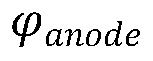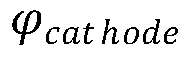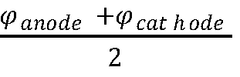How AMOLED competes with liquid crystal technologies?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED vs LCD: Background and Objectives
The competition between AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technologies has been a significant driving force in the evolution of display technologies over the past two decades. This rivalry has pushed both technologies to continually improve, resulting in enhanced visual experiences for consumers across various devices.
AMOLED technology emerged as a promising alternative to LCD in the early 2000s, offering several advantages such as better contrast ratios, wider color gamut, and faster response times. The development of AMOLED displays was primarily driven by the need for more energy-efficient and thinner displays in mobile devices. As smartphones and tablets became ubiquitous, the demand for high-quality, power-efficient displays grew exponentially.
LCD technology, on the other hand, has a longer history dating back to the 1960s. It has been the dominant display technology for decades, powering everything from calculators to large-screen televisions. The widespread adoption of LCD has led to significant improvements in manufacturing processes, resulting in cost-effective production and consistent quality.
The competition between these two technologies has centered around several key performance metrics: color accuracy, contrast ratio, power efficiency, viewing angles, and production costs. AMOLED displays have generally excelled in producing deeper blacks and more vibrant colors, while LCD technology has maintained advantages in brightness and cost-effectiveness, especially for larger screen sizes.
As the display market continues to evolve, both technologies are adapting to meet new challenges. AMOLED is making strides in addressing issues such as burn-in and color shift, while LCD manufacturers are developing advanced technologies like quantum dot displays to enhance color performance and energy efficiency.
The objectives of this technological competition are multifaceted. For manufacturers, the goal is to develop displays that offer the best possible visual experience while minimizing production costs and energy consumption. For consumers, the competition drives innovation, resulting in better quality displays across a wide range of devices and price points.
Looking ahead, the rivalry between AMOLED and LCD is expected to intensify as new applications emerge, such as foldable devices, augmented reality, and virtual reality systems. These new form factors and use cases will likely push both technologies to their limits, potentially leading to hybrid solutions or entirely new display technologies.
AMOLED technology emerged as a promising alternative to LCD in the early 2000s, offering several advantages such as better contrast ratios, wider color gamut, and faster response times. The development of AMOLED displays was primarily driven by the need for more energy-efficient and thinner displays in mobile devices. As smartphones and tablets became ubiquitous, the demand for high-quality, power-efficient displays grew exponentially.
LCD technology, on the other hand, has a longer history dating back to the 1960s. It has been the dominant display technology for decades, powering everything from calculators to large-screen televisions. The widespread adoption of LCD has led to significant improvements in manufacturing processes, resulting in cost-effective production and consistent quality.
The competition between these two technologies has centered around several key performance metrics: color accuracy, contrast ratio, power efficiency, viewing angles, and production costs. AMOLED displays have generally excelled in producing deeper blacks and more vibrant colors, while LCD technology has maintained advantages in brightness and cost-effectiveness, especially for larger screen sizes.
As the display market continues to evolve, both technologies are adapting to meet new challenges. AMOLED is making strides in addressing issues such as burn-in and color shift, while LCD manufacturers are developing advanced technologies like quantum dot displays to enhance color performance and energy efficiency.
The objectives of this technological competition are multifaceted. For manufacturers, the goal is to develop displays that offer the best possible visual experience while minimizing production costs and energy consumption. For consumers, the competition drives innovation, resulting in better quality displays across a wide range of devices and price points.
Looking ahead, the rivalry between AMOLED and LCD is expected to intensify as new applications emerge, such as foldable devices, augmented reality, and virtual reality systems. These new form factors and use cases will likely push both technologies to their limits, potentially leading to hybrid solutions or entirely new display technologies.
Market Demand Analysis for Display Technologies
The display technology market has witnessed significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for high-quality visual experiences across various devices. AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has emerged as a strong competitor to traditional liquid crystal technologies, reshaping the landscape of the display industry.
Consumer electronics, particularly smartphones and televisions, have been the primary drivers of demand for advanced display technologies. The global smartphone market, which has been a major adopter of AMOLED displays, continues to grow, with consumers showing a preference for devices featuring vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and energy efficiency. This trend has led to a surge in demand for AMOLED panels, challenging the dominance of LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology.
In the television segment, there is a growing appetite for larger screen sizes and higher resolutions. AMOLED technology, with its ability to deliver deep blacks, infinite contrast ratios, and wide color gamuts, has gained traction in premium TV models. However, LCD technology, particularly with advancements like quantum dot enhancement, continues to hold a significant market share due to its cost-effectiveness in larger screen sizes.
The automotive industry represents an emerging market for advanced display technologies. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, there is an increasing need for high-quality, durable displays for infotainment systems and digital dashboards. AMOLED's flexibility and form factor advantages make it an attractive option for curved and uniquely shaped displays in vehicle interiors.
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, have also contributed to the growing demand for AMOLED displays. The technology's power efficiency and ability to produce vivid colors in a compact form factor align well with the requirements of these devices, where battery life and display quality are crucial factors.
The commercial and industrial sectors are showing interest in large-format displays for digital signage, control rooms, and interactive kiosks. While LCD technology has traditionally dominated this space, AMOLED is making inroads, particularly in high-end applications where image quality and viewing angles are paramount.
Despite the growing adoption of AMOLED, LCD technology continues to evolve and maintain a strong presence in the market. Innovations such as mini-LED backlighting and advanced IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels have allowed LCD to remain competitive, especially in mid-range products where cost considerations are significant.
The display technology market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by technological advancements, increasing consumer expectations, and the proliferation of smart devices across various industries. While AMOLED is gaining market share, the competition with liquid crystal technologies remains intense, with each technology finding its niche in different market segments and price points.
Consumer electronics, particularly smartphones and televisions, have been the primary drivers of demand for advanced display technologies. The global smartphone market, which has been a major adopter of AMOLED displays, continues to grow, with consumers showing a preference for devices featuring vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and energy efficiency. This trend has led to a surge in demand for AMOLED panels, challenging the dominance of LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology.
In the television segment, there is a growing appetite for larger screen sizes and higher resolutions. AMOLED technology, with its ability to deliver deep blacks, infinite contrast ratios, and wide color gamuts, has gained traction in premium TV models. However, LCD technology, particularly with advancements like quantum dot enhancement, continues to hold a significant market share due to its cost-effectiveness in larger screen sizes.
The automotive industry represents an emerging market for advanced display technologies. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, there is an increasing need for high-quality, durable displays for infotainment systems and digital dashboards. AMOLED's flexibility and form factor advantages make it an attractive option for curved and uniquely shaped displays in vehicle interiors.
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, have also contributed to the growing demand for AMOLED displays. The technology's power efficiency and ability to produce vivid colors in a compact form factor align well with the requirements of these devices, where battery life and display quality are crucial factors.
The commercial and industrial sectors are showing interest in large-format displays for digital signage, control rooms, and interactive kiosks. While LCD technology has traditionally dominated this space, AMOLED is making inroads, particularly in high-end applications where image quality and viewing angles are paramount.
Despite the growing adoption of AMOLED, LCD technology continues to evolve and maintain a strong presence in the market. Innovations such as mini-LED backlighting and advanced IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels have allowed LCD to remain competitive, especially in mid-range products where cost considerations are significant.
The display technology market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by technological advancements, increasing consumer expectations, and the proliferation of smart devices across various industries. While AMOLED is gaining market share, the competition with liquid crystal technologies remains intense, with each technology finding its niche in different market segments and price points.
Current State and Challenges of AMOLED and LCD
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technologies are currently the two dominant display technologies in the consumer electronics market. Both have their strengths and challenges, which shape their competitive landscape and future development trajectories.
AMOLED displays have made significant strides in recent years, offering superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD panels. They can produce true blacks by turning off individual pixels, resulting in infinite contrast ratios. This technology also allows for thinner and more flexible displays, opening up new design possibilities for manufacturers.
However, AMOLED faces challenges in terms of production costs and longevity. The organic compounds used in AMOLED displays are susceptible to degradation over time, potentially leading to color shifts and burn-in issues. Additionally, the manufacturing process for AMOLED panels is more complex and expensive than that of LCDs, which impacts their overall cost-effectiveness, especially in larger screen sizes.
LCD technology, on the other hand, has a long-standing presence in the market and benefits from mature manufacturing processes. This maturity translates to lower production costs and higher yields, making LCD panels more cost-effective, particularly for larger displays. LCDs also tend to have longer lifespans and are less prone to burn-in issues compared to AMOLED displays.
Nevertheless, LCD technology faces its own set of challenges. It struggles to match the deep blacks and high contrast ratios of AMOLED displays due to the need for backlighting. This also impacts energy efficiency, as LCD panels require constant backlighting even when displaying dark content. Furthermore, LCD response times are generally slower than those of AMOLED, which can result in motion blur in fast-moving content.
Both technologies are continuously evolving to address their respective weaknesses. AMOLED manufacturers are working on improving production efficiency and developing more durable organic compounds to enhance longevity and reduce costs. Meanwhile, LCD technology is advancing with innovations like quantum dot technology and mini-LED backlighting to improve color accuracy and contrast ratios.
The competition between AMOLED and LCD is driving innovation in the display industry, with each technology pushing the boundaries of what's possible. As manufacturers strive to overcome the inherent limitations of each technology, consumers benefit from a wider range of options and improved display quality across various devices and price points.
AMOLED displays have made significant strides in recent years, offering superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD panels. They can produce true blacks by turning off individual pixels, resulting in infinite contrast ratios. This technology also allows for thinner and more flexible displays, opening up new design possibilities for manufacturers.
However, AMOLED faces challenges in terms of production costs and longevity. The organic compounds used in AMOLED displays are susceptible to degradation over time, potentially leading to color shifts and burn-in issues. Additionally, the manufacturing process for AMOLED panels is more complex and expensive than that of LCDs, which impacts their overall cost-effectiveness, especially in larger screen sizes.
LCD technology, on the other hand, has a long-standing presence in the market and benefits from mature manufacturing processes. This maturity translates to lower production costs and higher yields, making LCD panels more cost-effective, particularly for larger displays. LCDs also tend to have longer lifespans and are less prone to burn-in issues compared to AMOLED displays.
Nevertheless, LCD technology faces its own set of challenges. It struggles to match the deep blacks and high contrast ratios of AMOLED displays due to the need for backlighting. This also impacts energy efficiency, as LCD panels require constant backlighting even when displaying dark content. Furthermore, LCD response times are generally slower than those of AMOLED, which can result in motion blur in fast-moving content.
Both technologies are continuously evolving to address their respective weaknesses. AMOLED manufacturers are working on improving production efficiency and developing more durable organic compounds to enhance longevity and reduce costs. Meanwhile, LCD technology is advancing with innovations like quantum dot technology and mini-LED backlighting to improve color accuracy and contrast ratios.
The competition between AMOLED and LCD is driving innovation in the display industry, with each technology pushing the boundaries of what's possible. As manufacturers strive to overcome the inherent limitations of each technology, consumers benefit from a wider range of options and improved display quality across various devices and price points.
Comparative Analysis of AMOLED and LCD Solutions
01 AMOLED display driving techniques
Various driving techniques are employed to improve the performance of AMOLED displays. These include methods for controlling pixel brightness, reducing power consumption, and enhancing image quality. Advanced driving schemes can compensate for variations in OLED characteristics and optimize display performance across different operating conditions.- AMOLED display structure and manufacturing: This category focuses on the structure and manufacturing processes of AMOLED displays. It includes innovations in pixel arrangements, thin-film transistor (TFT) designs, and fabrication techniques to improve display performance, efficiency, and durability.
- AMOLED driving and control methods: This point covers various driving and control methods for AMOLED displays. It includes techniques for pixel compensation, voltage control, and current driving to enhance image quality, reduce power consumption, and extend the lifespan of AMOLED panels.
- AMOLED power management and efficiency: This category addresses power management and efficiency improvements in AMOLED displays. It includes techniques for reducing power consumption, optimizing brightness control, and enhancing overall energy efficiency of AMOLED panels.
- AMOLED color management and image quality: This point focuses on color management and image quality enhancements for AMOLED displays. It includes methods for improving color accuracy, contrast, and overall visual performance of AMOLED panels in various lighting conditions.
- AMOLED integration with other technologies: This category covers the integration of AMOLED technology with other advanced features and technologies. It includes innovations in touch sensing, fingerprint recognition, and flexible display applications to enhance the functionality and versatility of AMOLED displays.
02 AMOLED pixel circuit designs
Innovative pixel circuit designs are crucial for AMOLED displays. These circuits aim to improve uniformity, reduce power consumption, and enhance display quality. Advanced pixel architectures may incorporate compensation mechanisms for threshold voltage shifts and incorporate additional transistors or capacitors for better control over OLED current.Expand Specific Solutions03 AMOLED panel structure and fabrication
The structure and fabrication processes of AMOLED panels are continually evolving. Innovations in this area focus on improving panel efficiency, increasing resolution, and enhancing durability. Advanced techniques may include novel electrode designs, improved encapsulation methods, and integration of additional functional layers.Expand Specific Solutions04 AMOLED power management and efficiency
Power management is a critical aspect of AMOLED display technology. Techniques are developed to reduce power consumption while maintaining display quality. These may include adaptive brightness control, selective pixel dimming, and optimized voltage regulation schemes for the OLED and driving circuitry.Expand Specific Solutions05 AMOLED display integration and applications
AMOLED displays are integrated into various devices and applications. This involves developing techniques for seamless integration with touch sensors, fingerprint scanners, and other functionalities. Additionally, specialized AMOLED designs are created for specific applications such as foldable displays, automotive displays, and wearable devices.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in AMOLED and LCD Industries
The competition between AMOLED and liquid crystal technologies is intensifying as the display industry evolves. Currently, the market is in a transitional phase, with AMOLED gaining traction due to its superior performance characteristics. The global display market size is substantial, with key players like Samsung, LG Display, BOE, and Japan Display competing fiercely. AMOLED technology is maturing rapidly, with companies like Samsung and LG Display leading in commercialization. However, LCD technology remains dominant in many applications due to its cost-effectiveness and established manufacturing processes. Companies like BOE, Innolux, and Sharp continue to innovate in LCD technology, maintaining its competitiveness against AMOLED.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed advanced AMOLED technologies to compete with liquid crystal displays. Their flexible AMOLED panels utilize low-temperature polycrystalline oxide (LTPO) backplanes, which enable variable refresh rates from 1-120Hz, significantly reducing power consumption[1]. BOE has also implemented advanced pixel compensation circuits to address OLED aging and maintain consistent image quality over time[2]. Their latest AMOLED displays feature pixel densities exceeding 500 PPI and support wide color gamuts covering over 100% of the DCI-P3 color space[3]. To enhance durability, BOE employs advanced encapsulation techniques that protect OLED materials from moisture and oxygen degradation[4].
Strengths: Flexible form factors, high contrast ratios, and wide color gamuts. Weaknesses: Higher production costs and potential for burn-in compared to LCD.
LG Display Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Display has pioneered large-scale OLED production for both small and large displays. Their WOLED (White OLED) technology uses a stack of white OLED materials with color filters, allowing for efficient manufacturing of large OLED panels[5]. For mobile devices, LG has developed advanced AMOLED displays with on-cell touch sensors, reducing overall thickness and improving optical performance[6]. LG's latest AMOLED panels incorporate advanced driving schemes that minimize power consumption, achieving up to 25% lower power usage compared to conventional AMOLED displays[7]. To address the challenge of blue OLED longevity, LG has invested in developing more stable blue emitters, including phosphorescent and TADF (Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence) materials[8].
Strengths: Expertise in large OLED panels, efficient WOLED technology for TVs. Weaknesses: Higher cost for smaller displays compared to some competitors.
Core Innovations in AMOLED Technology
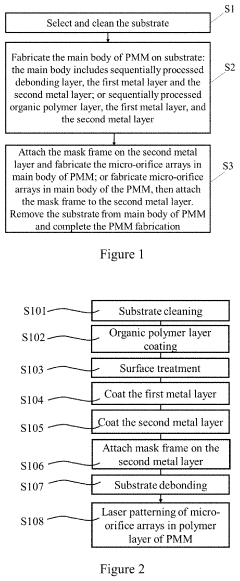
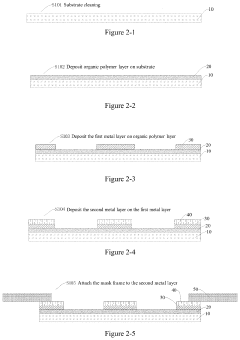
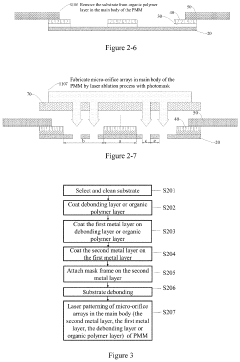
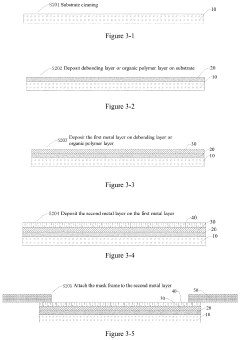
Production of Precision Micro-Mask and the AMOLED Display Manufactured Therefrom
PatentActiveUS20220131076A1
Innovation
- A new Precision Micro-Mask (PMM) fabrication process involving a debonding layer, first and second metal layers, and laser welding to create micro-orifice arrays, allowing for the production of high-resolution AMOLED displays with the RGB SBS architecture, using materials like nickel-cobalt alloys and organic polymer layers for enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability.
Organic light-emitting diode structure and fabrication method thereof, related display panel, and related display device
PatentWO2017070892A1
Innovation
- AMOLED display panels offer advantages over LCD panels, including shorter response time, higher brightness contrast, and wider viewing angles.
- The invention addresses the specific challenges of blue light-emitting organic materials in AMOLED displays, which have low efficiency and short service time.
- The technology aims to overcome limitations in AMOLED products, potentially expanding their application in various display devices.
Environmental Impact of Display Technologies
The environmental impact of display technologies has become an increasingly important consideration in the electronics industry. As AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and liquid crystal technologies compete for market dominance, their respective environmental footprints play a crucial role in determining their long-term viability and consumer acceptance.
AMOLED displays have several environmental advantages over traditional liquid crystal displays (LCDs). They consume less power, particularly when displaying darker content, which can lead to reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions over the lifetime of devices. Additionally, AMOLED panels are thinner and lighter, potentially reducing the overall material usage and transportation costs associated with device manufacturing and distribution.
However, the production of AMOLED displays involves the use of rare earth elements and other precious metals, which can have significant environmental implications in terms of mining and extraction processes. The organic compounds used in AMOLED screens also raise concerns about disposal and recycling at the end of the product lifecycle.
Liquid crystal technologies, on the other hand, have benefited from decades of refinement in manufacturing processes, leading to more efficient production methods and established recycling infrastructure. LCDs typically use less complex materials compared to AMOLEDs, which can make them easier to recycle and dispose of safely.
Recent advancements in LCD technology, such as the development of quantum dot displays, have improved energy efficiency and color reproduction, narrowing the performance gap with AMOLED while maintaining some of the environmental benefits of traditional LCD manufacturing.
Both technologies face challenges in terms of e-waste management. The rapid turnover of consumer electronics leads to a significant amount of discarded displays, regardless of the technology used. Improving the longevity of devices and developing more effective recycling methods are critical for mitigating the environmental impact of both AMOLED and LCD technologies.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, manufacturers of both AMOLED and LCD displays are investing in research and development to reduce their ecological footprint. This includes efforts to minimize the use of hazardous materials, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the recyclability of display components.
The competition between AMOLED and liquid crystal technologies in the environmental arena is driving innovation in sustainable manufacturing practices. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the ability of each technology to demonstrate superior eco-friendliness may become a key differentiator in the market, influencing purchasing decisions and shaping the future of display technology adoption.
AMOLED displays have several environmental advantages over traditional liquid crystal displays (LCDs). They consume less power, particularly when displaying darker content, which can lead to reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions over the lifetime of devices. Additionally, AMOLED panels are thinner and lighter, potentially reducing the overall material usage and transportation costs associated with device manufacturing and distribution.
However, the production of AMOLED displays involves the use of rare earth elements and other precious metals, which can have significant environmental implications in terms of mining and extraction processes. The organic compounds used in AMOLED screens also raise concerns about disposal and recycling at the end of the product lifecycle.
Liquid crystal technologies, on the other hand, have benefited from decades of refinement in manufacturing processes, leading to more efficient production methods and established recycling infrastructure. LCDs typically use less complex materials compared to AMOLEDs, which can make them easier to recycle and dispose of safely.
Recent advancements in LCD technology, such as the development of quantum dot displays, have improved energy efficiency and color reproduction, narrowing the performance gap with AMOLED while maintaining some of the environmental benefits of traditional LCD manufacturing.
Both technologies face challenges in terms of e-waste management. The rapid turnover of consumer electronics leads to a significant amount of discarded displays, regardless of the technology used. Improving the longevity of devices and developing more effective recycling methods are critical for mitigating the environmental impact of both AMOLED and LCD technologies.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, manufacturers of both AMOLED and LCD displays are investing in research and development to reduce their ecological footprint. This includes efforts to minimize the use of hazardous materials, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the recyclability of display components.
The competition between AMOLED and liquid crystal technologies in the environmental arena is driving innovation in sustainable manufacturing practices. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the ability of each technology to demonstrate superior eco-friendliness may become a key differentiator in the market, influencing purchasing decisions and shaping the future of display technology adoption.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of AMOLED vs LCD
The cost-benefit analysis of AMOLED versus LCD technologies reveals significant trade-offs that influence their adoption in various applications. AMOLED displays offer superior image quality with deeper blacks, higher contrast ratios, and more vibrant colors. They also provide faster response times, wider viewing angles, and the potential for flexible and foldable designs. These advantages make AMOLED particularly attractive for high-end smartphones, wearables, and premium televisions.
However, AMOLED technology comes with higher production costs, primarily due to the complex manufacturing process and lower yield rates. The organic materials used in AMOLED displays are also more susceptible to degradation over time, potentially leading to issues like burn-in and shorter overall lifespan compared to LCD panels.
LCD technology, on the other hand, benefits from decades of refinement and economies of scale. It offers lower production costs, making it more suitable for budget-friendly devices and larger displays. LCD panels also tend to have longer lifespans and are less prone to burn-in issues. They generally provide higher brightness levels, which can be advantageous in outdoor or brightly lit environments.
Energy efficiency is another crucial factor in the comparison. AMOLED displays can be more power-efficient, especially when displaying darker content, as they can selectively illuminate only the necessary pixels. This characteristic makes them particularly suitable for mobile devices where battery life is a priority. LCD displays, however, require constant backlighting, which can lead to higher power consumption, especially when displaying darker images.
The choice between AMOLED and LCD often depends on the specific application and target market. High-end consumer electronics and premium devices tend to favor AMOLED for its superior image quality and potential for innovative form factors. In contrast, LCD remains dominant in markets where cost-effectiveness is paramount, such as in budget smartphones, monitors, and large-format displays.
As manufacturing processes continue to evolve, the cost gap between AMOLED and LCD is gradually narrowing. This trend may lead to increased adoption of AMOLED technology across a broader range of products in the future. However, LCD technology is also advancing, with improvements in areas like quantum dot technology and mini-LED backlighting, which aim to close the performance gap with AMOLED while maintaining cost advantages.
However, AMOLED technology comes with higher production costs, primarily due to the complex manufacturing process and lower yield rates. The organic materials used in AMOLED displays are also more susceptible to degradation over time, potentially leading to issues like burn-in and shorter overall lifespan compared to LCD panels.
LCD technology, on the other hand, benefits from decades of refinement and economies of scale. It offers lower production costs, making it more suitable for budget-friendly devices and larger displays. LCD panels also tend to have longer lifespans and are less prone to burn-in issues. They generally provide higher brightness levels, which can be advantageous in outdoor or brightly lit environments.
Energy efficiency is another crucial factor in the comparison. AMOLED displays can be more power-efficient, especially when displaying darker content, as they can selectively illuminate only the necessary pixels. This characteristic makes them particularly suitable for mobile devices where battery life is a priority. LCD displays, however, require constant backlighting, which can lead to higher power consumption, especially when displaying darker images.
The choice between AMOLED and LCD often depends on the specific application and target market. High-end consumer electronics and premium devices tend to favor AMOLED for its superior image quality and potential for innovative form factors. In contrast, LCD remains dominant in markets where cost-effectiveness is paramount, such as in budget smartphones, monitors, and large-format displays.
As manufacturing processes continue to evolve, the cost gap between AMOLED and LCD is gradually narrowing. This trend may lead to increased adoption of AMOLED technology across a broader range of products in the future. However, LCD technology is also advancing, with improvements in areas like quantum dot technology and mini-LED backlighting, which aim to close the performance gap with AMOLED while maintaining cost advantages.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!