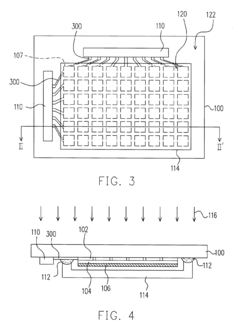
Strategic mergers improving AMOLED production processes.
JUL 17, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Evolution Goals
The evolution of AMOLED technology has been driven by the continuous pursuit of enhanced display performance, improved production efficiency, and reduced manufacturing costs. As the industry progresses, several key goals have emerged to shape the future of AMOLED production processes.
One primary objective is to increase the overall yield rate of AMOLED panels. This involves refining manufacturing techniques to minimize defects and improve consistency across large-scale production. By achieving higher yield rates, manufacturers can significantly reduce costs and make AMOLED displays more accessible to a broader market.
Another crucial goal is to enhance the color accuracy and brightness of AMOLED displays. This includes developing more precise deposition methods for organic materials and improving the efficiency of light-emitting compounds. The aim is to produce displays with wider color gamuts, higher peak brightness, and better color consistency across different viewing angles.
Extending the lifespan of AMOLED displays remains a critical focus area. Researchers are working on developing more stable organic materials and implementing advanced encapsulation techniques to protect the sensitive OLED components from moisture and oxygen degradation. These efforts are essential for ensuring long-term reliability, particularly in applications where displays are expected to operate for extended periods.
Power efficiency is another key target for AMOLED evolution. By optimizing the electrical characteristics of OLED materials and refining pixel designs, manufacturers aim to reduce power consumption without compromising display quality. This is particularly important for mobile devices where battery life is a crucial factor.
Flexibility and form factor innovation continue to drive AMOLED development. The goal is to create ultra-thin, flexible, and even foldable displays that can be integrated into a wide range of devices and surfaces. This requires advancements in substrate materials, encapsulation methods, and production processes that can maintain display integrity under various bending and folding conditions.
Scaling up production capabilities for larger AMOLED panels is also a significant objective. As demand grows for AMOLED technology in televisions and other large-format displays, manufacturers are focusing on developing processes that can efficiently produce high-quality panels at sizes exceeding 65 inches diagonally.
Lastly, there is a strong emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility in AMOLED production. Goals in this area include reducing the use of rare earth materials, implementing more energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and developing recycling methods for end-of-life AMOLED products.
One primary objective is to increase the overall yield rate of AMOLED panels. This involves refining manufacturing techniques to minimize defects and improve consistency across large-scale production. By achieving higher yield rates, manufacturers can significantly reduce costs and make AMOLED displays more accessible to a broader market.
Another crucial goal is to enhance the color accuracy and brightness of AMOLED displays. This includes developing more precise deposition methods for organic materials and improving the efficiency of light-emitting compounds. The aim is to produce displays with wider color gamuts, higher peak brightness, and better color consistency across different viewing angles.
Extending the lifespan of AMOLED displays remains a critical focus area. Researchers are working on developing more stable organic materials and implementing advanced encapsulation techniques to protect the sensitive OLED components from moisture and oxygen degradation. These efforts are essential for ensuring long-term reliability, particularly in applications where displays are expected to operate for extended periods.
Power efficiency is another key target for AMOLED evolution. By optimizing the electrical characteristics of OLED materials and refining pixel designs, manufacturers aim to reduce power consumption without compromising display quality. This is particularly important for mobile devices where battery life is a crucial factor.
Flexibility and form factor innovation continue to drive AMOLED development. The goal is to create ultra-thin, flexible, and even foldable displays that can be integrated into a wide range of devices and surfaces. This requires advancements in substrate materials, encapsulation methods, and production processes that can maintain display integrity under various bending and folding conditions.
Scaling up production capabilities for larger AMOLED panels is also a significant objective. As demand grows for AMOLED technology in televisions and other large-format displays, manufacturers are focusing on developing processes that can efficiently produce high-quality panels at sizes exceeding 65 inches diagonally.
Lastly, there is a strong emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility in AMOLED production. Goals in this area include reducing the use of rare earth materials, implementing more energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and developing recycling methods for end-of-life AMOLED products.
AMOLED Market Analysis
The AMOLED market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for high-quality displays in smartphones, televisions, and other electronic devices. This trend is expected to continue, with the global AMOLED market projected to reach substantial value in the coming years.
The smartphone segment remains the largest application area for AMOLED displays, accounting for a major portion of the market share. The adoption of AMOLED technology in smartphones has been particularly strong among premium and mid-range devices, as manufacturers seek to differentiate their products with superior display quality and energy efficiency.
Beyond smartphones, AMOLED displays are gaining traction in other consumer electronics sectors. The television market has seen a notable increase in AMOLED adoption, particularly in the high-end segment where consumers are willing to pay a premium for superior picture quality. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, have also contributed to market growth, leveraging AMOLED's advantages in power efficiency and flexibility.
The automotive industry represents an emerging opportunity for AMOLED technology. As vehicles become more technologically advanced, there is growing demand for high-quality displays in infotainment systems and digital dashboards. AMOLED's ability to deliver vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and wide viewing angles makes it an attractive option for automotive applications.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the AMOLED market, with South Korea and China being the primary manufacturing hubs. However, there is increasing investment in AMOLED production capabilities in other regions, including Europe and North America, as companies seek to diversify their supply chains and reduce dependence on Asian manufacturers.
The market is characterized by intense competition among a few key players, with Samsung Display holding a dominant position. Other significant manufacturers include LG Display, BOE Technology, and Visionox. These companies are continuously investing in research and development to improve AMOLED technology and production processes.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the AMOLED market faces challenges. Production costs remain relatively high compared to traditional LCD technology, which can limit adoption in price-sensitive market segments. Additionally, concerns about screen burn-in and color shift over time persist, although manufacturers are making progress in addressing these issues through technological improvements.
Looking ahead, the AMOLED market is poised for continued expansion, driven by technological advancements, increasing adoption across various industries, and growing consumer demand for high-quality displays. Strategic mergers and acquisitions in the industry are likely to play a crucial role in shaping the competitive landscape and driving innovation in AMOLED production processes.
The smartphone segment remains the largest application area for AMOLED displays, accounting for a major portion of the market share. The adoption of AMOLED technology in smartphones has been particularly strong among premium and mid-range devices, as manufacturers seek to differentiate their products with superior display quality and energy efficiency.
Beyond smartphones, AMOLED displays are gaining traction in other consumer electronics sectors. The television market has seen a notable increase in AMOLED adoption, particularly in the high-end segment where consumers are willing to pay a premium for superior picture quality. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, have also contributed to market growth, leveraging AMOLED's advantages in power efficiency and flexibility.
The automotive industry represents an emerging opportunity for AMOLED technology. As vehicles become more technologically advanced, there is growing demand for high-quality displays in infotainment systems and digital dashboards. AMOLED's ability to deliver vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and wide viewing angles makes it an attractive option for automotive applications.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the AMOLED market, with South Korea and China being the primary manufacturing hubs. However, there is increasing investment in AMOLED production capabilities in other regions, including Europe and North America, as companies seek to diversify their supply chains and reduce dependence on Asian manufacturers.
The market is characterized by intense competition among a few key players, with Samsung Display holding a dominant position. Other significant manufacturers include LG Display, BOE Technology, and Visionox. These companies are continuously investing in research and development to improve AMOLED technology and production processes.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the AMOLED market faces challenges. Production costs remain relatively high compared to traditional LCD technology, which can limit adoption in price-sensitive market segments. Additionally, concerns about screen burn-in and color shift over time persist, although manufacturers are making progress in addressing these issues through technological improvements.
Looking ahead, the AMOLED market is poised for continued expansion, driven by technological advancements, increasing adoption across various industries, and growing consumer demand for high-quality displays. Strategic mergers and acquisitions in the industry are likely to play a crucial role in shaping the competitive landscape and driving innovation in AMOLED production processes.
AMOLED Tech Challenges
AMOLED technology, while revolutionary in display quality, faces several significant challenges in its production processes. One of the primary hurdles is the complexity and cost associated with manufacturing high-quality OLED materials. The organic compounds used in AMOLED displays are sensitive to moisture and oxygen, requiring stringent production environments and sophisticated encapsulation techniques.
Another major challenge lies in the scalability of production. As demand for larger AMOLED displays grows, manufacturers struggle to maintain consistent quality across larger substrate sizes. This issue is particularly pronounced in the production of TV-sized panels, where yield rates tend to be lower compared to smaller displays for mobile devices.
The lifespan of OLED materials, especially blue OLEDs, remains a concern. Blue OLEDs typically have shorter lifespans compared to red and green, leading to color shift over time. This necessitates ongoing research into more stable blue OLED materials and compensation algorithms to maintain color accuracy throughout the display's lifetime.
Burn-in, or image retention, is another persistent challenge. Static elements on AMOLED displays can cause uneven wear of the organic materials, resulting in ghosting effects. While various mitigation techniques have been developed, a definitive solution remains elusive.
Power efficiency, particularly for mobile applications, continues to be an area of focus. While AMOLED displays can be more energy-efficient than LCD in certain scenarios, there's still room for improvement, especially when displaying bright, white content.
The intricate patterning required for high-resolution AMOLED displays poses another technical challenge. As pixel densities increase, the precision required for depositing organic materials becomes more demanding, pushing the limits of current deposition technologies.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in reducing production costs while maintaining quality. The high-precision equipment and materials required for AMOLED production contribute to higher manufacturing costs compared to traditional LCD technology. This cost factor has been a barrier to wider adoption, particularly in mid-range consumer electronics.
Another major challenge lies in the scalability of production. As demand for larger AMOLED displays grows, manufacturers struggle to maintain consistent quality across larger substrate sizes. This issue is particularly pronounced in the production of TV-sized panels, where yield rates tend to be lower compared to smaller displays for mobile devices.
The lifespan of OLED materials, especially blue OLEDs, remains a concern. Blue OLEDs typically have shorter lifespans compared to red and green, leading to color shift over time. This necessitates ongoing research into more stable blue OLED materials and compensation algorithms to maintain color accuracy throughout the display's lifetime.
Burn-in, or image retention, is another persistent challenge. Static elements on AMOLED displays can cause uneven wear of the organic materials, resulting in ghosting effects. While various mitigation techniques have been developed, a definitive solution remains elusive.
Power efficiency, particularly for mobile applications, continues to be an area of focus. While AMOLED displays can be more energy-efficient than LCD in certain scenarios, there's still room for improvement, especially when displaying bright, white content.
The intricate patterning required for high-resolution AMOLED displays poses another technical challenge. As pixel densities increase, the precision required for depositing organic materials becomes more demanding, pushing the limits of current deposition technologies.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in reducing production costs while maintaining quality. The high-precision equipment and materials required for AMOLED production contribute to higher manufacturing costs compared to traditional LCD technology. This cost factor has been a barrier to wider adoption, particularly in mid-range consumer electronics.
Current AMOLED Solutions
01 OLED material deposition techniques
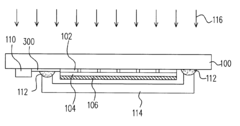
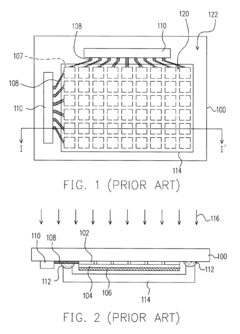
Various deposition techniques are employed in AMOLED production, including thermal evaporation, inkjet printing, and organic vapor phase deposition. These methods allow for precise control of organic layer thickness and uniformity, which are crucial for display performance and efficiency.- OLED material deposition techniques: Various deposition techniques are used in AMOLED production, including thermal evaporation, inkjet printing, and organic vapor phase deposition. These methods allow for precise control of organic layer thickness and uniformity, which are crucial for display performance and efficiency.
- Thin-film transistor (TFT) fabrication: The production of AMOLED displays involves the fabrication of thin-film transistors (TFTs) as the backplane. This process includes deposition of semiconductor materials, patterning, and formation of electrodes. Advanced TFT technologies, such as low-temperature polysilicon (LTPS) or oxide TFTs, are used to improve display performance and power efficiency.
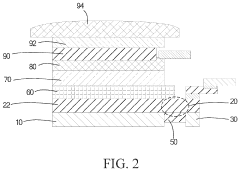
- Encapsulation and protection techniques: AMOLED displays require effective encapsulation to protect the organic materials from moisture and oxygen. Advanced encapsulation techniques, such as thin-film encapsulation (TFE) or hybrid encapsulation, are employed to ensure long-term stability and reliability of the displays while maintaining flexibility and thinness.
- Color patterning and pixel formation: The production of full-color AMOLED displays involves precise patterning of red, green, and blue subpixels. Various methods are used, including fine metal mask (FMM) deposition, white OLED with color filters, and direct patterning techniques. These processes aim to achieve high color accuracy, resolution, and efficiency in the final display.
- Integration and quality control processes: AMOLED production involves complex integration processes, including module assembly, driver IC bonding, and flexible printed circuit (FPC) attachment. Rigorous quality control measures are implemented throughout the production line, utilizing advanced inspection and testing equipment to ensure high yield rates and product reliability.
02 Thin-film transistor (TFT) fabrication
The production of AMOLED displays involves the fabrication of thin-film transistors, which are essential for controlling individual pixels. Advanced TFT technologies, such as low-temperature polysilicon (LTPS) and oxide TFTs, are used to improve display performance and power efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Encapsulation and protection methods
AMOLED displays require effective encapsulation to protect the organic materials from moisture and oxygen. Advanced techniques like thin-film encapsulation (TFE) and hybrid encapsulation are used to enhance the longevity and reliability of AMOLED devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Color patterning and pixel structure design
Color patterning techniques, such as fine metal mask (FMM) deposition and white OLED with color filters, are crucial in AMOLED production. Innovative pixel structures and subpixel arrangements are developed to improve display resolution, color gamut, and power efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quality control and testing processes
AMOLED production involves rigorous quality control and testing procedures to ensure display uniformity, color accuracy, and longevity. Advanced inspection techniques, including automated optical inspection (AOI) and electrical testing, are implemented throughout the manufacturing process.Expand Specific Solutions
AMOLED Industry Players
The strategic mergers in AMOLED production processes are shaping a competitive landscape in a rapidly evolving industry. The market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand for AMOLED displays in smartphones, TVs, and other consumer electronics. Major players like Samsung Display, BOE Technology, and LG Display are investing heavily in R&D and production capacity expansion. The technology is maturing, but there's still room for innovation in areas like flexible displays and improved efficiency. Companies like Visionox, TCL CSOT, and Tianma are also making significant strides, intensifying competition and driving technological advancements in the AMOLED sector.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has pursued strategic mergers to enhance its AMOLED production capabilities. The company acquired a significant stake in Sino Wealth Electronic, a driver IC manufacturer, to secure a stable supply of critical components for AMOLED displays[4]. BOE has also merged with CEC Panda, consolidating its position in the LCD market while freeing up resources for AMOLED development[5]. In terms of production processes, BOE has implemented advanced OLED printing technology through a partnership with JOLED, improving efficiency and reducing material waste in AMOLED manufacturing[6]. The company has invested in flexible OLED production lines and has been working on integrating AI and big data analytics into its production processes to optimize yield and quality control[7].
Strengths: Vertical integration, diversified display technology portfolio, advanced manufacturing techniques. Weaknesses: Relatively new entrant in AMOLED market compared to Korean competitors, potential overcapacity risks.
TCL China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: TCL CSOT has implemented strategic mergers and partnerships to improve its AMOLED production processes. The company acquired Samsung Display's Suzhou LCD production line in 2020, which it has been repurposing for OLED production[14]. This acquisition has allowed TCL CSOT to expand its display manufacturing capabilities and leverage Samsung's expertise in display technologies. The company has also formed partnerships with equipment manufacturers and material suppliers to enhance its AMOLED production processes. TCL CSOT has invested in developing inkjet printing technology for OLED manufacturing, aiming to improve production efficiency and reduce costs[15]. The company has also focused on implementing advanced oxide backplane technology and developing its own OLED materials to improve display performance and production yield[16]. TCL CSOT has been working on integrating smart manufacturing technologies, including AI and IoT, into its production lines to optimize processes and quality control.
Strengths: Rapid expansion in AMOLED production capacity, strong backing from TCL Group, diverse display technology portfolio. Weaknesses: Relatively new entrant in AMOLED market, potential challenges in competing with more established players.
Key AMOLED Innovations
Active matrix organic light emitting diode panel
PatentInactiveUS20200185645A1
Innovation
- An AMOLED panel design featuring a hydrogel layer coated between two backing plates at the bent portion, which is then solidified with ultraviolet light, providing structural strength and toughness to the fillet formed when the panel is folded, thereby preventing deformation and breakage.
Active matrix organic light emitting diode display and fabrication method of the same
PatentInactiveUS6786788B2
Innovation
- The use of transparent conductive lines, made of indium tin oxide or indium zinc oxide, to connect pixel structures to the driving chip, allowing simultaneous formation and curing of photosensitive glue for complete sealing, replacing the conventional fan-outs and ensuring proper encapsulation.
Merger Impact Analysis
Strategic mergers in the AMOLED production industry have significantly impacted the landscape of display technology manufacturing. These consolidations have led to improved production processes, enhanced efficiency, and accelerated technological advancements. By combining resources, expertise, and intellectual property, merged entities have been able to overcome production challenges more effectively.
One of the primary benefits of these mergers has been the optimization of supply chains. Integrated companies can now manage the entire production process from raw materials to finished displays, reducing costs and improving quality control. This vertical integration has resulted in more streamlined operations and faster time-to-market for new AMOLED products.
The pooling of research and development resources has also been a crucial outcome of these strategic mergers. Combined R&D teams have been able to tackle complex technical issues more efficiently, leading to breakthroughs in areas such as pixel density, color accuracy, and power consumption. This collaborative approach has accelerated the development of next-generation AMOLED technologies, including foldable and rollable displays.
Mergers have also facilitated the sharing of patented technologies and manufacturing techniques. This cross-pollination of ideas has led to the creation of hybrid production methods that combine the strengths of different approaches. As a result, yields have improved, and production costs have decreased, making AMOLED displays more accessible to a wider range of consumer electronics.
The consolidation of market power through mergers has enabled companies to invest more heavily in advanced manufacturing equipment. State-of-the-art facilities with cutting-edge machinery have been established, allowing for higher precision in AMOLED panel production and the ability to manufacture at larger scales. This has been particularly important in meeting the growing demand for AMOLED displays in smartphones, televisions, and emerging applications like automotive displays.
Furthermore, these mergers have had a profound impact on the competitive landscape. The formation of larger, more capable entities has intensified competition among the top players, driving further innovation and efficiency improvements. Smaller companies have been forced to specialize or seek partnerships to remain relevant in this evolving market.
However, the impact of these mergers has not been without challenges. Integration of different corporate cultures and alignment of business strategies have posed significant hurdles for some merged entities. Additionally, concerns about market concentration and potential anti-competitive practices have drawn regulatory scrutiny in some regions.
One of the primary benefits of these mergers has been the optimization of supply chains. Integrated companies can now manage the entire production process from raw materials to finished displays, reducing costs and improving quality control. This vertical integration has resulted in more streamlined operations and faster time-to-market for new AMOLED products.
The pooling of research and development resources has also been a crucial outcome of these strategic mergers. Combined R&D teams have been able to tackle complex technical issues more efficiently, leading to breakthroughs in areas such as pixel density, color accuracy, and power consumption. This collaborative approach has accelerated the development of next-generation AMOLED technologies, including foldable and rollable displays.
Mergers have also facilitated the sharing of patented technologies and manufacturing techniques. This cross-pollination of ideas has led to the creation of hybrid production methods that combine the strengths of different approaches. As a result, yields have improved, and production costs have decreased, making AMOLED displays more accessible to a wider range of consumer electronics.
The consolidation of market power through mergers has enabled companies to invest more heavily in advanced manufacturing equipment. State-of-the-art facilities with cutting-edge machinery have been established, allowing for higher precision in AMOLED panel production and the ability to manufacture at larger scales. This has been particularly important in meeting the growing demand for AMOLED displays in smartphones, televisions, and emerging applications like automotive displays.
Furthermore, these mergers have had a profound impact on the competitive landscape. The formation of larger, more capable entities has intensified competition among the top players, driving further innovation and efficiency improvements. Smaller companies have been forced to specialize or seek partnerships to remain relevant in this evolving market.
However, the impact of these mergers has not been without challenges. Integration of different corporate cultures and alignment of business strategies have posed significant hurdles for some merged entities. Additionally, concerns about market concentration and potential anti-competitive practices have drawn regulatory scrutiny in some regions.
Synergy Opportunities
Strategic mergers in the AMOLED production industry present significant synergy opportunities that can revolutionize manufacturing processes and enhance overall efficiency. By combining complementary strengths and resources, merged entities can achieve economies of scale, streamline operations, and accelerate technological advancements.
One key area of synergy lies in the integration of research and development capabilities. Merging companies can pool their intellectual property, expertise, and innovation pipelines to create a more robust and diverse portfolio of AMOLED technologies. This collaborative approach can lead to breakthrough advancements in areas such as material science, pixel architecture, and manufacturing techniques.
Production capacity optimization is another crucial synergy opportunity. Merged entities can rationalize their manufacturing facilities, eliminating redundancies and maximizing utilization rates. This consolidation can result in improved cost structures and increased production volumes, enabling the combined company to meet growing market demand more effectively.
Supply chain integration presents a significant avenue for synergy realization. By leveraging their combined purchasing power and supplier relationships, merged companies can negotiate better terms, reduce procurement costs, and enhance supply chain resilience. This integration can also lead to the development of more efficient logistics networks, reducing lead times and improving overall operational agility.
Technology transfer and knowledge sharing between merged entities can accelerate the adoption of best practices across the organization. This cross-pollination of ideas and expertise can lead to the rapid implementation of process improvements, quality enhancements, and yield optimization techniques throughout the production cycle.
Vertical integration opportunities may also arise from strategic mergers, allowing companies to control more stages of the AMOLED production process. This integration can lead to better quality control, reduced dependency on external suppliers, and increased flexibility in responding to market demands.
Lastly, mergers can create synergies in talent acquisition and retention. By combining human resources, the merged entity can attract and retain top talent in the industry, fostering a culture of innovation and excellence. This pooling of expertise can drive continuous improvement in AMOLED production processes and maintain a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving display technology market.
One key area of synergy lies in the integration of research and development capabilities. Merging companies can pool their intellectual property, expertise, and innovation pipelines to create a more robust and diverse portfolio of AMOLED technologies. This collaborative approach can lead to breakthrough advancements in areas such as material science, pixel architecture, and manufacturing techniques.
Production capacity optimization is another crucial synergy opportunity. Merged entities can rationalize their manufacturing facilities, eliminating redundancies and maximizing utilization rates. This consolidation can result in improved cost structures and increased production volumes, enabling the combined company to meet growing market demand more effectively.
Supply chain integration presents a significant avenue for synergy realization. By leveraging their combined purchasing power and supplier relationships, merged companies can negotiate better terms, reduce procurement costs, and enhance supply chain resilience. This integration can also lead to the development of more efficient logistics networks, reducing lead times and improving overall operational agility.
Technology transfer and knowledge sharing between merged entities can accelerate the adoption of best practices across the organization. This cross-pollination of ideas and expertise can lead to the rapid implementation of process improvements, quality enhancements, and yield optimization techniques throughout the production cycle.
Vertical integration opportunities may also arise from strategic mergers, allowing companies to control more stages of the AMOLED production process. This integration can lead to better quality control, reduced dependency on external suppliers, and increased flexibility in responding to market demands.
Lastly, mergers can create synergies in talent acquisition and retention. By combining human resources, the merged entity can attract and retain top talent in the industry, fostering a culture of innovation and excellence. This pooling of expertise can drive continuous improvement in AMOLED production processes and maintain a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving display technology market.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!