How AMOLED scales up for large public digital displays?
JUL 17, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Large Display Evolution and Objectives
AMOLED technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception, particularly in the realm of large-scale displays for public spaces. The journey from small smartphone screens to expansive digital billboards represents a remarkable technological leap. Initially, AMOLED displays were limited to small form factors due to manufacturing challenges and cost constraints. However, continuous advancements in materials science, production techniques, and display engineering have paved the way for increasingly larger AMOLED panels.
The primary objective in scaling up AMOLED for large public displays is to maintain the technology's inherent advantages while overcoming size-related challenges. These advantages include superior contrast ratios, vibrant colors, and energy efficiency. As displays grow in size, maintaining uniform brightness and color across the entire panel becomes more complex. Additionally, the goal is to enhance durability and longevity, crucial factors for outdoor public displays exposed to various environmental conditions.
Another key objective is to improve the cost-effectiveness of large AMOLED displays. As the technology scales up, reducing production costs while maintaining quality is essential for widespread adoption in public spaces. This involves optimizing manufacturing processes, developing new materials, and improving yield rates for larger panels.
Enhancing the visual performance of large AMOLED displays is also a critical goal. This includes increasing resolution and pixel density to maintain image quality at greater viewing distances, typical in public settings. Moreover, improving the displays' visibility in bright outdoor environments is crucial for their effectiveness as public information systems.
The evolution of AMOLED technology for large displays also aims to address specific requirements of public digital signage. This includes developing solutions for modular designs, allowing for easier installation and maintenance of large-scale displays. Additionally, integrating advanced features such as touch capabilities, environmental sensors, and connectivity options is part of the ongoing development to make these displays more interactive and adaptable to various public applications.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, a significant focus is placed on sustainability. This involves developing more energy-efficient designs, using eco-friendly materials, and improving the recyclability of display components. These environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important as large public displays become more prevalent in urban landscapes.
The primary objective in scaling up AMOLED for large public displays is to maintain the technology's inherent advantages while overcoming size-related challenges. These advantages include superior contrast ratios, vibrant colors, and energy efficiency. As displays grow in size, maintaining uniform brightness and color across the entire panel becomes more complex. Additionally, the goal is to enhance durability and longevity, crucial factors for outdoor public displays exposed to various environmental conditions.
Another key objective is to improve the cost-effectiveness of large AMOLED displays. As the technology scales up, reducing production costs while maintaining quality is essential for widespread adoption in public spaces. This involves optimizing manufacturing processes, developing new materials, and improving yield rates for larger panels.
Enhancing the visual performance of large AMOLED displays is also a critical goal. This includes increasing resolution and pixel density to maintain image quality at greater viewing distances, typical in public settings. Moreover, improving the displays' visibility in bright outdoor environments is crucial for their effectiveness as public information systems.
The evolution of AMOLED technology for large displays also aims to address specific requirements of public digital signage. This includes developing solutions for modular designs, allowing for easier installation and maintenance of large-scale displays. Additionally, integrating advanced features such as touch capabilities, environmental sensors, and connectivity options is part of the ongoing development to make these displays more interactive and adaptable to various public applications.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, a significant focus is placed on sustainability. This involves developing more energy-efficient designs, using eco-friendly materials, and improving the recyclability of display components. These environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important as large public displays become more prevalent in urban landscapes.
Market Demand Analysis for Large Public Displays
The market demand for large public digital displays has been experiencing significant growth, driven by various factors across multiple sectors. In the retail industry, there is an increasing need for eye-catching, high-resolution displays to enhance customer engagement and improve brand visibility. Shopping malls, department stores, and flagship retail outlets are adopting large AMOLED displays to create immersive shopping experiences and showcase products in vivid detail.
The transportation sector is another key driver of market demand for large public displays. Airports, train stations, and bus terminals are investing in AMOLED technology to provide real-time information, advertisements, and entertainment to travelers. These displays offer superior visibility, even in bright environments, making them ideal for public spaces with varying lighting conditions.
In the entertainment and hospitality industries, there is a growing trend towards using large-scale AMOLED displays for creating immersive experiences. Theme parks, museums, and hotels are incorporating these displays to enhance visitor engagement and create memorable visual spectacles. The ability of AMOLED technology to deliver deep blacks and vibrant colors makes it particularly suitable for these applications.
The outdoor advertising market is also contributing to the demand for large public AMOLED displays. Billboard owners and advertising agencies are transitioning from traditional static billboards to dynamic digital displays, allowing for more flexible and targeted advertising campaigns. The energy efficiency and brightness capabilities of AMOLED technology make it an attractive option for outdoor installations.
Corporate environments and conference centers represent another significant market segment. Large AMOLED displays are being used for video conferencing, presentations, and digital signage in lobbies and meeting rooms. The superior image quality and wide viewing angles of AMOLED technology enhance communication and collaboration in these settings.
The education sector is showing increased interest in large public displays for interactive learning environments. Universities, schools, and training centers are adopting AMOLED displays to create engaging classroom experiences and facilitate distance learning initiatives. The high refresh rates and color accuracy of AMOLED technology contribute to reduced eye strain during extended viewing periods.
As smart cities continue to develop, there is a growing demand for large public displays integrated into urban infrastructure. These displays serve multiple purposes, including providing public information, emergency alerts, and interactive city guides. The durability and longevity of AMOLED technology make it suitable for long-term outdoor installations in various weather conditions.
The market size for large public digital displays is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with AMOLED technology playing a crucial role in this growth. As manufacturers overcome scaling challenges and improve production efficiencies, the adoption of large AMOLED displays in public spaces is expected to accelerate, further driving market demand across diverse industries and applications.
The transportation sector is another key driver of market demand for large public displays. Airports, train stations, and bus terminals are investing in AMOLED technology to provide real-time information, advertisements, and entertainment to travelers. These displays offer superior visibility, even in bright environments, making them ideal for public spaces with varying lighting conditions.
In the entertainment and hospitality industries, there is a growing trend towards using large-scale AMOLED displays for creating immersive experiences. Theme parks, museums, and hotels are incorporating these displays to enhance visitor engagement and create memorable visual spectacles. The ability of AMOLED technology to deliver deep blacks and vibrant colors makes it particularly suitable for these applications.
The outdoor advertising market is also contributing to the demand for large public AMOLED displays. Billboard owners and advertising agencies are transitioning from traditional static billboards to dynamic digital displays, allowing for more flexible and targeted advertising campaigns. The energy efficiency and brightness capabilities of AMOLED technology make it an attractive option for outdoor installations.
Corporate environments and conference centers represent another significant market segment. Large AMOLED displays are being used for video conferencing, presentations, and digital signage in lobbies and meeting rooms. The superior image quality and wide viewing angles of AMOLED technology enhance communication and collaboration in these settings.
The education sector is showing increased interest in large public displays for interactive learning environments. Universities, schools, and training centers are adopting AMOLED displays to create engaging classroom experiences and facilitate distance learning initiatives. The high refresh rates and color accuracy of AMOLED technology contribute to reduced eye strain during extended viewing periods.
As smart cities continue to develop, there is a growing demand for large public displays integrated into urban infrastructure. These displays serve multiple purposes, including providing public information, emergency alerts, and interactive city guides. The durability and longevity of AMOLED technology make it suitable for long-term outdoor installations in various weather conditions.
The market size for large public digital displays is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with AMOLED technology playing a crucial role in this growth. As manufacturers overcome scaling challenges and improve production efficiencies, the adoption of large AMOLED displays in public spaces is expected to accelerate, further driving market demand across diverse industries and applications.
AMOLED Scaling Challenges and Current Limitations
AMOLED technology, while widely adopted in small-scale devices like smartphones and tablets, faces significant challenges when scaling up for large public digital displays. One of the primary limitations is the complexity of manufacturing large AMOLED panels. As the display size increases, the probability of defects in the organic layers also rises, leading to potential issues with uniformity and yield rates. This challenge is particularly acute for displays exceeding 65 inches, where even minor imperfections can result in visible artifacts.
Another critical limitation is the susceptibility of AMOLED displays to burn-in, especially in static content scenarios common in public digital signage. The organic compounds in AMOLED pixels degrade over time with use, and this degradation can occur unevenly across the display when certain areas are used more frequently than others. For large public displays that often show static content like logos or navigation elements, this poses a significant risk to long-term image quality and display longevity.
Power consumption presents another hurdle for large-scale AMOLED displays. While AMOLED is known for its energy efficiency in small devices, particularly when displaying dark content, the power requirements scale dramatically with size. In large public displays, the increased power consumption can lead to heat generation issues, potentially affecting the display's performance and lifespan. This challenge is compounded by the need for sophisticated thermal management systems in outdoor or semi-outdoor environments where many public displays are installed.
Cost remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption of large AMOLED displays in public spaces. The manufacturing process for large AMOLED panels is complex and expensive, with lower yield rates compared to traditional LCD technology. This translates to higher costs per square inch, making AMOLED less economically viable for large-format applications where cost-effectiveness is often a key consideration.
Lastly, the current limitations in AMOLED scaling also include challenges in achieving consistent color accuracy and brightness across large surfaces. As the display size increases, maintaining uniform organic layer deposition becomes more difficult, potentially leading to color and brightness variations across the panel. This issue is particularly noticeable in large displays where viewers can easily compare different areas of the screen simultaneously.
Another critical limitation is the susceptibility of AMOLED displays to burn-in, especially in static content scenarios common in public digital signage. The organic compounds in AMOLED pixels degrade over time with use, and this degradation can occur unevenly across the display when certain areas are used more frequently than others. For large public displays that often show static content like logos or navigation elements, this poses a significant risk to long-term image quality and display longevity.
Power consumption presents another hurdle for large-scale AMOLED displays. While AMOLED is known for its energy efficiency in small devices, particularly when displaying dark content, the power requirements scale dramatically with size. In large public displays, the increased power consumption can lead to heat generation issues, potentially affecting the display's performance and lifespan. This challenge is compounded by the need for sophisticated thermal management systems in outdoor or semi-outdoor environments where many public displays are installed.
Cost remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption of large AMOLED displays in public spaces. The manufacturing process for large AMOLED panels is complex and expensive, with lower yield rates compared to traditional LCD technology. This translates to higher costs per square inch, making AMOLED less economically viable for large-format applications where cost-effectiveness is often a key consideration.
Lastly, the current limitations in AMOLED scaling also include challenges in achieving consistent color accuracy and brightness across large surfaces. As the display size increases, maintaining uniform organic layer deposition becomes more difficult, potentially leading to color and brightness variations across the panel. This issue is particularly noticeable in large displays where viewers can easily compare different areas of the screen simultaneously.
Current AMOLED Scaling Solutions for Large Displays
01 AMOLED display scaling techniques
Various methods for scaling AMOLED displays are employed to adjust image size, resolution, and aspect ratio. These techniques involve pixel interpolation, image processing algorithms, and adaptive scaling to maintain image quality while accommodating different screen sizes and resolutions.- AMOLED display scaling techniques: Various methods for scaling AMOLED displays are employed to adjust image size, resolution, and aspect ratio. These techniques involve pixel interpolation, image processing algorithms, and adaptive scaling to maintain image quality while accommodating different screen sizes and resolutions.
- Compensation for AMOLED display characteristics: Compensation techniques are used to address inherent characteristics of AMOLED displays, such as non-uniform brightness and color shift. These methods involve pixel-level adjustments, voltage compensation, and color correction algorithms to improve overall display quality and consistency.
- AMOLED pixel structure and layout optimization: Innovations in AMOLED pixel structure and layout aim to enhance display performance and efficiency. These include sub-pixel arrangements, pixel circuit designs, and optimization of pixel density to improve resolution, color accuracy, and power consumption.
- Driving schemes for AMOLED displays: Advanced driving schemes are developed to improve AMOLED display performance and lifespan. These include methods for reducing power consumption, enhancing refresh rates, and implementing variable frame rates to optimize display quality and efficiency.
- AMOLED display integration and manufacturing: Techniques for integrating AMOLED displays into various devices and improving manufacturing processes are developed. These include methods for flexible and foldable displays, thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane technologies, and scalable production processes to enhance display quality and yield.
02 Compensation for AMOLED display characteristics
Compensation techniques are used to address inherent characteristics of AMOLED displays, such as non-uniform brightness and color shift. These methods involve pixel-level adjustments, voltage compensation, and color correction algorithms to improve overall display quality and consistency.Expand Specific Solutions03 AMOLED pixel structure and layout optimization
Innovations in AMOLED pixel structure and layout are developed to enhance display performance and efficiency. These include sub-pixel arrangements, pixel circuit designs, and optimized driving schemes to improve resolution, color accuracy, and power consumption.Expand Specific Solutions04 AMOLED display driving and control methods
Advanced driving and control methods for AMOLED displays are implemented to improve image quality and reduce power consumption. These techniques include adaptive refresh rates, dynamic voltage scaling, and intelligent power management systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of sensors and additional functionalities in AMOLED displays
AMOLED displays are enhanced with integrated sensors and additional functionalities to improve user interaction and device capabilities. These innovations include in-display fingerprint sensors, touch sensitivity improvements, and integration of other sensing technologies within the display structure.Expand Specific Solutions
Key AMOLED Display Manufacturers and Competitors
The AMOLED technology for large public digital displays is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and evolving technical maturity. The industry is transitioning from traditional LCD to AMOLED for improved visual quality and energy efficiency. Key players like Samsung, LG Display, and BOE are driving innovation, with companies such as TCL China Star and Everdisplay Optronics also contributing. The market is seeing advancements in scalability, durability, and cost-effectiveness, crucial for widespread adoption in public spaces. As the technology matures, we can expect further improvements in resolution, brightness, and lifespan, making AMOLED increasingly viable for large-scale applications.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed advanced AMOLED technology for large public displays, utilizing their proprietary oxide semiconductor backplane technology. This allows for higher electron mobility and better current uniformity across large panels[1]. Their AMOLED displays incorporate a unique pixel compensation circuit that mitigates the effects of threshold voltage shifts in TFTs, ensuring consistent brightness and color accuracy over extended periods[2]. BOE has also implemented a novel encapsulation technique using alternating layers of inorganic and organic materials, significantly enhancing the lifespan of large AMOLED displays in outdoor environments[3].
Strengths: Advanced oxide backplane technology, innovative pixel compensation, and robust encapsulation for outdoor use. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional LCD technology, potential for image retention in static content scenarios.
TCL China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: TCL CSOT has developed a proprietary AMOLED scaling technology for large public displays, focusing on their t1 series. They utilize a modular design approach, allowing for seamless integration of multiple AMOLED panels to create expansive displays[4]. Their technology incorporates advanced color management systems that maintain color consistency across the entire display surface, crucial for large-scale implementations[5]. TCL CSOT has also implemented a thermal management solution that efficiently dissipates heat in large AMOLED displays, ensuring longevity and stable performance in various environmental conditions[6].
Strengths: Modular design for scalability, advanced color management, and efficient thermal dissipation. Weaknesses: Potential visible seams in multi-panel configurations, higher initial investment compared to traditional display technologies.
Core Innovations in AMOLED Scaling Technologies
Active matrix organic light emitting diode array substrate, fabricating method, and display apparatus
PatentWO2017024851A1
Innovation
- Utilization of an independent thin film transistor (TFT) for controlling each pixel in AMOLED, allowing continuous and independent driving for lighting.
- Application of AMOLED technology to large-size flat display areas due to its low driving voltage and long lifetime.
- Recognition of the potential issue where incomplete coverage of via holes by the pixel defining layer can lead to defective pixel display dark spots, affecting product quality.
Array substrate, display device, and method for manufacturing array substrate
PatentActiveUS20170148862A1
Innovation
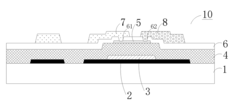
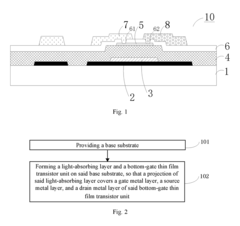
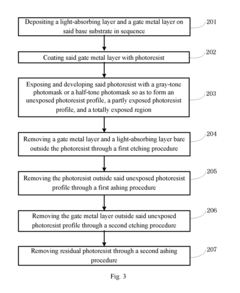
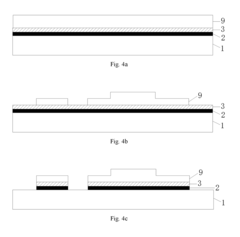
- An array substrate with a light-absorbing layer covering the gate, source, and drain metal layers of a bottom-gate thin film transistor unit, preventing ambient light irradiation while allowing useful light to pass through.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
The energy efficiency and environmental impact of AMOLED technology in large public digital displays are crucial considerations as these displays become increasingly prevalent in urban environments. AMOLED displays offer significant advantages in terms of power consumption compared to traditional LCD technology, particularly when displaying darker content. This is due to the self-emissive nature of OLED pixels, which only consume power when lit.
As AMOLED scales up for large public displays, the energy savings become more pronounced. In outdoor settings, where displays often need to operate at high brightness levels, AMOLED's ability to selectively illuminate pixels results in substantial power reductions. This is especially beneficial during nighttime operations when ambient light levels are lower, allowing for further dimming of the display without compromising visibility.
The environmental impact of large AMOLED displays extends beyond energy consumption. The manufacturing process for AMOLED panels has become more efficient over time, reducing the carbon footprint associated with production. Additionally, the longer lifespan of AMOLED displays compared to some other technologies means less frequent replacement, potentially reducing electronic waste.
However, challenges remain in scaling AMOLED technology for large public displays. The organic materials used in AMOLED panels can degrade over time, especially when exposed to harsh outdoor conditions. This necessitates the development of more robust materials and protective technologies to ensure longevity in public settings. Manufacturers are also focusing on improving the recycling processes for AMOLED displays to minimize end-of-life environmental impact.
The use of AMOLED in large public displays contributes to the broader trend of smart city initiatives. These energy-efficient displays can integrate with city-wide energy management systems, adjusting brightness and content based on time of day, weather conditions, and public events. This adaptive capability not only conserves energy but also reduces light pollution in urban areas.
Looking forward, advancements in AMOLED technology for large displays are likely to focus on further improving energy efficiency, enhancing durability for outdoor use, and developing more sustainable production and recycling methods. These improvements will be crucial in ensuring that as AMOLED scales up for large public digital displays, it continues to offer both economic and environmental benefits to cities and communities.
As AMOLED scales up for large public displays, the energy savings become more pronounced. In outdoor settings, where displays often need to operate at high brightness levels, AMOLED's ability to selectively illuminate pixels results in substantial power reductions. This is especially beneficial during nighttime operations when ambient light levels are lower, allowing for further dimming of the display without compromising visibility.
The environmental impact of large AMOLED displays extends beyond energy consumption. The manufacturing process for AMOLED panels has become more efficient over time, reducing the carbon footprint associated with production. Additionally, the longer lifespan of AMOLED displays compared to some other technologies means less frequent replacement, potentially reducing electronic waste.
However, challenges remain in scaling AMOLED technology for large public displays. The organic materials used in AMOLED panels can degrade over time, especially when exposed to harsh outdoor conditions. This necessitates the development of more robust materials and protective technologies to ensure longevity in public settings. Manufacturers are also focusing on improving the recycling processes for AMOLED displays to minimize end-of-life environmental impact.
The use of AMOLED in large public displays contributes to the broader trend of smart city initiatives. These energy-efficient displays can integrate with city-wide energy management systems, adjusting brightness and content based on time of day, weather conditions, and public events. This adaptive capability not only conserves energy but also reduces light pollution in urban areas.
Looking forward, advancements in AMOLED technology for large displays are likely to focus on further improving energy efficiency, enhancing durability for outdoor use, and developing more sustainable production and recycling methods. These improvements will be crucial in ensuring that as AMOLED scales up for large public digital displays, it continues to offer both economic and environmental benefits to cities and communities.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
The cost analysis and economic feasibility of scaling up AMOLED technology for large public digital displays is a critical consideration for manufacturers and potential adopters. The primary challenge lies in the production costs associated with larger AMOLED panels, which increase exponentially with size due to the complexity of the manufacturing process and the need for high-quality materials.
Currently, the production of large AMOLED displays remains significantly more expensive than traditional LCD technology. This cost disparity is primarily attributed to lower yield rates in AMOLED manufacturing, especially for larger sizes. However, as production techniques improve and economies of scale are achieved, the cost gap is expected to narrow over time.
The economic viability of AMOLED in large public displays depends on several factors. Firstly, the longevity and durability of AMOLED panels in outdoor environments must be considered, as frequent replacements would negate any potential long-term cost benefits. Secondly, the energy efficiency of AMOLED technology could lead to reduced operational costs over the lifespan of the display, potentially offsetting higher initial investments.
Market demand plays a crucial role in determining economic feasibility. As consumers and businesses increasingly prioritize visual quality and energy efficiency, the willingness to pay a premium for AMOLED displays may increase. This shift could accelerate adoption and drive down production costs through increased volume.
Technological advancements, such as the development of more efficient OLED materials and improved manufacturing processes, are expected to significantly impact the cost structure. Innovations in areas like inkjet printing of OLED materials could potentially reduce production costs and make large-scale AMOLED displays more economically viable.
Government regulations and incentives related to energy efficiency and environmental impact could also influence the economic landscape for AMOLED technology in public displays. Favorable policies could accelerate adoption and improve the cost-benefit ratio for businesses considering the technology.
In conclusion, while the current cost analysis may not favor widespread adoption of large AMOLED displays in public spaces, the economic feasibility is likely to improve in the coming years. As technology advances and market demand grows, the balance between cost and performance benefits is expected to shift, potentially making AMOLED a more attractive option for large public digital displays in the future.
Currently, the production of large AMOLED displays remains significantly more expensive than traditional LCD technology. This cost disparity is primarily attributed to lower yield rates in AMOLED manufacturing, especially for larger sizes. However, as production techniques improve and economies of scale are achieved, the cost gap is expected to narrow over time.
The economic viability of AMOLED in large public displays depends on several factors. Firstly, the longevity and durability of AMOLED panels in outdoor environments must be considered, as frequent replacements would negate any potential long-term cost benefits. Secondly, the energy efficiency of AMOLED technology could lead to reduced operational costs over the lifespan of the display, potentially offsetting higher initial investments.
Market demand plays a crucial role in determining economic feasibility. As consumers and businesses increasingly prioritize visual quality and energy efficiency, the willingness to pay a premium for AMOLED displays may increase. This shift could accelerate adoption and drive down production costs through increased volume.
Technological advancements, such as the development of more efficient OLED materials and improved manufacturing processes, are expected to significantly impact the cost structure. Innovations in areas like inkjet printing of OLED materials could potentially reduce production costs and make large-scale AMOLED displays more economically viable.
Government regulations and incentives related to energy efficiency and environmental impact could also influence the economic landscape for AMOLED technology in public displays. Favorable policies could accelerate adoption and improve the cost-benefit ratio for businesses considering the technology.
In conclusion, while the current cost analysis may not favor widespread adoption of large AMOLED displays in public spaces, the economic feasibility is likely to improve in the coming years. As technology advances and market demand grows, the balance between cost and performance benefits is expected to shift, potentially making AMOLED a more attractive option for large public digital displays in the future.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!