Glycerol in Formulating Enhanced Nutraceutical Products
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Glycerol in Nutraceuticals: Background and Objectives
Glycerol, also known as glycerin or glycerine, has been a subject of increasing interest in the nutraceutical industry due to its versatile properties and potential health benefits. This research aims to explore the innovative applications of glycerol in formulating enhanced nutraceutical products, with a focus on improving efficacy, bioavailability, and consumer appeal.
The use of glycerol in nutraceuticals has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially employed primarily as a sweetener and humectant, glycerol's role has expanded to include functions such as solvent, preservative, and bioenhancer. This evolution reflects the growing understanding of glycerol's physiological effects and its potential to enhance the delivery and absorption of active ingredients in nutraceutical formulations.
Recent advancements in glycerol research have revealed its potential as a prebiotic, supporting gut health and microbiome balance. Additionally, glycerol's ability to improve the solubility and stability of various bioactive compounds has opened new avenues for developing more effective and longer-lasting nutraceutical products.
The global nutraceutical market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of preventive healthcare and the desire for natural, functional food ingredients. This trend has created a demand for innovative formulations that can deliver enhanced nutritional benefits while maintaining product stability and palatability.
In this context, the objectives of this research are multifaceted. Firstly, it aims to comprehensively review the current applications of glycerol in nutraceutical formulations, identifying successful case studies and areas of untapped potential. Secondly, the research seeks to explore novel techniques for incorporating glycerol into nutraceutical products to enhance their efficacy, bioavailability, and sensory properties.
Furthermore, this study will investigate the potential synergies between glycerol and other bioactive compounds commonly used in nutraceuticals, with the goal of developing innovative formulations that offer superior health benefits. The research will also address the challenges associated with glycerol use in nutraceuticals, such as regulatory considerations, stability issues, and consumer acceptance.
By focusing on these objectives, this research aims to contribute to the advancement of nutraceutical science and technology, potentially leading to the development of next-generation products that can more effectively meet consumer needs and address various health concerns. The findings from this study are expected to provide valuable insights for nutraceutical manufacturers, researchers, and healthcare professionals, ultimately contributing to the improvement of public health through enhanced nutritional interventions.
The use of glycerol in nutraceuticals has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially employed primarily as a sweetener and humectant, glycerol's role has expanded to include functions such as solvent, preservative, and bioenhancer. This evolution reflects the growing understanding of glycerol's physiological effects and its potential to enhance the delivery and absorption of active ingredients in nutraceutical formulations.
Recent advancements in glycerol research have revealed its potential as a prebiotic, supporting gut health and microbiome balance. Additionally, glycerol's ability to improve the solubility and stability of various bioactive compounds has opened new avenues for developing more effective and longer-lasting nutraceutical products.
The global nutraceutical market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of preventive healthcare and the desire for natural, functional food ingredients. This trend has created a demand for innovative formulations that can deliver enhanced nutritional benefits while maintaining product stability and palatability.
In this context, the objectives of this research are multifaceted. Firstly, it aims to comprehensively review the current applications of glycerol in nutraceutical formulations, identifying successful case studies and areas of untapped potential. Secondly, the research seeks to explore novel techniques for incorporating glycerol into nutraceutical products to enhance their efficacy, bioavailability, and sensory properties.
Furthermore, this study will investigate the potential synergies between glycerol and other bioactive compounds commonly used in nutraceuticals, with the goal of developing innovative formulations that offer superior health benefits. The research will also address the challenges associated with glycerol use in nutraceuticals, such as regulatory considerations, stability issues, and consumer acceptance.
By focusing on these objectives, this research aims to contribute to the advancement of nutraceutical science and technology, potentially leading to the development of next-generation products that can more effectively meet consumer needs and address various health concerns. The findings from this study are expected to provide valuable insights for nutraceutical manufacturers, researchers, and healthcare professionals, ultimately contributing to the improvement of public health through enhanced nutritional interventions.
Market Analysis for Glycerol-Enhanced Nutraceuticals
The global nutraceutical market has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health and wellness, aging populations, and a shift towards preventive healthcare. Within this expanding sector, glycerol-enhanced nutraceuticals represent a promising niche with substantial market potential.
Glycerol, also known as glycerin, has gained attention in the nutraceutical industry due to its versatile properties and potential health benefits. As a natural humectant and sweetener, glycerol can enhance the texture, stability, and palatability of various nutraceutical products. Its ability to improve moisture retention and extend shelf life makes it particularly attractive for formulating supplements, functional foods, and beverages.
The market demand for glycerol-enhanced nutraceuticals is expected to grow steadily over the coming years. This growth is fueled by several factors, including the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, increasing consumer interest in natural and clean-label products, and the growing popularity of sports nutrition and weight management supplements.
In the functional food and beverage segment, glycerol-enhanced products are gaining traction due to their potential to improve texture and mouthfeel without adding excessive calories. This aligns well with the current consumer trends towards reduced sugar consumption and healthier snacking options. The sports nutrition market, in particular, shows strong potential for glycerol-enhanced products, as glycerol's hydrating properties can benefit athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
The pharmaceutical and dietary supplement sectors also present significant opportunities for glycerol-enhanced nutraceuticals. Glycerol's ability to act as a carrier for active ingredients and its potential to enhance bioavailability make it an attractive component in various supplement formulations. Additionally, its use in soft gel capsules and liquid supplements continues to drive demand in these segments.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for glycerol-enhanced nutraceuticals, owing to their well-established nutraceutical industries and health-conscious consumer bases. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by increasing disposable incomes, changing dietary habits, and a growing awareness of preventive healthcare.
Despite the positive outlook, the market for glycerol-enhanced nutraceuticals faces certain challenges. These include regulatory hurdles in some regions, competition from alternative ingredients, and the need for extensive research to substantiate health claims. Nonetheless, ongoing research and development efforts are likely to unlock new applications and expand the market potential for glycerol in nutraceutical formulations.
Glycerol, also known as glycerin, has gained attention in the nutraceutical industry due to its versatile properties and potential health benefits. As a natural humectant and sweetener, glycerol can enhance the texture, stability, and palatability of various nutraceutical products. Its ability to improve moisture retention and extend shelf life makes it particularly attractive for formulating supplements, functional foods, and beverages.
The market demand for glycerol-enhanced nutraceuticals is expected to grow steadily over the coming years. This growth is fueled by several factors, including the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, increasing consumer interest in natural and clean-label products, and the growing popularity of sports nutrition and weight management supplements.
In the functional food and beverage segment, glycerol-enhanced products are gaining traction due to their potential to improve texture and mouthfeel without adding excessive calories. This aligns well with the current consumer trends towards reduced sugar consumption and healthier snacking options. The sports nutrition market, in particular, shows strong potential for glycerol-enhanced products, as glycerol's hydrating properties can benefit athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
The pharmaceutical and dietary supplement sectors also present significant opportunities for glycerol-enhanced nutraceuticals. Glycerol's ability to act as a carrier for active ingredients and its potential to enhance bioavailability make it an attractive component in various supplement formulations. Additionally, its use in soft gel capsules and liquid supplements continues to drive demand in these segments.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for glycerol-enhanced nutraceuticals, owing to their well-established nutraceutical industries and health-conscious consumer bases. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by increasing disposable incomes, changing dietary habits, and a growing awareness of preventive healthcare.
Despite the positive outlook, the market for glycerol-enhanced nutraceuticals faces certain challenges. These include regulatory hurdles in some regions, competition from alternative ingredients, and the need for extensive research to substantiate health claims. Nonetheless, ongoing research and development efforts are likely to unlock new applications and expand the market potential for glycerol in nutraceutical formulations.
Current Challenges in Glycerol-Based Formulations
Despite the promising potential of glycerol in nutraceutical formulations, several challenges persist in its effective utilization. One of the primary obstacles is the hygroscopic nature of glycerol, which can lead to moisture absorption in the final product. This property, while beneficial in some applications, can cause stability issues in certain formulations, particularly those intended for long-term storage or in humid environments.
Another significant challenge lies in the organoleptic properties of glycerol. Its inherent sweetness and viscosity can alter the taste and texture of nutraceutical products, potentially affecting consumer acceptance. Balancing these sensory attributes while maintaining the desired therapeutic effects requires careful formulation and often necessitates the use of additional excipients or flavor masking agents.
The high viscosity of glycerol also presents difficulties in processing and manufacturing. It can complicate mixing procedures, affect flow properties during production, and impact the overall consistency of the final product. This challenge is particularly pronounced in the development of liquid or semi-solid nutraceutical formulations.
Compatibility issues with certain active ingredients pose another hurdle. While glycerol is generally considered inert, it can interact with some nutraceutical compounds, potentially affecting their stability or bioavailability. This necessitates extensive compatibility studies and careful selection of complementary ingredients in formulation development.
The regulatory landscape surrounding glycerol use in nutraceuticals adds another layer of complexity. Although generally recognized as safe (GRAS), the acceptable levels and specific applications of glycerol can vary across different regulatory jurisdictions, requiring manufacturers to navigate a complex web of guidelines and restrictions.
From a formulation perspective, achieving the right balance between glycerol concentration and its functional benefits remains challenging. Higher concentrations may enhance certain properties but can also exacerbate issues related to hygroscopicity and organoleptic changes. Conversely, lower concentrations might not provide the desired functional benefits, necessitating a delicate balance in formulation design.
Lastly, the sourcing and quality control of glycerol present ongoing challenges. Ensuring consistent purity and quality across batches is crucial for maintaining product efficacy and safety. This is particularly important given the various sources of glycerol, including synthetic and natural origins, each with its own potential impurities and quality variations.
Another significant challenge lies in the organoleptic properties of glycerol. Its inherent sweetness and viscosity can alter the taste and texture of nutraceutical products, potentially affecting consumer acceptance. Balancing these sensory attributes while maintaining the desired therapeutic effects requires careful formulation and often necessitates the use of additional excipients or flavor masking agents.
The high viscosity of glycerol also presents difficulties in processing and manufacturing. It can complicate mixing procedures, affect flow properties during production, and impact the overall consistency of the final product. This challenge is particularly pronounced in the development of liquid or semi-solid nutraceutical formulations.
Compatibility issues with certain active ingredients pose another hurdle. While glycerol is generally considered inert, it can interact with some nutraceutical compounds, potentially affecting their stability or bioavailability. This necessitates extensive compatibility studies and careful selection of complementary ingredients in formulation development.
The regulatory landscape surrounding glycerol use in nutraceuticals adds another layer of complexity. Although generally recognized as safe (GRAS), the acceptable levels and specific applications of glycerol can vary across different regulatory jurisdictions, requiring manufacturers to navigate a complex web of guidelines and restrictions.
From a formulation perspective, achieving the right balance between glycerol concentration and its functional benefits remains challenging. Higher concentrations may enhance certain properties but can also exacerbate issues related to hygroscopicity and organoleptic changes. Conversely, lower concentrations might not provide the desired functional benefits, necessitating a delicate balance in formulation design.
Lastly, the sourcing and quality control of glycerol present ongoing challenges. Ensuring consistent purity and quality across batches is crucial for maintaining product efficacy and safety. This is particularly important given the various sources of glycerol, including synthetic and natural origins, each with its own potential impurities and quality variations.
Existing Glycerol Formulation Techniques
01 Production of glycerol from renewable resources
Methods for producing glycerol from renewable resources, such as biomass or plant-based materials, have been developed. These processes often involve fermentation or chemical conversion of organic compounds to yield glycerol as a valuable product or byproduct.- Production of glycerol from renewable resources: Methods for producing glycerol from renewable resources, such as biomass or plant-based materials, have been developed. These processes often involve fermentation or chemical conversion of organic matter to yield glycerol as a valuable product or byproduct.
- Purification and refining of glycerol: Various techniques have been invented for purifying and refining crude glycerol, particularly from biodiesel production. These methods may include distillation, ion exchange, membrane filtration, or other separation processes to obtain high-purity glycerol suitable for industrial applications.
- Use of glycerol in polymer production: Glycerol has been utilized as a raw material or additive in the production of various polymers and plastics. It can serve as a plasticizer, crosslinking agent, or monomer in polymerization reactions, contributing to the development of bio-based and biodegradable materials.
- Glycerol as a platform chemical for value-added products: Research has focused on converting glycerol into higher-value chemicals through catalytic processes, oxidation, or microbial fermentation. This approach aims to produce specialty chemicals, fuel additives, or pharmaceutical intermediates from glycerol, enhancing its economic value.
- Applications of glycerol in fuel and energy production: Glycerol has been explored for use in fuel and energy production, including as a feedstock for biodiesel, a component in fuel cells, or as a precursor for hydrogen production. These applications aim to utilize glycerol as a renewable energy source or to improve the efficiency of existing energy systems.
02 Purification and refining of glycerol
Various techniques have been invented for purifying and refining crude glycerol to obtain high-quality glycerol suitable for industrial applications. These methods may include distillation, ion exchange, membrane filtration, or other separation processes to remove impurities and increase glycerol concentration.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of glycerol in biodiesel production
Glycerol is a significant byproduct of biodiesel production. Innovations have been made to utilize this glycerol effectively, either by converting it into value-added products or incorporating it back into the biodiesel production process to improve efficiency and reduce waste.Expand Specific Solutions04 Glycerol as a platform chemical
Research has focused on using glycerol as a platform chemical for the synthesis of various valuable compounds. This includes the development of catalytic processes to convert glycerol into other chemicals such as propylene glycol, acrolein, or other specialty chemicals with industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications of glycerol in pharmaceuticals and personal care
Glycerol has found extensive use in pharmaceutical and personal care products due to its moisturizing and stabilizing properties. Innovations in this area include formulations for topical applications, oral medications, and cosmetic products that leverage glycerol's unique characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Glycerol and Nutraceutical Sectors
The research on using glycerol in formulating enhanced nutraceutical products is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global nutraceutical market is expanding rapidly, driven by growing health consciousness and demand for functional foods. Major players like DSM IP Assets BV, BASF Corp., and Archer-Daniels-Midland Co. are investing in R&D to develop innovative glycerol-based formulations. The technology is maturing, with companies like Kaneka Corp. and Ajinomoto Co., Inc. focusing on improving bioavailability and efficacy. Academic institutions such as North Carolina State University and Jiangnan University are contributing to fundamental research, while collaborations between industry and academia are accelerating product development and commercialization.
DSM IP Assets BV
Technical Solution: DSM IP Assets BV has focused on leveraging glycerol in nutraceutical formulations to enhance product stability and bioavailability. Their research approach involves using glycerol as a multifunctional excipient in various nutraceutical delivery systems. DSM has developed innovative microencapsulation techniques that utilize glycerol to protect sensitive ingredients from degradation and improve their shelf life[13]. They have also explored the use of glycerol-based matrices for controlled release of active compounds, enhancing their absorption and efficacy[15]. Additionally, DSM has investigated the potential of glycerol as a solubilizer for poorly water-soluble nutraceutical ingredients, improving their bioavailability and overall product performance[17].
Strengths: Broad portfolio of nutritional ingredients, strong scientific expertise, and global market presence. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in differentiating products in a competitive market and adapting to rapidly changing consumer trends.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed innovative formulations incorporating glycerol for enhanced nutraceutical products. Their approach involves using glycerol as a multifunctional ingredient, serving as a solvent, sweetener, and texture modifier. BASF's research has focused on optimizing glycerol's hygroscopic properties to improve the stability and shelf-life of nutraceutical formulations[1]. They have also explored the use of glycerol in microencapsulation techniques to enhance the bioavailability of active ingredients in nutraceuticals[3]. Additionally, BASF has investigated the synergistic effects of glycerol with other functional ingredients to create more effective and palatable nutraceutical products[5].
Strengths: Extensive expertise in chemical formulations, global research capabilities, and a strong patent portfolio. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges in different markets and competition from specialized nutraceutical companies.
Innovative Glycerol Applications in Nutraceuticals
New uses of Glycerol derivatives in particular in cosmetics
PatentInactiveEP1733731A1
Innovation
- The use of glycosylglycerides, specifically galactosylglycerides, in cosmetic and pharmaceutical compositions to directly inhibit MMPs, thereby rebalancing the degradation and synthesis of the dermal extracellular matrix without affecting fibronectin synthesis or neo-angiogenesis.
Novel nutraceutical compositions and use thereof
PatentWO2004105517A1
Innovation
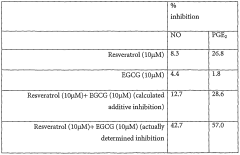
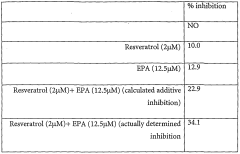
- A novel nutraceutical composition combining resveratrol, EGCG, genistein, vitamin E, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and vitamin K, which are administered in various formulations, including capsules, tablets, and beverages, to provide synergistic anti-inflammatory effects by modulating inflammatory mediators and maintaining equilibrium in inflammatory responses.
Regulatory Framework for Glycerol in Nutraceuticals
The regulatory framework for glycerol in nutraceuticals is a complex and evolving landscape that varies across different regions and jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of nutraceuticals, including those containing glycerol. The FDA classifies glycerol as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food and dietary supplements, provided it meets certain purity standards and is used within specified limits.
The European Union (EU) has established specific regulations for the use of glycerol in food and nutraceutical products through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EFSA has set an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) for glycerol and requires manufacturers to adhere to strict labeling and safety guidelines when incorporating glycerol into their products.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have their own regulatory bodies that oversee the use of glycerol in nutraceuticals. The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety have established guidelines for the use of glycerol in functional foods and health supplements, with specific requirements for product registration and safety assessments.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides international standards for food additives, including glycerol. These standards serve as a reference for many countries in developing their national regulations.
Manufacturers of nutraceutical products containing glycerol must navigate these diverse regulatory frameworks to ensure compliance across different markets. This often involves conducting extensive safety studies, obtaining necessary certifications, and adhering to specific labeling requirements. The regulatory landscape also impacts the formulation process, as manufacturers must consider the maximum allowable levels of glycerol in their products based on regional regulations.
As research on the potential health benefits of glycerol in nutraceuticals continues to advance, regulatory bodies are likely to update their guidelines and requirements. This dynamic regulatory environment necessitates ongoing vigilance and adaptation from manufacturers to ensure continued compliance and market access for their glycerol-containing nutraceutical products.
The European Union (EU) has established specific regulations for the use of glycerol in food and nutraceutical products through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EFSA has set an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) for glycerol and requires manufacturers to adhere to strict labeling and safety guidelines when incorporating glycerol into their products.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have their own regulatory bodies that oversee the use of glycerol in nutraceuticals. The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety have established guidelines for the use of glycerol in functional foods and health supplements, with specific requirements for product registration and safety assessments.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides international standards for food additives, including glycerol. These standards serve as a reference for many countries in developing their national regulations.
Manufacturers of nutraceutical products containing glycerol must navigate these diverse regulatory frameworks to ensure compliance across different markets. This often involves conducting extensive safety studies, obtaining necessary certifications, and adhering to specific labeling requirements. The regulatory landscape also impacts the formulation process, as manufacturers must consider the maximum allowable levels of glycerol in their products based on regional regulations.
As research on the potential health benefits of glycerol in nutraceuticals continues to advance, regulatory bodies are likely to update their guidelines and requirements. This dynamic regulatory environment necessitates ongoing vigilance and adaptation from manufacturers to ensure continued compliance and market access for their glycerol-containing nutraceutical products.
Safety and Efficacy Studies of Glycerol in Nutraceuticals
The safety and efficacy of glycerol in nutraceutical products have been extensively studied, providing a solid foundation for its use in formulations. Numerous clinical trials and toxicological assessments have demonstrated glycerol's favorable safety profile when used within recommended dosages.
Acute toxicity studies in various animal models have shown that glycerol has a low toxicity potential, with oral LD50 values ranging from 12.6 to 27.2 g/kg body weight in rats. Long-term studies have also indicated no significant adverse effects at doses typically used in nutraceutical applications.
Glycerol's efficacy in nutraceutical products has been demonstrated across multiple health domains. Its osmotic properties make it particularly useful in hydration-focused formulations. Studies have shown that glycerol-enhanced beverages can improve fluid retention and maintain plasma volume more effectively than water alone during prolonged exercise or in hot environments.
In weight management applications, glycerol has shown promise as a potential appetite suppressant. Clinical trials have reported reduced hunger sensations and decreased food intake when glycerol is consumed before meals, although more research is needed to fully elucidate its mechanisms of action in this context.
Glycerol's role in supporting cognitive function has also been investigated. Some studies suggest that glycerol supplementation may enhance memory and cognitive performance, particularly in situations of mild dehydration or cognitive stress. However, results in this area have been mixed, and further research is warranted to establish definitive cognitive benefits.
The use of glycerol in sports nutrition products has been extensively studied. Research has shown that glycerol loading can significantly increase total body water, potentially improving endurance performance in certain conditions. However, it's important to note that some sports governing bodies have restrictions on glycerol use due to its potential masking effects on doping tests.
Safety studies have also examined potential interactions between glycerol and other common nutraceutical ingredients. Generally, glycerol has been found to be compatible with a wide range of compounds, including vitamins, minerals, and herbal extracts. However, formulators should be aware of potential synergistic effects, particularly with other osmotically active substances.
While the overall safety profile of glycerol is favorable, some studies have reported mild side effects such as headaches, nausea, and gastrointestinal discomfort, particularly at higher doses. These effects are typically transient and dose-dependent, underscoring the importance of appropriate dosing in nutraceutical formulations.
Acute toxicity studies in various animal models have shown that glycerol has a low toxicity potential, with oral LD50 values ranging from 12.6 to 27.2 g/kg body weight in rats. Long-term studies have also indicated no significant adverse effects at doses typically used in nutraceutical applications.
Glycerol's efficacy in nutraceutical products has been demonstrated across multiple health domains. Its osmotic properties make it particularly useful in hydration-focused formulations. Studies have shown that glycerol-enhanced beverages can improve fluid retention and maintain plasma volume more effectively than water alone during prolonged exercise or in hot environments.
In weight management applications, glycerol has shown promise as a potential appetite suppressant. Clinical trials have reported reduced hunger sensations and decreased food intake when glycerol is consumed before meals, although more research is needed to fully elucidate its mechanisms of action in this context.
Glycerol's role in supporting cognitive function has also been investigated. Some studies suggest that glycerol supplementation may enhance memory and cognitive performance, particularly in situations of mild dehydration or cognitive stress. However, results in this area have been mixed, and further research is warranted to establish definitive cognitive benefits.
The use of glycerol in sports nutrition products has been extensively studied. Research has shown that glycerol loading can significantly increase total body water, potentially improving endurance performance in certain conditions. However, it's important to note that some sports governing bodies have restrictions on glycerol use due to its potential masking effects on doping tests.
Safety studies have also examined potential interactions between glycerol and other common nutraceutical ingredients. Generally, glycerol has been found to be compatible with a wide range of compounds, including vitamins, minerals, and herbal extracts. However, formulators should be aware of potential synergistic effects, particularly with other osmotically active substances.
While the overall safety profile of glycerol is favorable, some studies have reported mild side effects such as headaches, nausea, and gastrointestinal discomfort, particularly at higher doses. These effects are typically transient and dose-dependent, underscoring the importance of appropriate dosing in nutraceutical formulations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!