Investigating security solutions with AMOLED bio-authentication.
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Bio-Auth Background and Objectives
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) bio-authentication represents a cutting-edge approach to security in mobile and wearable devices. This technology integrates biometric sensors directly into the display, offering a seamless and secure user authentication experience. The evolution of this technology stems from the increasing demand for more robust and user-friendly security solutions in personal electronics.
The primary objective of AMOLED bio-authentication is to enhance device security while improving user convenience. By embedding biometric sensors within the display itself, this technology aims to eliminate the need for separate hardware components, such as dedicated fingerprint sensors or facial recognition cameras. This integration not only streamlines device design but also potentially reduces manufacturing costs and improves overall device aesthetics.
The development of AMOLED bio-authentication technology can be traced back to the early 2010s when smartphone manufacturers began exploring alternatives to traditional PIN codes and pattern locks. The introduction of capacitive fingerprint sensors marked a significant milestone, but these often required dedicated hardware space on the device's front or back. As bezels shrunk and screen-to-body ratios increased, the industry sought more innovative solutions.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards in-display fingerprint sensors, with optical and ultrasonic technologies leading the way. However, AMOLED bio-authentication aims to take this concept further by leveraging the unique properties of OLED displays. By integrating light-sensitive elements directly into the OLED panel, this technology can potentially capture high-resolution biometric data without compromising display quality or adding significant thickness to the device.
The objectives of AMOLED bio-authentication extend beyond mere fingerprint recognition. Researchers and developers are exploring the possibility of incorporating multiple biometric modalities, such as facial recognition and even vein pattern analysis, all within the display itself. This multi-factor approach could significantly enhance security by combining different biometric identifiers, making it exponentially more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access.
Another key goal of this technology is to improve the user experience by making authentication more natural and less obtrusive. With sensors integrated into the display, users could potentially authenticate by simply looking at their device or touching any part of the screen, eliminating the need for specific gestures or dedicated sensor areas. This seamless interaction could lead to faster, more intuitive device unlocking and secure app access.
As the technology progresses, researchers are also focusing on addressing potential vulnerabilities and enhancing the overall reliability of AMOLED bio-authentication. This includes developing advanced algorithms to distinguish between live biometric inputs and potential spoofing attempts, as well as improving the sensors' ability to function accurately under various environmental conditions, such as different lighting scenarios or when the user's hands are wet or dirty.
The primary objective of AMOLED bio-authentication is to enhance device security while improving user convenience. By embedding biometric sensors within the display itself, this technology aims to eliminate the need for separate hardware components, such as dedicated fingerprint sensors or facial recognition cameras. This integration not only streamlines device design but also potentially reduces manufacturing costs and improves overall device aesthetics.
The development of AMOLED bio-authentication technology can be traced back to the early 2010s when smartphone manufacturers began exploring alternatives to traditional PIN codes and pattern locks. The introduction of capacitive fingerprint sensors marked a significant milestone, but these often required dedicated hardware space on the device's front or back. As bezels shrunk and screen-to-body ratios increased, the industry sought more innovative solutions.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards in-display fingerprint sensors, with optical and ultrasonic technologies leading the way. However, AMOLED bio-authentication aims to take this concept further by leveraging the unique properties of OLED displays. By integrating light-sensitive elements directly into the OLED panel, this technology can potentially capture high-resolution biometric data without compromising display quality or adding significant thickness to the device.
The objectives of AMOLED bio-authentication extend beyond mere fingerprint recognition. Researchers and developers are exploring the possibility of incorporating multiple biometric modalities, such as facial recognition and even vein pattern analysis, all within the display itself. This multi-factor approach could significantly enhance security by combining different biometric identifiers, making it exponentially more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access.
Another key goal of this technology is to improve the user experience by making authentication more natural and less obtrusive. With sensors integrated into the display, users could potentially authenticate by simply looking at their device or touching any part of the screen, eliminating the need for specific gestures or dedicated sensor areas. This seamless interaction could lead to faster, more intuitive device unlocking and secure app access.
As the technology progresses, researchers are also focusing on addressing potential vulnerabilities and enhancing the overall reliability of AMOLED bio-authentication. This includes developing advanced algorithms to distinguish between live biometric inputs and potential spoofing attempts, as well as improving the sensors' ability to function accurately under various environmental conditions, such as different lighting scenarios or when the user's hands are wet or dirty.
Market Analysis for Secure Authentication
The market for secure authentication solutions has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing need for robust security measures across various industries. The global biometric system market, which includes AMOLED bio-authentication technologies, is projected to reach substantial market value in the coming years. This growth is primarily fueled by the rising concerns over data breaches, identity theft, and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
AMOLED bio-authentication, particularly in the context of mobile devices and wearables, has emerged as a promising segment within the broader secure authentication market. The integration of biometric sensors with AMOLED displays offers a unique value proposition, combining enhanced security features with improved user experience and device aesthetics.
The demand for AMOLED bio-authentication solutions is particularly strong in sectors such as finance, healthcare, government, and enterprise mobility. Financial institutions are increasingly adopting biometric authentication methods to enhance the security of mobile banking applications and prevent fraudulent transactions. Healthcare organizations are leveraging these technologies to ensure patient data privacy and streamline access to electronic health records.
In the consumer electronics sector, smartphone manufacturers are at the forefront of adopting AMOLED bio-authentication technologies. The integration of under-display fingerprint sensors and facial recognition systems in high-end smartphones has set new standards for device security and user convenience. This trend is expected to trickle down to mid-range devices, further expanding the market potential.
The Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate in the AMOLED bio-authentication market, driven by the rapid adoption of advanced smartphones and the increasing focus on digital identity verification in countries like China and India. North America and Europe are also significant markets, with a strong emphasis on data protection regulations and cybersecurity measures.
Key market drivers include the growing awareness of cybersecurity threats, the need for frictionless authentication methods, and the increasing adoption of IoT devices. However, challenges such as high implementation costs and concerns over biometric data privacy may impact market growth to some extent.
As the technology matures, we can expect to see broader applications of AMOLED bio-authentication in areas such as automotive (for driver authentication and personalized vehicle settings), smart home devices (for secure access control), and even in public spaces for seamless identity verification.
AMOLED bio-authentication, particularly in the context of mobile devices and wearables, has emerged as a promising segment within the broader secure authentication market. The integration of biometric sensors with AMOLED displays offers a unique value proposition, combining enhanced security features with improved user experience and device aesthetics.
The demand for AMOLED bio-authentication solutions is particularly strong in sectors such as finance, healthcare, government, and enterprise mobility. Financial institutions are increasingly adopting biometric authentication methods to enhance the security of mobile banking applications and prevent fraudulent transactions. Healthcare organizations are leveraging these technologies to ensure patient data privacy and streamline access to electronic health records.
In the consumer electronics sector, smartphone manufacturers are at the forefront of adopting AMOLED bio-authentication technologies. The integration of under-display fingerprint sensors and facial recognition systems in high-end smartphones has set new standards for device security and user convenience. This trend is expected to trickle down to mid-range devices, further expanding the market potential.
The Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate in the AMOLED bio-authentication market, driven by the rapid adoption of advanced smartphones and the increasing focus on digital identity verification in countries like China and India. North America and Europe are also significant markets, with a strong emphasis on data protection regulations and cybersecurity measures.
Key market drivers include the growing awareness of cybersecurity threats, the need for frictionless authentication methods, and the increasing adoption of IoT devices. However, challenges such as high implementation costs and concerns over biometric data privacy may impact market growth to some extent.
As the technology matures, we can expect to see broader applications of AMOLED bio-authentication in areas such as automotive (for driver authentication and personalized vehicle settings), smart home devices (for secure access control), and even in public spaces for seamless identity verification.
Current AMOLED Bio-Auth Challenges
AMOLED bio-authentication technology, while promising, faces several significant challenges in its current state of development. One of the primary obstacles is the integration of biometric sensors into AMOLED displays without compromising display quality or increasing device thickness. The need for seamless integration often results in reduced sensor performance or increased manufacturing complexity.
Another major challenge lies in the accuracy and reliability of biometric data capture through AMOLED screens. Environmental factors such as ambient light, temperature variations, and screen contamination can significantly impact the quality of biometric readings. This variability poses a substantial hurdle in maintaining consistent authentication performance across different usage scenarios.
Power consumption remains a critical concern for AMOLED bio-authentication systems. The continuous operation of biometric sensors and the associated processing requirements can lead to increased battery drain, potentially offsetting the energy efficiency advantages typically associated with AMOLED displays. Balancing power efficiency with authentication speed and accuracy presents a complex engineering challenge.
Security vulnerabilities are also a pressing issue in current AMOLED bio-authentication solutions. The potential for spoofing attacks, where artificial biometric data is used to deceive the system, necessitates the development of robust liveness detection mechanisms. Additionally, ensuring the secure storage and processing of biometric data on devices with integrated display-based sensors presents unique cryptographic and hardware security challenges.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing AMOLED displays with integrated bio-authentication capabilities remain significant hurdles. The intricate production processes required to incorporate biometric sensors into displays while maintaining high yield rates and reasonable costs pose substantial challenges for widespread adoption.
User experience considerations present another set of challenges. Ensuring consistent performance across various lighting conditions, accommodating different user behaviors, and maintaining fast and intuitive authentication processes are crucial for user acceptance. Moreover, addressing privacy concerns and providing transparent user controls over biometric data usage are essential for building trust in the technology.
Standardization and interoperability issues also persist in the AMOLED bio-authentication landscape. The lack of unified standards for integrating biometric capabilities into displays hinders cross-platform compatibility and may slow industry-wide adoption. Developing common protocols and interfaces for AMOLED bio-authentication systems is crucial for fostering a robust ecosystem and ensuring seamless integration with various devices and applications.
Another major challenge lies in the accuracy and reliability of biometric data capture through AMOLED screens. Environmental factors such as ambient light, temperature variations, and screen contamination can significantly impact the quality of biometric readings. This variability poses a substantial hurdle in maintaining consistent authentication performance across different usage scenarios.
Power consumption remains a critical concern for AMOLED bio-authentication systems. The continuous operation of biometric sensors and the associated processing requirements can lead to increased battery drain, potentially offsetting the energy efficiency advantages typically associated with AMOLED displays. Balancing power efficiency with authentication speed and accuracy presents a complex engineering challenge.
Security vulnerabilities are also a pressing issue in current AMOLED bio-authentication solutions. The potential for spoofing attacks, where artificial biometric data is used to deceive the system, necessitates the development of robust liveness detection mechanisms. Additionally, ensuring the secure storage and processing of biometric data on devices with integrated display-based sensors presents unique cryptographic and hardware security challenges.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing AMOLED displays with integrated bio-authentication capabilities remain significant hurdles. The intricate production processes required to incorporate biometric sensors into displays while maintaining high yield rates and reasonable costs pose substantial challenges for widespread adoption.
User experience considerations present another set of challenges. Ensuring consistent performance across various lighting conditions, accommodating different user behaviors, and maintaining fast and intuitive authentication processes are crucial for user acceptance. Moreover, addressing privacy concerns and providing transparent user controls over biometric data usage are essential for building trust in the technology.
Standardization and interoperability issues also persist in the AMOLED bio-authentication landscape. The lack of unified standards for integrating biometric capabilities into displays hinders cross-platform compatibility and may slow industry-wide adoption. Developing common protocols and interfaces for AMOLED bio-authentication systems is crucial for fostering a robust ecosystem and ensuring seamless integration with various devices and applications.
Existing AMOLED Bio-Auth Solutions
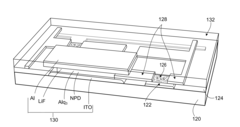
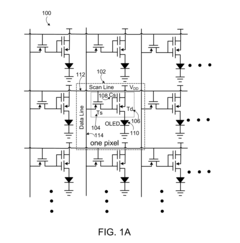
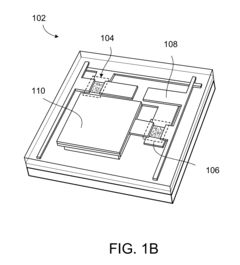
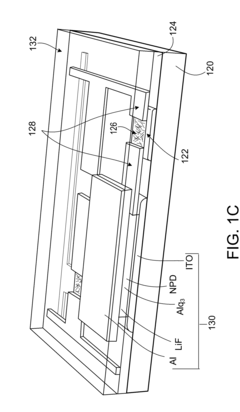
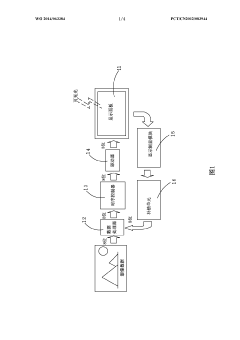
01 AMOLED display integration with biometric sensors
Integration of biometric sensors, such as fingerprint or iris scanners, directly into AMOLED displays for enhanced security and user authentication. This approach allows for seamless and secure device access without the need for separate hardware components.- AMOLED display integration with biometric sensors: Integration of biometric sensors, such as fingerprint or iris scanners, directly into AMOLED displays for enhanced security and user authentication. This approach allows for seamless and secure device access without the need for separate hardware components.
- Multi-factor authentication using AMOLED technology: Implementing multi-factor authentication systems that utilize AMOLED display features in combination with other biometric or security measures. This can include facial recognition, voice authentication, or gesture-based inputs displayed on the AMOLED screen.
- Secure data visualization on AMOLED screens: Developing secure methods for displaying sensitive information on AMOLED screens, such as encryption techniques or dynamic pixel arrangements that prevent unauthorized viewing or screen capture attempts.
- AMOLED-based anti-spoofing measures: Implementing anti-spoofing techniques specifically designed for AMOLED displays, such as liveness detection or unique display patterns that are difficult to replicate, enhancing the overall security of biometric authentication systems.
- Secure communication protocols for AMOLED bio-authentication: Developing secure communication protocols and encryption methods specifically tailored for transmitting biometric data captured through AMOLED-integrated sensors, ensuring the protection of sensitive information during authentication processes.
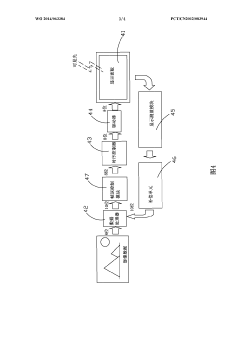
02 Multi-factor authentication using AMOLED technology
Implementing multi-factor authentication systems that utilize AMOLED display features in combination with other biometric methods. This can include facial recognition, voice recognition, or gesture-based authentication, enhancing overall security.Expand Specific Solutions03 In-display fingerprint sensing for AMOLED screens
Development of in-display fingerprint sensing technology specifically designed for AMOLED screens. This allows for secure authentication without compromising the aesthetics or functionality of the display.Expand Specific Solutions04 Secure data transmission and storage in AMOLED devices
Implementation of encryption and secure data handling methods for biometric information captured and processed through AMOLED displays. This ensures that sensitive user data remains protected from unauthorized access or interception.Expand Specific Solutions05 AMOLED display anti-spoofing measures
Development of anti-spoofing techniques specifically for AMOLED-based biometric authentication systems. These measures can include liveness detection, pattern recognition, and other methods to prevent unauthorized access through fake biometric data.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in AMOLED Bio-Auth
The security solutions market for AMOLED bio-authentication is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption of biometric technologies in consumer electronics. The market size is expanding rapidly, driven by the rising demand for secure authentication methods in smartphones and other devices. Technologically, AMOLED bio-authentication is advancing, with companies like Samsung, Apple, and Huawei leading innovation. BOE Technology and TCL China Star Optoelectronics are also making significant strides in AMOLED display technology, while specialized firms like Shenzhen Goodix and FaceTec are developing cutting-edge biometric solutions. The integration of these technologies is progressing, but there's still room for improvement in terms of accuracy, speed, and security.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei has developed a novel AMOLED bio-authentication solution that combines in-display fingerprint sensing with facial recognition. Their system utilizes ultrasonic technology for fingerprint scanning, allowing for improved accuracy and the ability to work with wet or dirty fingers[4]. For facial recognition, Huawei employs a 3D depth-sensing camera system integrated into the display, using structured light projection for enhanced security[5]. The company has also implemented AI-driven liveness detection to prevent spoofing attempts, analyzing micro-expressions and blood flow patterns in real-time[6].
Strengths: High accuracy ultrasonic fingerprint sensing, 3D facial recognition, AI-enhanced security. Weaknesses: Potential for higher power consumption, complexity of integrating multiple sensors.
Shenzhen Goodix Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Goodix has developed an innovative AMOLED bio-authentication solution that focuses on optical in-display fingerprint sensing technology. Their system utilizes a thin-film optical sensor array integrated directly into the OLED panel, allowing for a large sensing area without compromising display quality[10]. The company has also implemented advanced algorithms for fingerprint image enhancement and matching, improving accuracy and speed. Goodix's solution includes anti-spoofing measures such as liveness detection through pulse oximetry and AI-based pattern recognition to distinguish between real fingers and fake prints[11]. Additionally, they have developed a low-power operating mode to minimize battery drain during always-on authentication.
Strengths: Large sensing area, advanced anti-spoofing, energy-efficient operation. Weaknesses: Limited to fingerprint biometrics, potential for reduced accuracy with screen protectors.
Core AMOLED Bio-Auth Innovations
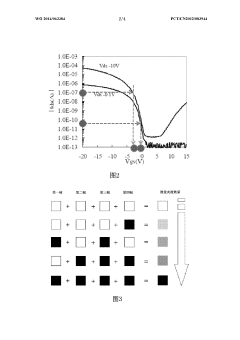
Separated Carbon Nanotube-Based Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode Displays
PatentInactiveUS20140070169A1
Innovation
- The use of separated semiconducting nanotubes as the active channel material in transistors, with a network of nanotubes disposed over a functionalized gate dielectric layer, and integrated into a display control circuit to drive OLED pixels, enabling high on/off ratios and current density.
Amoled display device and precision ageing compensation method thereof
PatentWO2014063384A1
Innovation
- By increasing the number of color depth digits of the display panel from 8 to 10 bits, combined with the frame rate control module and the lookup table of the compensation unit, compensation data with 10-bit color depth is generated, and the image data is accurately adjusted to drive the display panel to ensure Shows uniformity.
Regulatory Framework for Bio-Auth
The regulatory framework for bio-authentication technologies, particularly those involving AMOLED displays, is a complex and evolving landscape. As these technologies become more prevalent in consumer devices, governments and international bodies are developing guidelines and regulations to ensure privacy, security, and ethical use.
In the United States, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has taken a leading role in overseeing the implementation of biometric technologies. The FTC's guidelines emphasize the importance of transparency, consent, and data protection. Companies utilizing AMOLED bio-authentication must clearly disclose their data collection and usage practices, obtain explicit user consent, and implement robust security measures to protect biometric data.
The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has set a global standard for data protection, including biometric information. Under GDPR, biometric data is classified as sensitive personal data, subject to stricter processing conditions. Organizations implementing AMOLED bio-authentication solutions must ensure compliance with GDPR principles, including data minimization, purpose limitation, and the right to erasure.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have introduced specific regulations for biometric data. China's Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) includes provisions for the collection and processing of biometric information, requiring explicit consent and imposing strict data localization requirements. Japan's Act on the Protection of Personal Information also addresses biometric data, emphasizing the need for proper handling and security measures.
International standards bodies, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), have developed standards relevant to biometric technologies. ISO/IEC 24745 provides guidelines for the protection of biometric information, while ISO/IEC 19794 series defines biometric data interchange formats. These standards serve as important references for manufacturers and developers of AMOLED bio-authentication systems.
The regulatory landscape also addresses specific aspects of AMOLED bio-authentication, such as liveness detection and anti-spoofing measures. Regulatory bodies are increasingly requiring manufacturers to implement robust security features to prevent unauthorized access through fake biometric samples or replay attacks.
As the technology continues to evolve, regulators are grappling with emerging challenges, such as the potential for bias in biometric systems and the long-term implications of storing biometric data. Future regulatory frameworks are likely to address these issues, potentially mandating regular audits, bias testing, and stricter data retention policies.
In the United States, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has taken a leading role in overseeing the implementation of biometric technologies. The FTC's guidelines emphasize the importance of transparency, consent, and data protection. Companies utilizing AMOLED bio-authentication must clearly disclose their data collection and usage practices, obtain explicit user consent, and implement robust security measures to protect biometric data.
The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has set a global standard for data protection, including biometric information. Under GDPR, biometric data is classified as sensitive personal data, subject to stricter processing conditions. Organizations implementing AMOLED bio-authentication solutions must ensure compliance with GDPR principles, including data minimization, purpose limitation, and the right to erasure.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have introduced specific regulations for biometric data. China's Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) includes provisions for the collection and processing of biometric information, requiring explicit consent and imposing strict data localization requirements. Japan's Act on the Protection of Personal Information also addresses biometric data, emphasizing the need for proper handling and security measures.
International standards bodies, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), have developed standards relevant to biometric technologies. ISO/IEC 24745 provides guidelines for the protection of biometric information, while ISO/IEC 19794 series defines biometric data interchange formats. These standards serve as important references for manufacturers and developers of AMOLED bio-authentication systems.
The regulatory landscape also addresses specific aspects of AMOLED bio-authentication, such as liveness detection and anti-spoofing measures. Regulatory bodies are increasingly requiring manufacturers to implement robust security features to prevent unauthorized access through fake biometric samples or replay attacks.
As the technology continues to evolve, regulators are grappling with emerging challenges, such as the potential for bias in biometric systems and the long-term implications of storing biometric data. Future regulatory frameworks are likely to address these issues, potentially mandating regular audits, bias testing, and stricter data retention policies.
Privacy Implications of AMOLED Bio-Auth
The integration of AMOLED bio-authentication technology in security solutions raises significant privacy concerns that must be carefully addressed. As this technology becomes more prevalent in consumer devices, it is crucial to examine the potential risks and implications for user privacy.
One of the primary privacy concerns is the collection and storage of biometric data. AMOLED bio-authentication systems typically capture and process unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints, facial features, or iris patterns. This sensitive information, if compromised, could lead to severe privacy breaches and identity theft. Unlike passwords or PINs, biometric data cannot be easily changed, making any breach potentially more damaging in the long term.
The continuous nature of AMOLED displays also introduces new privacy challenges. These displays can potentially be used for constant monitoring and data collection, even when the device appears to be in a dormant state. This raises questions about user consent and the extent to which individuals are aware of when and how their biometric data is being captured and processed.
Data transmission and storage present additional privacy risks. As biometric information is transmitted between the AMOLED sensor and the device's secure enclave or cloud servers, it becomes vulnerable to interception. Robust encryption protocols and secure communication channels are essential to protect this data in transit. Similarly, the storage of biometric templates on devices or in centralized databases creates potential targets for cybercriminals.
The use of AMOLED bio-authentication in public spaces or shared devices introduces further privacy implications. In scenarios where multiple users interact with the same device, there is a risk of inadvertent data collection or cross-contamination of biometric profiles. This could lead to unauthorized access or privacy violations if proper safeguards are not in place.
Another consideration is the potential for function creep, where biometric data collected for authentication purposes could be repurposed for other uses without user consent. This might include behavioral tracking, targeted advertising, or even surveillance activities. Clear regulations and transparent policies are necessary to prevent the misuse of this sensitive information.
The accuracy and reliability of AMOLED bio-authentication systems also have privacy implications. False positives or negatives could lead to unauthorized access or denial of service, potentially exposing users to privacy risks or compromising their ability to access their own information and services.
One of the primary privacy concerns is the collection and storage of biometric data. AMOLED bio-authentication systems typically capture and process unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints, facial features, or iris patterns. This sensitive information, if compromised, could lead to severe privacy breaches and identity theft. Unlike passwords or PINs, biometric data cannot be easily changed, making any breach potentially more damaging in the long term.
The continuous nature of AMOLED displays also introduces new privacy challenges. These displays can potentially be used for constant monitoring and data collection, even when the device appears to be in a dormant state. This raises questions about user consent and the extent to which individuals are aware of when and how their biometric data is being captured and processed.
Data transmission and storage present additional privacy risks. As biometric information is transmitted between the AMOLED sensor and the device's secure enclave or cloud servers, it becomes vulnerable to interception. Robust encryption protocols and secure communication channels are essential to protect this data in transit. Similarly, the storage of biometric templates on devices or in centralized databases creates potential targets for cybercriminals.
The use of AMOLED bio-authentication in public spaces or shared devices introduces further privacy implications. In scenarios where multiple users interact with the same device, there is a risk of inadvertent data collection or cross-contamination of biometric profiles. This could lead to unauthorized access or privacy violations if proper safeguards are not in place.
Another consideration is the potential for function creep, where biometric data collected for authentication purposes could be repurposed for other uses without user consent. This might include behavioral tracking, targeted advertising, or even surveillance activities. Clear regulations and transparent policies are necessary to prevent the misuse of this sensitive information.
The accuracy and reliability of AMOLED bio-authentication systems also have privacy implications. False positives or negatives could lead to unauthorized access or denial of service, potentially exposing users to privacy risks or compromising their ability to access their own information and services.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!