How AMOLED enhances remote working environments?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Tech Evolution
AMOLED technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception, with each advancement bringing new possibilities for remote working environments. The journey began in the late 1990s when Kodak researchers developed the first OLED display. However, it wasn't until the mid-2000s that AMOLED displays started to gain traction in consumer electronics.
The early AMOLED displays faced challenges such as limited lifespan and high production costs. These issues were gradually addressed through innovations in materials science and manufacturing processes. By the early 2010s, AMOLED displays had become a viable option for high-end smartphones and tablets, offering superior color reproduction and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD screens.
As remote work gained prominence, the advantages of AMOLED technology became increasingly relevant. The deep blacks and high contrast ratios of AMOLED displays significantly reduced eye strain during long working hours, a crucial factor for remote workers who spend extended periods in front of screens. The technology's ability to display true blacks by turning off individual pixels also contributed to improved power efficiency, extending battery life for mobile devices used in remote work settings.
The mid-2010s saw a surge in AMOLED adoption across various device categories, including laptops and monitors specifically designed for professional use. This expansion coincided with the growing trend of flexible work arrangements, setting the stage for AMOLED's role in enhancing remote working environments.
Recent years have witnessed remarkable advancements in AMOLED technology, particularly in areas that directly benefit remote workers. Higher refresh rates, such as 120Hz and beyond, have resulted in smoother scrolling and reduced motion blur, enhancing productivity when working with large documents or complex visual data. Additionally, improvements in color accuracy and gamut have made AMOLED displays increasingly suitable for color-critical work, such as graphic design and video editing, tasks often performed remotely.
The development of foldable and rollable AMOLED displays has opened up new possibilities for portable workstations, allowing remote workers to carry large screen real estate in compact form factors. This innovation addresses the need for versatile display solutions that can adapt to various working environments, from home offices to temporary workspaces.
Looking ahead, the evolution of AMOLED technology continues to focus on areas that will further enhance remote working experiences. These include advancements in energy efficiency to support longer battery life, improvements in outdoor visibility for those working in varied lighting conditions, and the integration of eye-care technologies to reduce digital eye strain during prolonged use.
The early AMOLED displays faced challenges such as limited lifespan and high production costs. These issues were gradually addressed through innovations in materials science and manufacturing processes. By the early 2010s, AMOLED displays had become a viable option for high-end smartphones and tablets, offering superior color reproduction and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD screens.
As remote work gained prominence, the advantages of AMOLED technology became increasingly relevant. The deep blacks and high contrast ratios of AMOLED displays significantly reduced eye strain during long working hours, a crucial factor for remote workers who spend extended periods in front of screens. The technology's ability to display true blacks by turning off individual pixels also contributed to improved power efficiency, extending battery life for mobile devices used in remote work settings.
The mid-2010s saw a surge in AMOLED adoption across various device categories, including laptops and monitors specifically designed for professional use. This expansion coincided with the growing trend of flexible work arrangements, setting the stage for AMOLED's role in enhancing remote working environments.
Recent years have witnessed remarkable advancements in AMOLED technology, particularly in areas that directly benefit remote workers. Higher refresh rates, such as 120Hz and beyond, have resulted in smoother scrolling and reduced motion blur, enhancing productivity when working with large documents or complex visual data. Additionally, improvements in color accuracy and gamut have made AMOLED displays increasingly suitable for color-critical work, such as graphic design and video editing, tasks often performed remotely.
The development of foldable and rollable AMOLED displays has opened up new possibilities for portable workstations, allowing remote workers to carry large screen real estate in compact form factors. This innovation addresses the need for versatile display solutions that can adapt to various working environments, from home offices to temporary workspaces.
Looking ahead, the evolution of AMOLED technology continues to focus on areas that will further enhance remote working experiences. These include advancements in energy efficiency to support longer battery life, improvements in outdoor visibility for those working in varied lighting conditions, and the integration of eye-care technologies to reduce digital eye strain during prolonged use.
Remote Work Market Trends
The remote work market has experienced unprecedented growth in recent years, driven by technological advancements and changing workplace dynamics. This trend has been further accelerated by the global COVID-19 pandemic, which forced many organizations to adopt remote work policies. As a result, the demand for technologies that enhance remote working environments has surged significantly.
Market research indicates that the global remote work market size was valued at $17.9 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach $30.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 9.3% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of cloud-based collaboration tools, video conferencing platforms, and virtual desktop infrastructure solutions.
The shift towards remote work has also led to a rise in demand for high-quality display technologies, such as AMOLED screens, which offer superior visual experiences for remote workers. The AMOLED display market is expected to grow from $28.4 billion in 2020 to $48.5 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 19.5% during the forecast period.
Key drivers of the remote work market include the need for business continuity during crises, cost savings for employers, improved work-life balance for employees, and access to a global talent pool. Additionally, advancements in communication technologies and the proliferation of high-speed internet connectivity have made remote work more feasible and efficient.
Industry sectors experiencing the highest adoption of remote work include IT and telecommunications, finance and insurance, professional services, and education. These sectors are increasingly investing in technologies that enhance remote collaboration, productivity, and employee engagement.
The remote work trend has also sparked innovation in related markets, such as ergonomic home office furniture, cybersecurity solutions for distributed workforces, and virtual team-building platforms. This ecosystem of supporting technologies and services is expected to continue expanding as remote work becomes a permanent fixture in the global business landscape.
However, challenges remain in the remote work market, including concerns about data security, employee productivity monitoring, and maintaining company culture in virtual environments. These challenges present opportunities for technology providers to develop innovative solutions that address these pain points and further enhance the remote working experience.
As the remote work market continues to evolve, the integration of advanced display technologies like AMOLED is expected to play a crucial role in improving visual comfort, reducing eye strain, and enhancing overall productivity for remote workers. This synergy between remote work trends and display technology advancements is likely to drive further innovation and market growth in the coming years.
Market research indicates that the global remote work market size was valued at $17.9 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach $30.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 9.3% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of cloud-based collaboration tools, video conferencing platforms, and virtual desktop infrastructure solutions.
The shift towards remote work has also led to a rise in demand for high-quality display technologies, such as AMOLED screens, which offer superior visual experiences for remote workers. The AMOLED display market is expected to grow from $28.4 billion in 2020 to $48.5 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 19.5% during the forecast period.
Key drivers of the remote work market include the need for business continuity during crises, cost savings for employers, improved work-life balance for employees, and access to a global talent pool. Additionally, advancements in communication technologies and the proliferation of high-speed internet connectivity have made remote work more feasible and efficient.
Industry sectors experiencing the highest adoption of remote work include IT and telecommunications, finance and insurance, professional services, and education. These sectors are increasingly investing in technologies that enhance remote collaboration, productivity, and employee engagement.
The remote work trend has also sparked innovation in related markets, such as ergonomic home office furniture, cybersecurity solutions for distributed workforces, and virtual team-building platforms. This ecosystem of supporting technologies and services is expected to continue expanding as remote work becomes a permanent fixture in the global business landscape.
However, challenges remain in the remote work market, including concerns about data security, employee productivity monitoring, and maintaining company culture in virtual environments. These challenges present opportunities for technology providers to develop innovative solutions that address these pain points and further enhance the remote working experience.
As the remote work market continues to evolve, the integration of advanced display technologies like AMOLED is expected to play a crucial role in improving visual comfort, reducing eye strain, and enhancing overall productivity for remote workers. This synergy between remote work trends and display technology advancements is likely to drive further innovation and market growth in the coming years.
AMOLED Display Challenges
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has revolutionized display quality in various devices, including those used for remote work. However, as with any advanced technology, AMOLED displays face several challenges that need to be addressed to enhance their performance in remote working environments.
One of the primary challenges is the issue of burn-in or image retention. AMOLED displays are susceptible to this problem, especially when static images are displayed for extended periods. In remote work scenarios, where users often have fixed elements on their screens for long durations, such as taskbars or video conferencing interfaces, the risk of burn-in increases significantly. This can lead to permanent damage to the display, affecting its longevity and user experience.
Power consumption is another critical challenge for AMOLED displays in remote working setups. While AMOLED technology is generally more energy-efficient than traditional LCD displays, especially when displaying darker content, the increased screen time associated with remote work can still lead to substantial battery drain. This is particularly problematic for mobile devices and laptops used in remote work settings where constant access to power sources may not be available.
Color accuracy and consistency pose additional challenges for AMOLED displays. While these displays are known for their vibrant colors and high contrast ratios, maintaining color accuracy across different viewing angles and ambient lighting conditions can be difficult. This becomes crucial in remote work environments where precise color representation is essential for tasks such as graphic design, video editing, or reviewing visual content.
The manufacturing cost of AMOLED displays remains a significant challenge, particularly for larger screens commonly used in remote work setups. The complex production process and materials used in AMOLED technology contribute to higher costs compared to traditional LCD displays. This can limit the widespread adoption of AMOLED technology in budget-friendly devices suitable for remote work.
Durability and lifespan concerns also present challenges for AMOLED displays in remote working environments. The organic materials used in these displays are susceptible to degradation over time, which can lead to decreased brightness and color shifts. Given the increased usage associated with remote work, ensuring the longevity of AMOLED displays becomes crucial for maintaining productivity and user satisfaction.
Lastly, the challenge of blue light emission is particularly relevant in the context of remote work. AMOLED displays, like other digital screens, emit blue light that can contribute to eye strain and disrupt sleep patterns. With extended screen time during remote work, mitigating the effects of blue light while maintaining the visual benefits of AMOLED technology becomes a significant challenge to address.
One of the primary challenges is the issue of burn-in or image retention. AMOLED displays are susceptible to this problem, especially when static images are displayed for extended periods. In remote work scenarios, where users often have fixed elements on their screens for long durations, such as taskbars or video conferencing interfaces, the risk of burn-in increases significantly. This can lead to permanent damage to the display, affecting its longevity and user experience.
Power consumption is another critical challenge for AMOLED displays in remote working setups. While AMOLED technology is generally more energy-efficient than traditional LCD displays, especially when displaying darker content, the increased screen time associated with remote work can still lead to substantial battery drain. This is particularly problematic for mobile devices and laptops used in remote work settings where constant access to power sources may not be available.
Color accuracy and consistency pose additional challenges for AMOLED displays. While these displays are known for their vibrant colors and high contrast ratios, maintaining color accuracy across different viewing angles and ambient lighting conditions can be difficult. This becomes crucial in remote work environments where precise color representation is essential for tasks such as graphic design, video editing, or reviewing visual content.
The manufacturing cost of AMOLED displays remains a significant challenge, particularly for larger screens commonly used in remote work setups. The complex production process and materials used in AMOLED technology contribute to higher costs compared to traditional LCD displays. This can limit the widespread adoption of AMOLED technology in budget-friendly devices suitable for remote work.
Durability and lifespan concerns also present challenges for AMOLED displays in remote working environments. The organic materials used in these displays are susceptible to degradation over time, which can lead to decreased brightness and color shifts. Given the increased usage associated with remote work, ensuring the longevity of AMOLED displays becomes crucial for maintaining productivity and user satisfaction.
Lastly, the challenge of blue light emission is particularly relevant in the context of remote work. AMOLED displays, like other digital screens, emit blue light that can contribute to eye strain and disrupt sleep patterns. With extended screen time during remote work, mitigating the effects of blue light while maintaining the visual benefits of AMOLED technology becomes a significant challenge to address.
Current AMOLED Solutions
01 Pixel circuit optimization for AMOLED displays
Improving pixel circuits in AMOLED displays to enhance overall performance. This includes techniques for reducing power consumption, improving brightness control, and increasing display uniformity. Advanced pixel designs can compensate for variations in OLED characteristics and transistor properties, resulting in better image quality and longer display lifespan.- Pixel circuit optimization: Enhancing AMOLED displays through improved pixel circuit designs. This includes optimizing transistor configurations, implementing compensation schemes, and developing new driving methods to improve display performance, uniformity, and power efficiency.
- OLED material advancements: Developing and incorporating advanced OLED materials to enhance display quality. This involves researching and implementing new emissive materials, electron transport layers, and hole transport layers to improve color gamut, efficiency, and longevity of AMOLED displays.
- Display driving techniques: Implementing innovative display driving techniques to enhance AMOLED performance. This includes developing new voltage control methods, current programming schemes, and timing algorithms to improve image quality, reduce power consumption, and extend display lifespan.
- Structural improvements: Enhancing AMOLED displays through structural modifications and improvements. This involves optimizing layer stacking, implementing new encapsulation techniques, and developing flexible or foldable AMOLED structures to improve durability and expand application possibilities.
- Image processing and compensation: Developing advanced image processing and compensation algorithms for AMOLED displays. This includes implementing techniques for color management, brightness control, and aging compensation to improve overall display quality and maintain consistent performance over time.
02 OLED material and structure enhancements
Developing advanced OLED materials and structures to improve display performance. This involves creating new organic compounds, optimizing layer structures, and enhancing electron transport layers. These improvements can lead to higher efficiency, better color accuracy, and increased longevity of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions03 Driving and compensation techniques for AMOLED
Implementing sophisticated driving and compensation methods to enhance AMOLED display quality. This includes developing algorithms for voltage compensation, current programming, and threshold voltage sensing. These techniques can mitigate issues such as image retention, non-uniformity, and color shift, resulting in improved visual performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of additional functionalities in AMOLED displays
Incorporating additional features into AMOLED displays to enhance their functionality. This can include integrating touch sensors, fingerprint recognition, and under-display cameras. These advancements can lead to more versatile and feature-rich display solutions while maintaining the benefits of AMOLED technology.Expand Specific Solutions05 Power efficiency and thermal management in AMOLED displays
Developing techniques to improve power efficiency and thermal management in AMOLED displays. This involves optimizing power consumption at both pixel and system levels, implementing advanced heat dissipation methods, and creating more efficient display architectures. These enhancements can lead to longer battery life and improved display performance in various environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key AMOLED Manufacturers
The AMOLED technology for enhancing remote working environments is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and improving technical maturity. Major players like Samsung Display, BOE Technology, and LG Display are driving innovation in this space. The market is expanding as more companies adopt remote work policies, creating demand for high-quality displays. AMOLED technology offers advantages such as better color reproduction, higher contrast ratios, and reduced eye strain, which are particularly beneficial for long hours of remote work. As the technology matures, we're seeing advancements in energy efficiency, durability, and integration with other smart features, further enhancing its applicability in remote working setups.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed flexible AMOLED displays that cater to remote working needs. Their latest innovation includes foldable AMOLED screens that can transform from compact mobile devices to larger displays, enhancing portability and workspace flexibility[3]. BOE's AMOLED technology incorporates low blue light emission and flicker-free features, reducing eye fatigue during prolonged use. The company has also introduced touch-integrated AMOLED panels with high refresh rates (up to 120Hz), ensuring smooth interactions and reduced motion blur for video conferencing and collaborative work[4]. BOE's AMOLED displays offer wide color gamut coverage (over 100% DCI-P3), ensuring accurate color representation for design and multimedia tasks in remote settings.
Strengths: Flexibility in display form factors, high refresh rates for smooth interactions. Weaknesses: Less established in the global market compared to some competitors, potential yield issues with cutting-edge technologies.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed advanced AMOLED displays specifically tailored for remote working environments. Their latest AMOLED panels feature Eye Comfort technology, which reduces blue light emission by up to 70% compared to conventional displays[1]. This technology helps minimize eye strain during long working hours. Samsung's AMOLED displays also offer true blacks and infinite contrast ratios, enhancing visibility in various lighting conditions. The company has introduced Ultra-High Definition (UHD) AMOLED panels with resolutions up to 4K, providing crisp and clear visuals for detailed work[2]. Additionally, Samsung's AMOLED displays incorporate touch sensitivity and stylus support, enabling more interactive remote collaboration experiences.
Strengths: Superior color accuracy, energy efficiency, and reduced eye strain. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to LCD technology, potential for burn-in over extended use.
AMOLED Display Innovations
Array substrate, display device, and method for manufacturing array substrate
PatentActiveUS20170148862A1
Innovation
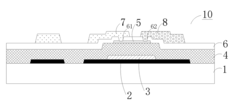
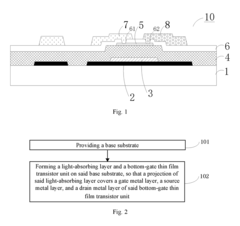
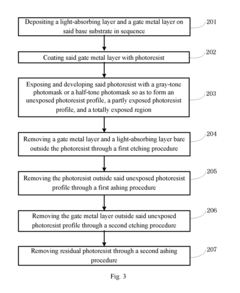
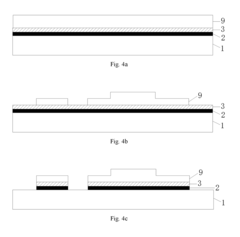
- An array substrate with a light-absorbing layer covering the gate, source, and drain metal layers of a bottom-gate thin film transistor unit, preventing ambient light irradiation while allowing useful light to pass through.
Active-matrix organic light emitting diode display module
PatentInactiveKR1020090117209A
Innovation
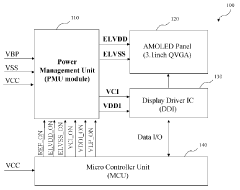
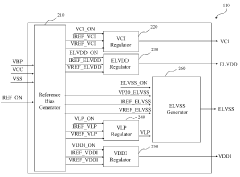
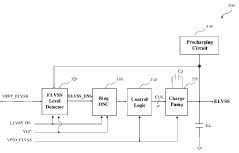
- An AMOLED display module comprising a Power Module Unit (PMU), an AMOLED panel, and a Display Driver IC (DDI) is provided, with the PMU generating panel driving and interface voltages using supply power sources in response to control signals, and the DDI driving the panel in response to display data, facilitated by a Micro Controller Unit (MCU).
Ergonomic Considerations
AMOLED technology has significantly impacted the ergonomics of remote working environments, offering several advantages that enhance user comfort and productivity. The high contrast ratio and deep blacks of AMOLED displays reduce eye strain during extended periods of screen use, a crucial factor for remote workers who spend long hours in front of their devices.
The ability of AMOLED screens to produce vibrant colors and true blacks contributes to improved visual clarity, making it easier for users to read text and view images without straining their eyes. This is particularly beneficial for remote workers who rely heavily on digital communication and collaboration tools.
AMOLED displays also offer better visibility in various lighting conditions, including bright sunlight, allowing remote workers to set up their workspaces in different environments without compromising screen readability. This flexibility is essential for those who may need to work from diverse locations or outdoor settings.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED technology translates to longer battery life for portable devices, reducing the need for frequent charging and allowing remote workers to maintain productivity even when power outlets are not readily available. This feature is especially valuable for those who work on-the-go or in unconventional settings.
AMOLED screens typically emit less blue light compared to traditional LCD displays, potentially reducing the negative impact on users' circadian rhythms. This can lead to improved sleep quality for remote workers who often work late hours or have flexible schedules.
The thin and lightweight nature of AMOLED displays contributes to the overall ergonomics of devices used in remote work setups. Lighter laptops and tablets with AMOLED screens are easier to carry and position, promoting better posture and reducing physical strain during extended use.
AMOLED's ability to support high refresh rates enhances the smoothness of on-screen motion, reducing visual fatigue and improving the overall user experience. This is particularly beneficial for remote workers who engage in video conferencing or work with dynamic content.
The ability of AMOLED screens to produce vibrant colors and true blacks contributes to improved visual clarity, making it easier for users to read text and view images without straining their eyes. This is particularly beneficial for remote workers who rely heavily on digital communication and collaboration tools.
AMOLED displays also offer better visibility in various lighting conditions, including bright sunlight, allowing remote workers to set up their workspaces in different environments without compromising screen readability. This flexibility is essential for those who may need to work from diverse locations or outdoor settings.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED technology translates to longer battery life for portable devices, reducing the need for frequent charging and allowing remote workers to maintain productivity even when power outlets are not readily available. This feature is especially valuable for those who work on-the-go or in unconventional settings.
AMOLED screens typically emit less blue light compared to traditional LCD displays, potentially reducing the negative impact on users' circadian rhythms. This can lead to improved sleep quality for remote workers who often work late hours or have flexible schedules.
The thin and lightweight nature of AMOLED displays contributes to the overall ergonomics of devices used in remote work setups. Lighter laptops and tablets with AMOLED screens are easier to carry and position, promoting better posture and reducing physical strain during extended use.
AMOLED's ability to support high refresh rates enhances the smoothness of on-screen motion, reducing visual fatigue and improving the overall user experience. This is particularly beneficial for remote workers who engage in video conferencing or work with dynamic content.
Energy Efficiency Analysis
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has emerged as a game-changer in remote working environments, particularly in terms of energy efficiency. The power-saving capabilities of AMOLED displays contribute significantly to the overall energy consumption of devices used in remote work settings.
AMOLED screens operate on a pixel-by-pixel basis, allowing for selective illumination of only the required pixels. This characteristic results in substantial power savings, especially when displaying darker content or using dark mode interfaces. In remote working scenarios, where users often spend extended hours in front of screens, this energy-efficient feature becomes increasingly valuable.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED displays is further enhanced by their ability to produce true blacks by completely turning off pixels. This not only conserves power but also reduces eye strain during prolonged use, a crucial factor for remote workers who rely heavily on digital devices throughout their workday.
Compared to traditional LCD screens, AMOLED displays consume significantly less power when displaying static or predominantly dark content. This is particularly beneficial for remote workers who frequently use productivity applications with dark themes or engage in video conferencing with dimmed backgrounds.
The power-saving advantages of AMOLED technology extend beyond the display itself. By reducing overall device power consumption, AMOLED screens contribute to longer battery life in portable devices such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones. This increased battery longevity is crucial for remote workers who may not always have immediate access to power sources.
Furthermore, the energy efficiency of AMOLED displays aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in remote work environments. As organizations strive to reduce their carbon footprint, the adoption of energy-efficient technologies like AMOLED becomes increasingly important in the context of large-scale remote work setups.
Recent advancements in AMOLED technology have led to even greater energy savings. Innovations such as variable refresh rates and adaptive brightness further optimize power consumption based on content and ambient lighting conditions. These features are particularly relevant in diverse remote working environments where lighting conditions may vary throughout the day.
In conclusion, the energy efficiency of AMOLED technology plays a crucial role in enhancing remote working environments. By reducing power consumption, extending battery life, and contributing to overall sustainability efforts, AMOLED displays offer significant advantages for remote workers and organizations alike. As remote work continues to evolve, the energy-efficient characteristics of AMOLED technology are likely to become increasingly valuable in shaping the future of digital workspaces.
AMOLED screens operate on a pixel-by-pixel basis, allowing for selective illumination of only the required pixels. This characteristic results in substantial power savings, especially when displaying darker content or using dark mode interfaces. In remote working scenarios, where users often spend extended hours in front of screens, this energy-efficient feature becomes increasingly valuable.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED displays is further enhanced by their ability to produce true blacks by completely turning off pixels. This not only conserves power but also reduces eye strain during prolonged use, a crucial factor for remote workers who rely heavily on digital devices throughout their workday.
Compared to traditional LCD screens, AMOLED displays consume significantly less power when displaying static or predominantly dark content. This is particularly beneficial for remote workers who frequently use productivity applications with dark themes or engage in video conferencing with dimmed backgrounds.
The power-saving advantages of AMOLED technology extend beyond the display itself. By reducing overall device power consumption, AMOLED screens contribute to longer battery life in portable devices such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones. This increased battery longevity is crucial for remote workers who may not always have immediate access to power sources.
Furthermore, the energy efficiency of AMOLED displays aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in remote work environments. As organizations strive to reduce their carbon footprint, the adoption of energy-efficient technologies like AMOLED becomes increasingly important in the context of large-scale remote work setups.
Recent advancements in AMOLED technology have led to even greater energy savings. Innovations such as variable refresh rates and adaptive brightness further optimize power consumption based on content and ambient lighting conditions. These features are particularly relevant in diverse remote working environments where lighting conditions may vary throughout the day.
In conclusion, the energy efficiency of AMOLED technology plays a crucial role in enhancing remote working environments. By reducing power consumption, extending battery life, and contributing to overall sustainability efforts, AMOLED displays offer significant advantages for remote workers and organizations alike. As remote work continues to evolve, the energy-efficient characteristics of AMOLED technology are likely to become increasingly valuable in shaping the future of digital workspaces.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!