How Glycerol Enhances Absorption of Mineral Nutrients
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Glycerol-Nutrient Absorption Background
Glycerol, a simple polyol compound, has been increasingly recognized for its potential role in enhancing the absorption of mineral nutrients in biological systems. This phenomenon has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its implications for both plant and animal nutrition. The interaction between glycerol and mineral nutrients represents a complex interplay of chemical and biological processes that have been the subject of extensive research.
The concept of using glycerol to improve nutrient absorption stems from its unique chemical properties. As a small, highly polar molecule, glycerol can interact with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances, making it an excellent solvent and carrier for various compounds, including minerals. This characteristic has led researchers to investigate its potential as a facilitator of nutrient uptake across cellular membranes.
Historically, glycerol has been widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries due to its hygroscopic nature and ability to act as a humectant. However, its role in nutrient absorption was not fully appreciated until more recent studies began to elucidate its mechanisms of action. The discovery of aquaporins, membrane proteins that facilitate the transport of water and small solutes like glycerol across cell membranes, has provided new insights into how glycerol might influence nutrient uptake.
In the context of plant nutrition, glycerol has been found to enhance the absorption of various essential minerals, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This has significant implications for agricultural practices, potentially leading to more efficient fertilizer use and improved crop yields. In animal nutrition, glycerol's effect on mineral absorption has been studied in relation to livestock feed efficiency and human dietary supplements.
The growing interest in glycerol's role in nutrient absorption is also driven by the increasing availability of glycerol as a byproduct of biodiesel production. This abundance has prompted researchers to explore novel applications, including its use as a nutrient absorption enhancer. As a result, the intersection of renewable energy production and nutritional science has opened up new avenues for research and development in this field.
Understanding the mechanisms by which glycerol enhances mineral nutrient absorption is crucial for optimizing its application in various sectors. This includes not only agriculture and animal husbandry but also human nutrition and health. The potential for glycerol to improve the bioavailability of essential minerals could have far-reaching implications for addressing nutritional deficiencies and improving overall health outcomes globally.
The concept of using glycerol to improve nutrient absorption stems from its unique chemical properties. As a small, highly polar molecule, glycerol can interact with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances, making it an excellent solvent and carrier for various compounds, including minerals. This characteristic has led researchers to investigate its potential as a facilitator of nutrient uptake across cellular membranes.
Historically, glycerol has been widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries due to its hygroscopic nature and ability to act as a humectant. However, its role in nutrient absorption was not fully appreciated until more recent studies began to elucidate its mechanisms of action. The discovery of aquaporins, membrane proteins that facilitate the transport of water and small solutes like glycerol across cell membranes, has provided new insights into how glycerol might influence nutrient uptake.
In the context of plant nutrition, glycerol has been found to enhance the absorption of various essential minerals, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This has significant implications for agricultural practices, potentially leading to more efficient fertilizer use and improved crop yields. In animal nutrition, glycerol's effect on mineral absorption has been studied in relation to livestock feed efficiency and human dietary supplements.
The growing interest in glycerol's role in nutrient absorption is also driven by the increasing availability of glycerol as a byproduct of biodiesel production. This abundance has prompted researchers to explore novel applications, including its use as a nutrient absorption enhancer. As a result, the intersection of renewable energy production and nutritional science has opened up new avenues for research and development in this field.
Understanding the mechanisms by which glycerol enhances mineral nutrient absorption is crucial for optimizing its application in various sectors. This includes not only agriculture and animal husbandry but also human nutrition and health. The potential for glycerol to improve the bioavailability of essential minerals could have far-reaching implications for addressing nutritional deficiencies and improving overall health outcomes globally.
Market Analysis for Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
The market for enhanced nutrient absorption technologies, particularly those utilizing glycerol, has shown significant growth potential in recent years. This trend is driven by increasing consumer awareness of the importance of optimal nutrient uptake for overall health and wellness. The global market for nutrient absorption enhancers is expected to expand substantially, with glycerol-based solutions playing a crucial role in this growth.
In the agricultural sector, there is a rising demand for technologies that can improve the efficiency of mineral nutrient uptake in crops. This demand is fueled by the need to increase crop yields while minimizing the use of fertilizers, addressing both food security concerns and environmental sustainability. Glycerol-enhanced nutrient absorption solutions are positioned to capture a significant share of this market, offering farmers a cost-effective means to improve crop nutrition and productivity.
The nutraceutical and dietary supplement industry represents another key market segment for glycerol-enhanced nutrient absorption technologies. As consumers become more health-conscious and seek ways to maximize the benefits of their nutritional intake, products that can enhance the absorption of essential minerals are gaining traction. This trend is particularly evident in developed markets where consumers are willing to pay a premium for products that offer improved bioavailability of nutrients.
In the pharmaceutical industry, there is growing interest in using glycerol as an excipient to enhance the absorption of mineral-based medications. This application has the potential to improve the efficacy of various treatments, particularly those targeting mineral deficiencies or related health conditions. The market for such pharmaceutical formulations is expected to grow as research continues to demonstrate the benefits of glycerol in enhancing mineral nutrient absorption.
The sports nutrition market is another area where glycerol-enhanced nutrient absorption technologies are gaining popularity. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are increasingly looking for ways to optimize their mineral intake to support performance and recovery. Products that can improve the absorption of key minerals such as magnesium, zinc, and iron are likely to see strong demand in this segment.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for enhanced nutrient absorption technologies, including those based on glycerol. However, rapid growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific markets, particularly in countries like China and India, where there is increasing awareness of nutritional health and a growing middle class willing to invest in advanced nutritional products.
Overall, the market for glycerol-enhanced mineral nutrient absorption technologies shows promising growth prospects across multiple sectors. As research continues to validate the efficacy of these solutions, and as consumer awareness grows, the demand for products leveraging this technology is expected to increase significantly in the coming years.
In the agricultural sector, there is a rising demand for technologies that can improve the efficiency of mineral nutrient uptake in crops. This demand is fueled by the need to increase crop yields while minimizing the use of fertilizers, addressing both food security concerns and environmental sustainability. Glycerol-enhanced nutrient absorption solutions are positioned to capture a significant share of this market, offering farmers a cost-effective means to improve crop nutrition and productivity.
The nutraceutical and dietary supplement industry represents another key market segment for glycerol-enhanced nutrient absorption technologies. As consumers become more health-conscious and seek ways to maximize the benefits of their nutritional intake, products that can enhance the absorption of essential minerals are gaining traction. This trend is particularly evident in developed markets where consumers are willing to pay a premium for products that offer improved bioavailability of nutrients.
In the pharmaceutical industry, there is growing interest in using glycerol as an excipient to enhance the absorption of mineral-based medications. This application has the potential to improve the efficacy of various treatments, particularly those targeting mineral deficiencies or related health conditions. The market for such pharmaceutical formulations is expected to grow as research continues to demonstrate the benefits of glycerol in enhancing mineral nutrient absorption.
The sports nutrition market is another area where glycerol-enhanced nutrient absorption technologies are gaining popularity. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are increasingly looking for ways to optimize their mineral intake to support performance and recovery. Products that can improve the absorption of key minerals such as magnesium, zinc, and iron are likely to see strong demand in this segment.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for enhanced nutrient absorption technologies, including those based on glycerol. However, rapid growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific markets, particularly in countries like China and India, where there is increasing awareness of nutritional health and a growing middle class willing to invest in advanced nutritional products.
Overall, the market for glycerol-enhanced mineral nutrient absorption technologies shows promising growth prospects across multiple sectors. As research continues to validate the efficacy of these solutions, and as consumer awareness grows, the demand for products leveraging this technology is expected to increase significantly in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Mineral Nutrient Uptake
Despite significant advancements in agricultural practices, mineral nutrient uptake by plants remains a critical challenge in modern agriculture. One of the primary obstacles is the complex interaction between soil properties and nutrient availability. Soil pH, for instance, plays a crucial role in determining the solubility and accessibility of various minerals. Acidic soils can lead to increased aluminum and manganese toxicity, while alkaline soils may result in reduced availability of iron, zinc, and phosphorus.
Another major challenge is the competition between beneficial nutrients and potentially harmful elements in the soil. For example, the presence of high levels of phosphorus can inhibit the uptake of zinc and iron, leading to deficiencies in these essential micronutrients. Similarly, excessive calcium in the soil can interfere with the absorption of magnesium and potassium, creating imbalances in plant nutrition.
The efficiency of nutrient uptake is further complicated by environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, and aeration. Drought conditions can significantly reduce nutrient mobility in the soil, limiting their availability to plant roots. Conversely, waterlogged soils can lead to anaerobic conditions, affecting root respiration and nutrient absorption processes.
Plant-specific factors also contribute to the challenges in mineral nutrient uptake. Different crop varieties have varying abilities to access and utilize nutrients from the soil. Some plants have developed specialized mechanisms to enhance nutrient acquisition, such as the release of organic acids or the formation of symbiotic relationships with mycorrhizal fungi. However, these adaptations are not universal across all crop species, leading to disparities in nutrient use efficiency.
The increasing trend towards intensive agriculture and monoculture practices has led to soil degradation and depletion of essential nutrients. This has created a dependency on synthetic fertilizers, which, while effective in the short term, can lead to long-term issues such as soil acidification, reduced microbial activity, and environmental pollution through nutrient runoff.
Furthermore, the bioavailability of nutrients is often compromised by various soil and plant factors. For instance, the presence of antinutritional compounds like phytates can bind to minerals, making them unavailable for plant uptake. Additionally, the form in which nutrients are present in the soil (e.g., organic vs. inorganic) can significantly affect their accessibility to plants.
In the context of using glycerol to enhance mineral nutrient absorption, researchers face the challenge of understanding the complex interactions between glycerol, soil components, and plant physiology. While glycerol shows promise in improving nutrient uptake, its effectiveness can vary depending on soil type, plant species, and environmental conditions. Developing a comprehensive understanding of these interactions is crucial for optimizing the use of glycerol as a nutrient uptake enhancer.
Another major challenge is the competition between beneficial nutrients and potentially harmful elements in the soil. For example, the presence of high levels of phosphorus can inhibit the uptake of zinc and iron, leading to deficiencies in these essential micronutrients. Similarly, excessive calcium in the soil can interfere with the absorption of magnesium and potassium, creating imbalances in plant nutrition.
The efficiency of nutrient uptake is further complicated by environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, and aeration. Drought conditions can significantly reduce nutrient mobility in the soil, limiting their availability to plant roots. Conversely, waterlogged soils can lead to anaerobic conditions, affecting root respiration and nutrient absorption processes.
Plant-specific factors also contribute to the challenges in mineral nutrient uptake. Different crop varieties have varying abilities to access and utilize nutrients from the soil. Some plants have developed specialized mechanisms to enhance nutrient acquisition, such as the release of organic acids or the formation of symbiotic relationships with mycorrhizal fungi. However, these adaptations are not universal across all crop species, leading to disparities in nutrient use efficiency.
The increasing trend towards intensive agriculture and monoculture practices has led to soil degradation and depletion of essential nutrients. This has created a dependency on synthetic fertilizers, which, while effective in the short term, can lead to long-term issues such as soil acidification, reduced microbial activity, and environmental pollution through nutrient runoff.
Furthermore, the bioavailability of nutrients is often compromised by various soil and plant factors. For instance, the presence of antinutritional compounds like phytates can bind to minerals, making them unavailable for plant uptake. Additionally, the form in which nutrients are present in the soil (e.g., organic vs. inorganic) can significantly affect their accessibility to plants.
In the context of using glycerol to enhance mineral nutrient absorption, researchers face the challenge of understanding the complex interactions between glycerol, soil components, and plant physiology. While glycerol shows promise in improving nutrient uptake, its effectiveness can vary depending on soil type, plant species, and environmental conditions. Developing a comprehensive understanding of these interactions is crucial for optimizing the use of glycerol as a nutrient uptake enhancer.
Existing Glycerol-Based Absorption Solutions
01 Glycerol absorption in plants
Plants can absorb glycerol through their roots and leaves. This process is influenced by various factors such as plant species, environmental conditions, and the concentration of glycerol. The absorbed glycerol can be utilized by plants for various metabolic processes, potentially enhancing growth and stress tolerance.- Glycerol absorption in plants: Plants can absorb glycerol through their roots and leaves. This process is influenced by various factors such as plant species, environmental conditions, and the concentration of glycerol. The absorbed glycerol can be utilized by plants for various metabolic processes or as an energy source.
- Glycerol absorption in industrial processes: Industrial processes utilize glycerol absorption for various applications, including purification, separation, and recovery of glycerol from mixtures. These processes often involve the use of specialized equipment and techniques to enhance the efficiency of glycerol absorption.
- Glycerol absorption in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations: Glycerol is widely used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations due to its ability to be absorbed by the skin and mucous membranes. The absorption of glycerol in these applications can be enhanced through various formulation techniques and the use of specific delivery systems.
- Glycerol absorption in food and beverage products: The absorption of glycerol in food and beverage products is an important consideration for manufacturers. Factors such as the composition of the product, processing methods, and storage conditions can affect the absorption and retention of glycerol in these products.
- Glycerol absorption in biological systems: Biological systems, including microorganisms and animal tissues, have various mechanisms for glycerol absorption. These mechanisms can be influenced by factors such as membrane permeability, enzymatic activity, and the presence of specific transport proteins. Understanding glycerol absorption in biological systems is crucial for applications in biotechnology and medicine.
02 Glycerol absorption in industrial processes
Industrial applications utilize glycerol absorption for various purposes, including purification, separation, and recovery processes. This can involve the use of specialized materials or equipment designed to efficiently absorb glycerol from mixtures or solutions, improving process efficiency and product quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Glycerol absorption in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics
In pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations, glycerol absorption plays a crucial role in product efficacy. The rate and extent of glycerol absorption through the skin or mucous membranes can be optimized through various formulation techniques and delivery systems, enhancing the moisturizing and therapeutic effects of the products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Glycerol absorption in food and beverage applications
The absorption of glycerol in food and beverage products is important for texture, flavor, and preservation. Various techniques can be employed to control glycerol absorption in food matrices, affecting product characteristics such as moisture retention, sweetness, and shelf life.Expand Specific Solutions05 Glycerol absorption in biofuel production
In biofuel production processes, particularly biodiesel manufacturing, glycerol absorption is a critical step for purification and byproduct recovery. Efficient glycerol absorption techniques can improve the overall process economics and sustainability of biofuel production by maximizing glycerol recovery and utilization.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Nutrient Enhancement Industry
The market for glycerol-enhanced mineral nutrient absorption is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for improved agricultural productivity and plant nutrition. The global market size is expanding, with potential applications in both agriculture and food industries. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like Jiangnan University, Fuji Oil Co., Ltd., and BioGaia AB are at the forefront of research and development, while established firms such as Cargill, Inc. and Ajinomoto Co., Inc. are leveraging their resources to explore commercial applications. Academic institutions like Tianjin University and Huazhong Agricultural University are contributing significant research, indicating a collaborative ecosystem between industry and academia in this emerging field.
Jiangnan University
Technical Solution: Researchers at Jiangnan University have developed a novel glycerol-based nanocarrier system for enhancing mineral nutrient absorption. Their approach involves encapsulating mineral ions within glycerol-based nanoparticles, which are designed to improve stability and bioavailability. The nanocarriers are engineered with surface modifications that facilitate targeted delivery to intestinal cells, enhancing uptake efficiency. Studies have shown that this nanotechnology-based approach can increase the absorption of iron and zinc by up to 60% compared to conventional mineral supplements[7]. The university's research team has also explored the use of glycerol-based hydrogels as a delivery matrix for sustained release of minerals, demonstrating prolonged absorption over a 24-hour period[8]. This technology shows promise for addressing mineral deficiencies in both human and animal nutrition.
Strengths: Highly efficient mineral delivery, potential for targeted and sustained release, applicable to various minerals. Weaknesses: May face regulatory challenges due to use of nanotechnology, potential scalability issues for large-scale production.
Cargill, Inc.
Technical Solution: Cargill has developed a glycerol-based mineral nutrient absorption enhancer that utilizes a proprietary blend of glycerol and specific mineral chelates. This formulation creates a synergistic effect, improving the solubility and bioavailability of essential minerals such as iron, zinc, and calcium. The company's research has shown that their glycerol-enhanced mineral complexes can increase absorption rates by up to 30% compared to standard mineral supplements[1]. Cargill's technology also incorporates a pH-responsive delivery system, allowing for targeted release of minerals in the small intestine where absorption is most efficient[3]. This approach not only enhances mineral uptake but also reduces potential gastrointestinal side effects associated with high-dose mineral supplementation.
Strengths: Improved mineral bioavailability, reduced side effects, and versatile application in various food and supplement products. Weaknesses: May require specialized manufacturing processes and could potentially increase production costs.
Core Mechanisms of Glycerol-Enhanced Absorption
Method for protecting active principles using glycerol
PatentInactiveEP2358215A1
Innovation
- A process using glycerol and its derivatives, specifically glycerol monolaurate, for chelation and emulsification, followed by adsorption onto amorphous silica, offering multi-level protection through chelation, miscellar solutions, and physical/chemical adsorption, resulting in a stable dry organosilicon powder with reduced energy consumption and environmental impact.
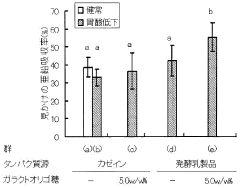
Mineral absorption improver, and method for improving absorption of minerals
PatentWO2010061877A1
Innovation
- A mineral absorption improver containing oligosaccharides, specifically galacto-oligosaccharides, and fermented milk products, which are combined to enhance zinc absorption at lower doses, minimizing interference with other minerals and reducing gastrointestinal side effects.
Environmental Impact of Glycerol Use
The use of glycerol as a nutrient absorption enhancer has potential environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. Glycerol, a byproduct of biodiesel production, is generally considered environmentally friendly due to its biodegradability and low toxicity. However, its increased use in agricultural practices may lead to unintended consequences.
One primary concern is the potential for soil and water contamination. While glycerol is biodegradable, excessive application could lead to temporary changes in soil composition and microbial communities. This may affect soil fertility and structure in the short term, potentially impacting local ecosystems. Additionally, runoff from glycerol-treated fields could enter water systems, potentially altering aquatic environments and affecting water quality.
The production and transportation of glycerol for agricultural use also contribute to its environmental footprint. Although glycerol is often a byproduct, increased demand may lead to purposeful production, consuming energy and resources. The transportation of glycerol to agricultural sites further adds to carbon emissions, albeit on a relatively small scale compared to other agricultural inputs.
On the positive side, the use of glycerol in enhancing mineral nutrient absorption could lead to more efficient use of fertilizers. This efficiency could result in reduced fertilizer application, potentially decreasing the environmental impact associated with excessive fertilizer use, such as eutrophication of water bodies and greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogen-based fertilizers.
The impact on biodiversity is another aspect to consider. Changes in soil composition due to glycerol application may affect soil microorganisms and, by extension, the broader ecosystem. However, if glycerol use leads to reduced chemical fertilizer application, it could have a net positive effect on local biodiversity by reducing chemical pollution.
From a sustainability perspective, the use of glycerol aligns with circular economy principles, as it repurposes a byproduct of biodiesel production. This could contribute to waste reduction and resource efficiency in the broader agricultural and energy sectors.
Long-term studies are needed to fully understand the environmental implications of widespread glycerol use in agriculture. These should focus on soil health, water quality, biodiversity impacts, and the overall carbon footprint of glycerol-enhanced nutrient absorption practices. Such research will be crucial in developing guidelines for sustainable glycerol use in agriculture, ensuring that the benefits of enhanced nutrient absorption are balanced against potential environmental risks.
One primary concern is the potential for soil and water contamination. While glycerol is biodegradable, excessive application could lead to temporary changes in soil composition and microbial communities. This may affect soil fertility and structure in the short term, potentially impacting local ecosystems. Additionally, runoff from glycerol-treated fields could enter water systems, potentially altering aquatic environments and affecting water quality.
The production and transportation of glycerol for agricultural use also contribute to its environmental footprint. Although glycerol is often a byproduct, increased demand may lead to purposeful production, consuming energy and resources. The transportation of glycerol to agricultural sites further adds to carbon emissions, albeit on a relatively small scale compared to other agricultural inputs.
On the positive side, the use of glycerol in enhancing mineral nutrient absorption could lead to more efficient use of fertilizers. This efficiency could result in reduced fertilizer application, potentially decreasing the environmental impact associated with excessive fertilizer use, such as eutrophication of water bodies and greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogen-based fertilizers.
The impact on biodiversity is another aspect to consider. Changes in soil composition due to glycerol application may affect soil microorganisms and, by extension, the broader ecosystem. However, if glycerol use leads to reduced chemical fertilizer application, it could have a net positive effect on local biodiversity by reducing chemical pollution.
From a sustainability perspective, the use of glycerol aligns with circular economy principles, as it repurposes a byproduct of biodiesel production. This could contribute to waste reduction and resource efficiency in the broader agricultural and energy sectors.
Long-term studies are needed to fully understand the environmental implications of widespread glycerol use in agriculture. These should focus on soil health, water quality, biodiversity impacts, and the overall carbon footprint of glycerol-enhanced nutrient absorption practices. Such research will be crucial in developing guidelines for sustainable glycerol use in agriculture, ensuring that the benefits of enhanced nutrient absorption are balanced against potential environmental risks.
Regulatory Framework for Nutrient Enhancers
The regulatory framework for nutrient enhancers, such as glycerol, plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of these substances in agricultural and food production. In the context of glycerol's potential to enhance mineral nutrient absorption, regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines and standards to govern its use.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies glycerol as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food and feed applications. This designation allows for its use as a nutrient enhancer, provided it adheres to good manufacturing practices and labeling requirements. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated glycerol and deemed it safe for use in food and feed, setting specific guidelines for its application in various products.
Regulatory agencies typically require manufacturers to provide scientific evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of glycerol as a nutrient enhancer. This includes data on its mechanism of action, potential interactions with other substances, and any possible adverse effects. The World Health Organization (WHO) and Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) have jointly established international standards for the use of glycerol in food and agriculture, which many countries use as a reference for their national regulations.
In the agricultural sector, the use of glycerol as a nutrient enhancer is subject to regulations governing fertilizers and soil amendments. These regulations often require registration of the product, along with detailed information on its composition, intended use, and environmental impact. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, for instance, oversees the registration of such products to ensure they do not pose unacceptable risks to human health or the environment.
Labeling requirements for products containing glycerol as a nutrient enhancer vary by jurisdiction but generally include information on its concentration, intended use, and any necessary precautions. In some regions, specific claims regarding enhanced nutrient absorption must be substantiated through scientific studies and approved by regulatory authorities before they can be used in marketing materials.
As research continues to elucidate the mechanisms by which glycerol enhances mineral nutrient absorption, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Ongoing scientific studies may lead to more specific guidelines for its use in different agricultural and food applications. Regulatory bodies will need to stay abreast of these developments to ensure that their frameworks remain relevant and effective in protecting public health while allowing for innovation in nutrient enhancement technologies.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies glycerol as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food and feed applications. This designation allows for its use as a nutrient enhancer, provided it adheres to good manufacturing practices and labeling requirements. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated glycerol and deemed it safe for use in food and feed, setting specific guidelines for its application in various products.
Regulatory agencies typically require manufacturers to provide scientific evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of glycerol as a nutrient enhancer. This includes data on its mechanism of action, potential interactions with other substances, and any possible adverse effects. The World Health Organization (WHO) and Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) have jointly established international standards for the use of glycerol in food and agriculture, which many countries use as a reference for their national regulations.
In the agricultural sector, the use of glycerol as a nutrient enhancer is subject to regulations governing fertilizers and soil amendments. These regulations often require registration of the product, along with detailed information on its composition, intended use, and environmental impact. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, for instance, oversees the registration of such products to ensure they do not pose unacceptable risks to human health or the environment.
Labeling requirements for products containing glycerol as a nutrient enhancer vary by jurisdiction but generally include information on its concentration, intended use, and any necessary precautions. In some regions, specific claims regarding enhanced nutrient absorption must be substantiated through scientific studies and approved by regulatory authorities before they can be used in marketing materials.
As research continues to elucidate the mechanisms by which glycerol enhances mineral nutrient absorption, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Ongoing scientific studies may lead to more specific guidelines for its use in different agricultural and food applications. Regulatory bodies will need to stay abreast of these developments to ensure that their frameworks remain relevant and effective in protecting public health while allowing for innovation in nutrient enhancement technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!