require lightweight, easy-to-use packaging. This trend has led to a surge in demand for flexible packaging across various sectors, including food and beverages, personal care, and pharmaceuticals.
The rise of e-commerce has also played a crucial role in boosting the flexible packaging market. Online retail requires packaging that is not only protective but also lightweight and cost-effective for shipping. Flexible packaging meets these requirements, offering superior protection while minimizing shipping costs and environmental impact.
Sustainability has emerged as a major factor influencing market dynamics. Consumers and regulatory bodies are increasingly demanding eco-friendly packaging solutions, pushing manufacturers to develop recyclable and biodegradable flexible packaging options. This shift towards sustainable materials is driving innovation in the industry and creating new opportunities for growth.
The food and beverage sector remains the largest end-user of flexible packaging, with a growing emphasis on extending shelf life and maintaining product freshness. Advanced barrier technologies and modified atmosphere packaging are becoming increasingly important in this segment, driving demand for high-performance flexible packaging solutions.
Emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are experiencing rapid growth in flexible packaging adoption. This is attributed to rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and changing consumer lifestyles in these regions. As a result, many global packaging companies are expanding their presence in these markets to capitalize on the growing demand.
Technological advancements are continually reshaping the flexible packaging landscape. Innovations in material science, such as the development of high-barrier films and smart packaging technologies, are opening up new possibilities for product differentiation and enhanced functionality. These advancements are not only improving packaging performance but also contributing to sustainability goals by reducing material usage and improving recyclability.
The competitive landscape of the flexible packaging market is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and smaller, specialized players. Consolidation through mergers and acquisitions has been a notable trend, as companies seek to expand their product portfolios and geographical reach. This consolidation is expected to continue as the industry evolves and companies strive to meet the changing demands of the market.
One of the primary drivers of market growth is the increasing demand for convenient and portable packaging solutions. As consumers lead busier lifestyles, there is a growing preference for on-the-go products that require lightweight, easy-to-use packaging. This trend has led to a surge in demand for flexible packaging across various sectors, including food and beverages, personal care, and pharmaceuticals.
The rise of e-commerce has also played a crucial role in boosting the flexible packaging market. Online retail requires packaging that is not only protective but also lightweight and cost-effective for shipping. Flexible packaging meets these requirements, offering superior protection while minimizing shipping costs and environmental impact.
Sustainability has emerged as a major factor influencing market dynamics. Consumers and regulatory bodies are increasingly demanding eco-friendly packaging solutions, pushing manufacturers to develop recyclable and biodegradable flexible packaging options. This shift towards sustainable materials is driving innovation in the industry and creating new opportunities for growth.
The food and beverage sector remains the largest end-user of flexible packaging, with a growing emphasis on extending shelf life and maintaining product freshness. Advanced barrier technologies and modified atmosphere packaging are becoming increasingly important in this segment, driving demand for high-performance flexible packaging solutions.
Emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are experiencing rapid growth in flexible packaging adoption. This is attributed to rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and changing consumer lifestyles in these regions. As a result, many global packaging companies are expanding their presence in these markets to capitalize on the growing demand.
Technological advancements are continually reshaping the flexible packaging landscape. Innovations in material science, such as the development of high-barrier films and smart packaging technologies, are opening up new possibilities for product differentiation and enhanced functionality. These advancements are not only improving packaging performance but also contributing to sustainability goals by reducing material usage and improving recyclability.
The competitive landscape of the flexible packaging market is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and smaller, specialized players. Consolidation through mergers and acquisitions has been a notable trend, as companies seek to expand their product portfolios and geographical reach. This consolidation is expected to continue as the industry evolves and companies strive to meet the changing demands of the market.
LDPE Technical Challenges in Packaging
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone in flexible packaging for decades, but it now faces significant technical challenges as the industry evolves. One of the primary issues is the material's limited barrier properties, which can lead to reduced shelf life for packaged products. This is particularly problematic for food and pharmaceutical applications where protection against moisture, oxygen, and other external factors is crucial.
Another challenge lies in LDPE's recyclability. While it is technically recyclable, the process is often complicated by the presence of multi-layer structures and additives commonly used in flexible packaging. This complexity makes it difficult to achieve high-quality recycled materials, hindering the industry's efforts towards a circular economy.
The mechanical properties of LDPE also present challenges in certain applications. Its relatively low tensile strength and puncture resistance can limit its use in high-performance packaging scenarios. This necessitates the use of thicker films or additional layers, which can increase material usage and packaging weight.
LDPE's thermal stability is another area of concern. At higher temperatures, the material can soften and lose its structural integrity, limiting its use in hot-fill applications or in packaging that may be exposed to elevated temperatures during transportation or storage.
The manufacturing process for LDPE films also faces challenges in terms of energy efficiency and production speed. Current extrusion technologies, while well-established, have limitations in terms of output rates and film uniformity, especially for thinner gauges.
Environmental concerns pose perhaps the most significant challenge for LDPE in packaging. Its fossil fuel-based origin and slow degradation in the environment have led to increased scrutiny and regulatory pressure. This has spurred research into bio-based alternatives and more easily degradable versions of polyethylene.
Lastly, LDPE faces competition from newer, high-performance materials that offer improved barrier properties, better mechanical strength, or enhanced sustainability profiles. These alternatives, such as metallocene polyethylenes or bio-based plastics, are challenging LDPE's dominance in certain market segments.
Addressing these technical challenges is crucial for the continued relevance of LDPE in the flexible packaging industry. Innovations in material science, processing technologies, and recycling methods will be key to overcoming these hurdles and ensuring LDPE's place in the future of sustainable packaging solutions.
Another challenge lies in LDPE's recyclability. While it is technically recyclable, the process is often complicated by the presence of multi-layer structures and additives commonly used in flexible packaging. This complexity makes it difficult to achieve high-quality recycled materials, hindering the industry's efforts towards a circular economy.
The mechanical properties of LDPE also present challenges in certain applications. Its relatively low tensile strength and puncture resistance can limit its use in high-performance packaging scenarios. This necessitates the use of thicker films or additional layers, which can increase material usage and packaging weight.
LDPE's thermal stability is another area of concern. At higher temperatures, the material can soften and lose its structural integrity, limiting its use in hot-fill applications or in packaging that may be exposed to elevated temperatures during transportation or storage.
The manufacturing process for LDPE films also faces challenges in terms of energy efficiency and production speed. Current extrusion technologies, while well-established, have limitations in terms of output rates and film uniformity, especially for thinner gauges.
Environmental concerns pose perhaps the most significant challenge for LDPE in packaging. Its fossil fuel-based origin and slow degradation in the environment have led to increased scrutiny and regulatory pressure. This has spurred research into bio-based alternatives and more easily degradable versions of polyethylene.
Lastly, LDPE faces competition from newer, high-performance materials that offer improved barrier properties, better mechanical strength, or enhanced sustainability profiles. These alternatives, such as metallocene polyethylenes or bio-based plastics, are challenging LDPE's dominance in certain market segments.
Addressing these technical challenges is crucial for the continued relevance of LDPE in the flexible packaging industry. Innovations in material science, processing technologies, and recycling methods will be key to overcoming these hurdles and ensuring LDPE's place in the future of sustainable packaging solutions.
Current LDPE Flexible Packaging Solutions
01 Composition and properties of LDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a low density and high flexibility. It is characterized by its branched structure, which results in lower crystallinity and density compared to other polyethylene types. LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance, low water absorption, and excellent electrical insulation properties.- Composition and properties of LDPE: Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a low density and high flexibility. It is characterized by its branched structure, which results in lower crystallinity and density compared to other polyethylene types. LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance, electrical insulation properties, and processability, making it suitable for various applications.
- Manufacturing processes for LDPE: LDPE is typically produced through high-pressure polymerization of ethylene using free-radical initiators. Various manufacturing techniques have been developed to improve the production efficiency and control the properties of LDPE. These may include modifications to reactor design, catalyst systems, and process conditions to achieve desired molecular weight distribution and branching characteristics.
- Applications of LDPE in packaging: LDPE is widely used in the packaging industry due to its flexibility, transparency, and moisture resistance. It is commonly employed in the production of plastic bags, food packaging films, and squeeze bottles. Recent developments focus on improving the barrier properties and recyclability of LDPE packaging materials to meet environmental concerns and regulatory requirements.
- LDPE blends and composites: To enhance the performance of LDPE, it is often blended with other polymers or reinforced with various fillers and additives. These blends and composites aim to improve mechanical properties, thermal stability, or introduce specific functionalities such as flame retardancy or biodegradability. Research in this area focuses on optimizing blend ratios and developing novel compatibilization techniques.
- Recycling and sustainability of LDPE: With increasing environmental concerns, significant efforts are being made to improve the recyclability and sustainability of LDPE products. This includes developing more efficient recycling processes, incorporating recycled LDPE into new products, and exploring bio-based alternatives. Research also focuses on reducing the environmental impact of LDPE production and enhancing its biodegradability.
02 Manufacturing processes for LDPE
LDPE is typically produced through high-pressure polymerization of ethylene using free-radical initiators. Various manufacturing techniques have been developed to improve the production efficiency and control the properties of LDPE, including the use of different catalysts, reactor designs, and process conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of LDPE
LDPE finds widespread use in various industries due to its unique properties. Common applications include packaging materials, such as plastic bags and films, agricultural films, wire and cable insulation, and disposable containers. It is also used in the production of toys, laboratory equipment, and certain medical devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modifications and blends of LDPE
To enhance its properties and expand its applications, LDPE is often modified or blended with other materials. This includes the incorporation of additives, crosslinking, and the creation of composite materials. These modifications can improve mechanical strength, thermal stability, and other specific properties tailored for particular applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Recycling and environmental considerations of LDPE
As a widely used plastic, the recycling and environmental impact of LDPE have become important considerations. Research and development efforts focus on improving recycling processes, developing biodegradable alternatives, and finding new ways to reuse LDPE waste. This includes the exploration of chemical recycling methods and the incorporation of recycled LDPE into new products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key LDPE Packaging Industry Players
The impact of LDPE on flexible packaging is shaping a competitive landscape characterized by rapid growth and technological advancements. The market is in an expansion phase, driven by increasing demand for sustainable and efficient packaging solutions. Major players like Dow Global Technologies, ExxonMobil Chemical, and SABIC are leading innovation in LDPE technology, focusing on improving material properties and sustainability. The market size is substantial and growing, with emerging economies presenting significant opportunities. While LDPE technology is mature, ongoing research and development efforts by key companies are pushing the boundaries of its applications in flexible packaging, indicating a dynamic and evolving technological landscape.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed advanced LDPE resins specifically for flexible packaging applications. Their ELITE™ Enhanced Polyethylene Resins offer improved toughness, stiffness, and optical properties[1]. These resins are designed to create thinner, stronger films that reduce material usage while maintaining package integrity. Dow's AGILITY™ EC series provides excellent sealability and hot tack performance, crucial for high-speed packaging lines[2]. They have also introduced bio-based polyethylene made from renewable feedstocks, addressing sustainability concerns in flexible packaging[3].
Strengths: Wide range of specialized LDPE products, strong R&D capabilities, focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: Dependence on petrochemical feedstocks for most products, potential regulatory challenges related to plastic use.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed Exceed™ XP performance polymers, which are metallocene polyethylene resins that offer exceptional toughness and optical properties for flexible packaging[4]. Their Enable™ metallocene polyethylene resins provide improved seal strength and hot tack performance, allowing for faster packaging speeds and reduced material usage[5]. ExxonMobil's Vistamaxx™ performance polymers enhance flexibility and seal performance in multi-layer packaging structures. They have also introduced recycled content polymers to address circular economy demands in flexible packaging[6].
Strengths: Advanced metallocene catalyst technology, broad product portfolio, global manufacturing capabilities. Weaknesses: Heavy reliance on fossil-based raw materials, potential vulnerability to oil price fluctuations.
LDPE Packaging Material Advancements
Plastic modification method for enhancing transparency of LLDPE (Linear Low Density Polyethylene) packaging bag
PatentPendingCN112940386A
Innovation
- Using LLDPE linear low-density polyethylene, LDPE low-density polyethylene and PC polycarbonate and other materials mixed and heat-treated, combined with calcium carbonate, light stabilizer, coupling agent, dispersant and antioxidant, through extrusion and blown film Craftsmanship improves transparency.
Laminated packaging material for paper container
PatentWO2000044632A1
Innovation
- A packaging material comprising a thermoplastic layer, a paper layer, and a barrier layer, with an innermost thermoplastic layer made of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) having specific molecular weight distribution and melting properties, enhancing sealability and preventing leakage while maintaining quality.
Environmental Impact of LDPE Packaging
The environmental impact of LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) packaging is a critical concern in the flexible packaging industry. LDPE, while offering numerous benefits in terms of flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness, poses significant challenges to environmental sustainability.
One of the primary environmental issues associated with LDPE packaging is its persistence in the environment. LDPE is not biodegradable, meaning it can remain in landfills or natural ecosystems for hundreds of years. This longevity contributes to the accumulation of plastic waste in terrestrial and marine environments, leading to pollution and harm to wildlife.
The production of LDPE also has environmental implications. The manufacturing process relies heavily on fossil fuels, both as a raw material and energy source. This dependence contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and the depletion of non-renewable resources. Additionally, the production of LDPE involves the use of various chemicals and additives, some of which may have negative environmental impacts if not properly managed.
Recycling of LDPE packaging presents another set of challenges. While technically recyclable, LDPE often ends up in landfills due to inadequate recycling infrastructure and consumer behavior. The recycling process itself can be energy-intensive and may not always be economically viable, especially for contaminated or mixed plastic waste.
The widespread use of LDPE in single-use packaging applications exacerbates its environmental impact. Items such as plastic bags and food packaging, often used for short periods before disposal, contribute significantly to plastic waste generation. This disposable culture has led to increased pressure on waste management systems and heightened environmental concerns.
However, it's important to note that LDPE packaging does offer some environmental benefits when compared to alternative materials. Its lightweight nature can reduce transportation-related emissions, and its durability can help prevent food waste by extending shelf life. These factors must be considered in a comprehensive environmental assessment.
In response to these environmental challenges, the packaging industry is exploring various solutions. These include the development of biodegradable alternatives, improvements in recycling technologies, and the implementation of circular economy principles. Additionally, there is a growing focus on reducing the overall use of plastic packaging through innovative design and consumer education.
The future of LDPE in flexible packaging will likely be shaped by evolving environmental regulations, consumer preferences, and technological advancements. As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in packaging decisions, the industry must balance the functional benefits of LDPE with its environmental impact, driving innovation towards more eco-friendly solutions.
One of the primary environmental issues associated with LDPE packaging is its persistence in the environment. LDPE is not biodegradable, meaning it can remain in landfills or natural ecosystems for hundreds of years. This longevity contributes to the accumulation of plastic waste in terrestrial and marine environments, leading to pollution and harm to wildlife.
The production of LDPE also has environmental implications. The manufacturing process relies heavily on fossil fuels, both as a raw material and energy source. This dependence contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and the depletion of non-renewable resources. Additionally, the production of LDPE involves the use of various chemicals and additives, some of which may have negative environmental impacts if not properly managed.
Recycling of LDPE packaging presents another set of challenges. While technically recyclable, LDPE often ends up in landfills due to inadequate recycling infrastructure and consumer behavior. The recycling process itself can be energy-intensive and may not always be economically viable, especially for contaminated or mixed plastic waste.
The widespread use of LDPE in single-use packaging applications exacerbates its environmental impact. Items such as plastic bags and food packaging, often used for short periods before disposal, contribute significantly to plastic waste generation. This disposable culture has led to increased pressure on waste management systems and heightened environmental concerns.
However, it's important to note that LDPE packaging does offer some environmental benefits when compared to alternative materials. Its lightweight nature can reduce transportation-related emissions, and its durability can help prevent food waste by extending shelf life. These factors must be considered in a comprehensive environmental assessment.
In response to these environmental challenges, the packaging industry is exploring various solutions. These include the development of biodegradable alternatives, improvements in recycling technologies, and the implementation of circular economy principles. Additionally, there is a growing focus on reducing the overall use of plastic packaging through innovative design and consumer education.
The future of LDPE in flexible packaging will likely be shaped by evolving environmental regulations, consumer preferences, and technological advancements. As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in packaging decisions, the industry must balance the functional benefits of LDPE with its environmental impact, driving innovation towards more eco-friendly solutions.
Regulatory Framework for LDPE in Packaging
The regulatory framework for LDPE in packaging is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the future of flexible packaging. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the environmental implications of plastic packaging, including LDPE, which has led to a diverse array of regulations and policies.
In the European Union, the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (PPWD) sets targets for the recycling of plastic packaging, including LDPE. The directive aims to increase the recycling rate of plastic packaging to 55% by 2030. This has prompted manufacturers to invest in recyclable LDPE packaging solutions and improve collection and recycling infrastructure.
The United States lacks a comprehensive federal policy on plastic packaging, resulting in a patchwork of state and local regulations. Some states, such as California, have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws for packaging materials, including LDPE. These laws require manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their packaging products, from design to disposal.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have implemented stringent recycling laws that affect LDPE packaging. Japan's Container and Packaging Recycling Law mandates that businesses and consumers sort their waste, including LDPE packaging, for recycling. South Korea has implemented a volume-based waste fee system, encouraging the reduction of packaging waste.
Many countries have introduced or are considering taxes on single-use plastics, which may include certain LDPE packaging applications. For instance, the UK's Plastic Packaging Tax, implemented in April 2022, applies to plastic packaging with less than 30% recycled content, incentivizing the use of recycled LDPE in packaging.
The regulatory landscape also includes restrictions on certain additives used in LDPE packaging. For example, the EU's REACH regulation restricts the use of certain chemicals in plastic packaging, affecting the formulation of LDPE products.
Global initiatives, such as the New Plastics Economy Global Commitment led by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, are driving voluntary commitments from businesses to reduce plastic waste and improve recyclability. These initiatives, while not legally binding, are influencing corporate policies and indirectly shaping the regulatory environment for LDPE packaging.
As concerns about microplastics grow, some jurisdictions are considering or implementing regulations that may affect LDPE packaging. For instance, the EU is developing a policy to address microplastics, which could impact the design and disposal of LDPE packaging products.
The regulatory framework for LDPE in packaging is likely to continue evolving, with a trend towards more stringent environmental standards, increased recycling requirements, and a push for circular economy principles. This dynamic regulatory environment will be a key driver in shaping the future of LDPE in flexible packaging, influencing innovation, design, and market strategies in the coming years.
In the European Union, the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (PPWD) sets targets for the recycling of plastic packaging, including LDPE. The directive aims to increase the recycling rate of plastic packaging to 55% by 2030. This has prompted manufacturers to invest in recyclable LDPE packaging solutions and improve collection and recycling infrastructure.
The United States lacks a comprehensive federal policy on plastic packaging, resulting in a patchwork of state and local regulations. Some states, such as California, have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws for packaging materials, including LDPE. These laws require manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their packaging products, from design to disposal.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have implemented stringent recycling laws that affect LDPE packaging. Japan's Container and Packaging Recycling Law mandates that businesses and consumers sort their waste, including LDPE packaging, for recycling. South Korea has implemented a volume-based waste fee system, encouraging the reduction of packaging waste.
Many countries have introduced or are considering taxes on single-use plastics, which may include certain LDPE packaging applications. For instance, the UK's Plastic Packaging Tax, implemented in April 2022, applies to plastic packaging with less than 30% recycled content, incentivizing the use of recycled LDPE in packaging.
The regulatory landscape also includes restrictions on certain additives used in LDPE packaging. For example, the EU's REACH regulation restricts the use of certain chemicals in plastic packaging, affecting the formulation of LDPE products.
Global initiatives, such as the New Plastics Economy Global Commitment led by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, are driving voluntary commitments from businesses to reduce plastic waste and improve recyclability. These initiatives, while not legally binding, are influencing corporate policies and indirectly shaping the regulatory environment for LDPE packaging.
As concerns about microplastics grow, some jurisdictions are considering or implementing regulations that may affect LDPE packaging. For instance, the EU is developing a policy to address microplastics, which could impact the design and disposal of LDPE packaging products.
The regulatory framework for LDPE in packaging is likely to continue evolving, with a trend towards more stringent environmental standards, increased recycling requirements, and a push for circular economy principles. This dynamic regulatory environment will be a key driver in shaping the future of LDPE in flexible packaging, influencing innovation, design, and market strategies in the coming years.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!