How AMOLED alters interactive display systems in museums?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED in Museums: Evolution and Objectives
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has revolutionized the display industry since its inception in the late 1990s. This advanced display technology has found its way into various applications, including interactive display systems in museums. The evolution of AMOLED in museum settings has been driven by the need for more immersive, engaging, and visually stunning exhibits that can captivate visitors and enhance their learning experience.
The journey of AMOLED in museums began with the recognition of its superior visual qualities compared to traditional LCD displays. AMOLED screens offer deeper blacks, more vibrant colors, and wider viewing angles, making them ideal for showcasing high-quality images and videos in museum environments. As the technology matured, museums started incorporating AMOLED displays into their interactive exhibits, allowing visitors to explore content with unprecedented clarity and detail.
The objectives of implementing AMOLED technology in museum display systems are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to create more engaging and memorable experiences for visitors by providing visually striking and interactive content. AMOLED displays enable museums to present artifacts, historical information, and scientific concepts in a more dynamic and appealing manner, potentially increasing visitor engagement and retention of information.
Another key objective is to improve the overall aesthetic appeal of museum exhibits. AMOLED's slim profile and flexibility allow for more creative and space-efficient display designs, enabling curators to integrate technology seamlessly into exhibit spaces without compromising the museum's ambiance. This technology also supports the creation of curved or uniquely shaped displays, opening up new possibilities for innovative exhibit designs.
Energy efficiency is an additional goal in the adoption of AMOLED technology. As museums often operate for extended hours and rely heavily on visual displays, the reduced power consumption of AMOLED screens compared to traditional LCD displays can lead to significant energy savings over time. This aligns with many museums' sustainability initiatives and helps reduce operational costs.
Looking ahead, the evolution of AMOLED in museum settings is expected to continue, with objectives focusing on even greater interactivity and personalization. Future developments may include the integration of touch-free gesture controls, eye-tracking technology, and AI-driven content adaptation, all leveraging the unique properties of AMOLED displays to create more intuitive and responsive exhibit experiences.
The journey of AMOLED in museums began with the recognition of its superior visual qualities compared to traditional LCD displays. AMOLED screens offer deeper blacks, more vibrant colors, and wider viewing angles, making them ideal for showcasing high-quality images and videos in museum environments. As the technology matured, museums started incorporating AMOLED displays into their interactive exhibits, allowing visitors to explore content with unprecedented clarity and detail.
The objectives of implementing AMOLED technology in museum display systems are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to create more engaging and memorable experiences for visitors by providing visually striking and interactive content. AMOLED displays enable museums to present artifacts, historical information, and scientific concepts in a more dynamic and appealing manner, potentially increasing visitor engagement and retention of information.
Another key objective is to improve the overall aesthetic appeal of museum exhibits. AMOLED's slim profile and flexibility allow for more creative and space-efficient display designs, enabling curators to integrate technology seamlessly into exhibit spaces without compromising the museum's ambiance. This technology also supports the creation of curved or uniquely shaped displays, opening up new possibilities for innovative exhibit designs.
Energy efficiency is an additional goal in the adoption of AMOLED technology. As museums often operate for extended hours and rely heavily on visual displays, the reduced power consumption of AMOLED screens compared to traditional LCD displays can lead to significant energy savings over time. This aligns with many museums' sustainability initiatives and helps reduce operational costs.
Looking ahead, the evolution of AMOLED in museum settings is expected to continue, with objectives focusing on even greater interactivity and personalization. Future developments may include the integration of touch-free gesture controls, eye-tracking technology, and AI-driven content adaptation, all leveraging the unique properties of AMOLED displays to create more intuitive and responsive exhibit experiences.
Market Demand for Interactive Museum Displays
The demand for interactive display systems in museums has been steadily growing, driven by the need to enhance visitor engagement and provide immersive educational experiences. AMOLED technology is poised to revolutionize this market by offering superior visual quality, energy efficiency, and design flexibility. Museums worldwide are increasingly recognizing the potential of interactive displays to transform static exhibits into dynamic, participatory experiences.
The global museum market has shown a significant shift towards digital transformation, with interactive displays becoming a key component of this change. According to recent industry reports, the market for interactive display systems in museums is expected to grow substantially over the next five years. This growth is fueled by the increasing number of museums adopting technology-driven exhibits to attract younger audiences and compete with other forms of entertainment.
AMOLED displays are particularly well-suited for museum applications due to their ability to produce vibrant colors, deep blacks, and high contrast ratios. These features allow for more realistic and captivating representations of artifacts, artworks, and historical scenes. The technology's wide viewing angles and fast response times also contribute to a more immersive experience, especially in interactive installations where multiple visitors may be viewing the display simultaneously.
Energy efficiency is another crucial factor driving the demand for AMOLED displays in museums. As cultural institutions face increasing pressure to reduce their carbon footprint and operational costs, the lower power consumption of AMOLED technology compared to traditional LCD displays becomes a significant advantage. This aligns with the growing trend of sustainable and eco-friendly museum practices.
The flexibility of AMOLED displays opens up new possibilities for exhibit design. Curved or even foldable displays can be integrated seamlessly into various museum spaces, allowing for more creative and engaging presentations. This adaptability is particularly valuable in museums with limited space or those looking to create unique, eye-catching installations.
Interactive touch capabilities combined with AMOLED technology enable museums to create highly responsive and intuitive interfaces for visitors. This synergy allows for the development of interactive timelines, virtual artifact manipulation, and augmented reality experiences that can significantly enhance learning outcomes and visitor satisfaction.
As museums increasingly focus on accessibility and inclusivity, AMOLED displays offer advantages in terms of readability and visibility for visitors with visual impairments. The technology's high contrast and brightness capabilities can be adjusted to accommodate different needs, making exhibits more accessible to a wider range of visitors.
The market demand for AMOLED-based interactive displays in museums is also driven by the need for durability and longevity. Museums require display solutions that can withstand continuous operation and maintain image quality over extended periods. AMOLED technology's resistance to image burn-in and its long lifespan make it an attractive option for these high-use environments.
The global museum market has shown a significant shift towards digital transformation, with interactive displays becoming a key component of this change. According to recent industry reports, the market for interactive display systems in museums is expected to grow substantially over the next five years. This growth is fueled by the increasing number of museums adopting technology-driven exhibits to attract younger audiences and compete with other forms of entertainment.
AMOLED displays are particularly well-suited for museum applications due to their ability to produce vibrant colors, deep blacks, and high contrast ratios. These features allow for more realistic and captivating representations of artifacts, artworks, and historical scenes. The technology's wide viewing angles and fast response times also contribute to a more immersive experience, especially in interactive installations where multiple visitors may be viewing the display simultaneously.
Energy efficiency is another crucial factor driving the demand for AMOLED displays in museums. As cultural institutions face increasing pressure to reduce their carbon footprint and operational costs, the lower power consumption of AMOLED technology compared to traditional LCD displays becomes a significant advantage. This aligns with the growing trend of sustainable and eco-friendly museum practices.
The flexibility of AMOLED displays opens up new possibilities for exhibit design. Curved or even foldable displays can be integrated seamlessly into various museum spaces, allowing for more creative and engaging presentations. This adaptability is particularly valuable in museums with limited space or those looking to create unique, eye-catching installations.
Interactive touch capabilities combined with AMOLED technology enable museums to create highly responsive and intuitive interfaces for visitors. This synergy allows for the development of interactive timelines, virtual artifact manipulation, and augmented reality experiences that can significantly enhance learning outcomes and visitor satisfaction.
As museums increasingly focus on accessibility and inclusivity, AMOLED displays offer advantages in terms of readability and visibility for visitors with visual impairments. The technology's high contrast and brightness capabilities can be adjusted to accommodate different needs, making exhibits more accessible to a wider range of visitors.
The market demand for AMOLED-based interactive displays in museums is also driven by the need for durability and longevity. Museums require display solutions that can withstand continuous operation and maintain image quality over extended periods. AMOLED technology's resistance to image burn-in and its long lifespan make it an attractive option for these high-use environments.
AMOLED Technology: Current State and Challenges
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has made significant strides in recent years, revolutionizing display systems across various industries, including museum interactive displays. The current state of AMOLED technology showcases its superior performance in terms of color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD displays.
One of the key advantages of AMOLED displays is their ability to produce deep blacks and vibrant colors, making them ideal for showcasing high-quality images and videos in museum settings. The technology allows for individual pixel control, enabling precise color representation and enhanced visual experiences for museum visitors.
Despite its advancements, AMOLED technology still faces several challenges in its widespread adoption for interactive display systems in museums. One of the primary concerns is the potential for screen burn-in, where static images displayed for extended periods can leave permanent marks on the screen. This issue is particularly relevant in museum environments where exhibits may feature fixed elements for long durations.
Another challenge is the higher production cost of AMOLED displays compared to traditional LCD panels. This cost factor can be a significant barrier for museums with limited budgets, potentially slowing down the adoption of this advanced technology in interactive exhibits.
The lifespan of AMOLED displays is another area of concern. While improvements have been made, the organic compounds used in these displays can degrade over time, potentially leading to reduced brightness and color accuracy. This degradation can be accelerated by exposure to high temperatures and humidity, conditions that may be present in certain museum environments.
Power consumption is a double-edged sword for AMOLED technology. While it can be more energy-efficient than LCD displays when showing darker content, it may consume more power when displaying bright, white backgrounds, which are common in many museum interfaces.
Lastly, the sensitivity of AMOLED displays to physical damage poses a challenge in high-traffic museum settings. The organic layers in these displays are more susceptible to damage from impacts or pressure, which could be a concern in interactive exhibits where visitors frequently touch or interact with the screens.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development in AMOLED technology are addressing many of these issues. Innovations in materials science and manufacturing processes are improving the durability, lifespan, and cost-effectiveness of AMOLED displays, making them increasingly viable for interactive museum applications.
One of the key advantages of AMOLED displays is their ability to produce deep blacks and vibrant colors, making them ideal for showcasing high-quality images and videos in museum settings. The technology allows for individual pixel control, enabling precise color representation and enhanced visual experiences for museum visitors.
Despite its advancements, AMOLED technology still faces several challenges in its widespread adoption for interactive display systems in museums. One of the primary concerns is the potential for screen burn-in, where static images displayed for extended periods can leave permanent marks on the screen. This issue is particularly relevant in museum environments where exhibits may feature fixed elements for long durations.
Another challenge is the higher production cost of AMOLED displays compared to traditional LCD panels. This cost factor can be a significant barrier for museums with limited budgets, potentially slowing down the adoption of this advanced technology in interactive exhibits.
The lifespan of AMOLED displays is another area of concern. While improvements have been made, the organic compounds used in these displays can degrade over time, potentially leading to reduced brightness and color accuracy. This degradation can be accelerated by exposure to high temperatures and humidity, conditions that may be present in certain museum environments.
Power consumption is a double-edged sword for AMOLED technology. While it can be more energy-efficient than LCD displays when showing darker content, it may consume more power when displaying bright, white backgrounds, which are common in many museum interfaces.
Lastly, the sensitivity of AMOLED displays to physical damage poses a challenge in high-traffic museum settings. The organic layers in these displays are more susceptible to damage from impacts or pressure, which could be a concern in interactive exhibits where visitors frequently touch or interact with the screens.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development in AMOLED technology are addressing many of these issues. Innovations in materials science and manufacturing processes are improving the durability, lifespan, and cost-effectiveness of AMOLED displays, making them increasingly viable for interactive museum applications.
Existing AMOLED Solutions for Museums
01 AMOLED display pixel structures and driving methods
This category focuses on the pixel structures and driving methods specific to AMOLED displays. It includes innovations in pixel circuit designs, compensation techniques for non-uniform brightness, and methods to improve display quality and efficiency. These advancements aim to enhance the overall performance of AMOLED interactive display systems.- AMOLED display panel structure and fabrication: This category focuses on the structural design and manufacturing processes of AMOLED display panels. It includes innovations in pixel arrangements, thin-film transistor (TFT) designs, and layer compositions to improve display performance, efficiency, and durability. These advancements contribute to better image quality, power consumption, and overall display functionality in interactive systems.
- Touch sensing integration in AMOLED displays: This area covers the integration of touch sensing capabilities directly into AMOLED displays. It includes in-cell and on-cell touch technologies, as well as novel electrode designs and sensing methods. These innovations allow for thinner device profiles, improved touch accuracy, and enhanced user interaction with AMOLED displays.
- Driving and control circuits for AMOLED displays: This category encompasses the development of driving and control circuits specifically designed for AMOLED displays. It includes innovations in pixel driving schemes, compensation circuits for OLED degradation, and power management techniques. These advancements aim to improve display uniformity, extend panel lifespan, and optimize power efficiency in interactive AMOLED systems.
- Interactive features and user interface enhancements: This area focuses on developing interactive features and user interface enhancements specific to AMOLED display systems. It includes innovations in gesture recognition, haptic feedback integration, and adaptive display modes. These advancements aim to improve user experience, accessibility, and the overall interactivity of AMOLED-based devices.
- Power efficiency and image quality optimization: This category covers techniques for optimizing power efficiency and image quality in AMOLED interactive display systems. It includes innovations in local dimming, color management, and content-adaptive brightness control. These advancements aim to reduce power consumption while maintaining or improving display quality, particularly in mobile and wearable devices with AMOLED screens.
02 Touch sensing integration in AMOLED displays
This point covers the integration of touch sensing capabilities within AMOLED displays. It includes techniques for combining touch sensors with display elements, methods for improving touch sensitivity and accuracy, and solutions for reducing interference between touch and display functions in interactive AMOLED systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Power management and energy efficiency in AMOLED systems
This category addresses power management and energy efficiency improvements in AMOLED interactive display systems. It includes techniques for reducing power consumption, optimizing display brightness based on ambient conditions, and implementing power-saving modes without compromising display quality or user experience.Expand Specific Solutions04 AMOLED display manufacturing and fabrication techniques
This point focuses on manufacturing and fabrication techniques specific to AMOLED displays. It covers innovations in materials, deposition methods, encapsulation technologies, and production processes aimed at improving the quality, yield, and cost-effectiveness of AMOLED interactive display systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 User interface and interaction methods for AMOLED displays
This category explores user interface designs and interaction methods tailored for AMOLED interactive display systems. It includes innovations in gesture recognition, haptic feedback integration, adaptive user interfaces, and novel ways of presenting information on AMOLED screens to enhance user experience and interactivity.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in AMOLED and Museum Tech
The AMOLED interactive display systems in museums are in a growth phase, with increasing market size due to rising demand for immersive and engaging museum experiences. The technology's maturity is advancing rapidly, driven by innovations from key players. Companies like Samsung Electronics and BOE Technology Group are leading in AMOLED development, while others such as TCL China Star Optoelectronics and Tianma Microelectronics are also making significant contributions. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established electronics giants and specialized display manufacturers, all vying to enhance the technology's application in museum settings.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed AMOLED displays specifically tailored for museum applications. Their solution focuses on flexible AMOLED panels that can be curved or shaped to fit unique exhibit designs. BOE's technology incorporates low-temperature polysilicon (LTPS) backplanes for improved resolution and power efficiency[4]. The company has also implemented advanced touch integration directly into the AMOLED structure, reducing overall thickness and improving responsiveness for interactive exhibits[5]. BOE's AMOLED displays for museums feature enhanced color accuracy and brightness uniformity, crucial for accurately representing artifacts and artwork[6].
Strengths: Flexible form factors, high color accuracy, and integrated touch functionality. Weaknesses: Limited production capacity compared to some competitors, potentially higher costs for custom designs.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has pioneered AMOLED technology for interactive display systems in museums. Their solution incorporates high-resolution, energy-efficient AMOLED panels with touch sensitivity and wide color gamut. The displays feature ultra-thin designs, allowing for seamless integration into museum exhibits. Samsung's AMOLED technology offers superior contrast ratios and deep blacks, enhancing the visual experience for museum visitors[1][3]. The company has also developed specialized coatings to reduce glare and improve visibility under various lighting conditions, which is crucial for museum environments[2].
Strengths: Superior image quality, energy efficiency, and thin form factor. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional LCD displays, potential for burn-in with static images.
Core AMOLED Innovations for Interactive Displays
Active matrix organic light-emitting diode display panel
PatentInactiveUS20200185467A1
Innovation
- The AMOLED display panel design includes a driving circuit region with a smaller area than the display light-emitting region, where the display light-emitting region completely covers the driving circuit and fan-out regions, with optimized placement of driving units and display units to reduce the area of the lower edge region and fan-out trace, allowing for a narrower frame.
Method for driving a display panel to display image, display apparatus thereof, and driver enabled to perform the method
PatentWO2018223643A1
Innovation
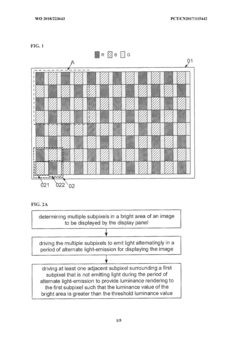
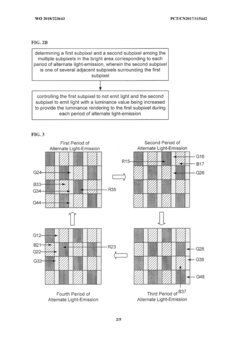
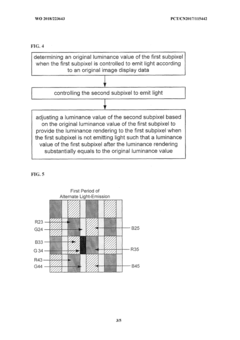
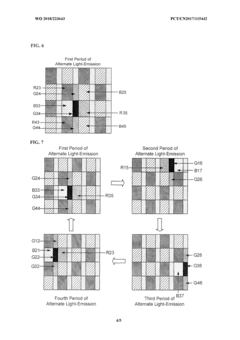
- AMOLED displays offer ultra-thin panels, high contrast ratios, wide color gamut, fast response rates, wide viewing angles, and large curvature deflection, making them ideal for museum interactive displays.
- The display panel uses thin-film transistors (TFTs) to control individual subpixels, allowing for precise control of image quality and brightness at the subpixel level.
- The method allows for dynamic adjustment of subpixel luminance to enhance image contrast, improving the overall visual experience in museum displays.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Aspects
The integration of AMOLED technology in interactive display systems for museums brings significant advantages in terms of energy efficiency and sustainability. AMOLED displays consume less power compared to traditional LCD screens, particularly when displaying darker content. This characteristic is especially beneficial in museum environments where ambient lighting is often subdued to protect artifacts and create atmosphere.
AMOLED's ability to selectively illuminate individual pixels results in substantial energy savings, as only the necessary pixels are activated. This feature is particularly advantageous for interactive displays in museums, where content may frequently change or remain static for extended periods. The reduced power consumption translates to lower operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint for museums implementing AMOLED-based interactive systems.
Furthermore, AMOLED displays offer improved longevity and durability compared to conventional display technologies. Their resistance to image retention and burn-in issues contributes to a longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated electronic waste. This durability aligns well with the sustainability goals of many modern museums, which aim to minimize their environmental impact.
The superior color reproduction and contrast ratios of AMOLED displays also contribute to energy efficiency. These displays can achieve vibrant colors and deep blacks without the need for additional backlighting, further reducing power consumption. In museum settings, this capability allows for more engaging and visually striking interactive exhibits without compromising on energy efficiency.
AMOLED technology's potential for flexible and transparent displays opens up new possibilities for sustainable exhibit design. These innovative display formats can be seamlessly integrated into existing museum architecture, potentially reducing the need for additional construction or renovation. This adaptability contributes to the overall sustainability of museum spaces by minimizing material usage and construction-related environmental impacts.
As museums increasingly prioritize sustainability in their operations, the adoption of AMOLED technology in interactive display systems represents a significant step towards achieving these goals. The combination of reduced energy consumption, improved durability, and innovative display capabilities positions AMOLED as a sustainable choice for museums looking to enhance their interactive exhibits while minimizing their environmental footprint.
AMOLED's ability to selectively illuminate individual pixels results in substantial energy savings, as only the necessary pixels are activated. This feature is particularly advantageous for interactive displays in museums, where content may frequently change or remain static for extended periods. The reduced power consumption translates to lower operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint for museums implementing AMOLED-based interactive systems.
Furthermore, AMOLED displays offer improved longevity and durability compared to conventional display technologies. Their resistance to image retention and burn-in issues contributes to a longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated electronic waste. This durability aligns well with the sustainability goals of many modern museums, which aim to minimize their environmental impact.
The superior color reproduction and contrast ratios of AMOLED displays also contribute to energy efficiency. These displays can achieve vibrant colors and deep blacks without the need for additional backlighting, further reducing power consumption. In museum settings, this capability allows for more engaging and visually striking interactive exhibits without compromising on energy efficiency.
AMOLED technology's potential for flexible and transparent displays opens up new possibilities for sustainable exhibit design. These innovative display formats can be seamlessly integrated into existing museum architecture, potentially reducing the need for additional construction or renovation. This adaptability contributes to the overall sustainability of museum spaces by minimizing material usage and construction-related environmental impacts.
As museums increasingly prioritize sustainability in their operations, the adoption of AMOLED technology in interactive display systems represents a significant step towards achieving these goals. The combination of reduced energy consumption, improved durability, and innovative display capabilities positions AMOLED as a sustainable choice for museums looking to enhance their interactive exhibits while minimizing their environmental footprint.
Visitor Engagement and Learning Impact
The integration of AMOLED technology in interactive display systems has significantly transformed visitor engagement and learning experiences in museums. These advanced displays offer superior visual quality, enhanced interactivity, and improved energy efficiency, leading to more immersive and captivating exhibits.
AMOLED displays provide vibrant colors, deep blacks, and high contrast ratios, resulting in more visually appealing and realistic representations of artifacts and exhibits. This enhanced visual quality helps capture visitors' attention and maintains their interest for longer periods, promoting deeper engagement with the displayed content.
The touch-responsive nature of AMOLED screens enables more intuitive and interactive experiences. Visitors can manipulate digital representations of artifacts, zoom in on details, and access additional information through touch gestures. This hands-on approach to learning fosters active participation and encourages visitors to explore exhibits at their own pace, catering to different learning styles and preferences.
AMOLED technology also allows for the creation of flexible and curved displays, enabling museums to design more creative and immersive exhibit layouts. These unique display configurations can be seamlessly integrated into the museum environment, enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal and creating more engaging spaces for visitors to explore and learn.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED displays contributes to longer battery life in portable interactive devices and reduced power consumption in fixed installations. This allows museums to deploy more interactive elements throughout their spaces without significant increases in energy costs, ultimately leading to a more comprehensive and engaging visitor experience.
Furthermore, AMOLED's ability to display true blacks by turning off individual pixels enables the creation of seamless transitions between physical and digital elements in exhibits. This feature can be leveraged to create more immersive and atmospheric displays, blending real-world objects with digital information in a visually cohesive manner.
The improved visibility of AMOLED displays in various lighting conditions ensures that interactive content remains clear and legible throughout the museum, regardless of ambient light levels. This consistency in display quality across different exhibit areas helps maintain visitor engagement and facilitates a more uniform learning experience throughout the museum visit.
In conclusion, the integration of AMOLED technology in museum display systems has revolutionized visitor engagement and learning impact. By offering superior visual quality, enhanced interactivity, and improved energy efficiency, AMOLED displays create more immersive, engaging, and effective educational experiences in museum settings.
AMOLED displays provide vibrant colors, deep blacks, and high contrast ratios, resulting in more visually appealing and realistic representations of artifacts and exhibits. This enhanced visual quality helps capture visitors' attention and maintains their interest for longer periods, promoting deeper engagement with the displayed content.
The touch-responsive nature of AMOLED screens enables more intuitive and interactive experiences. Visitors can manipulate digital representations of artifacts, zoom in on details, and access additional information through touch gestures. This hands-on approach to learning fosters active participation and encourages visitors to explore exhibits at their own pace, catering to different learning styles and preferences.
AMOLED technology also allows for the creation of flexible and curved displays, enabling museums to design more creative and immersive exhibit layouts. These unique display configurations can be seamlessly integrated into the museum environment, enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal and creating more engaging spaces for visitors to explore and learn.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED displays contributes to longer battery life in portable interactive devices and reduced power consumption in fixed installations. This allows museums to deploy more interactive elements throughout their spaces without significant increases in energy costs, ultimately leading to a more comprehensive and engaging visitor experience.
Furthermore, AMOLED's ability to display true blacks by turning off individual pixels enables the creation of seamless transitions between physical and digital elements in exhibits. This feature can be leveraged to create more immersive and atmospheric displays, blending real-world objects with digital information in a visually cohesive manner.
The improved visibility of AMOLED displays in various lighting conditions ensures that interactive content remains clear and legible throughout the museum, regardless of ambient light levels. This consistency in display quality across different exhibit areas helps maintain visitor engagement and facilitates a more uniform learning experience throughout the museum visit.
In conclusion, the integration of AMOLED technology in museum display systems has revolutionized visitor engagement and learning impact. By offering superior visual quality, enhanced interactivity, and improved energy efficiency, AMOLED displays create more immersive, engaging, and effective educational experiences in museum settings.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!