Glycerol's Role in Moisture Regulation of Agricultural Products
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Glycerol in Agriculture
Glycerol, a versatile organic compound, has gained significant attention in the agricultural sector due to its unique properties and potential applications. Its role in moisture regulation of agricultural products has become a focal point for researchers and industry professionals alike. Glycerol's hygroscopic nature allows it to absorb and retain moisture, making it an ideal candidate for various agricultural applications.
In the context of agriculture, glycerol serves multiple purposes, primarily centered around moisture management. One of its key applications is in the preservation of harvested crops. By creating a protective barrier, glycerol helps maintain optimal moisture levels in fruits, vegetables, and grains during storage and transportation. This property significantly extends the shelf life of agricultural products, reducing post-harvest losses and ensuring better quality produce reaches consumers.
Furthermore, glycerol's moisture-regulating capabilities have been harnessed in the development of advanced seed coatings. These coatings help seeds retain moisture during storage and provide a controlled release of water during germination. This application has shown promising results in improving seed viability and germination rates, particularly in arid or semi-arid regions where water scarcity is a major concern.
In addition to post-harvest applications, glycerol has found its way into soil amendments and fertilizers. When incorporated into soil, it enhances water retention capacity, reducing the frequency of irrigation required. This property is particularly beneficial in water-stressed areas, contributing to more sustainable agricultural practices and improved crop yields.
The use of glycerol in agriculture extends to the formulation of pesticides and herbicides as well. Its ability to act as a humectant in these formulations ensures better adherence to plant surfaces and prolongs the effectiveness of active ingredients. This results in more efficient pest and weed control while potentially reducing the overall amount of chemicals applied to crops.
Recent research has also explored glycerol's potential in developing biodegradable mulch films. These films, when applied to soil surfaces, help regulate soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and maintain soil temperature. The biodegradable nature of glycerol-based mulch films addresses the environmental concerns associated with traditional plastic mulches, offering a more sustainable alternative for farmers.
As the agricultural sector continues to face challenges related to climate change and water scarcity, the role of glycerol in moisture regulation becomes increasingly important. Its versatility and effectiveness in various agricultural applications position it as a valuable tool in enhancing crop productivity, reducing waste, and promoting sustainable farming practices.
In the context of agriculture, glycerol serves multiple purposes, primarily centered around moisture management. One of its key applications is in the preservation of harvested crops. By creating a protective barrier, glycerol helps maintain optimal moisture levels in fruits, vegetables, and grains during storage and transportation. This property significantly extends the shelf life of agricultural products, reducing post-harvest losses and ensuring better quality produce reaches consumers.
Furthermore, glycerol's moisture-regulating capabilities have been harnessed in the development of advanced seed coatings. These coatings help seeds retain moisture during storage and provide a controlled release of water during germination. This application has shown promising results in improving seed viability and germination rates, particularly in arid or semi-arid regions where water scarcity is a major concern.
In addition to post-harvest applications, glycerol has found its way into soil amendments and fertilizers. When incorporated into soil, it enhances water retention capacity, reducing the frequency of irrigation required. This property is particularly beneficial in water-stressed areas, contributing to more sustainable agricultural practices and improved crop yields.
The use of glycerol in agriculture extends to the formulation of pesticides and herbicides as well. Its ability to act as a humectant in these formulations ensures better adherence to plant surfaces and prolongs the effectiveness of active ingredients. This results in more efficient pest and weed control while potentially reducing the overall amount of chemicals applied to crops.
Recent research has also explored glycerol's potential in developing biodegradable mulch films. These films, when applied to soil surfaces, help regulate soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and maintain soil temperature. The biodegradable nature of glycerol-based mulch films addresses the environmental concerns associated with traditional plastic mulches, offering a more sustainable alternative for farmers.
As the agricultural sector continues to face challenges related to climate change and water scarcity, the role of glycerol in moisture regulation becomes increasingly important. Its versatility and effectiveness in various agricultural applications position it as a valuable tool in enhancing crop productivity, reducing waste, and promoting sustainable farming practices.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for glycerol in agricultural product moisture regulation has been steadily increasing due to its effectiveness and versatility. Glycerol, also known as glycerin, has gained significant attention in the agricultural sector for its ability to control moisture content in various products, enhancing their shelf life and quality.
In the fruit and vegetable industry, glycerol-based coatings have shown promising results in reducing water loss and maintaining freshness. This application has led to a growing demand from producers and distributors seeking to extend the marketability of their produce. The global fresh fruit and vegetable market, valued at over $1 trillion, presents a substantial opportunity for glycerol-based solutions.
The grain storage sector has also recognized the potential of glycerol in moisture regulation. With annual global grain production exceeding 2 billion metric tons, the need for effective moisture control is paramount. Glycerol's hygroscopic properties make it an attractive option for maintaining optimal moisture levels in stored grains, reducing spoilage and economic losses.
In the meat and poultry industry, glycerol has found applications in packaging and processing to regulate moisture content and improve product quality. The global meat market, valued at hundreds of billions of dollars, represents another significant avenue for glycerol-based moisture regulation technologies.
The organic and natural food segment has shown particular interest in glycerol as a moisture regulator due to its natural origin and food-safe status. As consumer demand for clean label products continues to rise, glycerol's market potential in this sector is expected to grow substantially.
Agricultural biotechnology companies are investing in research and development to create innovative glycerol-based formulations for moisture regulation. This trend is driven by the increasing need for sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions in agriculture.
The market demand is further bolstered by the growing awareness of food waste reduction. Glycerol's role in extending the shelf life of agricultural products aligns with global initiatives to minimize food loss, creating additional market opportunities.
Geographically, the demand for glycerol in moisture regulation is particularly strong in regions with challenging climatic conditions or limited cold chain infrastructure. Developing countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America are expected to be key growth markets as they seek to improve their agricultural storage and transportation capabilities.
In the fruit and vegetable industry, glycerol-based coatings have shown promising results in reducing water loss and maintaining freshness. This application has led to a growing demand from producers and distributors seeking to extend the marketability of their produce. The global fresh fruit and vegetable market, valued at over $1 trillion, presents a substantial opportunity for glycerol-based solutions.
The grain storage sector has also recognized the potential of glycerol in moisture regulation. With annual global grain production exceeding 2 billion metric tons, the need for effective moisture control is paramount. Glycerol's hygroscopic properties make it an attractive option for maintaining optimal moisture levels in stored grains, reducing spoilage and economic losses.
In the meat and poultry industry, glycerol has found applications in packaging and processing to regulate moisture content and improve product quality. The global meat market, valued at hundreds of billions of dollars, represents another significant avenue for glycerol-based moisture regulation technologies.
The organic and natural food segment has shown particular interest in glycerol as a moisture regulator due to its natural origin and food-safe status. As consumer demand for clean label products continues to rise, glycerol's market potential in this sector is expected to grow substantially.
Agricultural biotechnology companies are investing in research and development to create innovative glycerol-based formulations for moisture regulation. This trend is driven by the increasing need for sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions in agriculture.
The market demand is further bolstered by the growing awareness of food waste reduction. Glycerol's role in extending the shelf life of agricultural products aligns with global initiatives to minimize food loss, creating additional market opportunities.
Geographically, the demand for glycerol in moisture regulation is particularly strong in regions with challenging climatic conditions or limited cold chain infrastructure. Developing countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America are expected to be key growth markets as they seek to improve their agricultural storage and transportation capabilities.
Current Challenges
The current challenges in utilizing glycerol for moisture regulation of agricultural products are multifaceted and complex. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardized application methods across diverse agricultural commodities. Different fruits, vegetables, and grains require varying levels of moisture retention, and developing a one-size-fits-all approach with glycerol has proven difficult.
Another significant challenge lies in the potential for over-application of glycerol, which can lead to undesirable effects on product quality. Excessive moisture retention may result in accelerated microbial growth, compromising food safety and shelf life. Striking the right balance between moisture preservation and product integrity remains a delicate task for researchers and industry professionals.
The cost-effectiveness of glycerol application on a large scale is also a concern. While glycerol is a byproduct of biodiesel production and relatively abundant, the logistics and equipment required for uniform application across vast agricultural operations can be prohibitively expensive for some producers. This economic barrier hinders widespread adoption, particularly among smaller farms and in developing regions.
Environmental considerations pose additional challenges. The long-term effects of glycerol application on soil health and local ecosystems are not yet fully understood. There are concerns about potential soil saturation and its impact on microbial communities, as well as the possibility of glycerol runoff affecting nearby water sources.
From a regulatory standpoint, the use of glycerol as a moisture regulator in agricultural products faces scrutiny. Different countries have varying regulations regarding food additives and post-harvest treatments. Navigating these regulatory landscapes and obtaining necessary approvals for glycerol use across international markets presents a significant hurdle for global trade in treated agricultural products.
Technical challenges also persist in the formulation of glycerol-based solutions. Achieving consistent viscosity and ensuring even distribution of glycerol on product surfaces remain areas of ongoing research. Additionally, the interaction between glycerol and other post-harvest treatments or packaging materials needs further investigation to prevent unforeseen chemical reactions or degradation of product quality.
Lastly, consumer perception and acceptance of glycerol-treated agricultural products represent a critical challenge. As consumers increasingly demand "natural" and minimally processed foods, the use of glycerol, despite its natural origins, may face resistance in certain markets. Educating consumers about the benefits and safety of glycerol application while addressing concerns about food authenticity is crucial for widespread acceptance of this moisture regulation technology.
Another significant challenge lies in the potential for over-application of glycerol, which can lead to undesirable effects on product quality. Excessive moisture retention may result in accelerated microbial growth, compromising food safety and shelf life. Striking the right balance between moisture preservation and product integrity remains a delicate task for researchers and industry professionals.
The cost-effectiveness of glycerol application on a large scale is also a concern. While glycerol is a byproduct of biodiesel production and relatively abundant, the logistics and equipment required for uniform application across vast agricultural operations can be prohibitively expensive for some producers. This economic barrier hinders widespread adoption, particularly among smaller farms and in developing regions.
Environmental considerations pose additional challenges. The long-term effects of glycerol application on soil health and local ecosystems are not yet fully understood. There are concerns about potential soil saturation and its impact on microbial communities, as well as the possibility of glycerol runoff affecting nearby water sources.
From a regulatory standpoint, the use of glycerol as a moisture regulator in agricultural products faces scrutiny. Different countries have varying regulations regarding food additives and post-harvest treatments. Navigating these regulatory landscapes and obtaining necessary approvals for glycerol use across international markets presents a significant hurdle for global trade in treated agricultural products.
Technical challenges also persist in the formulation of glycerol-based solutions. Achieving consistent viscosity and ensuring even distribution of glycerol on product surfaces remain areas of ongoing research. Additionally, the interaction between glycerol and other post-harvest treatments or packaging materials needs further investigation to prevent unforeseen chemical reactions or degradation of product quality.
Lastly, consumer perception and acceptance of glycerol-treated agricultural products represent a critical challenge. As consumers increasingly demand "natural" and minimally processed foods, the use of glycerol, despite its natural origins, may face resistance in certain markets. Educating consumers about the benefits and safety of glycerol application while addressing concerns about food authenticity is crucial for widespread acceptance of this moisture regulation technology.
Existing Solutions
01 Glycerol as a moisturizing agent in skincare products
Glycerol is widely used in skincare formulations as an effective moisturizing agent. It helps to attract and retain water in the skin, improving hydration and maintaining the skin's moisture barrier. This humectant property of glycerol makes it a valuable ingredient in various cosmetic and personal care products for moisture regulation.- Glycerol as a moisturizing agent in skincare products: Glycerol is widely used in skincare formulations as an effective moisturizing agent. It helps to attract and retain moisture in the skin, improving hydration and maintaining the skin's barrier function. This humectant property of glycerol makes it a valuable ingredient in various cosmetic and personal care products for moisture regulation.
- Glycerol in moisture-regulating textiles and fabrics: Glycerol is incorporated into textile and fabric treatments to enhance moisture regulation properties. It can be used in the production of moisture-wicking fabrics, helping to control humidity and improve comfort in clothing and other textile applications. This technology is particularly useful in sportswear and functional textiles.
- Glycerol-based moisture regulation in food preservation: Glycerol is utilized in food preservation techniques to regulate moisture content. It acts as a humectant in food products, helping to maintain optimal moisture levels and prevent spoilage. This application of glycerol is particularly important in extending the shelf life of various food items and maintaining their quality.
- Glycerol in pharmaceutical formulations for moisture control: In pharmaceutical applications, glycerol is used to regulate moisture in various formulations. It helps in maintaining the stability of drugs, preventing moisture-related degradation, and improving the overall efficacy of medications. Glycerol's moisture-regulating properties are particularly valuable in topical and oral pharmaceutical products.
- Glycerol-based moisture regulation in industrial processes: Glycerol finds applications in various industrial processes for moisture regulation. It is used in the production of plastics, resins, and other materials to control moisture content during manufacturing. This helps in improving product quality, preventing defects, and enhancing the overall efficiency of industrial processes that are sensitive to moisture levels.
02 Glycerol in moisture-regulating textiles and fabrics
Glycerol is incorporated into textile and fabric treatments to enhance moisture regulation properties. It can be used in the production of moisture-wicking fabrics, helping to control humidity and improve comfort in clothing and other textile applications. This technology is particularly useful in sportswear and functional textiles.Expand Specific Solutions03 Glycerol-based moisture regulation in food preservation
Glycerol is utilized in food preservation techniques to regulate moisture content. It acts as a humectant in food products, helping to maintain optimal moisture levels and prevent spoilage. This application of glycerol is particularly important in extending the shelf life of various food items and improving their texture and quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Glycerol in pharmaceutical formulations for moisture control
In pharmaceutical applications, glycerol is used to regulate moisture in various formulations. It helps in maintaining the stability of drugs, preventing moisture-related degradation, and improving the overall efficacy of medications. Glycerol's moisture-regulating properties are particularly valuable in topical and oral pharmaceutical products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Glycerol-based moisture regulation in industrial processes
Glycerol finds applications in industrial processes for moisture regulation. It is used in various manufacturing processes to control humidity levels, prevent corrosion, and maintain optimal moisture conditions. This includes applications in paper production, chemical processing, and other industrial settings where moisture control is critical.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The glycerol moisture regulation market for agricultural products is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for sustainable solutions. The market size is expanding, with potential for significant growth in coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like BASF, DuPont, and Sinopec leading research and development efforts. These industry giants are investing heavily in innovative formulations and applications, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities. Smaller players such as Genecor and Arr-Maz are also contributing specialized solutions. Academic institutions like Zhejiang University and North Carolina State University are partnering with industry to advance fundamental research, indicating a collaborative ecosystem driving technological maturity in this field.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a glycerol-based moisture regulation system for agricultural products. Their approach involves creating a hydrogel matrix incorporating glycerol, which acts as a humectant and plasticizer. This matrix can be applied as a coating or incorporated into packaging materials. The glycerol-based system helps maintain optimal moisture levels in fruits, vegetables, and grains during storage and transportation, significantly extending shelf life[1][3]. The technology utilizes glycerol's hygroscopic properties to absorb excess moisture or release moisture as needed, creating a stable microenvironment around the produce[2]. BASF's solution also includes antimicrobial agents to prevent mold growth, further enhancing product preservation[4].
Strengths: Effective moisture control, extended shelf life, versatile application methods. Weaknesses: Potential cost implications for large-scale implementation, may require additional research for specific crop types.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has innovated a glycerol-based moisture regulation technology for agricultural products, focusing on sustainable and bio-based solutions. Their approach involves creating a biodegradable film containing glycerol as a key component. This film acts as a semi-permeable membrane, allowing controlled moisture exchange between the product and its environment[1]. The glycerol in the film helps maintain optimal water activity levels, crucial for preserving freshness and nutritional value[2]. DuPont's technology also incorporates nanoparticles to enhance the film's barrier properties and mechanical strength[3]. The company has demonstrated that their glycerol-based films can reduce weight loss in fruits and vegetables by up to 40% during storage, significantly extending shelf life[4].
Strengths: Biodegradable solution, effective moisture control, enhanced mechanical properties. Weaknesses: Potential scalability challenges, may require specialized application equipment.
Core Innovations
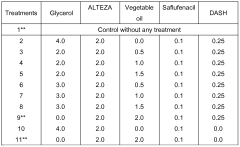
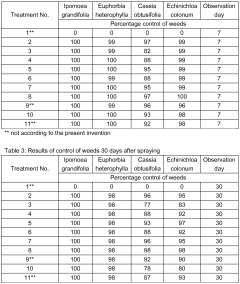
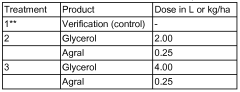
Use of glycerol, method of crop treatment, composition for tank mixing and a method of preparation of a composition for tank mixing
PatentWO2009056494A2
Innovation
- The use of raw glycerol as an adjuvant or coadjuvant in agricultural spraying solutions, combined with agrochemical compositions and optionally vegetable or mineral oil, to create a low-volume spraying system that enhances the efficacy of herbicides, fungicides, insecticides, and foliar fertilizers, reducing water consumption and optimizing treatment performance.
Use of glycerol as an agent to improve the self-dispersing properties of a mineral material to be added to an aqueous composition
PatentWO2011077232A1
Innovation
- The use of glycerol and poly-glycerols as dry grinding agents during the dry grinding of mineral materials, such as calcium carbonate, improves their self-dispersing nature in aqueous compositions by reducing initial viscosity and enhancing long-term viscosity stability while minimizing foam formation.
Environmental Impact
The use of glycerol in moisture regulation of agricultural products has significant environmental implications. Glycerol, a byproduct of biodiesel production, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional moisture-regulating agents. Its biodegradability and non-toxic nature contribute to reduced environmental pollution and waste accumulation.
When applied to agricultural products, glycerol forms a protective barrier that helps maintain optimal moisture levels. This natural moisture regulation mechanism reduces the need for synthetic preservatives and packaging materials, thereby decreasing plastic waste and chemical runoff. The extended shelf life of treated products also contributes to food waste reduction, addressing a major environmental concern in the agricultural sector.
Glycerol's hygroscopic properties allow for more efficient water management in agriculture. By retaining moisture in products, it reduces the water requirements for storage and transportation, leading to conservation of this precious resource. This is particularly beneficial in water-stressed regions, where sustainable water use is crucial for environmental preservation.
The production of glycerol from renewable sources, such as vegetable oils or animal fats, aligns with circular economy principles. It promotes the utilization of byproducts and waste streams, reducing the overall environmental footprint of agricultural and industrial processes. This approach not only minimizes waste but also decreases the demand for petroleum-based alternatives.
Furthermore, the use of glycerol in agricultural products can lead to a reduction in energy consumption. By maintaining optimal moisture levels, it helps preserve the quality and freshness of products without the need for energy-intensive cold storage or modified atmosphere packaging. This energy efficiency translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with product preservation and distribution.
The environmental benefits of glycerol extend to soil health when used in agricultural applications. Unlike some synthetic moisture regulators, glycerol does not accumulate in soil or cause long-term environmental damage. Its natural decomposition contributes to soil organic matter, potentially enhancing soil structure and microbial activity.
However, it is important to consider the potential environmental impacts of increased glycerol production. While it is a byproduct of biodiesel manufacturing, large-scale adoption in agriculture could drive demand beyond current supply levels. This may lead to increased cultivation of oil crops, potentially impacting land use and biodiversity. Careful management and sustainable sourcing practices are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure that the environmental benefits of glycerol use in moisture regulation are not outweighed by negative impacts in other areas.
When applied to agricultural products, glycerol forms a protective barrier that helps maintain optimal moisture levels. This natural moisture regulation mechanism reduces the need for synthetic preservatives and packaging materials, thereby decreasing plastic waste and chemical runoff. The extended shelf life of treated products also contributes to food waste reduction, addressing a major environmental concern in the agricultural sector.
Glycerol's hygroscopic properties allow for more efficient water management in agriculture. By retaining moisture in products, it reduces the water requirements for storage and transportation, leading to conservation of this precious resource. This is particularly beneficial in water-stressed regions, where sustainable water use is crucial for environmental preservation.
The production of glycerol from renewable sources, such as vegetable oils or animal fats, aligns with circular economy principles. It promotes the utilization of byproducts and waste streams, reducing the overall environmental footprint of agricultural and industrial processes. This approach not only minimizes waste but also decreases the demand for petroleum-based alternatives.
Furthermore, the use of glycerol in agricultural products can lead to a reduction in energy consumption. By maintaining optimal moisture levels, it helps preserve the quality and freshness of products without the need for energy-intensive cold storage or modified atmosphere packaging. This energy efficiency translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with product preservation and distribution.
The environmental benefits of glycerol extend to soil health when used in agricultural applications. Unlike some synthetic moisture regulators, glycerol does not accumulate in soil or cause long-term environmental damage. Its natural decomposition contributes to soil organic matter, potentially enhancing soil structure and microbial activity.
However, it is important to consider the potential environmental impacts of increased glycerol production. While it is a byproduct of biodiesel manufacturing, large-scale adoption in agriculture could drive demand beyond current supply levels. This may lead to increased cultivation of oil crops, potentially impacting land use and biodiversity. Careful management and sustainable sourcing practices are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure that the environmental benefits of glycerol use in moisture regulation are not outweighed by negative impacts in other areas.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding glycerol's use in moisture regulation of agricultural products is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental agencies and international bodies. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the use of glycerol in food products, including its application in moisture regulation. The FDA classifies glycerol as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food, which allows for its widespread application in the agricultural sector.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also has jurisdiction over glycerol's use in agriculture, particularly concerning its potential environmental impact. The EPA regulates the use of glycerol-based products in pest control and as a soil amendment, ensuring that its application does not adversely affect ecosystems or water resources.
Internationally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides global standards for food additives, including glycerol. These standards influence national regulations and facilitate international trade in agricultural products treated with glycerol for moisture regulation.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated glycerol's safety and efficacy in food applications, including its use in moisture regulation of agricultural products. Their assessments often inform EU-wide regulations and directives concerning glycerol's use in the food and agriculture industries.
In addition to food safety regulations, the use of glycerol in moisture regulation must comply with organic farming standards in various jurisdictions. For instance, the USDA National Organic Program provides guidelines on the use of glycerol in organic agriculture, specifying conditions under which it can be applied to organic crops.
Trade agreements and international standards, such as those set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), further influence the regulatory landscape. These agreements often include provisions on the use of food additives and processing aids, which can impact the global trade of agricultural products treated with glycerol for moisture regulation.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration, regulations are evolving to address the environmental impact of glycerol production and use. This includes guidelines on sustainable sourcing of glycerol, particularly when derived from biodiesel production, and regulations on waste management and emissions associated with its manufacture and application.
The regulatory framework also extends to labeling requirements for agricultural products treated with glycerol. Various countries have implemented regulations mandating the disclosure of glycerol use in product packaging, ensuring transparency for consumers and facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also has jurisdiction over glycerol's use in agriculture, particularly concerning its potential environmental impact. The EPA regulates the use of glycerol-based products in pest control and as a soil amendment, ensuring that its application does not adversely affect ecosystems or water resources.
Internationally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides global standards for food additives, including glycerol. These standards influence national regulations and facilitate international trade in agricultural products treated with glycerol for moisture regulation.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated glycerol's safety and efficacy in food applications, including its use in moisture regulation of agricultural products. Their assessments often inform EU-wide regulations and directives concerning glycerol's use in the food and agriculture industries.
In addition to food safety regulations, the use of glycerol in moisture regulation must comply with organic farming standards in various jurisdictions. For instance, the USDA National Organic Program provides guidelines on the use of glycerol in organic agriculture, specifying conditions under which it can be applied to organic crops.
Trade agreements and international standards, such as those set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), further influence the regulatory landscape. These agreements often include provisions on the use of food additives and processing aids, which can impact the global trade of agricultural products treated with glycerol for moisture regulation.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration, regulations are evolving to address the environmental impact of glycerol production and use. This includes guidelines on sustainable sourcing of glycerol, particularly when derived from biodiesel production, and regulations on waste management and emissions associated with its manufacture and application.
The regulatory framework also extends to labeling requirements for agricultural products treated with glycerol. Various countries have implemented regulations mandating the disclosure of glycerol use in product packaging, ensuring transparency for consumers and facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!