How AMOLED fosters convergence in multimedia platforms?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Evolution and Convergence Goals
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception, revolutionizing the display industry and fostering convergence in multimedia platforms. The journey of AMOLED displays began with small, low-resolution screens and has progressed to large, high-resolution panels that offer superior image quality, energy efficiency, and form factor flexibility.
The primary goal of AMOLED evolution has been to enhance the user experience across various multimedia platforms. This includes improving color accuracy, contrast ratios, and response times to deliver more immersive visual experiences. AMOLED displays aim to achieve perfect black levels and infinite contrast ratios, which are crucial for high-quality video playback and gaming applications.
Another key objective in AMOLED development has been to reduce power consumption while maintaining or improving display performance. This aligns with the broader trend of energy efficiency in consumer electronics and is particularly important for mobile devices where battery life is a critical factor.
Convergence goals for AMOLED technology focus on integrating displays seamlessly into various devices and form factors. This includes the development of flexible and foldable displays, which are opening up new possibilities for device design and user interaction. The ability to create curved, bendable, and even rollable screens is pushing the boundaries of what's possible in multimedia devices.
AMOLED technology also aims to support the increasing demand for higher refresh rates and touch responsiveness, which are essential for gaming and interactive applications. The goal is to eliminate motion blur and provide a more fluid visual experience across all types of content.
Furthermore, AMOLED evolution is driven by the need to support emerging technologies such as virtual and augmented reality. These applications require displays with extremely high pixel densities, low latency, and wide color gamuts to create convincing and comfortable immersive experiences.
The convergence of AMOLED with other technologies, such as in-display fingerprint sensors and under-display cameras, is another important goal. This integration allows for cleaner device designs and more screen real estate, which is particularly valuable in the era of edge-to-edge displays.
Lastly, AMOLED technology aims to become more cost-effective and scalable to production, enabling its adoption across a wider range of devices and price points. This democratization of high-quality display technology is crucial for fostering convergence in multimedia platforms, ensuring that advanced visual experiences are accessible to a broader audience.
The primary goal of AMOLED evolution has been to enhance the user experience across various multimedia platforms. This includes improving color accuracy, contrast ratios, and response times to deliver more immersive visual experiences. AMOLED displays aim to achieve perfect black levels and infinite contrast ratios, which are crucial for high-quality video playback and gaming applications.
Another key objective in AMOLED development has been to reduce power consumption while maintaining or improving display performance. This aligns with the broader trend of energy efficiency in consumer electronics and is particularly important for mobile devices where battery life is a critical factor.
Convergence goals for AMOLED technology focus on integrating displays seamlessly into various devices and form factors. This includes the development of flexible and foldable displays, which are opening up new possibilities for device design and user interaction. The ability to create curved, bendable, and even rollable screens is pushing the boundaries of what's possible in multimedia devices.
AMOLED technology also aims to support the increasing demand for higher refresh rates and touch responsiveness, which are essential for gaming and interactive applications. The goal is to eliminate motion blur and provide a more fluid visual experience across all types of content.
Furthermore, AMOLED evolution is driven by the need to support emerging technologies such as virtual and augmented reality. These applications require displays with extremely high pixel densities, low latency, and wide color gamuts to create convincing and comfortable immersive experiences.
The convergence of AMOLED with other technologies, such as in-display fingerprint sensors and under-display cameras, is another important goal. This integration allows for cleaner device designs and more screen real estate, which is particularly valuable in the era of edge-to-edge displays.
Lastly, AMOLED technology aims to become more cost-effective and scalable to production, enabling its adoption across a wider range of devices and price points. This democratization of high-quality display technology is crucial for fostering convergence in multimedia platforms, ensuring that advanced visual experiences are accessible to a broader audience.
Multimedia Platform Market Trends
The multimedia platform market has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. The integration of AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has played a crucial role in fostering convergence within this market, leading to enhanced user experiences and new opportunities for content creators and platform providers.
One of the key trends in the multimedia platform market is the increasing demand for high-quality visual experiences. AMOLED displays, with their superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency, have become a preferred choice for smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices. This trend has led to a convergence of multimedia consumption on mobile platforms, as users increasingly rely on their personal devices for various forms of entertainment, including video streaming, gaming, and social media.
The rise of mobile-first content consumption has prompted content creators and platform providers to optimize their offerings for AMOLED displays. Streaming services, for instance, have begun to offer HDR (High Dynamic Range) content specifically tailored for AMOLED screens, taking advantage of the technology's ability to display deep blacks and vibrant colors. This convergence of content and display technology has resulted in a more immersive and engaging multimedia experience for users across different platforms.
Another significant trend is the growing importance of energy efficiency in multimedia devices. AMOLED's ability to selectively illuminate pixels and power off unused ones has made it an attractive option for device manufacturers looking to extend battery life without compromising on display quality. This has led to a convergence of power-efficient hardware and software optimizations, enabling longer multimedia consumption sessions on portable devices.
The gaming industry has also been significantly impacted by AMOLED technology, driving convergence between mobile and console gaming experiences. The high refresh rates and low response times of AMOLED displays have made mobile devices increasingly viable for competitive gaming, blurring the lines between different gaming platforms. This trend has encouraged game developers to create cross-platform titles that offer consistent visual quality across various devices, further fostering convergence in the multimedia ecosystem.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, we are witnessing a convergence of form factors in multimedia devices. Foldable and rollable AMOLED displays are enabling the creation of hybrid devices that can transform from smartphones to tablets or even larger displays. This flexibility is reshaping the way users interact with multimedia content, allowing for seamless transitions between different viewing modes and use cases.
One of the key trends in the multimedia platform market is the increasing demand for high-quality visual experiences. AMOLED displays, with their superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency, have become a preferred choice for smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices. This trend has led to a convergence of multimedia consumption on mobile platforms, as users increasingly rely on their personal devices for various forms of entertainment, including video streaming, gaming, and social media.
The rise of mobile-first content consumption has prompted content creators and platform providers to optimize their offerings for AMOLED displays. Streaming services, for instance, have begun to offer HDR (High Dynamic Range) content specifically tailored for AMOLED screens, taking advantage of the technology's ability to display deep blacks and vibrant colors. This convergence of content and display technology has resulted in a more immersive and engaging multimedia experience for users across different platforms.
Another significant trend is the growing importance of energy efficiency in multimedia devices. AMOLED's ability to selectively illuminate pixels and power off unused ones has made it an attractive option for device manufacturers looking to extend battery life without compromising on display quality. This has led to a convergence of power-efficient hardware and software optimizations, enabling longer multimedia consumption sessions on portable devices.
The gaming industry has also been significantly impacted by AMOLED technology, driving convergence between mobile and console gaming experiences. The high refresh rates and low response times of AMOLED displays have made mobile devices increasingly viable for competitive gaming, blurring the lines between different gaming platforms. This trend has encouraged game developers to create cross-platform titles that offer consistent visual quality across various devices, further fostering convergence in the multimedia ecosystem.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, we are witnessing a convergence of form factors in multimedia devices. Foldable and rollable AMOLED displays are enabling the creation of hybrid devices that can transform from smartphones to tablets or even larger displays. This flexibility is reshaping the way users interact with multimedia content, allowing for seamless transitions between different viewing modes and use cases.
AMOLED Technology Challenges
AMOLED technology, while revolutionary in display quality, faces several significant challenges that impact its widespread adoption and integration into multimedia platforms. One of the primary hurdles is the high production cost associated with AMOLED displays. The complex manufacturing process and the need for specialized materials contribute to elevated prices, making it difficult for AMOLED to compete with more established technologies in price-sensitive markets.
Durability and lifespan issues present another major challenge. AMOLED displays are susceptible to burn-in, where static images can leave permanent marks on the screen over time. This is particularly problematic for multimedia platforms that often display static elements like logos or user interface components. Additionally, the organic materials used in AMOLED screens degrade faster than those in traditional LCD displays, potentially shortening the overall lifespan of devices.
Power consumption remains a concern, especially for mobile devices. While AMOLED screens can be more energy-efficient when displaying dark content, they tend to consume more power when displaying bright or white images, which are common in many multimedia applications. This variability in power consumption complicates battery management and device design.
Color accuracy and consistency across different viewing angles pose technical challenges. AMOLED displays can suffer from color shifts when viewed from off-center angles, which can be detrimental to the user experience in multimedia applications where precise color reproduction is crucial. Achieving uniform brightness across the entire display area is also a persistent issue, with some AMOLED screens exhibiting inconsistencies that can be noticeable during multimedia playback.
Scalability in production is another significant hurdle. As demand for larger AMOLED displays grows, manufacturers face difficulties in scaling up production while maintaining quality and yield rates. This challenge is particularly relevant for the integration of AMOLED technology into larger screens for multimedia platforms like televisions or public displays.
The blue pixel degradation problem continues to be a technological challenge. Blue OLED materials tend to degrade faster than red and green, leading to color imbalance over time. This issue is particularly noticeable in multimedia applications where color accuracy is paramount, and it necessitates ongoing research into more stable blue OLED materials.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for AMOLED technology to fully realize its potential in fostering convergence across multimedia platforms. Overcoming these hurdles will not only improve the technology's performance and longevity but also enhance its economic viability, ultimately leading to wider adoption and integration in diverse multimedia applications.
Durability and lifespan issues present another major challenge. AMOLED displays are susceptible to burn-in, where static images can leave permanent marks on the screen over time. This is particularly problematic for multimedia platforms that often display static elements like logos or user interface components. Additionally, the organic materials used in AMOLED screens degrade faster than those in traditional LCD displays, potentially shortening the overall lifespan of devices.
Power consumption remains a concern, especially for mobile devices. While AMOLED screens can be more energy-efficient when displaying dark content, they tend to consume more power when displaying bright or white images, which are common in many multimedia applications. This variability in power consumption complicates battery management and device design.
Color accuracy and consistency across different viewing angles pose technical challenges. AMOLED displays can suffer from color shifts when viewed from off-center angles, which can be detrimental to the user experience in multimedia applications where precise color reproduction is crucial. Achieving uniform brightness across the entire display area is also a persistent issue, with some AMOLED screens exhibiting inconsistencies that can be noticeable during multimedia playback.
Scalability in production is another significant hurdle. As demand for larger AMOLED displays grows, manufacturers face difficulties in scaling up production while maintaining quality and yield rates. This challenge is particularly relevant for the integration of AMOLED technology into larger screens for multimedia platforms like televisions or public displays.
The blue pixel degradation problem continues to be a technological challenge. Blue OLED materials tend to degrade faster than red and green, leading to color imbalance over time. This issue is particularly noticeable in multimedia applications where color accuracy is paramount, and it necessitates ongoing research into more stable blue OLED materials.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for AMOLED technology to fully realize its potential in fostering convergence across multimedia platforms. Overcoming these hurdles will not only improve the technology's performance and longevity but also enhance its economic viability, ultimately leading to wider adoption and integration in diverse multimedia applications.
Current AMOLED Integration Solutions
01 AMOLED display driving techniques
Various driving techniques are employed to improve the performance of AMOLED displays. These include methods for controlling pixel brightness, reducing power consumption, and enhancing image quality. Advanced driving schemes can compensate for non-uniformities and aging effects in OLED panels, resulting in more consistent and longer-lasting displays.- AMOLED display driving techniques: Various driving techniques are employed to improve the performance of AMOLED displays. These include methods for controlling pixel brightness, reducing power consumption, and enhancing image quality. Advanced driving schemes can compensate for variations in OLED characteristics and optimize display performance across different operating conditions.
- AMOLED pixel structure and layout: Innovations in AMOLED pixel structure and layout focus on improving display resolution, color accuracy, and efficiency. This includes designs for sub-pixel arrangements, pixel circuits, and integration of additional components like sensors within the display area. These advancements contribute to higher pixel densities and enhanced functionality in AMOLED displays.
- Touch integration in AMOLED displays: Integration of touch functionality directly into AMOLED displays is a key area of development. This involves incorporating touch sensors within the display stack or using the display elements themselves for touch sensing. Such integration can lead to thinner device profiles, improved touch responsiveness, and potentially reduced manufacturing costs.
- AMOLED power management and efficiency: Techniques for improving power efficiency in AMOLED displays are crucial for extending battery life in mobile devices. This includes methods for selective pixel dimming, adaptive brightness control, and optimized power distribution across the display. Advanced power management schemes can significantly reduce energy consumption while maintaining display quality.
- AMOLED display compensation and calibration: Compensation and calibration techniques are essential for maintaining consistent performance in AMOLED displays over time. These methods address issues such as pixel aging, color shift, and brightness variations. Advanced algorithms and sensing technologies are employed to detect and correct display irregularities, ensuring long-term image quality and uniformity.
02 AMOLED pixel structure and layout
Innovations in AMOLED pixel structure and layout focus on improving display resolution, color accuracy, and energy efficiency. This includes developing new sub-pixel arrangements, optimizing the placement of transistors and capacitors within pixels, and implementing novel light-emitting structures to enhance overall display performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 AMOLED panel manufacturing and materials
Advancements in AMOLED panel manufacturing processes and materials aim to improve yield rates, reduce costs, and enhance display quality. This includes developing new OLED materials with better efficiency and longevity, as well as refining deposition and encapsulation techniques to create more durable and flexible displays.Expand Specific Solutions04 AMOLED integration with touch and biometric sensors
The convergence of AMOLED technology with touch and biometric sensors enables the creation of more integrated and versatile display systems. This includes developing in-display fingerprint sensors, integrating touch functionality directly into the OLED layers, and implementing advanced haptic feedback systems for improved user interaction.Expand Specific Solutions05 AMOLED power management and efficiency
Techniques for improving power management and efficiency in AMOLED displays focus on reducing energy consumption while maintaining or enhancing image quality. This includes developing adaptive brightness control algorithms, implementing selective pixel dimming, and optimizing voltage regulation for different display content and ambient lighting conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key AMOLED Manufacturers
The AMOLED technology market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption in multimedia platforms due to its superior display quality and energy efficiency. The global AMOLED market size is projected to expand significantly, driven by demand in smartphones, TVs, and wearables. Technologically, AMOLED is maturing rapidly, with key players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology, and Visionox leading innovation. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to improve AMOLED performance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Other significant contributors include LG Display, TCL CSOT, and Tianma Microelectronics, all working to enhance AMOLED's capabilities for diverse multimedia applications.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed advanced AMOLED technologies that foster convergence in multimedia platforms. Their flexible AMOLED displays enable the creation of foldable and rollable devices, enhancing user interaction and content consumption. BOE's AMOLED panels feature high color accuracy, wide color gamut (up to 100% DCI-P3), and HDR support, providing immersive visual experiences across various multimedia applications[1]. The company has also integrated touch functionality directly into AMOLED panels, reducing device thickness and improving responsiveness. BOE's AMOLED displays support high refresh rates (up to 144Hz) and low response times, catering to gaming and high-performance multimedia applications[2].
Strengths: Advanced flexible display technology, high color accuracy, and integrated touch functionality. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional LCD, potential for screen burn-in over extended use.
Tianma Microelectronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Tianma has made significant strides in AMOLED technology for multimedia convergence. Their AMOLED displays feature high contrast ratios (over 1,000,000:1) and wide color gamuts, enhancing visual quality across various devices[5]. Tianma has developed flexible AMOLED panels that enable curved and foldable designs, expanding the possibilities for innovative device form factors. The company's AMOLED technology incorporates low-temperature polycrystalline oxide (LTPO) backplanes, allowing for variable refresh rates and improved power efficiency in multimedia applications[6]. Tianma has also focused on integrating touch and display drivers (TDDI) in their AMOLED panels, streamlining device design and improving overall performance.
Strengths: High contrast ratios, flexible display capabilities, and power-efficient LTPO technology. Weaknesses: Smaller production capacity compared to industry leaders, potentially limiting widespread adoption.
AMOLED Patents and Innovations
Active-matrix organic light emitting diode display module
PatentInactiveKR1020090117209A
Innovation
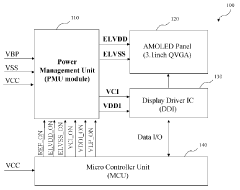
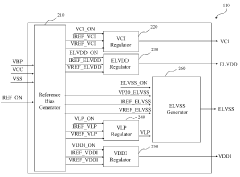
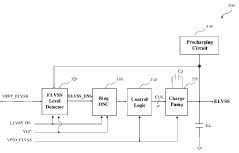
- An AMOLED display module comprising a Power Module Unit (PMU), an AMOLED panel, and a Display Driver IC (DDI) is provided, with the PMU generating panel driving and interface voltages using supply power sources in response to control signals, and the DDI driving the panel in response to display data, facilitated by a Micro Controller Unit (MCU).
Active-matrix organic light-emitting diode (amoled) display module
PatentActiveUS20210335973A1
Innovation
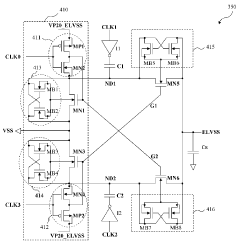
- A second conductive layer is uniformly arranged across the AMOLED display panel to ensure consistent common ground voltage distribution to each OLED element, maintaining a consistent voltage difference between the operating and common ground voltages, thereby enhancing luminance uniformity.
Energy Efficiency in AMOLED Displays
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays have revolutionized the multimedia landscape, offering superior energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD screens. This efficiency stems from AMOLED's unique pixel-by-pixel illumination, where each pixel emits its own light, eliminating the need for a backlight.
The energy-saving capabilities of AMOLED displays are particularly evident in dark or black images. Unlike LCDs, which require constant backlighting regardless of content, AMOLED pixels can be completely turned off when displaying black, resulting in significant power savings. This feature is especially beneficial for multimedia platforms that often utilize dark themes or display content with large black areas.
AMOLED's energy efficiency extends beyond static images to video playback. The technology's ability to rapidly switch pixels on and off allows for smoother motion and reduced power consumption during video streaming. This efficiency translates to longer battery life in portable devices, a crucial factor in the convergence of multimedia platforms.
The power-saving advantages of AMOLED displays have led to their widespread adoption in smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. These platforms serve as hubs for multimedia consumption, benefiting from extended usage times and improved overall user experience. The energy efficiency of AMOLED also enables the integration of larger, higher-resolution displays without compromising battery life, further enhancing the multimedia capabilities of these devices.
In the realm of virtual and augmented reality, AMOLED's energy efficiency plays a pivotal role. These immersive technologies demand high refresh rates and low latency, which AMOLED can deliver while maintaining reasonable power consumption. This efficiency allows for longer usage times in VR headsets and AR glasses, critical for the adoption and convergence of these emerging multimedia platforms.
AMOLED's energy efficiency also contributes to the development of foldable and flexible displays. These innovative form factors open new possibilities for multimedia consumption, allowing devices to transform between compact and expanded states. The power-saving characteristics of AMOLED enable these displays to maintain functionality across various configurations without excessive battery drain.
As multimedia platforms continue to evolve, the energy efficiency of AMOLED displays will remain a key driver of convergence. The technology's ability to deliver vibrant visuals with lower power consumption enables the integration of advanced display features across a wide range of devices, fostering a more seamless and interconnected multimedia ecosystem.
The energy-saving capabilities of AMOLED displays are particularly evident in dark or black images. Unlike LCDs, which require constant backlighting regardless of content, AMOLED pixels can be completely turned off when displaying black, resulting in significant power savings. This feature is especially beneficial for multimedia platforms that often utilize dark themes or display content with large black areas.
AMOLED's energy efficiency extends beyond static images to video playback. The technology's ability to rapidly switch pixels on and off allows for smoother motion and reduced power consumption during video streaming. This efficiency translates to longer battery life in portable devices, a crucial factor in the convergence of multimedia platforms.
The power-saving advantages of AMOLED displays have led to their widespread adoption in smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. These platforms serve as hubs for multimedia consumption, benefiting from extended usage times and improved overall user experience. The energy efficiency of AMOLED also enables the integration of larger, higher-resolution displays without compromising battery life, further enhancing the multimedia capabilities of these devices.
In the realm of virtual and augmented reality, AMOLED's energy efficiency plays a pivotal role. These immersive technologies demand high refresh rates and low latency, which AMOLED can deliver while maintaining reasonable power consumption. This efficiency allows for longer usage times in VR headsets and AR glasses, critical for the adoption and convergence of these emerging multimedia platforms.
AMOLED's energy efficiency also contributes to the development of foldable and flexible displays. These innovative form factors open new possibilities for multimedia consumption, allowing devices to transform between compact and expanded states. The power-saving characteristics of AMOLED enable these displays to maintain functionality across various configurations without excessive battery drain.
As multimedia platforms continue to evolve, the energy efficiency of AMOLED displays will remain a key driver of convergence. The technology's ability to deliver vibrant visuals with lower power consumption enables the integration of advanced display features across a wide range of devices, fostering a more seamless and interconnected multimedia ecosystem.
AMOLED Supply Chain Analysis
The AMOLED supply chain plays a crucial role in the convergence of multimedia platforms, as it provides the foundation for high-quality display technology essential for immersive multimedia experiences. This supply chain encompasses various stages, from raw material sourcing to final product integration.
At the upstream level, key suppliers of AMOLED panel components include manufacturers of organic materials, glass substrates, and thin-film transistors. Companies like Universal Display Corporation and Merck KGaA dominate the organic material market, while Corning and AGC Inc. are major players in glass substrate production. These suppliers continuously innovate to improve AMOLED performance and reduce production costs.
The midstream segment consists of panel manufacturers who integrate these components to produce AMOLED displays. Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE Technology Group are among the leading manufacturers in this space. These companies invest heavily in research and development to enhance AMOLED technology, focusing on aspects such as color accuracy, energy efficiency, and flexible form factors.
Downstream, we find device manufacturers who incorporate AMOLED displays into various multimedia platforms. Smartphone makers like Samsung, Apple, and Huawei are significant consumers of AMOLED panels. However, the application of AMOLED technology is expanding rapidly into other sectors, including tablets, laptops, televisions, and wearable devices.
The AMOLED supply chain is characterized by its global nature and interdependence. While South Korea and China dominate panel production, raw materials and components are sourced from various countries. This global network allows for the rapid dissemination of technological advancements and economies of scale, driving down costs and accelerating innovation.
As multimedia platforms continue to evolve, the AMOLED supply chain is adapting to meet new demands. There is a growing focus on developing more sustainable production processes, improving yield rates, and exploring new applications for AMOLED technology. The integration of AMOLED displays into emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) devices is opening up new opportunities and challenges for the supply chain.
The convergence of multimedia platforms is both driving and being driven by advancements in AMOLED technology. As consumers demand more immersive and high-quality visual experiences across various devices, the AMOLED supply chain is responding by pushing the boundaries of display technology. This symbiotic relationship between supply chain innovation and multimedia convergence is shaping the future of digital experiences.
At the upstream level, key suppliers of AMOLED panel components include manufacturers of organic materials, glass substrates, and thin-film transistors. Companies like Universal Display Corporation and Merck KGaA dominate the organic material market, while Corning and AGC Inc. are major players in glass substrate production. These suppliers continuously innovate to improve AMOLED performance and reduce production costs.
The midstream segment consists of panel manufacturers who integrate these components to produce AMOLED displays. Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE Technology Group are among the leading manufacturers in this space. These companies invest heavily in research and development to enhance AMOLED technology, focusing on aspects such as color accuracy, energy efficiency, and flexible form factors.
Downstream, we find device manufacturers who incorporate AMOLED displays into various multimedia platforms. Smartphone makers like Samsung, Apple, and Huawei are significant consumers of AMOLED panels. However, the application of AMOLED technology is expanding rapidly into other sectors, including tablets, laptops, televisions, and wearable devices.
The AMOLED supply chain is characterized by its global nature and interdependence. While South Korea and China dominate panel production, raw materials and components are sourced from various countries. This global network allows for the rapid dissemination of technological advancements and economies of scale, driving down costs and accelerating innovation.
As multimedia platforms continue to evolve, the AMOLED supply chain is adapting to meet new demands. There is a growing focus on developing more sustainable production processes, improving yield rates, and exploring new applications for AMOLED technology. The integration of AMOLED displays into emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) devices is opening up new opportunities and challenges for the supply chain.
The convergence of multimedia platforms is both driving and being driven by advancements in AMOLED technology. As consumers demand more immersive and high-quality visual experiences across various devices, the AMOLED supply chain is responding by pushing the boundaries of display technology. This symbiotic relationship between supply chain innovation and multimedia convergence is shaping the future of digital experiences.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!