AMOLED as the catalyst for ultra-thin folding clamshell devices.
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Folding Evolution
The evolution of AMOLED technology has been a key driver in the development of ultra-thin folding clamshell devices. This journey began with the introduction of OLED displays in the early 2000s, which offered superior color reproduction and contrast compared to traditional LCD screens. As the technology matured, AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays emerged, providing even better performance and energy efficiency.
The breakthrough for foldable devices came with the development of flexible AMOLED panels. These displays could be bent and folded without compromising image quality or durability. The first commercially available foldable smartphones, introduced in 2019, utilized this technology to create devices that could transform from a phone to a tablet-like form factor.
As the demand for more compact foldable devices grew, manufacturers focused on developing ultra-thin AMOLED displays specifically designed for clamshell-style folding phones. This required overcoming several technical challenges, including reducing the thickness of the display layers, improving the folding mechanism, and enhancing the durability of the folding area.
The evolution of AMOLED technology for folding clamshell devices has seen significant improvements in several key areas. Display resolution and pixel density have increased dramatically, providing sharper images and text even on smaller screens. Color accuracy and brightness have also been enhanced, allowing for better visibility in various lighting conditions.
One of the most critical advancements has been the reduction of the folding radius. Early foldable devices had a noticeable crease at the fold, but newer AMOLED displays can achieve much tighter folding radii, resulting in a nearly seamless appearance when unfolded. This has been made possible through innovations in flexible substrate materials and ultra-thin glass technologies.
Durability has been another focus area in the evolution of AMOLED folding displays. Manufacturers have developed specialized protective layers and hinge mechanisms to prevent damage from repeated folding and unfolding. Some devices now boast impressive durability ratings, with screens capable of withstanding hundreds of thousands of fold cycles.
The integration of touch sensitivity and stylus support into folding AMOLED displays has further expanded the functionality of clamshell devices. This has enabled new use cases and interaction paradigms, blurring the lines between smartphones, tablets, and even laptops.
Looking ahead, the evolution of AMOLED technology for folding clamshell devices is expected to continue at a rapid pace. Future developments may include even thinner and more flexible displays, improved energy efficiency, and the integration of advanced features such as under-display cameras and sensors. As AMOLED technology advances, it will likely catalyze further innovations in the design and functionality of ultra-thin folding clamshell devices.
The breakthrough for foldable devices came with the development of flexible AMOLED panels. These displays could be bent and folded without compromising image quality or durability. The first commercially available foldable smartphones, introduced in 2019, utilized this technology to create devices that could transform from a phone to a tablet-like form factor.
As the demand for more compact foldable devices grew, manufacturers focused on developing ultra-thin AMOLED displays specifically designed for clamshell-style folding phones. This required overcoming several technical challenges, including reducing the thickness of the display layers, improving the folding mechanism, and enhancing the durability of the folding area.
The evolution of AMOLED technology for folding clamshell devices has seen significant improvements in several key areas. Display resolution and pixel density have increased dramatically, providing sharper images and text even on smaller screens. Color accuracy and brightness have also been enhanced, allowing for better visibility in various lighting conditions.
One of the most critical advancements has been the reduction of the folding radius. Early foldable devices had a noticeable crease at the fold, but newer AMOLED displays can achieve much tighter folding radii, resulting in a nearly seamless appearance when unfolded. This has been made possible through innovations in flexible substrate materials and ultra-thin glass technologies.
Durability has been another focus area in the evolution of AMOLED folding displays. Manufacturers have developed specialized protective layers and hinge mechanisms to prevent damage from repeated folding and unfolding. Some devices now boast impressive durability ratings, with screens capable of withstanding hundreds of thousands of fold cycles.
The integration of touch sensitivity and stylus support into folding AMOLED displays has further expanded the functionality of clamshell devices. This has enabled new use cases and interaction paradigms, blurring the lines between smartphones, tablets, and even laptops.
Looking ahead, the evolution of AMOLED technology for folding clamshell devices is expected to continue at a rapid pace. Future developments may include even thinner and more flexible displays, improved energy efficiency, and the integration of advanced features such as under-display cameras and sensors. As AMOLED technology advances, it will likely catalyze further innovations in the design and functionality of ultra-thin folding clamshell devices.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for ultra-thin folding clamshell devices incorporating AMOLED technology has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. This surge is driven by consumer preferences for more compact, versatile, and visually appealing smartphones that offer both portability and large screen real estate when unfolded.
AMOLED displays have become a key enabler for these innovative form factors due to their flexibility, thinness, and superior visual quality. The technology allows for vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and deep blacks, enhancing the overall user experience. As consumers increasingly prioritize immersive viewing experiences and sleek designs, AMOLED-equipped folding devices are well-positioned to meet these demands.
The global foldable smartphone market has shown remarkable expansion, with major players like Samsung, Huawei, and Motorola introducing various models. This market segment is expected to continue its upward trajectory, as more manufacturers enter the space and production costs decrease over time. The integration of AMOLED technology in these devices is a crucial factor driving consumer interest and market growth.
In terms of regional demand, Asia-Pacific leads the market, with countries like South Korea and China showing strong adoption rates. North America and Europe follow closely, as tech-savvy consumers in these regions demonstrate a willingness to invest in cutting-edge mobile technology. Emerging markets are also showing increasing interest, albeit at a slower pace due to higher price points.
The target demographic for ultra-thin folding clamshell devices primarily consists of early adopters, tech enthusiasts, and professionals who value both style and functionality. These consumers are often willing to pay premium prices for innovative features and designs. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, the market is expected to expand to include a broader range of consumers.
Industry analysts predict that the demand for AMOLED-based folding devices will continue to grow as manufacturers overcome technical challenges and improve durability. The ability to create thinner, more robust folding mechanisms and displays will be crucial in meeting consumer expectations and driving market expansion.
Furthermore, the integration of 5G technology in these devices is expected to boost demand, as users seek devices capable of leveraging high-speed networks for enhanced productivity and entertainment experiences. This convergence of AMOLED display technology, folding form factors, and advanced connectivity is likely to create new use cases and applications, further stimulating market growth.
AMOLED displays have become a key enabler for these innovative form factors due to their flexibility, thinness, and superior visual quality. The technology allows for vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and deep blacks, enhancing the overall user experience. As consumers increasingly prioritize immersive viewing experiences and sleek designs, AMOLED-equipped folding devices are well-positioned to meet these demands.
The global foldable smartphone market has shown remarkable expansion, with major players like Samsung, Huawei, and Motorola introducing various models. This market segment is expected to continue its upward trajectory, as more manufacturers enter the space and production costs decrease over time. The integration of AMOLED technology in these devices is a crucial factor driving consumer interest and market growth.
In terms of regional demand, Asia-Pacific leads the market, with countries like South Korea and China showing strong adoption rates. North America and Europe follow closely, as tech-savvy consumers in these regions demonstrate a willingness to invest in cutting-edge mobile technology. Emerging markets are also showing increasing interest, albeit at a slower pace due to higher price points.
The target demographic for ultra-thin folding clamshell devices primarily consists of early adopters, tech enthusiasts, and professionals who value both style and functionality. These consumers are often willing to pay premium prices for innovative features and designs. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, the market is expected to expand to include a broader range of consumers.
Industry analysts predict that the demand for AMOLED-based folding devices will continue to grow as manufacturers overcome technical challenges and improve durability. The ability to create thinner, more robust folding mechanisms and displays will be crucial in meeting consumer expectations and driving market expansion.
Furthermore, the integration of 5G technology in these devices is expected to boost demand, as users seek devices capable of leveraging high-speed networks for enhanced productivity and entertainment experiences. This convergence of AMOLED display technology, folding form factors, and advanced connectivity is likely to create new use cases and applications, further stimulating market growth.
Technical Challenges
The development of ultra-thin folding clamshell devices using AMOLED technology faces several significant technical challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the durability and longevity of the flexible display. AMOLED screens must withstand thousands of folding cycles without degradation in image quality or structural integrity. This requires innovative materials and manufacturing processes to create displays that can repeatedly bend without developing creases, dead pixels, or other defects.
Another major challenge lies in the design and implementation of the hinge mechanism. The hinge must be robust enough to support the device's structure while being compact and allowing for a seamless folding experience. Engineers must balance the need for a tight fold radius to minimize device thickness with the stress placed on the display and internal components during folding and unfolding operations.
Power management presents a unique set of difficulties in folding clamshell devices. The limited space available for batteries in ultra-thin designs constrains overall device capacity. This challenge is compounded by the power requirements of AMOLED displays, which can be more energy-intensive than traditional LCD screens. Developing efficient power management systems and optimizing software to maximize battery life is crucial for the success of these devices.
Heat dissipation is another critical concern in compact folding designs. The concentrated arrangement of components in a folded state can lead to thermal hotspots, potentially affecting performance and user comfort. Engineers must devise innovative cooling solutions that work effectively in both folded and unfolded configurations without adding significant bulk to the device.
The integration of touch sensitivity and protective layers on flexible AMOLED displays poses additional challenges. These layers must maintain functionality and clarity while being able to fold repeatedly. Achieving consistent touch response across the entire screen, including the folding area, requires advanced materials and precise manufacturing techniques.
Software optimization for folding clamshell devices presents its own set of challenges. Applications must seamlessly transition between different screen configurations, adapting their user interfaces and functionality accordingly. This requires close collaboration between hardware and software teams to create a cohesive user experience that takes full advantage of the device's unique form factor.
Lastly, manufacturing scalability remains a significant hurdle. Producing flexible AMOLED displays and assembling ultra-thin folding devices at scale requires substantial investments in new production technologies and processes. Achieving high yield rates and consistent quality across large production volumes is essential for making these devices commercially viable and accessible to a broad consumer market.
Another major challenge lies in the design and implementation of the hinge mechanism. The hinge must be robust enough to support the device's structure while being compact and allowing for a seamless folding experience. Engineers must balance the need for a tight fold radius to minimize device thickness with the stress placed on the display and internal components during folding and unfolding operations.
Power management presents a unique set of difficulties in folding clamshell devices. The limited space available for batteries in ultra-thin designs constrains overall device capacity. This challenge is compounded by the power requirements of AMOLED displays, which can be more energy-intensive than traditional LCD screens. Developing efficient power management systems and optimizing software to maximize battery life is crucial for the success of these devices.
Heat dissipation is another critical concern in compact folding designs. The concentrated arrangement of components in a folded state can lead to thermal hotspots, potentially affecting performance and user comfort. Engineers must devise innovative cooling solutions that work effectively in both folded and unfolded configurations without adding significant bulk to the device.
The integration of touch sensitivity and protective layers on flexible AMOLED displays poses additional challenges. These layers must maintain functionality and clarity while being able to fold repeatedly. Achieving consistent touch response across the entire screen, including the folding area, requires advanced materials and precise manufacturing techniques.
Software optimization for folding clamshell devices presents its own set of challenges. Applications must seamlessly transition between different screen configurations, adapting their user interfaces and functionality accordingly. This requires close collaboration between hardware and software teams to create a cohesive user experience that takes full advantage of the device's unique form factor.
Lastly, manufacturing scalability remains a significant hurdle. Producing flexible AMOLED displays and assembling ultra-thin folding devices at scale requires substantial investments in new production technologies and processes. Achieving high yield rates and consistent quality across large production volumes is essential for making these devices commercially viable and accessible to a broad consumer market.
Current Folding Solutions
01 Thin-film transistor structure for AMOLED displays
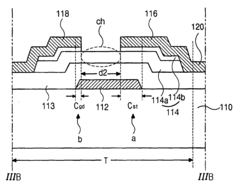
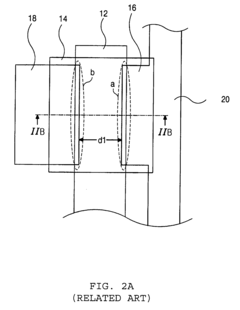
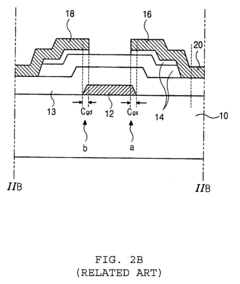
Advanced thin-film transistor (TFT) structures are used to reduce the overall thickness of AMOLED displays. These structures often involve optimized layer arrangements and materials to minimize the vertical profile while maintaining performance. Innovations in TFT design contribute to creating ultra-thin and flexible AMOLED panels.- Thin-film transistor (TFT) structure optimization: Improving the structure of thin-film transistors in AMOLED displays can lead to reduced overall thickness. This includes optimizing the layers, materials, and arrangement of TFTs to minimize their footprint while maintaining or enhancing performance.
- Flexible AMOLED design: Developing flexible AMOLED displays allows for thinner overall device profiles. This involves using flexible substrates, encapsulation methods, and designing the display components to withstand bending and folding while maintaining display quality and durability.
- Integration of touch and display layers: Combining touch functionality with the display layers can reduce the overall thickness of AMOLED devices. This integration eliminates the need for separate touch panels, resulting in a more compact design without compromising touch sensitivity or display performance.
- Advanced encapsulation techniques: Implementing innovative encapsulation methods for AMOLED displays can contribute to reducing overall thickness. These techniques aim to protect the organic materials from moisture and oxygen while minimizing the thickness of the protective layers.
- Pixel circuit design optimization: Enhancing the design of pixel circuits in AMOLED displays can lead to reduced thickness. This involves optimizing the layout, reducing the number of components, and improving the efficiency of pixel driving schemes to minimize the space required for each pixel.
02 Encapsulation techniques for thin AMOLED devices
Novel encapsulation methods are employed to protect AMOLED displays while minimizing thickness. These techniques may include thin-film encapsulation layers, hybrid inorganic-organic structures, or advanced barrier films. The goal is to provide adequate protection against moisture and oxygen ingress without significantly increasing the overall device thickness.Expand Specific Solutions03 Flexible substrate technologies for thin AMOLEDs
Flexible substrates, such as ultra-thin glass or plastic films, are utilized to reduce the thickness of AMOLED displays. These substrates allow for the creation of bendable or rollable displays while maintaining a minimal thickness profile. Advanced manufacturing processes are developed to handle these delicate substrates without compromising display quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of touch sensors in thin AMOLED displays
Innovative approaches are used to integrate touch functionality into AMOLED displays without significantly increasing thickness. This may involve in-cell or on-cell touch sensor designs, as well as novel electrode materials and structures that serve dual purposes for both display and touch functions, thereby reducing the need for additional layers.Expand Specific Solutions05 Optical stack optimization for thin AMOLEDs
The optical stack of AMOLED displays is optimized to reduce thickness while maintaining or improving display performance. This includes the development of ultra-thin color filters, polarizers, and light management films. Advanced materials and nano-scale structures are employed to achieve the desired optical properties with minimal thickness contribution.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The AMOLED technology for ultra-thin folding clamshell devices is in a growth phase, with increasing market demand and rapid technological advancements. The global market for foldable AMOLED displays is expanding, driven by consumer interest in innovative form factors. Technologically, while AMOLED for foldables is maturing, challenges remain in durability and production costs. Key players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology, and LG Display are leading the field, with companies such as Visionox and Tianma Microelectronics also making significant strides. These firms are investing heavily in R&D to overcome technical hurdles and improve manufacturing processes, indicating a competitive and dynamic landscape in this emerging sector.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has made significant advancements in AMOLED technology for foldable devices. They have developed a 12.3-inch rollable AMOLED display with a bending radius of just 5mm, showcasing their capability in flexible display technology[9]. For clamshell devices, BOE has introduced an ultra-thin flexible AMOLED panel with a thickness of only 0.03mm, allowing for a folding radius as small as 1mm without damage[10]. Their displays utilize a unique pixel compensation technology to maintain image quality even after repeated folding. BOE has also implemented an advanced touch integration method, embedding the touch sensors directly within the OLED layers to reduce overall thickness and improve touch sensitivity[11].
Strengths: Ultra-thin panel technology, advanced pixel compensation, integrated touch sensors. Weaknesses: Less established in the global smartphone market compared to some competitors, potential yield rate challenges for mass production.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has pioneered AMOLED technology for foldable devices, particularly in their Galaxy Z Flip series. Their latest innovation involves a ultra-thin glass (UTG) layer integrated with the AMOLED display, allowing for a folding radius as small as 1.4mm[1]. The company has also developed a "Flex Mode" that takes advantage of the folding mechanism, splitting the screen for multitasking[2]. Samsung's AMOLED displays for foldables feature a dynamic AMOLED 2X panel with a 120Hz refresh rate, offering vivid colors and smooth transitions even when folded[3]. They've also implemented a layer of "Ultra Thin Glass" (UTG) over the AMOLED panel to enhance durability while maintaining flexibility[4].
Strengths: Industry-leading AMOLED technology, innovative UTG integration, established market presence. Weaknesses: Higher production costs, potential for screen creasing over time.
AMOLED Innovations
Active matrix type organic light emitting diode device and thin film transistor thereof
PatentInactiveUS20040142502A1
Innovation
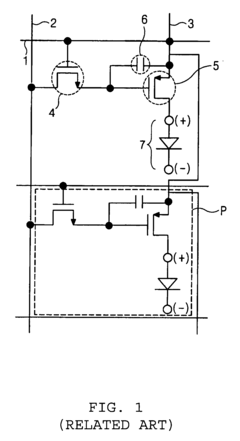
- A driving thin film transistor structure is designed with a larger overlapping area between the gate electrode and the source electrode compared to the gate electrode and drain electrode, forming a storage capacitor to stabilize pixel voltage and reduce parasitic capacitances, thereby enhancing image quality and preventing metal line disconnection.
Active matrix organic light emitting diode display
PatentInactiveUS20090201235A1
Innovation
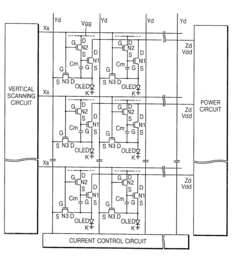
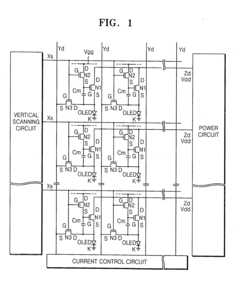
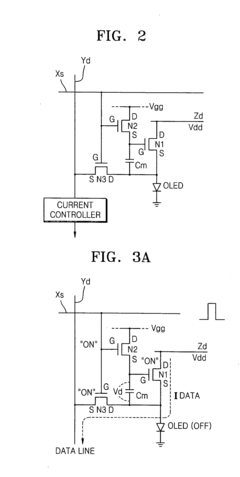
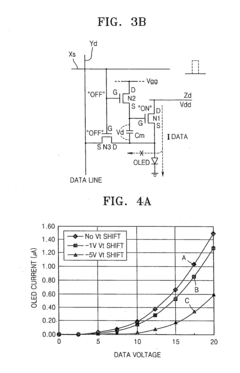
- An AMOLED display with a 3-transistor-1-capacitor structure using N-channel transistors, including a driving transistor, a switching transistor, and a programming transistor, along with a current controller, which determines the current flowing through the transistors to maintain uniform brightness by compensating for threshold voltage shifts, allowing for the use of amorphous silicon and simplifying the pixel structure.
Supply Chain Analysis
The supply chain for AMOLED displays in ultra-thin folding clamshell devices is complex and involves multiple key players across different regions. Samsung Display and LG Display, both based in South Korea, are the dominant manufacturers of AMOLED panels for mobile devices, including those used in foldable smartphones. These companies have invested heavily in research and development to create flexible AMOLED displays that can withstand repeated folding without degradation.
Chinese manufacturers such as BOE, Visionox, and TCL CSOT are also making significant strides in AMOLED technology, particularly for foldable devices. They are rapidly expanding their production capabilities and improving their technological expertise to compete with the Korean giants. This increased competition is likely to drive innovation and potentially reduce costs in the long term.
The production of AMOLED displays requires specialized materials and components. Key suppliers include companies like Universal Display Corporation for OLED materials, Corning for ultra-thin glass substrates, and Sumitomo Chemical for OLED-related chemicals. These suppliers play a crucial role in the development of more durable and flexible displays for clamshell devices.
Manufacturing equipment is another critical aspect of the AMOLED supply chain. Companies like Applied Materials, Canon Tokki, and Coherent provide the highly specialized machinery required for OLED panel production. The limited number of equipment suppliers can sometimes create bottlenecks in the supply chain, affecting the overall production capacity of AMOLED displays.
As the demand for ultra-thin folding clamshell devices grows, the supply chain is adapting to meet these new requirements. This includes developing new manufacturing processes for flexible substrates, improving the durability of folding mechanisms, and enhancing the integration of touch sensors with flexible displays. The supply chain is also focusing on yield improvement and cost reduction to make foldable AMOLED devices more accessible to a broader market.
Challenges in the AMOLED supply chain for foldable devices include ensuring consistent quality across large production volumes, managing the complexity of new form factors, and balancing the trade-offs between flexibility, durability, and display performance. Additionally, the supply chain must address potential disruptions due to geopolitical tensions and the ongoing efforts to diversify sourcing and production locations.
Chinese manufacturers such as BOE, Visionox, and TCL CSOT are also making significant strides in AMOLED technology, particularly for foldable devices. They are rapidly expanding their production capabilities and improving their technological expertise to compete with the Korean giants. This increased competition is likely to drive innovation and potentially reduce costs in the long term.
The production of AMOLED displays requires specialized materials and components. Key suppliers include companies like Universal Display Corporation for OLED materials, Corning for ultra-thin glass substrates, and Sumitomo Chemical for OLED-related chemicals. These suppliers play a crucial role in the development of more durable and flexible displays for clamshell devices.
Manufacturing equipment is another critical aspect of the AMOLED supply chain. Companies like Applied Materials, Canon Tokki, and Coherent provide the highly specialized machinery required for OLED panel production. The limited number of equipment suppliers can sometimes create bottlenecks in the supply chain, affecting the overall production capacity of AMOLED displays.
As the demand for ultra-thin folding clamshell devices grows, the supply chain is adapting to meet these new requirements. This includes developing new manufacturing processes for flexible substrates, improving the durability of folding mechanisms, and enhancing the integration of touch sensors with flexible displays. The supply chain is also focusing on yield improvement and cost reduction to make foldable AMOLED devices more accessible to a broader market.
Challenges in the AMOLED supply chain for foldable devices include ensuring consistent quality across large production volumes, managing the complexity of new form factors, and balancing the trade-offs between flexibility, durability, and display performance. Additionally, the supply chain must address potential disruptions due to geopolitical tensions and the ongoing efforts to diversify sourcing and production locations.
Durability Assessment
The durability assessment of AMOLED displays in ultra-thin folding clamshell devices is a critical aspect of their development and market viability. These displays must withstand repeated folding and unfolding actions without significant degradation in performance or visual quality. Manufacturers typically subject their devices to rigorous testing, simulating thousands of fold cycles to ensure long-term reliability.
One of the primary concerns in durability testing is the potential for creasing or damage at the fold line. Advanced AMOLED panels utilize flexible substrates and specialized protective layers to minimize visible creasing and maintain structural integrity. Testing protocols often include both automated folding machines and real-world usage simulations to comprehensively evaluate the display's resilience.
The impact of environmental factors on durability is another crucial consideration. AMOLED displays in folding devices must maintain their performance across a range of temperatures and humidity levels. Extreme conditions can affect the flexibility of materials and potentially lead to accelerated wear or failure. Manufacturers conduct extensive environmental testing to ensure the displays can withstand diverse usage scenarios.
Scratch resistance is an additional durability concern, particularly for the outer display of clamshell devices. While the folded configuration offers some protection, the exposed screen remains vulnerable during everyday use. Advanced coating technologies and materials such as ultra-thin glass are being developed to enhance scratch resistance without compromising flexibility.
The durability of the folding mechanism itself is intrinsically linked to the display's longevity. The hinge design must provide consistent support and tension to the AMOLED panel throughout its lifespan. Manufacturers are continually refining hinge mechanisms to distribute stress evenly and prevent localized damage to the display.
Long-term color stability and brightness retention are also key factors in durability assessments. AMOLED displays are known for their vibrant colors and deep blacks, but these qualities must be maintained over time, even with frequent folding. Accelerated aging tests are employed to predict and mitigate potential issues such as color shift or brightness degradation.
As the technology evolves, durability standards for AMOLED displays in folding devices are becoming increasingly stringent. Manufacturers are not only aiming to meet current consumer expectations but also to anticipate future demands for more robust and longer-lasting devices. This forward-looking approach drives continuous innovation in materials science and engineering, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in flexible display technology.
One of the primary concerns in durability testing is the potential for creasing or damage at the fold line. Advanced AMOLED panels utilize flexible substrates and specialized protective layers to minimize visible creasing and maintain structural integrity. Testing protocols often include both automated folding machines and real-world usage simulations to comprehensively evaluate the display's resilience.
The impact of environmental factors on durability is another crucial consideration. AMOLED displays in folding devices must maintain their performance across a range of temperatures and humidity levels. Extreme conditions can affect the flexibility of materials and potentially lead to accelerated wear or failure. Manufacturers conduct extensive environmental testing to ensure the displays can withstand diverse usage scenarios.
Scratch resistance is an additional durability concern, particularly for the outer display of clamshell devices. While the folded configuration offers some protection, the exposed screen remains vulnerable during everyday use. Advanced coating technologies and materials such as ultra-thin glass are being developed to enhance scratch resistance without compromising flexibility.
The durability of the folding mechanism itself is intrinsically linked to the display's longevity. The hinge design must provide consistent support and tension to the AMOLED panel throughout its lifespan. Manufacturers are continually refining hinge mechanisms to distribute stress evenly and prevent localized damage to the display.
Long-term color stability and brightness retention are also key factors in durability assessments. AMOLED displays are known for their vibrant colors and deep blacks, but these qualities must be maintained over time, even with frequent folding. Accelerated aging tests are employed to predict and mitigate potential issues such as color shift or brightness degradation.
As the technology evolves, durability standards for AMOLED displays in folding devices are becoming increasingly stringent. Manufacturers are not only aiming to meet current consumer expectations but also to anticipate future demands for more robust and longer-lasting devices. This forward-looking approach drives continuous innovation in materials science and engineering, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in flexible display technology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!