Research potential of carbon-neutral AMOLED electronics.
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Carbon Neutrality: Background and Objectives
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has revolutionized the display industry with its superior image quality, energy efficiency, and flexibility. As global concerns about climate change intensify, the electronics industry faces increasing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint. This has led to a growing interest in developing carbon-neutral AMOLED electronics.
The concept of carbon neutrality in AMOLED electronics encompasses the entire lifecycle of these devices, from manufacturing to disposal. It involves minimizing greenhouse gas emissions during production, optimizing energy consumption during use, and implementing effective recycling and waste management strategies. The ultimate goal is to achieve a net-zero carbon impact across the entire value chain of AMOLED products.
The evolution of AMOLED technology has been marked by continuous improvements in efficiency and performance. Early AMOLED displays suffered from high power consumption and limited lifespan. However, advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes have significantly enhanced their energy efficiency and durability. These improvements have set the stage for exploring carbon-neutral solutions in AMOLED electronics.
The push towards carbon neutrality in AMOLED technology is driven by several factors. Firstly, there is increasing regulatory pressure on electronics manufacturers to reduce their environmental impact. Many countries have introduced stringent emissions targets and sustainability regulations that directly affect the electronics industry. Secondly, consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious, creating market demand for greener electronic products.
Achieving carbon neutrality in AMOLED electronics presents both challenges and opportunities. On the technical front, researchers are exploring novel materials and manufacturing processes that can reduce energy consumption and emissions. This includes the development of more efficient organic compounds, low-temperature fabrication techniques, and advanced recycling methods for AMOLED components.
The potential benefits of carbon-neutral AMOLED electronics extend beyond environmental considerations. By improving energy efficiency and reducing waste, manufacturers can potentially lower production costs and enhance product performance. This aligns with the broader industry trend towards sustainable and circular economy principles in electronics manufacturing.
As we delve deeper into the research potential of carbon-neutral AMOLED electronics, it is crucial to consider the interdisciplinary nature of this endeavor. It requires collaboration between materials scientists, electrical engineers, environmental experts, and industry stakeholders. The path to carbon neutrality in AMOLED technology will likely involve a combination of incremental improvements in existing processes and breakthrough innovations in materials and manufacturing techniques.
The concept of carbon neutrality in AMOLED electronics encompasses the entire lifecycle of these devices, from manufacturing to disposal. It involves minimizing greenhouse gas emissions during production, optimizing energy consumption during use, and implementing effective recycling and waste management strategies. The ultimate goal is to achieve a net-zero carbon impact across the entire value chain of AMOLED products.
The evolution of AMOLED technology has been marked by continuous improvements in efficiency and performance. Early AMOLED displays suffered from high power consumption and limited lifespan. However, advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes have significantly enhanced their energy efficiency and durability. These improvements have set the stage for exploring carbon-neutral solutions in AMOLED electronics.
The push towards carbon neutrality in AMOLED technology is driven by several factors. Firstly, there is increasing regulatory pressure on electronics manufacturers to reduce their environmental impact. Many countries have introduced stringent emissions targets and sustainability regulations that directly affect the electronics industry. Secondly, consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious, creating market demand for greener electronic products.
Achieving carbon neutrality in AMOLED electronics presents both challenges and opportunities. On the technical front, researchers are exploring novel materials and manufacturing processes that can reduce energy consumption and emissions. This includes the development of more efficient organic compounds, low-temperature fabrication techniques, and advanced recycling methods for AMOLED components.
The potential benefits of carbon-neutral AMOLED electronics extend beyond environmental considerations. By improving energy efficiency and reducing waste, manufacturers can potentially lower production costs and enhance product performance. This aligns with the broader industry trend towards sustainable and circular economy principles in electronics manufacturing.
As we delve deeper into the research potential of carbon-neutral AMOLED electronics, it is crucial to consider the interdisciplinary nature of this endeavor. It requires collaboration between materials scientists, electrical engineers, environmental experts, and industry stakeholders. The path to carbon neutrality in AMOLED technology will likely involve a combination of incremental improvements in existing processes and breakthrough innovations in materials and manufacturing techniques.
Market Demand for Eco-Friendly Display Technologies
The demand for eco-friendly display technologies has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing environmental concerns and stricter regulations on carbon emissions. AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays have emerged as a promising solution in this context, offering potential for carbon-neutral electronics. The market for these environmentally conscious display technologies is expanding across various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial applications.
Consumer electronics, particularly smartphones and tablets, represent the largest market segment for eco-friendly displays. As consumers become more environmentally aware, there is a growing preference for devices with reduced carbon footprints. This shift in consumer behavior has prompted major manufacturers to invest in developing and implementing carbon-neutral AMOLED technologies in their product lines.
The automotive industry is another significant driver of demand for eco-friendly display technologies. With the rise of electric vehicles and increasing focus on sustainability in the automotive sector, there is a growing need for energy-efficient, carbon-neutral displays for infotainment systems, digital dashboards, and heads-up displays. AMOLED technology's potential for reduced power consumption and carbon neutrality aligns well with the automotive industry's sustainability goals.
In the industrial sector, there is an emerging demand for eco-friendly displays in applications such as digital signage, control panels, and human-machine interfaces. Companies are increasingly looking to reduce their overall carbon footprint, and adopting carbon-neutral display technologies is seen as a step towards achieving this goal.
The healthcare industry is also showing interest in eco-friendly display technologies, particularly for medical imaging devices and patient monitoring systems. The potential for AMOLED displays to offer high-quality visuals while maintaining energy efficiency and environmental sustainability is attracting attention from healthcare providers and equipment manufacturers.
Market analysts project significant growth in the eco-friendly display technology sector over the next decade. This growth is expected to be driven by advancements in AMOLED technology, increasing adoption across various industries, and supportive government policies promoting sustainable technologies.
However, challenges remain in meeting the market demand for carbon-neutral AMOLED electronics. These include the need for further improvements in energy efficiency, development of sustainable manufacturing processes, and reduction in production costs to make the technology more accessible across different market segments.
As research and development in carbon-neutral AMOLED technologies progress, the market is likely to see an influx of innovative products and solutions. This will not only cater to the current demand but also create new opportunities and applications, further expanding the market for eco-friendly display technologies.
Consumer electronics, particularly smartphones and tablets, represent the largest market segment for eco-friendly displays. As consumers become more environmentally aware, there is a growing preference for devices with reduced carbon footprints. This shift in consumer behavior has prompted major manufacturers to invest in developing and implementing carbon-neutral AMOLED technologies in their product lines.
The automotive industry is another significant driver of demand for eco-friendly display technologies. With the rise of electric vehicles and increasing focus on sustainability in the automotive sector, there is a growing need for energy-efficient, carbon-neutral displays for infotainment systems, digital dashboards, and heads-up displays. AMOLED technology's potential for reduced power consumption and carbon neutrality aligns well with the automotive industry's sustainability goals.
In the industrial sector, there is an emerging demand for eco-friendly displays in applications such as digital signage, control panels, and human-machine interfaces. Companies are increasingly looking to reduce their overall carbon footprint, and adopting carbon-neutral display technologies is seen as a step towards achieving this goal.
The healthcare industry is also showing interest in eco-friendly display technologies, particularly for medical imaging devices and patient monitoring systems. The potential for AMOLED displays to offer high-quality visuals while maintaining energy efficiency and environmental sustainability is attracting attention from healthcare providers and equipment manufacturers.
Market analysts project significant growth in the eco-friendly display technology sector over the next decade. This growth is expected to be driven by advancements in AMOLED technology, increasing adoption across various industries, and supportive government policies promoting sustainable technologies.
However, challenges remain in meeting the market demand for carbon-neutral AMOLED electronics. These include the need for further improvements in energy efficiency, development of sustainable manufacturing processes, and reduction in production costs to make the technology more accessible across different market segments.
As research and development in carbon-neutral AMOLED technologies progress, the market is likely to see an influx of innovative products and solutions. This will not only cater to the current demand but also create new opportunities and applications, further expanding the market for eco-friendly display technologies.
Current Challenges in Carbon-Neutral AMOLED Production
The production of carbon-neutral AMOLED electronics faces several significant challenges that need to be addressed to achieve sustainability goals. One of the primary obstacles is the energy-intensive manufacturing process of AMOLED displays. The production of these displays requires high temperatures and complex chemical processes, which traditionally rely heavily on fossil fuels and contribute to substantial carbon emissions.
Material sourcing and supply chain management present another major challenge. Many of the raw materials used in AMOLED production, such as rare earth elements and precious metals, are often mined and processed in ways that are not environmentally friendly. Establishing a carbon-neutral supply chain for these materials requires significant restructuring and investment in sustainable extraction and processing methods.
The disposal and recycling of AMOLED devices at the end of their lifecycle also pose environmental concerns. The complex nature of these electronics makes them difficult to recycle efficiently, and improper disposal can lead to the release of harmful substances into the environment. Developing effective recycling technologies and implementing circular economy principles in the production process are crucial steps towards carbon neutrality.
Energy consumption during the use phase of AMOLED devices is another area that requires attention. While AMOLED displays are generally more energy-efficient than their LCD counterparts, there is still room for improvement in reducing power consumption, especially in larger displays and high-resolution applications.
The lack of standardized carbon accounting methods specific to the AMOLED industry makes it challenging to accurately measure and compare the carbon footprint of different production processes and products. This hinders the ability to set realistic targets and track progress towards carbon neutrality effectively.
Infrastructure limitations also present obstacles to achieving carbon-neutral production. Many existing manufacturing facilities are not designed with sustainability in mind and require significant retrofitting or complete rebuilding to incorporate renewable energy sources and more efficient production technologies.
Lastly, the economic viability of carbon-neutral AMOLED production remains a significant challenge. The transition to sustainable practices often involves substantial upfront costs, which can be a deterrent for manufacturers, especially in a highly competitive market. Balancing these costs with consumer demand for affordable products while maintaining profitability is a complex issue that the industry must navigate.
Material sourcing and supply chain management present another major challenge. Many of the raw materials used in AMOLED production, such as rare earth elements and precious metals, are often mined and processed in ways that are not environmentally friendly. Establishing a carbon-neutral supply chain for these materials requires significant restructuring and investment in sustainable extraction and processing methods.
The disposal and recycling of AMOLED devices at the end of their lifecycle also pose environmental concerns. The complex nature of these electronics makes them difficult to recycle efficiently, and improper disposal can lead to the release of harmful substances into the environment. Developing effective recycling technologies and implementing circular economy principles in the production process are crucial steps towards carbon neutrality.
Energy consumption during the use phase of AMOLED devices is another area that requires attention. While AMOLED displays are generally more energy-efficient than their LCD counterparts, there is still room for improvement in reducing power consumption, especially in larger displays and high-resolution applications.
The lack of standardized carbon accounting methods specific to the AMOLED industry makes it challenging to accurately measure and compare the carbon footprint of different production processes and products. This hinders the ability to set realistic targets and track progress towards carbon neutrality effectively.
Infrastructure limitations also present obstacles to achieving carbon-neutral production. Many existing manufacturing facilities are not designed with sustainability in mind and require significant retrofitting or complete rebuilding to incorporate renewable energy sources and more efficient production technologies.
Lastly, the economic viability of carbon-neutral AMOLED production remains a significant challenge. The transition to sustainable practices often involves substantial upfront costs, which can be a deterrent for manufacturers, especially in a highly competitive market. Balancing these costs with consumer demand for affordable products while maintaining profitability is a complex issue that the industry must navigate.
Existing Carbon Reduction Strategies in AMOLED Production
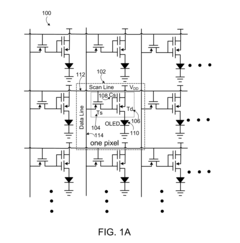
01 Energy-efficient AMOLED display technologies
Advanced AMOLED display technologies are being developed to reduce power consumption and improve energy efficiency. These innovations include optimized pixel structures, enhanced driving methods, and improved materials that contribute to lower energy usage while maintaining high display quality. Such advancements play a crucial role in achieving carbon neutrality goals in the electronics industry.- AMOLED display technology for energy efficiency: AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays are being developed with improved energy efficiency to contribute to carbon neutrality goals. These displays consume less power compared to traditional LCD screens, especially when displaying darker content, as individual pixels can be turned off completely. Advanced AMOLED technologies are being implemented to further reduce power consumption and extend device battery life.
- Carbon-neutral manufacturing processes for electronics: Electronics manufacturers are developing carbon-neutral production methods for AMOLED devices. This includes using renewable energy sources in manufacturing facilities, implementing energy-efficient production equipment, and optimizing supply chains to reduce carbon emissions. Some companies are also exploring carbon offset programs to achieve net-zero emissions in their AMOLED production lines.
- Recycling and sustainable materials in AMOLED devices: To promote carbon neutrality, researchers are developing AMOLED devices using recyclable and sustainable materials. This includes the use of bio-based organic compounds for light-emitting layers, recyclable substrates, and eco-friendly encapsulation materials. Additionally, improved recycling processes are being designed to recover valuable materials from end-of-life AMOLED displays, reducing the overall carbon footprint of these devices.
- Power management systems for AMOLED displays: Advanced power management systems are being integrated into AMOLED displays to optimize energy consumption and contribute to carbon neutrality efforts. These systems include adaptive brightness controls, selective pixel activation, and intelligent power-saving modes that adjust display parameters based on content and ambient conditions. Such technologies help reduce overall energy consumption in devices using AMOLED screens.
- Carbon footprint assessment tools for AMOLED production: Specialized carbon footprint assessment tools are being developed for the AMOLED industry to accurately measure and track emissions throughout the product lifecycle. These tools help manufacturers identify areas for improvement in their production processes, supply chains, and product designs. By providing detailed insights into carbon emissions, these assessment tools enable companies to make data-driven decisions to achieve carbon neutrality in AMOLED electronics production.
02 Carbon-neutral manufacturing processes for AMOLED displays
Manufacturers are implementing carbon-neutral production techniques for AMOLED displays. This involves using renewable energy sources, optimizing production lines, and adopting eco-friendly materials and processes. These efforts aim to minimize the carbon footprint associated with the manufacturing of AMOLED displays, contributing to overall carbon neutrality in the electronics sector.Expand Specific Solutions03 Recycling and circular economy strategies for AMOLED devices
Innovative recycling methods and circular economy approaches are being developed for AMOLED devices. These strategies focus on recovering valuable materials from used displays, refurbishing components, and designing products for easier disassembly and recycling. Such initiatives help reduce electronic waste and promote sustainable practices in the AMOLED industry.Expand Specific Solutions04 Low-carbon AMOLED panel production techniques
New production techniques are being explored to reduce carbon emissions in AMOLED panel manufacturing. These include the use of low-temperature processes, alternative materials with lower environmental impact, and advanced deposition methods that minimize energy consumption and waste. Such innovations contribute to the overall goal of carbon neutrality in AMOLED electronics.Expand Specific Solutions05 Smart power management systems for AMOLED displays
Advanced power management systems are being integrated into AMOLED displays to optimize energy usage. These systems include intelligent brightness control, selective pixel activation, and adaptive refresh rates. By reducing unnecessary power consumption, these technologies contribute to the carbon neutrality efforts in AMOLED-based devices and electronics.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable AMOLED Industry
The research potential of carbon-neutral AMOLED electronics is in an early development stage, with significant market growth anticipated. The global OLED market is projected to expand rapidly, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient displays. While the technology is advancing, it is not yet fully mature. Key players like BOE Technology, LG Display, and Universal Display Corporation are investing heavily in R&D to improve AMOLED efficiency and sustainability. Companies such as Merck and Sumitomo Bakelite are focusing on developing eco-friendly materials for OLED production. The competitive landscape is intensifying as both established firms and startups vie for technological breakthroughs in carbon-neutral AMOLED solutions.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has been actively pursuing carbon-neutral AMOLED technologies through various initiatives. They have developed a flexible AMOLED display with integrated solar cells, allowing the display to partially power itself and reduce overall energy consumption[7]. BOE has also implemented AI-driven manufacturing processes that optimize resource usage and reduce waste in AMOLED production. Their advanced oxide semiconductor technology improves electron mobility, leading to lower power consumption in AMOLED panels[8]. Additionally, BOE has invested in green factories that utilize renewable energy sources and implement circular economy principles in their manufacturing processes[9].
Strengths: Innovative integration of solar cells, AI-driven manufacturing optimization, and investment in green factories. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in balancing cost-effectiveness with sustainability goals and competition from other major display manufacturers.
LG Display Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Display has developed a carbon-neutral AMOLED technology that significantly reduces energy consumption and carbon emissions. Their approach involves using eco-friendly materials and optimizing the manufacturing process. They have implemented a low-temperature polycrystalline oxide (LTPO) backplane technology, which allows for variable refresh rates, reducing power consumption by up to 20% compared to traditional AMOLED displays[1]. Additionally, LG Display has invested in renewable energy sources for their production facilities, aiming to achieve carbon neutrality in their operations by 2030[2]. The company has also developed thinner and lighter AMOLED panels, reducing material usage and transportation-related emissions[3].
Strengths: Advanced LTPO technology, commitment to renewable energy, and reduced material usage. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs and potential challenges in scaling up production while maintaining carbon neutrality.
Innovative Materials for Carbon-Neutral AMOLED Displays
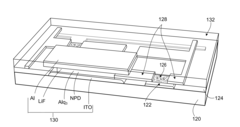
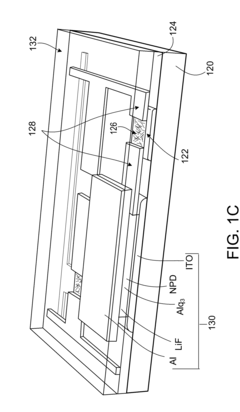
Separated Carbon Nanotube-Based Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode Displays
PatentInactiveUS20140070169A1
Innovation
- The use of separated semiconducting nanotubes as the active channel material in transistors, with a network of nanotubes disposed over a functionalized gate dielectric layer, and integrated into a display control circuit to drive OLED pixels, enabling high on/off ratios and current density.
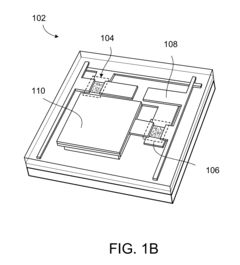
Display panel and manufacturing method thereof
PatentActiveUS20220344613A1
Innovation
- A display panel design featuring a light-emitting region and a non-light-emitting region with a retaining wall structure containing through-holes and retaining walls, where the light-emitting layer is positioned within the through-holes, and a packaging layer covers the structure, along with a second electrode extending from the light-emitting region to the non-light-emitting region, ensuring proper electrical connections and preventing short-circuiting.
Life Cycle Assessment of AMOLED Display Technologies
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of AMOLED display technologies is a crucial component in evaluating the environmental impact and potential for carbon neutrality in the electronics industry. This comprehensive analysis examines the entire lifecycle of AMOLED displays, from raw material extraction to manufacturing, use, and end-of-life disposal.
The production phase of AMOLED displays involves energy-intensive processes, including the fabrication of thin-film transistors, organic light-emitting materials, and encapsulation layers. These processes contribute significantly to the carbon footprint of the final product. However, advancements in manufacturing techniques, such as the use of low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) and organic thin-film transistors (OTFTs), have shown promise in reducing energy consumption during production.
During the use phase, AMOLED displays demonstrate superior energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD technologies. The self-emissive nature of OLED pixels eliminates the need for backlighting, resulting in lower power consumption, especially when displaying darker content. This efficiency translates to reduced carbon emissions over the lifespan of devices incorporating AMOLED displays.
End-of-life considerations for AMOLED displays present both challenges and opportunities. The organic materials used in these displays can be difficult to recycle, potentially leading to increased electronic waste. However, research into biodegradable OLED materials and improved recycling techniques shows promise for mitigating these issues and moving towards a more circular economy for display technologies.
Recent LCA studies have highlighted the importance of considering regional differences in energy grids when assessing the environmental impact of AMOLED production and use. Displays manufactured in regions with a higher proportion of renewable energy sources in their power mix demonstrate a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to those produced in areas reliant on fossil fuels.
Innovations in material science are playing a crucial role in improving the sustainability of AMOLED displays. The development of more efficient organic emitters, such as thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) materials, not only enhances display performance but also reduces energy consumption. Additionally, research into bio-based and recyclable substrates offers potential pathways to reduce the environmental impact of display production.
As the industry moves towards carbon neutrality, LCA studies are instrumental in identifying hotspots for improvement across the AMOLED display lifecycle. These assessments guide research and development efforts, focusing on areas with the greatest potential for reducing carbon emissions and environmental impact. By continually refining manufacturing processes, improving material efficiency, and enhancing end-of-life management, the AMOLED display industry is making strides towards more sustainable and carbon-neutral electronics.
The production phase of AMOLED displays involves energy-intensive processes, including the fabrication of thin-film transistors, organic light-emitting materials, and encapsulation layers. These processes contribute significantly to the carbon footprint of the final product. However, advancements in manufacturing techniques, such as the use of low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) and organic thin-film transistors (OTFTs), have shown promise in reducing energy consumption during production.
During the use phase, AMOLED displays demonstrate superior energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD technologies. The self-emissive nature of OLED pixels eliminates the need for backlighting, resulting in lower power consumption, especially when displaying darker content. This efficiency translates to reduced carbon emissions over the lifespan of devices incorporating AMOLED displays.
End-of-life considerations for AMOLED displays present both challenges and opportunities. The organic materials used in these displays can be difficult to recycle, potentially leading to increased electronic waste. However, research into biodegradable OLED materials and improved recycling techniques shows promise for mitigating these issues and moving towards a more circular economy for display technologies.
Recent LCA studies have highlighted the importance of considering regional differences in energy grids when assessing the environmental impact of AMOLED production and use. Displays manufactured in regions with a higher proportion of renewable energy sources in their power mix demonstrate a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to those produced in areas reliant on fossil fuels.
Innovations in material science are playing a crucial role in improving the sustainability of AMOLED displays. The development of more efficient organic emitters, such as thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) materials, not only enhances display performance but also reduces energy consumption. Additionally, research into bio-based and recyclable substrates offers potential pathways to reduce the environmental impact of display production.
As the industry moves towards carbon neutrality, LCA studies are instrumental in identifying hotspots for improvement across the AMOLED display lifecycle. These assessments guide research and development efforts, focusing on areas with the greatest potential for reducing carbon emissions and environmental impact. By continually refining manufacturing processes, improving material efficiency, and enhancing end-of-life management, the AMOLED display industry is making strides towards more sustainable and carbon-neutral electronics.
Policy Incentives for Green Electronics Manufacturing
Policy incentives play a crucial role in promoting the development and adoption of green electronics manufacturing, particularly in the context of carbon-neutral AMOLED electronics. Governments worldwide are implementing various measures to encourage sustainable practices in the electronics industry, recognizing the sector's significant environmental impact.
One of the primary policy tools is the introduction of tax incentives for companies investing in eco-friendly production methods. These may include tax credits for research and development in green technologies, reduced corporate tax rates for manufacturers meeting specific environmental standards, and accelerated depreciation allowances for investments in energy-efficient equipment.
Grants and subsidies form another essential component of policy incentives. Governments are allocating funds to support companies transitioning to more sustainable manufacturing processes. These financial aids can cover a portion of the costs associated with upgrading facilities, implementing new technologies, or training employees in green manufacturing techniques.
Regulatory frameworks are being established to set standards for energy efficiency and emissions in electronics manufacturing. These regulations often include mandatory targets for reducing carbon footprints, with penalties for non-compliance and rewards for exceeding expectations. Such policies create a level playing field and drive industry-wide improvements in sustainability.
Green procurement policies are increasingly being adopted by governments, favoring products manufactured using environmentally friendly processes. This approach creates a significant market pull for green electronics, incentivizing manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices to remain competitive in government contracts.
Research and development support is another critical area of policy focus. Governments are funding collaborative research projects between industry and academia to advance green manufacturing technologies. These initiatives often target specific challenges in AMOLED production, such as reducing energy consumption or developing eco-friendly materials.
Carbon pricing mechanisms, including carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems, are being implemented in various regions. These policies internalize the environmental costs of production, encouraging manufacturers to invest in cleaner technologies and processes to reduce their carbon emissions and associated financial burdens.
Lastly, governments are investing in infrastructure to support green manufacturing. This includes developing renewable energy sources, improving recycling facilities, and creating eco-industrial parks that facilitate resource sharing and waste reduction among electronics manufacturers.
One of the primary policy tools is the introduction of tax incentives for companies investing in eco-friendly production methods. These may include tax credits for research and development in green technologies, reduced corporate tax rates for manufacturers meeting specific environmental standards, and accelerated depreciation allowances for investments in energy-efficient equipment.
Grants and subsidies form another essential component of policy incentives. Governments are allocating funds to support companies transitioning to more sustainable manufacturing processes. These financial aids can cover a portion of the costs associated with upgrading facilities, implementing new technologies, or training employees in green manufacturing techniques.
Regulatory frameworks are being established to set standards for energy efficiency and emissions in electronics manufacturing. These regulations often include mandatory targets for reducing carbon footprints, with penalties for non-compliance and rewards for exceeding expectations. Such policies create a level playing field and drive industry-wide improvements in sustainability.
Green procurement policies are increasingly being adopted by governments, favoring products manufactured using environmentally friendly processes. This approach creates a significant market pull for green electronics, incentivizing manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices to remain competitive in government contracts.
Research and development support is another critical area of policy focus. Governments are funding collaborative research projects between industry and academia to advance green manufacturing technologies. These initiatives often target specific challenges in AMOLED production, such as reducing energy consumption or developing eco-friendly materials.
Carbon pricing mechanisms, including carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems, are being implemented in various regions. These policies internalize the environmental costs of production, encouraging manufacturers to invest in cleaner technologies and processes to reduce their carbon emissions and associated financial burdens.
Lastly, governments are investing in infrastructure to support green manufacturing. This includes developing renewable energy sources, improving recycling facilities, and creating eco-industrial parks that facilitate resource sharing and waste reduction among electronics manufacturers.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!