How AMOLED mitigates electrostatic discharge in electronics?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED ESD Mitigation Background and Objectives
Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode (AMOLED) technology has revolutionized the display industry, offering superior image quality, energy efficiency, and flexibility. However, as with all electronic components, AMOLED displays are susceptible to electrostatic discharge (ESD), which can cause significant damage and malfunction. This report aims to explore the background of AMOLED technology and its vulnerability to ESD, as well as the objectives for mitigating these risks.
AMOLED displays have evolved from their predecessor, OLED technology, which was first developed in the 1980s. The addition of an active matrix of thin-film transistors (TFTs) to control individual pixels has greatly enhanced display performance and enabled the creation of larger, higher-resolution screens. As AMOLED technology has advanced, it has become increasingly prevalent in smartphones, tablets, televisions, and wearable devices.
The susceptibility of AMOLED displays to ESD is a critical concern for manufacturers and users alike. ESD events can occur during manufacturing, assembly, or end-user handling, potentially causing immediate failure or long-term reliability issues. The organic materials used in AMOLED displays are particularly sensitive to electrical stress, making ESD protection a paramount consideration in device design and production.
The primary objective of ESD mitigation in AMOLED technology is to protect the delicate organic layers and TFTs from damage caused by sudden electrical discharges. This involves developing robust protection circuits, implementing effective grounding strategies, and utilizing materials with enhanced ESD resistance properties. Additionally, manufacturers aim to create ESD mitigation solutions that do not compromise the display's performance, aesthetics, or form factor.
Another key objective is to establish comprehensive ESD control protocols throughout the entire lifecycle of AMOLED devices. This includes implementing stringent ESD prevention measures during manufacturing and assembly processes, as well as educating end-users on proper handling techniques to minimize the risk of ESD-related failures in the field.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, researchers and engineers are focusing on developing innovative ESD mitigation strategies that can keep pace with advancements in display performance and form factor. This includes exploring new materials, circuit designs, and manufacturing techniques that can enhance ESD protection while maintaining the inherent advantages of AMOLED displays.
The pursuit of effective ESD mitigation in AMOLED technology is driven by the need to ensure product reliability, reduce manufacturing costs associated with ESD-related failures, and maintain consumer confidence in AMOLED-equipped devices. As such, this field of study represents a critical area of research and development within the broader context of display technology advancement.
AMOLED displays have evolved from their predecessor, OLED technology, which was first developed in the 1980s. The addition of an active matrix of thin-film transistors (TFTs) to control individual pixels has greatly enhanced display performance and enabled the creation of larger, higher-resolution screens. As AMOLED technology has advanced, it has become increasingly prevalent in smartphones, tablets, televisions, and wearable devices.
The susceptibility of AMOLED displays to ESD is a critical concern for manufacturers and users alike. ESD events can occur during manufacturing, assembly, or end-user handling, potentially causing immediate failure or long-term reliability issues. The organic materials used in AMOLED displays are particularly sensitive to electrical stress, making ESD protection a paramount consideration in device design and production.
The primary objective of ESD mitigation in AMOLED technology is to protect the delicate organic layers and TFTs from damage caused by sudden electrical discharges. This involves developing robust protection circuits, implementing effective grounding strategies, and utilizing materials with enhanced ESD resistance properties. Additionally, manufacturers aim to create ESD mitigation solutions that do not compromise the display's performance, aesthetics, or form factor.
Another key objective is to establish comprehensive ESD control protocols throughout the entire lifecycle of AMOLED devices. This includes implementing stringent ESD prevention measures during manufacturing and assembly processes, as well as educating end-users on proper handling techniques to minimize the risk of ESD-related failures in the field.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, researchers and engineers are focusing on developing innovative ESD mitigation strategies that can keep pace with advancements in display performance and form factor. This includes exploring new materials, circuit designs, and manufacturing techniques that can enhance ESD protection while maintaining the inherent advantages of AMOLED displays.
The pursuit of effective ESD mitigation in AMOLED technology is driven by the need to ensure product reliability, reduce manufacturing costs associated with ESD-related failures, and maintain consumer confidence in AMOLED-equipped devices. As such, this field of study represents a critical area of research and development within the broader context of display technology advancement.
Market Demand for ESD-Resistant AMOLED Displays
The market demand for ESD-resistant AMOLED displays has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing adoption of AMOLED technology in various electronic devices and the critical need for improved durability and reliability. As consumer electronics become more sophisticated and integrated into daily life, the risk of electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage has become a significant concern for manufacturers and end-users alike.
AMOLED displays are particularly vulnerable to ESD due to their thin-film transistor (TFT) structure and sensitive organic materials. ESD events can cause immediate failure or long-term degradation of display performance, leading to costly repairs or replacements. This vulnerability has created a strong market pull for ESD-resistant AMOLED solutions across multiple industries.
In the smartphone sector, which represents the largest market for AMOLED displays, manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing ESD resistance as a key feature. High-end smartphones, which often incorporate cutting-edge AMOLED technology, are especially at risk due to their premium pricing and consumer expectations for longevity. The demand for ESD-resistant AMOLED displays in this segment is expected to grow significantly as manufacturers seek to differentiate their products and reduce warranty claims.
The automotive industry is another major driver of demand for ESD-resistant AMOLED displays. As vehicles become more electrified and incorporate larger, more advanced infotainment systems, the need for robust display technologies has intensified. ESD protection is crucial in automotive environments due to the presence of various electrical systems and the potential for static buildup in different weather conditions.
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, represent a rapidly growing market segment for ESD-resistant AMOLED displays. These devices are frequently exposed to static electricity through contact with clothing and skin, making ESD protection essential for ensuring product reliability and user satisfaction.
The industrial and medical sectors are also contributing to the increased demand for ESD-resistant AMOLED displays. In industrial settings, where electronic equipment may be exposed to harsh environments and frequent human interaction, ESD protection is critical for maintaining operational continuity. Similarly, in medical devices, where display reliability can directly impact patient care, the demand for ESD-resistant AMOLED technology is on the rise.
Market analysts project that the global demand for ESD-resistant AMOLED displays will continue to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding that of standard AMOLED displays. This trend is expected to drive innovation in ESD mitigation technologies and materials, potentially leading to new market opportunities for suppliers and manufacturers specializing in ESD protection solutions for AMOLED displays.
AMOLED displays are particularly vulnerable to ESD due to their thin-film transistor (TFT) structure and sensitive organic materials. ESD events can cause immediate failure or long-term degradation of display performance, leading to costly repairs or replacements. This vulnerability has created a strong market pull for ESD-resistant AMOLED solutions across multiple industries.
In the smartphone sector, which represents the largest market for AMOLED displays, manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing ESD resistance as a key feature. High-end smartphones, which often incorporate cutting-edge AMOLED technology, are especially at risk due to their premium pricing and consumer expectations for longevity. The demand for ESD-resistant AMOLED displays in this segment is expected to grow significantly as manufacturers seek to differentiate their products and reduce warranty claims.
The automotive industry is another major driver of demand for ESD-resistant AMOLED displays. As vehicles become more electrified and incorporate larger, more advanced infotainment systems, the need for robust display technologies has intensified. ESD protection is crucial in automotive environments due to the presence of various electrical systems and the potential for static buildup in different weather conditions.
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, represent a rapidly growing market segment for ESD-resistant AMOLED displays. These devices are frequently exposed to static electricity through contact with clothing and skin, making ESD protection essential for ensuring product reliability and user satisfaction.
The industrial and medical sectors are also contributing to the increased demand for ESD-resistant AMOLED displays. In industrial settings, where electronic equipment may be exposed to harsh environments and frequent human interaction, ESD protection is critical for maintaining operational continuity. Similarly, in medical devices, where display reliability can directly impact patient care, the demand for ESD-resistant AMOLED technology is on the rise.
Market analysts project that the global demand for ESD-resistant AMOLED displays will continue to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding that of standard AMOLED displays. This trend is expected to drive innovation in ESD mitigation technologies and materials, potentially leading to new market opportunities for suppliers and manufacturers specializing in ESD protection solutions for AMOLED displays.
Current ESD Challenges in AMOLED Technology
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) poses significant challenges for AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology in modern electronics. As AMOLED displays become increasingly prevalent in smartphones, tablets, and other devices, the need to address ESD-related issues has become more critical than ever.
One of the primary ESD challenges in AMOLED technology is the susceptibility of organic materials to damage from electrostatic discharge. The thin-film transistors and organic light-emitting layers in AMOLED displays are particularly vulnerable to ESD events, which can lead to pixel defects, display malfunctions, or even complete device failure.
Another major concern is the impact of ESD on the overall lifespan and reliability of AMOLED displays. Repeated exposure to ESD events, even at low levels, can gradually degrade the performance of organic materials and thin-film transistors, leading to reduced brightness, color accuracy, and overall display quality over time.
The miniaturization trend in electronics further exacerbates ESD challenges for AMOLED technology. As devices become thinner and more compact, the space available for implementing traditional ESD protection measures becomes limited. This constraint necessitates the development of novel, space-efficient ESD mitigation strategies specifically tailored for AMOLED displays.
Manufacturing processes for AMOLED displays also present unique ESD challenges. The production of these displays involves multiple steps, including the deposition of organic materials and the fabrication of thin-film transistors. Each of these processes can generate static electricity, increasing the risk of ESD events during manufacturing and potentially impacting yield rates.
The integration of touch functionality into AMOLED displays introduces additional ESD concerns. The close proximity of touch sensors to the display elements creates new pathways for electrostatic discharge, requiring careful consideration of ESD protection measures that do not interfere with touch sensitivity or display performance.
Environmental factors also play a role in ESD challenges for AMOLED technology. Variations in humidity and temperature can affect the accumulation and dissipation of static charges, making it necessary to design ESD protection solutions that remain effective across a wide range of operating conditions.
As AMOLED displays continue to evolve, incorporating features such as flexible and foldable screens, new ESD challenges emerge. These innovative form factors introduce unique stress points and potential vulnerabilities to electrostatic discharge, requiring the development of specialized ESD mitigation techniques that can adapt to dynamic display configurations.
One of the primary ESD challenges in AMOLED technology is the susceptibility of organic materials to damage from electrostatic discharge. The thin-film transistors and organic light-emitting layers in AMOLED displays are particularly vulnerable to ESD events, which can lead to pixel defects, display malfunctions, or even complete device failure.
Another major concern is the impact of ESD on the overall lifespan and reliability of AMOLED displays. Repeated exposure to ESD events, even at low levels, can gradually degrade the performance of organic materials and thin-film transistors, leading to reduced brightness, color accuracy, and overall display quality over time.
The miniaturization trend in electronics further exacerbates ESD challenges for AMOLED technology. As devices become thinner and more compact, the space available for implementing traditional ESD protection measures becomes limited. This constraint necessitates the development of novel, space-efficient ESD mitigation strategies specifically tailored for AMOLED displays.
Manufacturing processes for AMOLED displays also present unique ESD challenges. The production of these displays involves multiple steps, including the deposition of organic materials and the fabrication of thin-film transistors. Each of these processes can generate static electricity, increasing the risk of ESD events during manufacturing and potentially impacting yield rates.
The integration of touch functionality into AMOLED displays introduces additional ESD concerns. The close proximity of touch sensors to the display elements creates new pathways for electrostatic discharge, requiring careful consideration of ESD protection measures that do not interfere with touch sensitivity or display performance.
Environmental factors also play a role in ESD challenges for AMOLED technology. Variations in humidity and temperature can affect the accumulation and dissipation of static charges, making it necessary to design ESD protection solutions that remain effective across a wide range of operating conditions.
As AMOLED displays continue to evolve, incorporating features such as flexible and foldable screens, new ESD challenges emerge. These innovative form factors introduce unique stress points and potential vulnerabilities to electrostatic discharge, requiring the development of specialized ESD mitigation techniques that can adapt to dynamic display configurations.
Existing ESD Mitigation Solutions for AMOLED
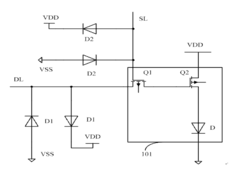
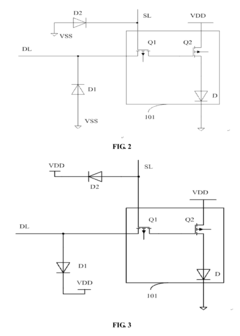
01 ESD protection circuits for AMOLED displays
Specialized circuits are designed to protect AMOLED displays from electrostatic discharge. These circuits typically include components such as diodes, transistors, and resistors to divert excess charge away from sensitive display elements, preventing damage to the organic light-emitting materials and thin-film transistors.- ESD protection circuits for AMOLED displays: Specialized circuits are designed to protect AMOLED displays from electrostatic discharge. These circuits typically include components such as diodes, transistors, and resistors to divert excess charge away from sensitive display elements, preventing damage to the organic light-emitting materials and thin-film transistors.
- Substrate and layer design for ESD mitigation: The structure and composition of AMOLED display substrates and layers are engineered to minimize the risk of electrostatic discharge. This includes the use of conductive or semi-conductive materials in specific layers, as well as the implementation of charge dissipation structures within the display stack.
- Touch panel integration with ESD considerations: When integrating touch functionality with AMOLED displays, special attention is given to ESD protection. This involves designing touch sensors and their associated circuitry to be resistant to electrostatic discharge while maintaining display performance and touch sensitivity.
- Manufacturing processes to reduce ESD risk: Specific manufacturing techniques and processes are employed to minimize the risk of electrostatic discharge during AMOLED display production. This includes the use of ionizers, conductive work surfaces, and specialized handling procedures to prevent charge accumulation and discharge events during fabrication and assembly.
- Testing and quality control for ESD resistance: Rigorous testing and quality control procedures are implemented to ensure AMOLED displays meet ESD resistance standards. This involves subjecting displays to controlled electrostatic discharge events and evaluating their performance and durability under various conditions to validate the effectiveness of protection measures.
02 Integration of ESD protection in AMOLED pixel circuits
ESD protection features are incorporated directly into AMOLED pixel circuits. This approach involves modifying the pixel circuit design to include protective elements that can absorb or redirect electrostatic charge, ensuring the integrity of individual pixels and the overall display performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Substrate-level ESD protection for AMOLED panels
ESD protection mechanisms are implemented at the substrate level of AMOLED panels. This involves incorporating conductive layers or patterns within the display substrate to create discharge paths for static electricity, protecting the entire panel from ESD events during manufacturing and operation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advanced materials for ESD mitigation in AMOLED displays
Novel materials are developed and utilized to enhance ESD protection in AMOLED displays. These materials may include conductive polymers, nanocomposites, or specially engineered thin films that can effectively dissipate static charge while maintaining the optical and electrical properties required for high-performance displays.Expand Specific Solutions05 Testing and quality control methods for ESD resistance in AMOLED production
Specialized testing procedures and quality control methods are developed to assess and ensure the ESD resistance of AMOLED displays during production. These may include automated testing equipment, simulation techniques, and standardized protocols to verify the effectiveness of ESD protection measures and identify potential vulnerabilities in the display design.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in AMOLED and ESD Protection Industries
The AMOLED technology for mitigating electrostatic discharge in electronics is in a mature development stage, with significant market growth and widespread adoption. The global AMOLED market size is projected to reach billions of dollars, driven by increasing demand in smartphones, wearables, and automotive displays. Major players like Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE Technology have achieved high technical maturity in AMOLED production, with advanced ESD protection mechanisms integrated into their display panels. Companies such as Tianma Microelectronics and Everdisplay Optronics are also making strides in AMOLED technology, focusing on improving ESD resilience and overall display performance. The competitive landscape is characterized by continuous innovation and investment in research and development to enhance AMOLED's ESD mitigation capabilities.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed several strategies to mitigate ESD in their AMOLED displays. They utilize a multi-layer protection scheme that includes conductive layers strategically placed within the display stack[7]. These layers help to dissipate static charges before they can damage sensitive components. BOE has also implemented advanced TFT designs with built-in ESD protection circuits, similar to those used by Samsung Display[8]. Additionally, BOE employs specialized edge sealing techniques that not only protect against environmental factors but also serve as an ESD barrier. The company has invested in developing flexible AMOLED displays with inherent ESD resistance, achieved through the use of novel materials and structural designs that allow for better charge distribution[9].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, diverse range of AMOLED products with integrated ESD protection. Weaknesses: May lag behind some competitors in cutting-edge AMOLED technologies.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed advanced AMOLED technologies to mitigate electrostatic discharge (ESD) in electronics. Their approach includes implementing on-cell touch AMOLED displays with built-in ESD protection layers[1]. These layers consist of conductive materials that can safely dissipate static charges before they reach sensitive components. Additionally, Samsung utilizes advanced thin-film encapsulation (TFE) technology, which not only protects AMOLED displays from moisture and oxygen but also serves as an additional barrier against ESD[2]. The company has also introduced flexible AMOLED displays with integrated ESD protection, allowing for better charge distribution across the panel surface[3].
Strengths: Industry-leading AMOLED technology, comprehensive ESD protection integrated into display design. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs, complexity in manufacturing process.
Core Innovations in AMOLED ESD Protection
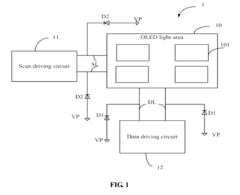
Display panel and electronic device with electrostatic discharge protection function
PatentInactiveUS20160098953A1
Innovation
- Incorporating organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) as ESD protection elements, connected via scan and data lines to prevent electrostatic discharge by reverse breakdown, eliminating the need for specialized MOS FETs.
Array substrate, display device, and method for manufacturing array substrate
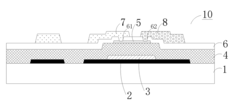
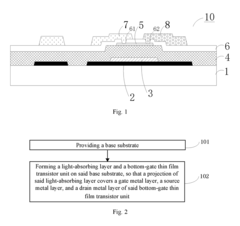
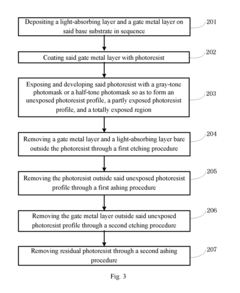
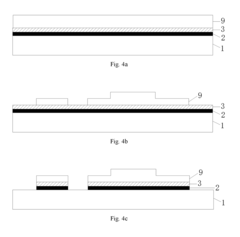
PatentActiveUS20170148862A1
Innovation
- An array substrate with a light-absorbing layer covering the gate, source, and drain metal layers of a bottom-gate thin film transistor unit, preventing ambient light irradiation while allowing useful light to pass through.
Environmental Impact of ESD Protection Materials
The environmental impact of ESD protection materials used in AMOLED displays is a critical consideration in the electronics industry. These materials, while essential for mitigating electrostatic discharge, can have significant ecological implications throughout their lifecycle. The production of ESD protection materials often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals, contributing to carbon emissions and environmental pollution.
Many ESD protection materials used in AMOLED displays contain heavy metals or toxic substances that can pose risks to ecosystems if not properly managed at the end of the product's life. The disposal of electronic waste containing these materials can lead to soil and water contamination if not handled correctly. This is particularly concerning in regions with inadequate e-waste management infrastructure.
However, the electronics industry has been making strides in developing more environmentally friendly ESD protection solutions for AMOLED displays. Some manufacturers are exploring bio-based and biodegradable materials that offer comparable ESD protection while reducing the environmental footprint. These innovative materials aim to minimize the use of harmful substances and improve the recyclability of electronic components.
The longevity of ESD protection materials in AMOLED displays also plays a role in their environmental impact. Materials that provide durable protection can extend the lifespan of electronic devices, reducing the frequency of replacements and, consequently, the overall e-waste generated. This aspect highlights the importance of balancing immediate environmental concerns with long-term sustainability in material selection.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the environmental aspects of electronic components, including ESD protection materials. This has led to the development of stricter guidelines for material composition and disposal practices. Manufacturers are now required to consider the entire lifecycle of their products, from sourcing raw materials to end-of-life management, which is driving innovation in more sustainable ESD protection solutions for AMOLED displays.
The recycling and recovery of ESD protection materials from AMOLED displays present both challenges and opportunities. While some materials can be reclaimed and reused, others may require specialized processing to prevent environmental contamination. Advancements in recycling technologies are crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of these materials and promoting a circular economy in the electronics industry.
Many ESD protection materials used in AMOLED displays contain heavy metals or toxic substances that can pose risks to ecosystems if not properly managed at the end of the product's life. The disposal of electronic waste containing these materials can lead to soil and water contamination if not handled correctly. This is particularly concerning in regions with inadequate e-waste management infrastructure.
However, the electronics industry has been making strides in developing more environmentally friendly ESD protection solutions for AMOLED displays. Some manufacturers are exploring bio-based and biodegradable materials that offer comparable ESD protection while reducing the environmental footprint. These innovative materials aim to minimize the use of harmful substances and improve the recyclability of electronic components.
The longevity of ESD protection materials in AMOLED displays also plays a role in their environmental impact. Materials that provide durable protection can extend the lifespan of electronic devices, reducing the frequency of replacements and, consequently, the overall e-waste generated. This aspect highlights the importance of balancing immediate environmental concerns with long-term sustainability in material selection.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the environmental aspects of electronic components, including ESD protection materials. This has led to the development of stricter guidelines for material composition and disposal practices. Manufacturers are now required to consider the entire lifecycle of their products, from sourcing raw materials to end-of-life management, which is driving innovation in more sustainable ESD protection solutions for AMOLED displays.
The recycling and recovery of ESD protection materials from AMOLED displays present both challenges and opportunities. While some materials can be reclaimed and reused, others may require specialized processing to prevent environmental contamination. Advancements in recycling technologies are crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of these materials and promoting a circular economy in the electronics industry.
Reliability Testing Standards for AMOLED ESD Resistance
Reliability testing standards for AMOLED ESD resistance play a crucial role in ensuring the durability and performance of AMOLED displays in electronic devices. These standards are designed to evaluate the ability of AMOLED panels to withstand electrostatic discharge events, which can potentially damage or degrade the display's functionality.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has established specific standards for ESD testing of electronic components, including AMOLED displays. The IEC 61000-4-2 standard is widely used for ESD immunity testing, providing guidelines for both contact discharge and air discharge tests. For AMOLED displays, manufacturers typically conduct tests at various voltage levels, ranging from 2 kV to 8 kV, to assess the panel's resilience against ESD events.
In addition to IEC standards, the Joint Electron Device Engineering Council (JEDEC) has developed the JESD22-A114 standard, which outlines procedures for human body model (HBM) ESD testing. This standard is particularly relevant for AMOLED displays, as it simulates the ESD events that may occur during human interaction with electronic devices.
To ensure comprehensive ESD protection, AMOLED manufacturers often incorporate multiple testing methodologies. These may include the charged device model (CDM) and machine model (MM) tests, which simulate different ESD scenarios that AMOLED displays might encounter during production, assembly, or use.
Reliability testing for AMOLED ESD resistance typically involves subjecting the display panels to repeated ESD pulses at various voltage levels and discharge points. The tests evaluate both the immediate effects of ESD events and the long-term impact on display performance. Key parameters monitored during these tests include pixel functionality, color accuracy, brightness uniformity, and overall display integrity.
Many AMOLED manufacturers have developed proprietary testing protocols that go beyond industry standards to address specific challenges related to their display technologies. These may include custom test fixtures, specialized discharge waveforms, or extended testing durations to simulate real-world usage scenarios more accurately.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, reliability testing standards are also adapting to address new challenges. For instance, the increasing use of flexible and foldable AMOLED displays has led to the development of modified testing procedures that account for the unique physical properties and potential vulnerabilities of these innovative form factors.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has established specific standards for ESD testing of electronic components, including AMOLED displays. The IEC 61000-4-2 standard is widely used for ESD immunity testing, providing guidelines for both contact discharge and air discharge tests. For AMOLED displays, manufacturers typically conduct tests at various voltage levels, ranging from 2 kV to 8 kV, to assess the panel's resilience against ESD events.
In addition to IEC standards, the Joint Electron Device Engineering Council (JEDEC) has developed the JESD22-A114 standard, which outlines procedures for human body model (HBM) ESD testing. This standard is particularly relevant for AMOLED displays, as it simulates the ESD events that may occur during human interaction with electronic devices.
To ensure comprehensive ESD protection, AMOLED manufacturers often incorporate multiple testing methodologies. These may include the charged device model (CDM) and machine model (MM) tests, which simulate different ESD scenarios that AMOLED displays might encounter during production, assembly, or use.
Reliability testing for AMOLED ESD resistance typically involves subjecting the display panels to repeated ESD pulses at various voltage levels and discharge points. The tests evaluate both the immediate effects of ESD events and the long-term impact on display performance. Key parameters monitored during these tests include pixel functionality, color accuracy, brightness uniformity, and overall display integrity.
Many AMOLED manufacturers have developed proprietary testing protocols that go beyond industry standards to address specific challenges related to their display technologies. These may include custom test fixtures, specialized discharge waveforms, or extended testing durations to simulate real-world usage scenarios more accurately.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, reliability testing standards are also adapting to address new challenges. For instance, the increasing use of flexible and foldable AMOLED displays has led to the development of modified testing procedures that account for the unique physical properties and potential vulnerabilities of these innovative form factors.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!