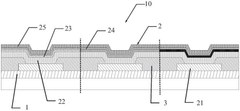
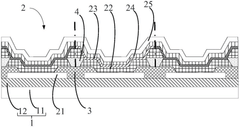
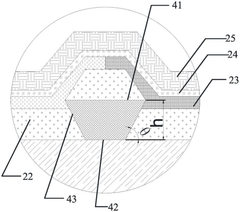
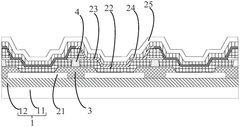
Complexities of incorporating AMOLED in medical imaging devices.
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED in Medical Imaging: Background and Objectives
Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode (AMOLED) technology has emerged as a revolutionary advancement in display systems, offering superior image quality, energy efficiency, and flexibility. The integration of AMOLED into medical imaging devices represents a significant leap forward in diagnostic capabilities and patient care. This technological fusion aims to enhance the accuracy, clarity, and accessibility of medical imaging, potentially transforming various fields within healthcare.
The evolution of medical imaging has been marked by continuous improvements in resolution, contrast, and portability. AMOLED technology, with its self-emitting pixels and high contrast ratios, presents an opportunity to address longstanding challenges in medical visualization. The primary objective of incorporating AMOLED in medical imaging devices is to provide healthcare professionals with more detailed, accurate, and easily interpretable visual data, ultimately leading to improved diagnostic precision and patient outcomes.
AMOLED displays offer several advantages that align well with the demands of medical imaging. These include deep black levels, wide color gamut, high refresh rates, and the ability to produce curved or flexible screens. Such features can significantly enhance the visibility of subtle details in X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasound images, potentially enabling earlier detection of abnormalities and more accurate assessments of patient conditions.
The development of AMOLED technology for medical imaging is driven by the increasing need for portable and versatile diagnostic tools. As healthcare systems worldwide strive for more efficient and accessible services, the integration of AMOLED displays in medical devices could facilitate point-of-care diagnostics and telemedicine applications. This aligns with the broader trend of digitalization and miniaturization in healthcare technology.
However, the incorporation of AMOLED in medical imaging devices is not without challenges. Key considerations include ensuring color accuracy and calibration for diagnostic purposes, maintaining image quality under varying lighting conditions, and addressing concerns related to long-term reliability and durability in clinical settings. Additionally, the integration must comply with stringent medical device regulations and standards, necessitating rigorous testing and validation processes.
The trajectory of AMOLED in medical imaging is closely tied to advancements in both display technology and medical science. As research progresses, we anticipate innovations that could further enhance the capabilities of AMOLED-equipped medical imaging devices, such as improved energy efficiency, higher resolutions, and novel form factors that could revolutionize how medical professionals interact with diagnostic images.
The evolution of medical imaging has been marked by continuous improvements in resolution, contrast, and portability. AMOLED technology, with its self-emitting pixels and high contrast ratios, presents an opportunity to address longstanding challenges in medical visualization. The primary objective of incorporating AMOLED in medical imaging devices is to provide healthcare professionals with more detailed, accurate, and easily interpretable visual data, ultimately leading to improved diagnostic precision and patient outcomes.
AMOLED displays offer several advantages that align well with the demands of medical imaging. These include deep black levels, wide color gamut, high refresh rates, and the ability to produce curved or flexible screens. Such features can significantly enhance the visibility of subtle details in X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasound images, potentially enabling earlier detection of abnormalities and more accurate assessments of patient conditions.
The development of AMOLED technology for medical imaging is driven by the increasing need for portable and versatile diagnostic tools. As healthcare systems worldwide strive for more efficient and accessible services, the integration of AMOLED displays in medical devices could facilitate point-of-care diagnostics and telemedicine applications. This aligns with the broader trend of digitalization and miniaturization in healthcare technology.
However, the incorporation of AMOLED in medical imaging devices is not without challenges. Key considerations include ensuring color accuracy and calibration for diagnostic purposes, maintaining image quality under varying lighting conditions, and addressing concerns related to long-term reliability and durability in clinical settings. Additionally, the integration must comply with stringent medical device regulations and standards, necessitating rigorous testing and validation processes.
The trajectory of AMOLED in medical imaging is closely tied to advancements in both display technology and medical science. As research progresses, we anticipate innovations that could further enhance the capabilities of AMOLED-equipped medical imaging devices, such as improved energy efficiency, higher resolutions, and novel form factors that could revolutionize how medical professionals interact with diagnostic images.
Market Analysis for AMOLED-based Medical Displays
The AMOLED-based medical display market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for high-quality imaging in healthcare settings. The global market for medical displays is projected to reach $2.5 billion by 2025, with AMOLED technology expected to capture a substantial share of this market. The adoption of AMOLED displays in medical imaging devices is primarily fueled by their superior image quality, high contrast ratios, and wide color gamut, which are crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
In the medical imaging sector, AMOLED displays are finding applications across various modalities, including radiology, surgical navigation, endoscopy, and point-of-care devices. The radiology segment, in particular, is showing strong demand for AMOLED displays due to their ability to render detailed images with exceptional clarity and color accuracy. This is especially valuable in mammography and digital pathology, where subtle tissue variations need to be discerned.
The surgical navigation market is another area where AMOLED displays are gaining traction. The technology's high refresh rates and wide viewing angles make it ideal for real-time intraoperative guidance systems. Additionally, the growing trend towards minimally invasive procedures is driving the adoption of AMOLED displays in endoscopic equipment, where image quality is paramount for precise visualization of internal structures.
Market analysis indicates that North America currently holds the largest share of the AMOLED-based medical display market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, is a key market due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and early adoption of cutting-edge medical technologies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and rapid technological advancements in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Despite the promising growth prospects, the AMOLED-based medical display market faces certain challenges. The high cost of AMOLED panels compared to traditional LCD displays remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption, especially in cost-sensitive healthcare markets. Additionally, concerns about the long-term reliability and potential burn-in issues of AMOLED displays in 24/7 medical environments need to be addressed to boost market confidence.
Looking ahead, the market for AMOLED-based medical displays is poised for continued expansion. Technological advancements, such as the development of flexible and transparent AMOLED displays, are expected to open up new applications in wearable medical devices and augmented reality surgical systems. Furthermore, the increasing focus on telemedicine and remote patient monitoring is likely to create additional opportunities for AMOLED displays in portable diagnostic devices and mobile health applications.
In the medical imaging sector, AMOLED displays are finding applications across various modalities, including radiology, surgical navigation, endoscopy, and point-of-care devices. The radiology segment, in particular, is showing strong demand for AMOLED displays due to their ability to render detailed images with exceptional clarity and color accuracy. This is especially valuable in mammography and digital pathology, where subtle tissue variations need to be discerned.
The surgical navigation market is another area where AMOLED displays are gaining traction. The technology's high refresh rates and wide viewing angles make it ideal for real-time intraoperative guidance systems. Additionally, the growing trend towards minimally invasive procedures is driving the adoption of AMOLED displays in endoscopic equipment, where image quality is paramount for precise visualization of internal structures.
Market analysis indicates that North America currently holds the largest share of the AMOLED-based medical display market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, is a key market due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and early adoption of cutting-edge medical technologies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and rapid technological advancements in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Despite the promising growth prospects, the AMOLED-based medical display market faces certain challenges. The high cost of AMOLED panels compared to traditional LCD displays remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption, especially in cost-sensitive healthcare markets. Additionally, concerns about the long-term reliability and potential burn-in issues of AMOLED displays in 24/7 medical environments need to be addressed to boost market confidence.
Looking ahead, the market for AMOLED-based medical displays is poised for continued expansion. Technological advancements, such as the development of flexible and transparent AMOLED displays, are expected to open up new applications in wearable medical devices and augmented reality surgical systems. Furthermore, the increasing focus on telemedicine and remote patient monitoring is likely to create additional opportunities for AMOLED displays in portable diagnostic devices and mobile health applications.
Technical Challenges in AMOLED Medical Integration
The integration of AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology into medical imaging devices presents a complex set of technical challenges that require careful consideration and innovative solutions. One of the primary obstacles is the need for high-resolution displays capable of rendering intricate medical images with exceptional clarity and accuracy. AMOLED displays must meet stringent requirements for contrast ratio, color accuracy, and brightness to ensure proper interpretation of diagnostic images.
Another significant challenge lies in the power consumption of AMOLED displays. Medical imaging devices often require extended operation times, and the energy demands of AMOLED screens can strain battery life or necessitate more robust power systems. Balancing power efficiency with display performance is crucial for practical implementation in portable medical devices.
Durability and longevity pose additional hurdles in AMOLED integration. Medical environments demand robust equipment that can withstand frequent cleaning and disinfection. The organic materials in AMOLED displays are sensitive to moisture and oxygen, requiring advanced encapsulation techniques to prevent degradation and ensure long-term reliability in clinical settings.
Color stability and uniformity across the display are critical for accurate medical image interpretation. AMOLED displays must maintain consistent color reproduction over time and across different viewing angles, which can be challenging due to the inherent characteristics of organic materials and their degradation patterns.
The integration of touch functionality, often required in modern medical devices, introduces further complexities. Implementing touch sensors without compromising display quality or increasing device thickness requires sophisticated engineering solutions. Moreover, ensuring the touch interface remains responsive even when users wear medical gloves adds another layer of technical difficulty.
Thermal management is a crucial consideration in AMOLED medical integration. Medical imaging devices often generate significant heat during operation, and AMOLED displays are sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Developing effective cooling systems that maintain optimal display performance without interfering with other device components is a complex engineering task.
Lastly, the challenge of scalability and manufacturing consistency cannot be overlooked. Producing AMOLED displays for medical devices requires stringent quality control measures to ensure uniformity across production batches. Achieving this level of consistency while scaling up production to meet market demands presents significant technical and logistical challenges for manufacturers.
Another significant challenge lies in the power consumption of AMOLED displays. Medical imaging devices often require extended operation times, and the energy demands of AMOLED screens can strain battery life or necessitate more robust power systems. Balancing power efficiency with display performance is crucial for practical implementation in portable medical devices.
Durability and longevity pose additional hurdles in AMOLED integration. Medical environments demand robust equipment that can withstand frequent cleaning and disinfection. The organic materials in AMOLED displays are sensitive to moisture and oxygen, requiring advanced encapsulation techniques to prevent degradation and ensure long-term reliability in clinical settings.
Color stability and uniformity across the display are critical for accurate medical image interpretation. AMOLED displays must maintain consistent color reproduction over time and across different viewing angles, which can be challenging due to the inherent characteristics of organic materials and their degradation patterns.
The integration of touch functionality, often required in modern medical devices, introduces further complexities. Implementing touch sensors without compromising display quality or increasing device thickness requires sophisticated engineering solutions. Moreover, ensuring the touch interface remains responsive even when users wear medical gloves adds another layer of technical difficulty.
Thermal management is a crucial consideration in AMOLED medical integration. Medical imaging devices often generate significant heat during operation, and AMOLED displays are sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Developing effective cooling systems that maintain optimal display performance without interfering with other device components is a complex engineering task.
Lastly, the challenge of scalability and manufacturing consistency cannot be overlooked. Producing AMOLED displays for medical devices requires stringent quality control measures to ensure uniformity across production batches. Achieving this level of consistency while scaling up production to meet market demands presents significant technical and logistical challenges for manufacturers.
Current AMOLED Solutions for Medical Imaging
01 AMOLED display structure and manufacturing
This category focuses on the structure and manufacturing processes of AMOLED displays. It includes innovations in pixel arrangements, thin-film transistor (TFT) designs, and fabrication techniques to improve display performance, efficiency, and yield.- AMOLED display technology: AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology is used in displays for various electronic devices. It offers advantages such as high contrast ratios, wide color gamut, and energy efficiency. AMOLED displays use organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied, resulting in vibrant and sharp images.
- Pixel circuit design for AMOLED displays: Pixel circuits are crucial components in AMOLED displays, responsible for controlling individual pixels. Advanced pixel circuit designs aim to improve display performance, reduce power consumption, and enhance image quality. These circuits often incorporate transistors, capacitors, and other electronic components to achieve precise control over each pixel's light emission.
- AMOLED panel manufacturing techniques: Manufacturing processes for AMOLED panels involve various techniques to ensure high-quality displays. These may include thin-film deposition, patterning, encapsulation, and integration of driver circuits. Advanced manufacturing methods aim to improve yield rates, reduce costs, and enhance the overall performance and durability of AMOLED displays.
- Power management in AMOLED displays: Efficient power management is crucial for AMOLED displays, especially in mobile devices. Various techniques are employed to reduce power consumption while maintaining image quality. These may include adaptive brightness control, selective pixel dimming, and optimized driving schemes. Power management solutions aim to extend battery life and improve overall device efficiency.
- Touch integration in AMOLED displays: Integrating touch functionality into AMOLED displays is essential for modern interactive devices. Various approaches are used to combine touch sensors with AMOLED panels, including in-cell and on-cell touch technologies. These integrated solutions aim to improve touch responsiveness, reduce display thickness, and enhance overall user experience.
02 AMOLED driving and control methods
This point covers various driving and control methods for AMOLED displays. It includes techniques for pixel compensation, voltage control, and current driving to enhance image quality, reduce power consumption, and extend the lifespan of AMOLED panels.Expand Specific Solutions03 AMOLED power management and efficiency
This category addresses power management and efficiency improvements in AMOLED displays. It includes techniques for reducing power consumption, optimizing brightness control, and enhancing overall energy efficiency of AMOLED panels.Expand Specific Solutions04 AMOLED color management and image quality
This point focuses on color management and image quality enhancements for AMOLED displays. It includes techniques for color calibration, gamut expansion, and image processing to improve visual performance and accuracy of AMOLED panels.Expand Specific Solutions05 AMOLED integration with other technologies
This category covers the integration of AMOLED technology with other advanced features and technologies. It includes innovations in touch sensing, fingerprint recognition, and flexible display applications to expand the functionality and versatility of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Medical AMOLED Development
The incorporation of AMOLED in medical imaging devices is in its early stages, with the market showing significant growth potential. The technology's maturity varies among key players, with companies like Samsung Electronics and BOE Technology Group leading in AMOLED development. While the market size is expanding, it remains relatively niche within the broader medical imaging sector. Companies such as Koninklijke Philips and IBM are exploring AMOLED applications in healthcare, leveraging their expertise in medical technology. The competitive landscape is diverse, with display manufacturers like Tianma Microelectronics and Everdisplay Optronics also entering the medical imaging space, indicating a growing interest in AMOLED's potential for advanced diagnostic visualization.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed AMOLED solutions specifically tailored for medical imaging applications, focusing on high resolution and color accuracy. Their approach involves using advanced oxide semiconductor technology to create backplanes with higher electron mobility, allowing for faster refresh rates and improved image quality[9]. BOE has implemented a unique pixel structure that enhances brightness uniformity across the display, crucial for accurate interpretation of medical images[10]. To address the challenges of power consumption in always-on medical environments, BOE has developed low-power driving schemes that optimize energy efficiency without compromising image quality[11]. They have also focused on improving the lifespan of AMOLED displays in medical settings by implementing advanced materials that resist degradation under continuous use[12].
Strengths: High-resolution displays with excellent color accuracy and uniformity. Advanced power-saving technologies. Weaknesses: Less experience in medical-specific applications compared to some competitors.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed advanced AMOLED technology for medical imaging devices, focusing on high-resolution displays with enhanced contrast and color accuracy. Their approach involves using organic materials that emit light when an electric current is applied, resulting in displays with deeper blacks and more vibrant colors[1]. For medical imaging, Samsung has implemented a specialized pixel structure that allows for higher pixel density and improved image sharpness, crucial for accurate diagnosis[2]. They have also addressed power efficiency concerns by incorporating low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) backplanes, which enable better electron mobility and lower power consumption[3]. To combat image retention issues, Samsung has developed advanced compensation algorithms that adjust pixel voltages in real-time, ensuring consistent image quality over extended use[4].
Strengths: Superior image quality, high contrast ratio, and wide color gamut. Excellent power efficiency and thin form factor. Weaknesses: Higher production costs and potential for burn-in over time.
Innovations in AMOLED for Medical Applications
Display device and display panel thereof
PatentPendingCN118785749A
Innovation
- A blocking structure is provided on the pixel defining layer of the display panel to block the first carrier layer connection between adjacent sub-pixels, and the second carrier layer is provided on one side of the blocking structure to ensure that multiple sub-pixels share the third carrier layer. The conduction between the two-carrier layer and the cathode electrode.
Organic light emitting display
PatentInactiveEP3098804A3
Innovation
- The proposed solution involves a pixel structure with a driving transistor, multiple transistors, and a capacitor to control the flow of current and compensate for threshold voltage changes, using an initial voltage lower than the low-level driving voltage to minimize unnecessary light emission and leakage current, and ensuring a sufficient sampling period for accurate compensation.
Regulatory Considerations for Medical Display Devices
The incorporation of AMOLED technology in medical imaging devices necessitates careful consideration of regulatory requirements to ensure patient safety and device efficacy. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the approval process for medical devices, including those with display components. Manufacturers must comply with the FDA's Quality System Regulation (QSR) and demonstrate that their devices meet safety and performance standards.
For AMOLED-equipped medical imaging devices, specific regulatory considerations include image quality, color accuracy, and long-term display performance. The FDA's guidance on display devices for diagnostic radiology emphasizes the importance of maintaining consistent image quality over time. This is particularly relevant for AMOLED displays, which may experience burn-in or color shift with prolonged use.
International standards, such as those set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), also play a crucial role in the regulatory landscape. IEC 62563-1, for instance, outlines the quality assurance requirements for medical display systems. Manufacturers must ensure that AMOLED displays in medical devices meet these standards, which cover aspects like luminance, contrast ratio, and uniformity.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is another critical regulatory consideration. Medical imaging devices must comply with IEC 60601-1-2, which specifies EMC requirements for medical electrical equipment. AMOLED displays and their associated electronics must not interfere with other medical equipment or be susceptible to external electromagnetic disturbances.
Software validation is an essential aspect of regulatory compliance for medical devices with advanced display technologies. The FDA's guidance on software validation emphasizes the need for thorough testing and documentation of software components, including those controlling AMOLED displays. This includes verification of display calibration, color management, and image processing algorithms.
Cybersecurity regulations are increasingly important for medical devices with digital components. The FDA has issued guidance on cybersecurity for networked medical devices, which applies to AMOLED-equipped imaging systems that may be connected to hospital networks. Manufacturers must implement robust security measures to protect patient data and prevent unauthorized access to device controls.
In the European Union, medical devices must comply with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into full effect in May 2021. The MDR places greater emphasis on post-market surveillance and clinical evidence, requiring manufacturers to continuously monitor the performance and safety of their devices, including the long-term reliability of AMOLED displays in medical applications.
For AMOLED-equipped medical imaging devices, specific regulatory considerations include image quality, color accuracy, and long-term display performance. The FDA's guidance on display devices for diagnostic radiology emphasizes the importance of maintaining consistent image quality over time. This is particularly relevant for AMOLED displays, which may experience burn-in or color shift with prolonged use.
International standards, such as those set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), also play a crucial role in the regulatory landscape. IEC 62563-1, for instance, outlines the quality assurance requirements for medical display systems. Manufacturers must ensure that AMOLED displays in medical devices meet these standards, which cover aspects like luminance, contrast ratio, and uniformity.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is another critical regulatory consideration. Medical imaging devices must comply with IEC 60601-1-2, which specifies EMC requirements for medical electrical equipment. AMOLED displays and their associated electronics must not interfere with other medical equipment or be susceptible to external electromagnetic disturbances.
Software validation is an essential aspect of regulatory compliance for medical devices with advanced display technologies. The FDA's guidance on software validation emphasizes the need for thorough testing and documentation of software components, including those controlling AMOLED displays. This includes verification of display calibration, color management, and image processing algorithms.
Cybersecurity regulations are increasingly important for medical devices with digital components. The FDA has issued guidance on cybersecurity for networked medical devices, which applies to AMOLED-equipped imaging systems that may be connected to hospital networks. Manufacturers must implement robust security measures to protect patient data and prevent unauthorized access to device controls.
In the European Union, medical devices must comply with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into full effect in May 2021. The MDR places greater emphasis on post-market surveillance and clinical evidence, requiring manufacturers to continuously monitor the performance and safety of their devices, including the long-term reliability of AMOLED displays in medical applications.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of AMOLED in Medical Imaging
The incorporation of AMOLED technology in medical imaging devices presents a complex cost-benefit scenario that requires careful analysis. On the cost side, AMOLED displays are generally more expensive to produce than traditional LCD screens, primarily due to the sophisticated manufacturing processes and materials involved. This higher production cost can significantly impact the overall price of medical imaging equipment, potentially limiting its accessibility to healthcare providers with budget constraints.
However, the benefits of AMOLED technology in medical imaging are substantial and may justify the increased costs. AMOLED displays offer superior image quality with higher contrast ratios, deeper blacks, and more vibrant colors. This enhanced visual performance can lead to more accurate diagnoses and improved patient outcomes, particularly in fields such as radiology and endoscopy where image clarity is crucial.
Energy efficiency is another important factor to consider. AMOLED screens typically consume less power than LCDs, especially when displaying darker images, which are common in medical imaging. This can result in longer battery life for portable devices and reduced energy costs for stationary equipment, potentially offsetting some of the initial investment over time.
Durability and lifespan are also key considerations. While AMOLED displays have historically been prone to issues like burn-in, advancements in technology have significantly mitigated these problems. Modern AMOLED screens often demonstrate comparable or even superior longevity to LCDs, which can translate to reduced maintenance and replacement costs over the lifetime of the medical imaging device.
The flexibility of AMOLED technology opens up new design possibilities for medical imaging equipment. Curved or even foldable displays could enable more ergonomic and space-efficient devices, potentially improving workflow in healthcare settings and enhancing the overall user experience for medical professionals.
In terms of market perception, the adoption of cutting-edge AMOLED technology can position medical imaging device manufacturers as industry leaders, potentially commanding premium prices and gaining market share. This could lead to increased revenue that helps offset the higher production costs.
Ultimately, the cost-benefit analysis of incorporating AMOLED in medical imaging devices must be evaluated on a case-by-case basis, considering factors such as the specific application, target market, and long-term strategic goals of the manufacturer. While the initial costs may be higher, the potential for improved diagnostic accuracy, energy savings, and market differentiation may well justify the investment in many scenarios.
However, the benefits of AMOLED technology in medical imaging are substantial and may justify the increased costs. AMOLED displays offer superior image quality with higher contrast ratios, deeper blacks, and more vibrant colors. This enhanced visual performance can lead to more accurate diagnoses and improved patient outcomes, particularly in fields such as radiology and endoscopy where image clarity is crucial.
Energy efficiency is another important factor to consider. AMOLED screens typically consume less power than LCDs, especially when displaying darker images, which are common in medical imaging. This can result in longer battery life for portable devices and reduced energy costs for stationary equipment, potentially offsetting some of the initial investment over time.
Durability and lifespan are also key considerations. While AMOLED displays have historically been prone to issues like burn-in, advancements in technology have significantly mitigated these problems. Modern AMOLED screens often demonstrate comparable or even superior longevity to LCDs, which can translate to reduced maintenance and replacement costs over the lifetime of the medical imaging device.
The flexibility of AMOLED technology opens up new design possibilities for medical imaging equipment. Curved or even foldable displays could enable more ergonomic and space-efficient devices, potentially improving workflow in healthcare settings and enhancing the overall user experience for medical professionals.
In terms of market perception, the adoption of cutting-edge AMOLED technology can position medical imaging device manufacturers as industry leaders, potentially commanding premium prices and gaining market share. This could lead to increased revenue that helps offset the higher production costs.
Ultimately, the cost-benefit analysis of incorporating AMOLED in medical imaging devices must be evaluated on a case-by-case basis, considering factors such as the specific application, target market, and long-term strategic goals of the manufacturer. While the initial costs may be higher, the potential for improved diagnostic accuracy, energy savings, and market differentiation may well justify the investment in many scenarios.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!