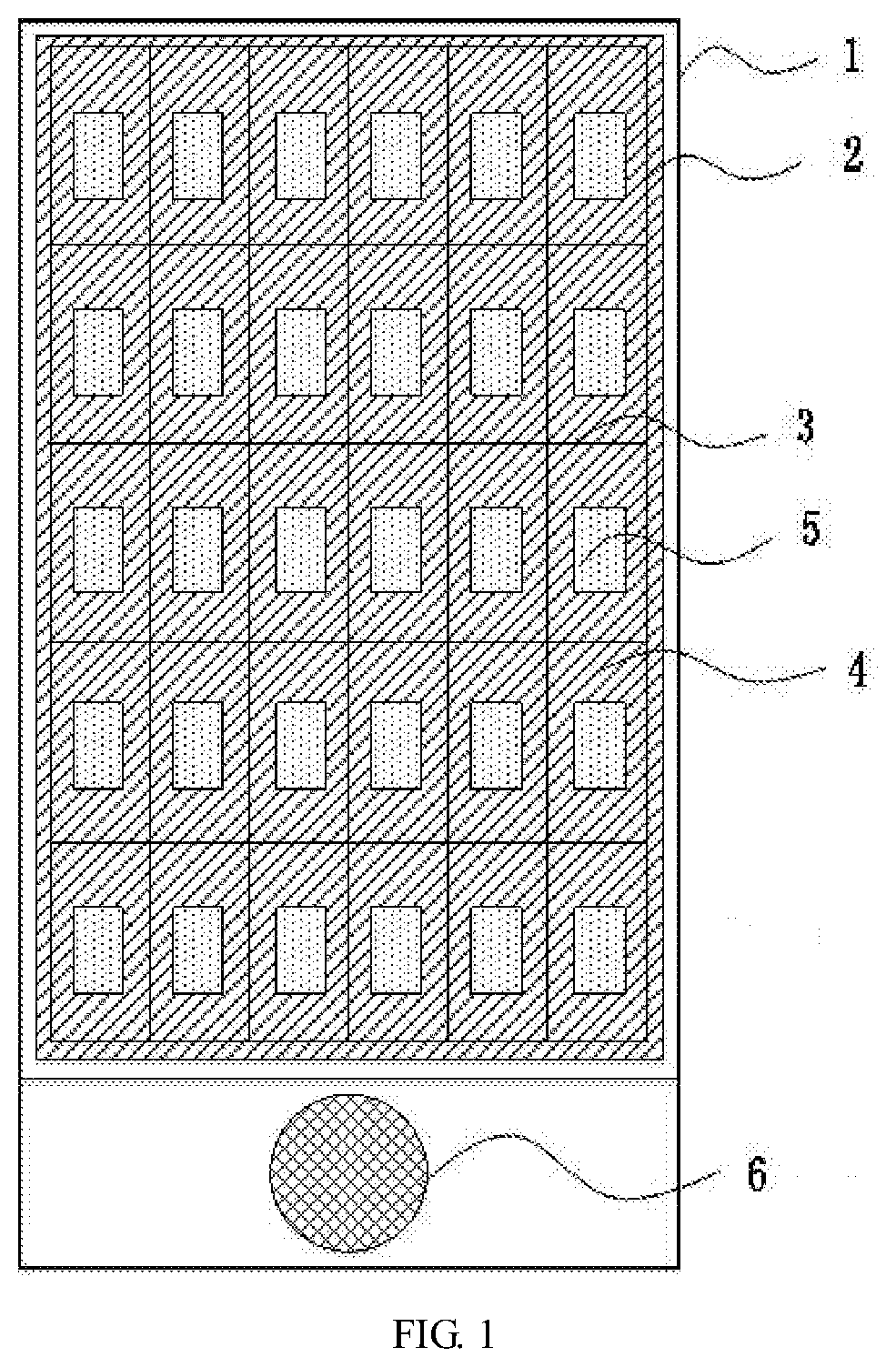
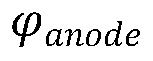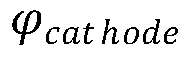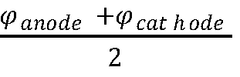Exploration of AMOLED's role in sustainable smart architecture.
JUL 17, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED in Architecture: Background and Objectives
Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode (AMOLED) technology has emerged as a revolutionary force in display systems, offering unprecedented visual quality, energy efficiency, and design flexibility. As the world grapples with the challenges of sustainable development, the integration of AMOLED into smart architecture presents a compelling opportunity to enhance both the functionality and environmental performance of buildings.
The evolution of AMOLED technology can be traced back to the late 1980s, with significant advancements occurring in the past two decades. Initially developed for small-scale consumer electronics, AMOLED displays have since expanded their application scope, now finding potential in large-scale architectural implementations. This technological progression aligns with the growing demand for smart, energy-efficient buildings that can adapt to user needs and environmental conditions.
In the context of sustainable smart architecture, AMOLED technology offers several key advantages. Its ability to produce vibrant colors and deep blacks while consuming less power than traditional LCD displays makes it an ideal candidate for energy-conscious building designs. Furthermore, the flexibility and thinness of AMOLED panels open up new possibilities for integrating displays into various architectural elements, from windows to walls, without compromising structural integrity.
The primary objective of exploring AMOLED's role in sustainable smart architecture is to leverage its unique properties to create buildings that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly functional and environmentally responsible. This includes investigating how AMOLED displays can be used to enhance natural lighting, reduce energy consumption, and improve the overall user experience within built environments.
Another critical goal is to examine the potential of AMOLED technology in creating dynamic and responsive building facades. These "smart skins" could adapt to changing environmental conditions, optimizing energy usage and occupant comfort. Additionally, the integration of AMOLED displays into architectural elements could revolutionize how information is conveyed within public spaces, enhancing wayfinding, accessibility, and community engagement.
As we delve into this exploration, it is essential to consider the technical challenges that must be overcome. These include scaling AMOLED technology to architectural dimensions, ensuring durability in various weather conditions, and developing control systems that can seamlessly integrate with existing building management systems. The environmental impact of AMOLED production and disposal must also be carefully evaluated to ensure that the technology truly contributes to sustainable architecture practices.
By thoroughly examining the background and setting clear objectives for AMOLED integration in architecture, we lay the foundation for innovative solutions that could transform our built environment. This exploration not only pushes the boundaries of what's possible in sustainable smart architecture but also paves the way for a more interconnected, efficient, and environmentally conscious urban future.
The evolution of AMOLED technology can be traced back to the late 1980s, with significant advancements occurring in the past two decades. Initially developed for small-scale consumer electronics, AMOLED displays have since expanded their application scope, now finding potential in large-scale architectural implementations. This technological progression aligns with the growing demand for smart, energy-efficient buildings that can adapt to user needs and environmental conditions.
In the context of sustainable smart architecture, AMOLED technology offers several key advantages. Its ability to produce vibrant colors and deep blacks while consuming less power than traditional LCD displays makes it an ideal candidate for energy-conscious building designs. Furthermore, the flexibility and thinness of AMOLED panels open up new possibilities for integrating displays into various architectural elements, from windows to walls, without compromising structural integrity.
The primary objective of exploring AMOLED's role in sustainable smart architecture is to leverage its unique properties to create buildings that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly functional and environmentally responsible. This includes investigating how AMOLED displays can be used to enhance natural lighting, reduce energy consumption, and improve the overall user experience within built environments.
Another critical goal is to examine the potential of AMOLED technology in creating dynamic and responsive building facades. These "smart skins" could adapt to changing environmental conditions, optimizing energy usage and occupant comfort. Additionally, the integration of AMOLED displays into architectural elements could revolutionize how information is conveyed within public spaces, enhancing wayfinding, accessibility, and community engagement.
As we delve into this exploration, it is essential to consider the technical challenges that must be overcome. These include scaling AMOLED technology to architectural dimensions, ensuring durability in various weather conditions, and developing control systems that can seamlessly integrate with existing building management systems. The environmental impact of AMOLED production and disposal must also be carefully evaluated to ensure that the technology truly contributes to sustainable architecture practices.
By thoroughly examining the background and setting clear objectives for AMOLED integration in architecture, we lay the foundation for innovative solutions that could transform our built environment. This exploration not only pushes the boundaries of what's possible in sustainable smart architecture but also paves the way for a more interconnected, efficient, and environmentally conscious urban future.
Smart Building Market Analysis
The smart building market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient and sustainable architectural solutions. As urbanization continues to accelerate globally, the need for intelligent and environmentally friendly buildings has become more pressing. This market encompasses a wide range of technologies and systems designed to enhance building performance, occupant comfort, and operational efficiency.
The integration of AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology into smart architecture represents a promising avenue for sustainable development. AMOLED displays offer several advantages over traditional lighting and display technologies, including higher energy efficiency, improved color accuracy, and greater flexibility in design. These characteristics make AMOLED an attractive option for smart building applications, particularly in areas such as lighting control, information displays, and interactive surfaces.
Market research indicates that the global smart building market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10% in the coming years. This growth is fueled by factors such as increasing awareness of environmental issues, government regulations promoting energy efficiency, and advancements in Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate, driven by rapid urbanization and infrastructure development in countries like China and India.
Key segments within the smart building market include energy management systems, security and access control, lighting control, HVAC control, and others. Among these, energy management systems are anticipated to hold the largest market share due to the growing emphasis on reducing energy consumption and operational costs in buildings. The integration of AMOLED technology is particularly relevant in the lighting control and information display segments, where its superior visual quality and energy efficiency can contribute significantly to overall building performance.
The adoption of AMOLED in smart architecture faces both opportunities and challenges. On the one hand, the technology's ability to provide high-quality, customizable displays with low power consumption aligns well with the goals of sustainable smart buildings. On the other hand, factors such as higher initial costs and the need for specialized expertise in implementation may slow down widespread adoption. However, as production scales up and technology matures, these barriers are expected to diminish over time.
Looking ahead, the integration of AMOLED technology in smart buildings is likely to play a crucial role in enhancing user experience, improving energy efficiency, and enabling more sophisticated building management systems. As the market continues to evolve, collaborations between technology providers, architects, and building developers will be essential to fully realize the potential of AMOLED in creating sustainable and intelligent architectural solutions.
The integration of AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology into smart architecture represents a promising avenue for sustainable development. AMOLED displays offer several advantages over traditional lighting and display technologies, including higher energy efficiency, improved color accuracy, and greater flexibility in design. These characteristics make AMOLED an attractive option for smart building applications, particularly in areas such as lighting control, information displays, and interactive surfaces.
Market research indicates that the global smart building market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10% in the coming years. This growth is fueled by factors such as increasing awareness of environmental issues, government regulations promoting energy efficiency, and advancements in Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate, driven by rapid urbanization and infrastructure development in countries like China and India.
Key segments within the smart building market include energy management systems, security and access control, lighting control, HVAC control, and others. Among these, energy management systems are anticipated to hold the largest market share due to the growing emphasis on reducing energy consumption and operational costs in buildings. The integration of AMOLED technology is particularly relevant in the lighting control and information display segments, where its superior visual quality and energy efficiency can contribute significantly to overall building performance.
The adoption of AMOLED in smart architecture faces both opportunities and challenges. On the one hand, the technology's ability to provide high-quality, customizable displays with low power consumption aligns well with the goals of sustainable smart buildings. On the other hand, factors such as higher initial costs and the need for specialized expertise in implementation may slow down widespread adoption. However, as production scales up and technology matures, these barriers are expected to diminish over time.
Looking ahead, the integration of AMOLED technology in smart buildings is likely to play a crucial role in enhancing user experience, improving energy efficiency, and enabling more sophisticated building management systems. As the market continues to evolve, collaborations between technology providers, architects, and building developers will be essential to fully realize the potential of AMOLED in creating sustainable and intelligent architectural solutions.
AMOLED Technology: Current State and Challenges
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has made significant strides in recent years, revolutionizing display technology across various industries. In the context of sustainable smart architecture, AMOLED displays offer unique advantages and face specific challenges that warrant careful consideration.
The current state of AMOLED technology is characterized by its superior image quality, energy efficiency, and flexibility. These displays provide vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and wide viewing angles, making them ideal for architectural applications where visual impact is crucial. The self-emissive nature of AMOLED pixels eliminates the need for backlighting, resulting in thinner and more energy-efficient displays compared to traditional LCD technology.
In smart architecture, AMOLED displays are being integrated into building facades, interior walls, and interactive surfaces. They offer the potential to create dynamic, responsive environments that can adapt to changing conditions and user needs. The technology's low power consumption aligns well with sustainable building practices, contributing to reduced energy usage in smart buildings.
However, AMOLED technology faces several challenges in the context of sustainable smart architecture. Durability and lifespan remain concerns, particularly in outdoor applications where displays are exposed to harsh environmental conditions. The organic materials used in AMOLED displays are susceptible to degradation from UV light and moisture, which can lead to reduced performance and shortened lifespans.
Another significant challenge is the cost of large-scale AMOLED displays. While prices have decreased over time, implementing expansive AMOLED surfaces in buildings still represents a substantial investment. This cost factor can limit widespread adoption in architectural projects, especially those with tight budgets.
Heat management is also a critical issue for AMOLED displays in architectural applications. As these displays generate heat during operation, integrating effective cooling systems without compromising the aesthetics or energy efficiency of the building design poses a significant engineering challenge.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of AMOLED production and disposal needs to be addressed. The manufacturing process involves rare earth elements and potentially harmful chemicals, raising concerns about sustainability and end-of-life management. Developing more eco-friendly production methods and improving recycling processes are crucial steps towards enhancing the technology's overall sustainability.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues. Innovations in materials science are yielding more durable and efficient OLED compounds, while advancements in manufacturing techniques are gradually reducing production costs. The integration of AMOLED technology with other smart building systems, such as IoT sensors and AI-driven control systems, is opening new possibilities for creating truly responsive and sustainable architectural environments.
The current state of AMOLED technology is characterized by its superior image quality, energy efficiency, and flexibility. These displays provide vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and wide viewing angles, making them ideal for architectural applications where visual impact is crucial. The self-emissive nature of AMOLED pixels eliminates the need for backlighting, resulting in thinner and more energy-efficient displays compared to traditional LCD technology.
In smart architecture, AMOLED displays are being integrated into building facades, interior walls, and interactive surfaces. They offer the potential to create dynamic, responsive environments that can adapt to changing conditions and user needs. The technology's low power consumption aligns well with sustainable building practices, contributing to reduced energy usage in smart buildings.
However, AMOLED technology faces several challenges in the context of sustainable smart architecture. Durability and lifespan remain concerns, particularly in outdoor applications where displays are exposed to harsh environmental conditions. The organic materials used in AMOLED displays are susceptible to degradation from UV light and moisture, which can lead to reduced performance and shortened lifespans.
Another significant challenge is the cost of large-scale AMOLED displays. While prices have decreased over time, implementing expansive AMOLED surfaces in buildings still represents a substantial investment. This cost factor can limit widespread adoption in architectural projects, especially those with tight budgets.
Heat management is also a critical issue for AMOLED displays in architectural applications. As these displays generate heat during operation, integrating effective cooling systems without compromising the aesthetics or energy efficiency of the building design poses a significant engineering challenge.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of AMOLED production and disposal needs to be addressed. The manufacturing process involves rare earth elements and potentially harmful chemicals, raising concerns about sustainability and end-of-life management. Developing more eco-friendly production methods and improving recycling processes are crucial steps towards enhancing the technology's overall sustainability.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues. Innovations in materials science are yielding more durable and efficient OLED compounds, while advancements in manufacturing techniques are gradually reducing production costs. The integration of AMOLED technology with other smart building systems, such as IoT sensors and AI-driven control systems, is opening new possibilities for creating truly responsive and sustainable architectural environments.
AMOLED Integration Solutions for Smart Buildings
01 AMOLED display panel structure and manufacturing
This category focuses on the structure and manufacturing processes of AMOLED display panels. It includes innovations in pixel arrangements, thin-film transistor (TFT) designs, and layer compositions to improve display performance, efficiency, and durability. Advanced manufacturing techniques are employed to enhance the overall quality and yield of AMOLED panels.- AMOLED display panel structure and manufacturing: This category focuses on the structure and manufacturing processes of AMOLED display panels. It includes innovations in pixel arrangements, thin-film transistor (TFT) designs, and layer compositions to improve display performance, efficiency, and durability. Advanced manufacturing techniques are employed to enhance the overall quality and yield of AMOLED panels.
- Driving and control methods for AMOLED displays: This point covers various driving and control methods for AMOLED displays. It includes techniques for pixel compensation, current control, and voltage regulation to improve display uniformity, reduce power consumption, and extend the lifespan of OLED devices. Advanced algorithms and circuits are developed to optimize display performance and address issues such as image sticking and color shift.
- AMOLED power management and efficiency: This category focuses on power management and efficiency improvements in AMOLED displays. It includes techniques for reducing power consumption, optimizing voltage distribution, and enhancing overall energy efficiency. Advanced power management circuits and algorithms are developed to extend battery life in mobile devices while maintaining high display quality.
- AMOLED color management and image quality enhancement: This point covers techniques for improving color management and image quality in AMOLED displays. It includes methods for color calibration, gamut expansion, and high dynamic range (HDR) implementation. Advanced algorithms are developed to enhance contrast, reduce motion blur, and improve overall visual experience on AMOLED screens.
- Integration of additional functionalities in AMOLED displays: This category focuses on integrating additional functionalities into AMOLED displays. It includes innovations such as in-display fingerprint sensors, touch sensitivity, and foldable or flexible display technologies. These advancements aim to expand the capabilities of AMOLED displays beyond traditional visual output, enhancing user interaction and device versatility.
02 Driving and control methods for AMOLED displays
This point covers various driving and control methods specifically designed for AMOLED displays. It includes techniques for pixel compensation, current control, and voltage regulation to improve image quality, reduce power consumption, and extend the lifespan of AMOLED panels. Advanced algorithms and circuit designs are implemented to address issues such as non-uniformity and degradation over time.Expand Specific Solutions03 Power management and efficiency optimization in AMOLED displays
This category focuses on power management strategies and efficiency optimization techniques for AMOLED displays. It includes innovations in power supply circuits, voltage regulation, and adaptive brightness control to reduce energy consumption while maintaining display quality. Advanced power-saving modes and intelligent dimming techniques are also explored to extend battery life in mobile devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Color management and image quality enhancement for AMOLED displays
This point covers techniques for improving color accuracy, contrast, and overall image quality in AMOLED displays. It includes color calibration methods, gamut mapping algorithms, and dynamic range enhancement techniques. Advanced image processing algorithms are implemented to optimize visual performance and address issues such as color shift and burn-in prevention.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of additional functionalities in AMOLED displays
This category explores the integration of additional functionalities within AMOLED display panels. It includes innovations such as in-display fingerprint sensors, touch sensitivity, and pressure detection. These advancements aim to enhance user interaction, improve device security, and enable new applications while maintaining the slim form factor of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions
Key AMOLED Manufacturers and Integrators
The exploration of AMOLED's role in sustainable smart architecture is at an early stage, with the market still developing. The technology's potential for energy efficiency and flexible design in buildings is driving interest, but widespread adoption remains limited. Key players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology, and LG Display are leading research and development efforts, leveraging their expertise in AMOLED display manufacturing. These companies are exploring applications such as smart windows, interactive surfaces, and energy-efficient lighting systems. While AMOLED technology shows promise for sustainable architecture, further advancements in durability, cost-effectiveness, and large-scale production are needed to accelerate market growth and integration into smart building designs.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has made significant strides in applying AMOLED technology to sustainable smart architecture. Their approach focuses on developing flexible AMOLED displays that can be curved or bent to fit various architectural designs. BOE's flexible AMOLED panels offer a thickness of less than 1mm, making them ideal for integration into building surfaces without adding significant bulk[4]. The company has also developed AMOLED displays with integrated solar cells, allowing the panels to generate their own power and reduce the overall energy consumption of smart buildings[5]. BOE's AMOLED solutions for architecture feature high refresh rates (up to 120Hz) and HDR support, ensuring smooth and vivid content display for information systems and interactive facades[6].
Strengths: Advanced flexible AMOLED technology, innovative power-generating displays, and seamless integration capabilities. Weaknesses: Limited large-scale production capacity for architectural-grade AMOLED panels and potential heat management issues in outdoor applications.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has pioneered the integration of AMOLED technology in sustainable smart architecture. Their approach involves developing energy-efficient AMOLED displays that can be seamlessly integrated into building facades and interiors. These displays utilize low-power consumption technology, reducing the overall energy footprint of smart buildings[1]. Samsung's AMOLED panels for architectural use feature high brightness levels (up to 1,500 nits) and wide color gamuts, enabling vibrant and clear information display even in bright sunlight[2]. The company has also developed transparent AMOLED displays that can be used as smart windows, allowing for dynamic control of natural light and information display without compromising the building's aesthetics[3].
Strengths: Industry-leading AMOLED technology, high energy efficiency, and innovative transparent display solutions. Weaknesses: Higher initial costs compared to traditional display technologies and potential long-term durability concerns in architectural applications.
AMOLED Innovations for Architectural Applications
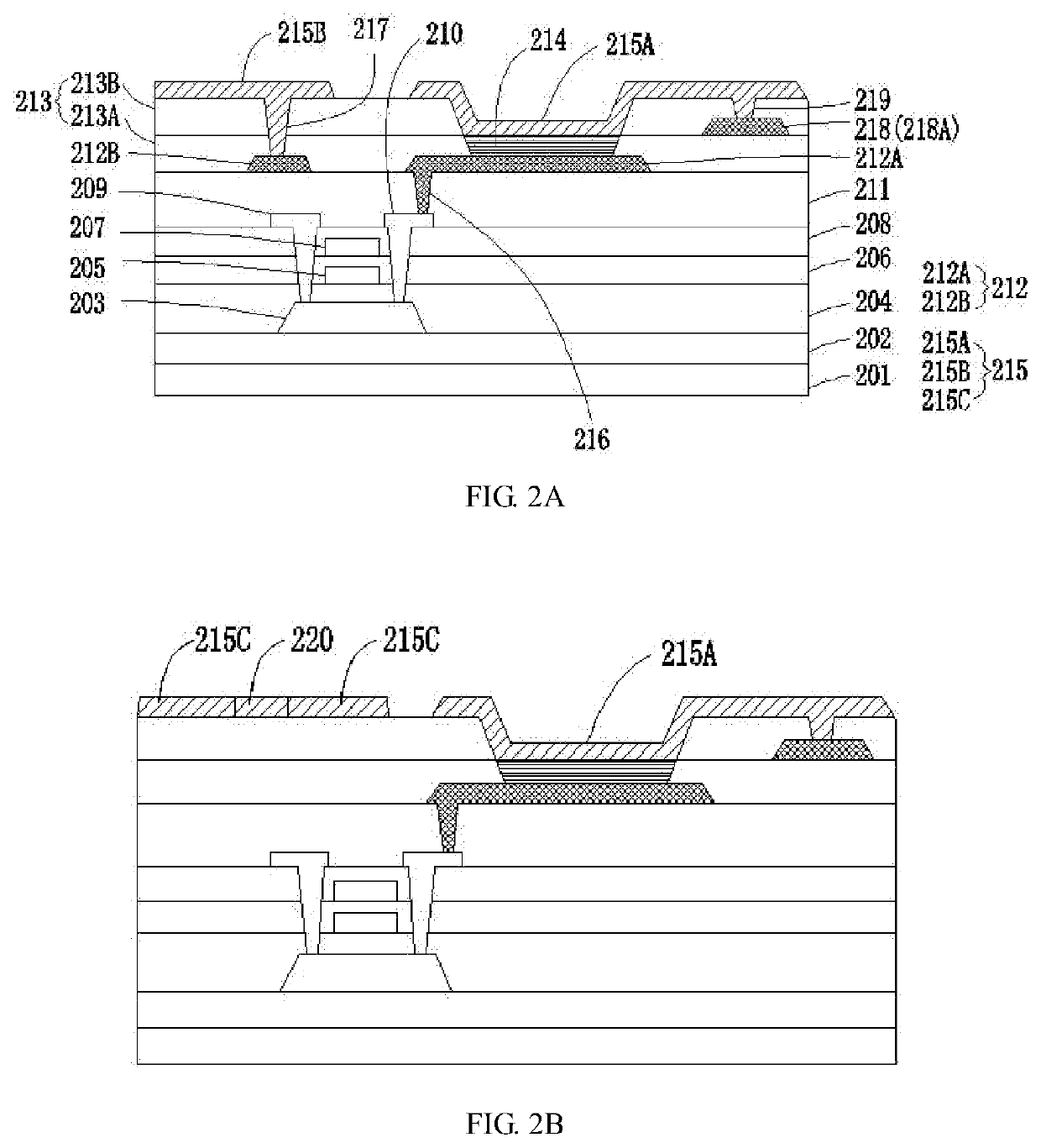
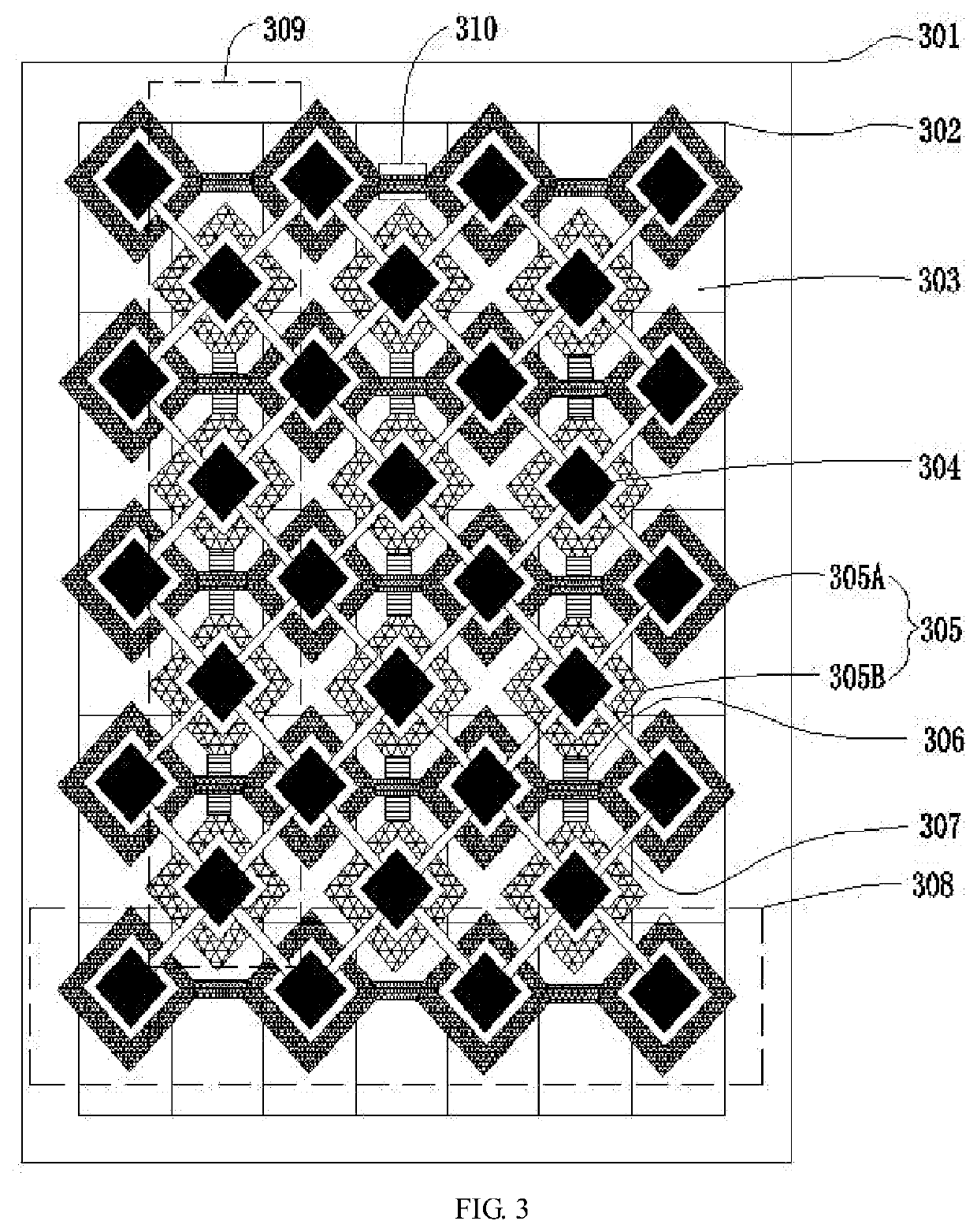
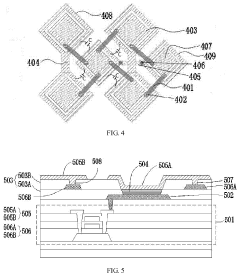
Organic light-emitting diode structure and fabrication method thereof, related display panel, and related display device
PatentWO2017070892A1
Innovation
- Development of an improved organic light-emitting diode (OLED) structure specifically addressing the issues of blue light-emitting materials.
- Implementation of a fabrication method tailored for the new OLED structure, potentially improving overall device performance.
- Integration of the new OLED structure into AMOLED display panels, potentially offering better display quality and longer device lifespan.
Active matrix organic light emitting diode (amoled) display panel
PatentInactiveUS20210343972A1
Innovation
- The integration of sensing electrodes into the AMOLED display panel allows for underscreen fingerprint identification, utilizing a patterned cathode layer with insulated first and second electrode rows and conductive bridges to form capacitors for fingerprint recognition, thereby embedding fingerprint identification within the screen and increasing the display area ratio.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Impact
AMOLED technology plays a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability in smart architecture. The integration of AMOLED displays in building systems offers significant advantages in terms of power consumption and environmental impact.
AMOLED screens consume less energy compared to traditional LCD displays, particularly when displaying darker content. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in smart building applications, where information displays are often required to operate continuously. The reduced power consumption translates directly into lower energy bills and decreased carbon footprint for buildings equipped with AMOLED-based smart systems.
Furthermore, AMOLED displays offer superior brightness and contrast ratios, allowing for better visibility in various lighting conditions. This feature enables architects and designers to create more effective and engaging information displays within buildings, potentially reducing the need for additional lighting and further contributing to energy savings.
The thin and flexible nature of AMOLED panels also contributes to sustainability in smart architecture. These displays can be seamlessly integrated into building surfaces, reducing the need for separate mounting hardware and minimizing material usage. This integration can lead to more streamlined and aesthetically pleasing designs while also reducing the overall environmental impact of construction.
AMOLED technology's long lifespan and durability further enhance its sustainability credentials. With proper implementation, AMOLED displays can operate efficiently for extended periods, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated electronic waste. This longevity aligns well with the principles of sustainable architecture, which emphasize the importance of using long-lasting, low-maintenance materials and technologies.
In the context of smart buildings, AMOLED displays can be utilized for various applications that contribute to overall energy efficiency. For instance, they can be used in smart energy management systems, providing real-time feedback on energy consumption and encouraging more sustainable behavior among building occupants. Additionally, AMOLED panels can be employed in adaptive façade systems, adjusting transparency or displaying information to optimize natural lighting and thermal management within the building.
The sustainability impact of AMOLED technology extends beyond energy efficiency. The production processes for AMOLED displays have been continuously improved, with manufacturers focusing on reducing harmful chemicals and increasing the use of recyclable materials. This trend aligns with the growing emphasis on circular economy principles in sustainable architecture, where the entire lifecycle of building components is considered.
AMOLED screens consume less energy compared to traditional LCD displays, particularly when displaying darker content. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in smart building applications, where information displays are often required to operate continuously. The reduced power consumption translates directly into lower energy bills and decreased carbon footprint for buildings equipped with AMOLED-based smart systems.
Furthermore, AMOLED displays offer superior brightness and contrast ratios, allowing for better visibility in various lighting conditions. This feature enables architects and designers to create more effective and engaging information displays within buildings, potentially reducing the need for additional lighting and further contributing to energy savings.
The thin and flexible nature of AMOLED panels also contributes to sustainability in smart architecture. These displays can be seamlessly integrated into building surfaces, reducing the need for separate mounting hardware and minimizing material usage. This integration can lead to more streamlined and aesthetically pleasing designs while also reducing the overall environmental impact of construction.
AMOLED technology's long lifespan and durability further enhance its sustainability credentials. With proper implementation, AMOLED displays can operate efficiently for extended periods, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated electronic waste. This longevity aligns well with the principles of sustainable architecture, which emphasize the importance of using long-lasting, low-maintenance materials and technologies.
In the context of smart buildings, AMOLED displays can be utilized for various applications that contribute to overall energy efficiency. For instance, they can be used in smart energy management systems, providing real-time feedback on energy consumption and encouraging more sustainable behavior among building occupants. Additionally, AMOLED panels can be employed in adaptive façade systems, adjusting transparency or displaying information to optimize natural lighting and thermal management within the building.
The sustainability impact of AMOLED technology extends beyond energy efficiency. The production processes for AMOLED displays have been continuously improved, with manufacturers focusing on reducing harmful chemicals and increasing the use of recyclable materials. This trend aligns with the growing emphasis on circular economy principles in sustainable architecture, where the entire lifecycle of building components is considered.
Regulatory Framework for Smart Building Technologies
The regulatory framework for smart building technologies plays a crucial role in shaping the integration of AMOLED displays into sustainable smart architecture. As governments and international organizations increasingly recognize the importance of energy efficiency and sustainability in the built environment, they are developing and implementing regulations that directly impact the adoption of smart technologies, including AMOLED displays.
One of the key aspects of the regulatory framework is the establishment of energy efficiency standards for buildings. Many countries have introduced building codes and regulations that mandate minimum energy performance requirements for new constructions and renovations. These standards often include provisions for smart building technologies, creating opportunities for AMOLED displays to contribute to energy savings through their low power consumption and high efficiency.
Environmental regulations also influence the adoption of AMOLED technology in smart architecture. Policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable practices in the construction industry indirectly support the use of energy-efficient technologies like AMOLED displays. These regulations may include incentives for buildings that incorporate smart, energy-saving features, further driving the demand for advanced display technologies.
Data privacy and security regulations are another critical component of the regulatory framework for smart building technologies. As AMOLED displays in smart architecture often serve as interfaces for building management systems and collect user data, they must comply with strict data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States.
Building safety codes and standards also impact the integration of AMOLED displays in smart architecture. Regulations regarding fire safety, electrical systems, and structural integrity must be considered when incorporating these displays into building designs. Manufacturers and architects must ensure that AMOLED installations meet all relevant safety requirements and do not compromise the overall safety of the building.
Furthermore, accessibility regulations play a significant role in shaping the design and implementation of AMOLED displays in smart buildings. Many countries have laws requiring that public buildings and spaces be accessible to individuals with disabilities. This necessitates careful consideration of display placement, interface design, and interaction methods to ensure that AMOLED-based smart building features are usable by all occupants.
As the field of smart architecture continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are working to keep pace with technological advancements. This includes developing new standards and guidelines specifically tailored to emerging technologies like AMOLED displays in building applications. These regulations aim to balance innovation with safety, privacy, and sustainability concerns, creating a framework that supports the responsible integration of AMOLED technology into the built environment.
One of the key aspects of the regulatory framework is the establishment of energy efficiency standards for buildings. Many countries have introduced building codes and regulations that mandate minimum energy performance requirements for new constructions and renovations. These standards often include provisions for smart building technologies, creating opportunities for AMOLED displays to contribute to energy savings through their low power consumption and high efficiency.
Environmental regulations also influence the adoption of AMOLED technology in smart architecture. Policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable practices in the construction industry indirectly support the use of energy-efficient technologies like AMOLED displays. These regulations may include incentives for buildings that incorporate smart, energy-saving features, further driving the demand for advanced display technologies.
Data privacy and security regulations are another critical component of the regulatory framework for smart building technologies. As AMOLED displays in smart architecture often serve as interfaces for building management systems and collect user data, they must comply with strict data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States.
Building safety codes and standards also impact the integration of AMOLED displays in smart architecture. Regulations regarding fire safety, electrical systems, and structural integrity must be considered when incorporating these displays into building designs. Manufacturers and architects must ensure that AMOLED installations meet all relevant safety requirements and do not compromise the overall safety of the building.
Furthermore, accessibility regulations play a significant role in shaping the design and implementation of AMOLED displays in smart buildings. Many countries have laws requiring that public buildings and spaces be accessible to individuals with disabilities. This necessitates careful consideration of display placement, interface design, and interaction methods to ensure that AMOLED-based smart building features are usable by all occupants.
As the field of smart architecture continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are working to keep pace with technological advancements. This includes developing new standards and guidelines specifically tailored to emerging technologies like AMOLED displays in building applications. These regulations aim to balance innovation with safety, privacy, and sustainability concerns, creating a framework that supports the responsible integration of AMOLED technology into the built environment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!