How CMOS Battery Influences Signal Processing Systems?
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
CMOS Battery Tech Evolution
The evolution of CMOS battery technology in signal processing systems has been marked by significant advancements over the past few decades. Initially, CMOS batteries were primarily used to maintain basic system settings and real-time clock functions in computers. However, as signal processing systems became more sophisticated, the role of CMOS batteries expanded to support critical operations in various electronic devices.
In the early stages, CMOS batteries were simple coin-cell lithium batteries with limited capacity and lifespan. These batteries were sufficient for maintaining low-power memory chips that stored system configuration data. As signal processing systems grew more complex, the demands on CMOS batteries increased, leading to improvements in battery chemistry and design.
The introduction of rechargeable CMOS batteries marked a significant milestone in the technology's evolution. These batteries could be charged by the main power supply, extending their operational life and reducing the need for frequent replacements. This development was particularly crucial for signal processing systems in industrial and medical applications, where continuous operation and data integrity were paramount.
Advancements in battery technology also led to the development of CMOS batteries with higher energy density and improved temperature tolerance. These enhancements allowed for more stable operation of signal processing systems in diverse environmental conditions, from extreme cold to high heat scenarios.
The miniaturization trend in electronics has driven the evolution of CMOS batteries towards smaller form factors without compromising performance. This has enabled the integration of CMOS batteries into increasingly compact signal processing devices, such as wearable technology and IoT sensors, where space is at a premium.
Recent developments have focused on enhancing the reliability and longevity of CMOS batteries in signal processing systems. Innovations in battery management systems have improved charge control and monitoring capabilities, ensuring optimal performance and extending battery life. Additionally, the integration of supercapacitors alongside CMOS batteries has provided a hybrid solution for applications requiring both long-term power backup and rapid charge/discharge cycles.
The evolution of CMOS battery technology has also addressed environmental concerns. Modern CMOS batteries are designed with eco-friendly materials and improved recyclability, aligning with global sustainability efforts. This shift has been particularly important in the context of the increasing ubiquity of signal processing systems in consumer and industrial applications.
Looking forward, the trajectory of CMOS battery technology in signal processing systems points towards even greater integration with energy harvesting technologies. This symbiosis aims to create self-sustaining power solutions for signal processing systems, particularly in remote or inaccessible locations where regular battery replacement is challenging.
In the early stages, CMOS batteries were simple coin-cell lithium batteries with limited capacity and lifespan. These batteries were sufficient for maintaining low-power memory chips that stored system configuration data. As signal processing systems grew more complex, the demands on CMOS batteries increased, leading to improvements in battery chemistry and design.
The introduction of rechargeable CMOS batteries marked a significant milestone in the technology's evolution. These batteries could be charged by the main power supply, extending their operational life and reducing the need for frequent replacements. This development was particularly crucial for signal processing systems in industrial and medical applications, where continuous operation and data integrity were paramount.
Advancements in battery technology also led to the development of CMOS batteries with higher energy density and improved temperature tolerance. These enhancements allowed for more stable operation of signal processing systems in diverse environmental conditions, from extreme cold to high heat scenarios.
The miniaturization trend in electronics has driven the evolution of CMOS batteries towards smaller form factors without compromising performance. This has enabled the integration of CMOS batteries into increasingly compact signal processing devices, such as wearable technology and IoT sensors, where space is at a premium.
Recent developments have focused on enhancing the reliability and longevity of CMOS batteries in signal processing systems. Innovations in battery management systems have improved charge control and monitoring capabilities, ensuring optimal performance and extending battery life. Additionally, the integration of supercapacitors alongside CMOS batteries has provided a hybrid solution for applications requiring both long-term power backup and rapid charge/discharge cycles.
The evolution of CMOS battery technology has also addressed environmental concerns. Modern CMOS batteries are designed with eco-friendly materials and improved recyclability, aligning with global sustainability efforts. This shift has been particularly important in the context of the increasing ubiquity of signal processing systems in consumer and industrial applications.
Looking forward, the trajectory of CMOS battery technology in signal processing systems points towards even greater integration with energy harvesting technologies. This symbiosis aims to create self-sustaining power solutions for signal processing systems, particularly in remote or inaccessible locations where regular battery replacement is challenging.
Signal Processing Market Trends
The signal processing market has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand across various industries. This market encompasses a wide range of applications, including telecommunications, consumer electronics, automotive, healthcare, and industrial automation.
One of the key trends shaping the signal processing market is the rapid adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms. These technologies are being integrated into signal processing systems to enhance performance, improve accuracy, and enable more sophisticated data analysis. As a result, there is a growing demand for high-performance processors and specialized hardware accelerators capable of handling complex AI and ML workloads.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has also emerged as a major driver of growth in the signal processing market. With billions of connected devices generating vast amounts of data, there is an increasing need for efficient signal processing solutions to handle real-time data analysis, edge computing, and low-power operation. This trend has led to the development of specialized signal processing chips and algorithms optimized for IoT applications.
Another significant trend is the shift towards software-defined signal processing systems. This approach allows for greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional hardware-based solutions. Software-defined radio (SDR) technology, for instance, has gained traction in both commercial and military applications, enabling dynamic reconfiguration of radio systems to support multiple communication standards and protocols.
The automotive industry has become a major consumer of signal processing technologies, driven by the development of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. Signal processing plays a crucial role in sensor fusion, image processing, and real-time decision-making in these applications. As a result, there is growing demand for high-performance, low-latency signal processing solutions tailored for automotive use cases.
In the healthcare sector, signal processing technologies are enabling advancements in medical imaging, diagnostics, and patient monitoring. The increasing adoption of wearable devices and remote patient monitoring systems has created new opportunities for signal processing in healthcare applications, driving innovation in areas such as biosignal analysis and telemedicine.
The rollout of 5G networks has also had a significant impact on the signal processing market. The need for higher data rates, lower latency, and improved spectral efficiency has led to the development of advanced signal processing techniques and hardware solutions to support 5G infrastructure and devices.
One of the key trends shaping the signal processing market is the rapid adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms. These technologies are being integrated into signal processing systems to enhance performance, improve accuracy, and enable more sophisticated data analysis. As a result, there is a growing demand for high-performance processors and specialized hardware accelerators capable of handling complex AI and ML workloads.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has also emerged as a major driver of growth in the signal processing market. With billions of connected devices generating vast amounts of data, there is an increasing need for efficient signal processing solutions to handle real-time data analysis, edge computing, and low-power operation. This trend has led to the development of specialized signal processing chips and algorithms optimized for IoT applications.
Another significant trend is the shift towards software-defined signal processing systems. This approach allows for greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional hardware-based solutions. Software-defined radio (SDR) technology, for instance, has gained traction in both commercial and military applications, enabling dynamic reconfiguration of radio systems to support multiple communication standards and protocols.
The automotive industry has become a major consumer of signal processing technologies, driven by the development of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. Signal processing plays a crucial role in sensor fusion, image processing, and real-time decision-making in these applications. As a result, there is growing demand for high-performance, low-latency signal processing solutions tailored for automotive use cases.
In the healthcare sector, signal processing technologies are enabling advancements in medical imaging, diagnostics, and patient monitoring. The increasing adoption of wearable devices and remote patient monitoring systems has created new opportunities for signal processing in healthcare applications, driving innovation in areas such as biosignal analysis and telemedicine.
The rollout of 5G networks has also had a significant impact on the signal processing market. The need for higher data rates, lower latency, and improved spectral efficiency has led to the development of advanced signal processing techniques and hardware solutions to support 5G infrastructure and devices.
CMOS Battery Challenges
CMOS batteries, also known as Real-Time Clock (RTC) batteries, play a crucial role in maintaining system settings and timekeeping functions in various electronic devices, including signal processing systems. However, these batteries face several challenges that can significantly impact the performance and reliability of signal processing systems.
One of the primary challenges is the limited lifespan of CMOS batteries. Typically, these batteries last between 2 to 10 years, depending on usage patterns and environmental conditions. As the battery deteriorates, it may lead to inconsistent power supply to the CMOS chip, resulting in erratic behavior of the signal processing system. This can manifest as incorrect time and date settings, loss of system configurations, or even complete system failure.
The sensitivity of CMOS batteries to temperature fluctuations poses another significant challenge. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can dramatically reduce the battery's lifespan and performance. In signal processing systems deployed in harsh environments, such as outdoor telecommunications equipment or industrial control systems, this temperature sensitivity can lead to premature battery failure and system instability.
Size constraints present a notable challenge in the design of modern signal processing systems. As devices become increasingly compact, the space allocated for CMOS batteries is often limited. This restriction can force designers to opt for smaller batteries with lower capacity, potentially compromising the longevity and reliability of the system's timekeeping and configuration retention capabilities.
The environmental impact of CMOS batteries is an emerging concern. Many of these batteries contain lithium, which can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly. As signal processing systems become more prevalent in various applications, the cumulative environmental impact of discarded CMOS batteries is becoming a significant issue that needs to be addressed.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is another challenge associated with CMOS batteries in signal processing systems. The battery and its associated circuitry can potentially generate or be susceptible to EMI, which can introduce noise and errors in sensitive signal processing operations. Shielding and proper circuit design are crucial to mitigate these effects, but they add complexity and cost to the system.
The cost of replacing CMOS batteries in signal processing systems, especially in large-scale deployments or remote locations, can be substantial. The process often requires skilled technicians and may involve system downtime, which can be particularly problematic in critical applications such as telecommunications or industrial control systems.
Lastly, the reliance on CMOS batteries for maintaining critical system settings creates a single point of failure in signal processing systems. A depleted or faulty battery can lead to loss of calibration data, encryption keys, or other vital information, potentially compromising the security and functionality of the entire system. Developing robust backup mechanisms and failsafe systems to mitigate this risk remains an ongoing challenge for system designers.
One of the primary challenges is the limited lifespan of CMOS batteries. Typically, these batteries last between 2 to 10 years, depending on usage patterns and environmental conditions. As the battery deteriorates, it may lead to inconsistent power supply to the CMOS chip, resulting in erratic behavior of the signal processing system. This can manifest as incorrect time and date settings, loss of system configurations, or even complete system failure.
The sensitivity of CMOS batteries to temperature fluctuations poses another significant challenge. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can dramatically reduce the battery's lifespan and performance. In signal processing systems deployed in harsh environments, such as outdoor telecommunications equipment or industrial control systems, this temperature sensitivity can lead to premature battery failure and system instability.
Size constraints present a notable challenge in the design of modern signal processing systems. As devices become increasingly compact, the space allocated for CMOS batteries is often limited. This restriction can force designers to opt for smaller batteries with lower capacity, potentially compromising the longevity and reliability of the system's timekeeping and configuration retention capabilities.
The environmental impact of CMOS batteries is an emerging concern. Many of these batteries contain lithium, which can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly. As signal processing systems become more prevalent in various applications, the cumulative environmental impact of discarded CMOS batteries is becoming a significant issue that needs to be addressed.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is another challenge associated with CMOS batteries in signal processing systems. The battery and its associated circuitry can potentially generate or be susceptible to EMI, which can introduce noise and errors in sensitive signal processing operations. Shielding and proper circuit design are crucial to mitigate these effects, but they add complexity and cost to the system.
The cost of replacing CMOS batteries in signal processing systems, especially in large-scale deployments or remote locations, can be substantial. The process often requires skilled technicians and may involve system downtime, which can be particularly problematic in critical applications such as telecommunications or industrial control systems.
Lastly, the reliance on CMOS batteries for maintaining critical system settings creates a single point of failure in signal processing systems. A depleted or faulty battery can lead to loss of calibration data, encryption keys, or other vital information, potentially compromising the security and functionality of the entire system. Developing robust backup mechanisms and failsafe systems to mitigate this risk remains an ongoing challenge for system designers.
Current CMOS Battery Solutions
01 CMOS image sensor signal processing
CMOS image sensors are used in digital cameras and other imaging devices. Signal processing techniques are applied to improve image quality, reduce noise, and enhance overall performance. This includes analog-to-digital conversion, pixel correction, and color processing.- CMOS image sensor signal processing: CMOS image sensors are used in digital cameras and other imaging devices. Signal processing techniques are applied to improve image quality, reduce noise, and enhance overall performance. This includes analog-to-digital conversion, pixel readout, and various image processing algorithms.
- Power management for CMOS circuits: Power management techniques are crucial for CMOS circuits, especially in battery-powered devices. This includes methods for reducing power consumption, managing battery life, and implementing low-power modes. Efficient power management helps extend the operational time of CMOS-based devices.
- CMOS-based clock and timing circuits: CMOS technology is used to implement clock generators, timing circuits, and synchronization systems. These circuits are essential for coordinating various operations within electronic devices and ensuring accurate timekeeping, especially in battery-powered systems.
- CMOS sensor interfaces and readout circuits: Specialized interfaces and readout circuits are designed for CMOS sensors to efficiently capture and process signals. These circuits handle tasks such as pixel addressing, charge transfer, and initial signal amplification, optimizing the performance of CMOS-based sensing devices.
- CMOS-based analog and mixed-signal processing: CMOS technology is used to implement analog and mixed-signal processing circuits. These circuits handle tasks such as signal amplification, filtering, and conversion between analog and digital domains, enabling efficient processing of various types of signals in battery-powered devices.
02 Power management for CMOS circuits
Power management techniques are implemented to optimize battery life in CMOS-based devices. This includes low-power modes, voltage scaling, and intelligent power distribution to various components. These methods help extend battery life while maintaining system performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 CMOS-based clock and timing circuits
CMOS technology is used to design efficient clock generation and timing circuits. These circuits are crucial for synchronizing various components in electronic systems and managing battery-powered operations. Techniques include frequency synthesis, clock gating, and low-power oscillator designs.Expand Specific Solutions04 CMOS battery monitoring and management
Systems and methods for monitoring battery status and managing power consumption in CMOS-based devices. This includes voltage level detection, charge state estimation, and implementing power-saving strategies based on battery conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Signal processing for CMOS-based communication systems
CMOS technology is utilized in communication systems for signal processing tasks. This includes modulation, demodulation, encoding, decoding, and filtering of signals. Low-power CMOS designs are employed to enhance battery life in portable communication devices.Expand Specific Solutions
Key CMOS Battery Manufacturers
The CMOS battery's influence on signal processing systems is an evolving field with moderate market growth and technological maturity. The industry is in a transitional phase, moving from traditional to more advanced applications. Key players like Samsung Electronics, Apple, and Qualcomm are driving innovation, particularly in mobile devices and IoT. Companies such as Hon Hai Precision and GLOBALFOUNDRIES are contributing to manufacturing advancements. The market size is expanding due to increased demand for energy-efficient and long-lasting power solutions in various electronic devices. While established technologies exist, ongoing research by companies like NXP Semiconductors and universities such as Beihang University is pushing the boundaries of CMOS battery integration with signal processing systems.
Apple, Inc.
Technical Solution: Apple has developed advanced power management systems that optimize CMOS battery usage in their signal processing systems. They employ a combination of hardware and software solutions to minimize power consumption and extend battery life. Their approach includes dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS) techniques, which adjust the processor's clock speed and voltage based on workload demands[1]. Additionally, Apple has implemented sophisticated power gating mechanisms that selectively shut down unused circuit blocks to reduce static power consumption[3]. Their A-series chips also incorporate dedicated low-power cores for background tasks, further enhancing energy efficiency in signal processing operations[5].
Strengths: Highly optimized power management, seamless integration of hardware and software, industry-leading battery life. Weaknesses: Proprietary technology limits wider adoption, potentially higher costs due to custom solutions.
QUALCOMM, Inc.
Technical Solution: Qualcomm has pioneered innovative approaches to manage CMOS battery influence on signal processing systems in mobile devices. Their Snapdragon platforms incorporate advanced power management integrated circuits (PMICs) that precisely control power distribution across various system components[2]. Qualcomm's solution includes adaptive voltage scaling (AVS) technology, which dynamically adjusts voltage levels based on real-time processing requirements, significantly reducing power consumption in signal processing tasks[4]. They have also developed a heterogeneous computing architecture that efficiently allocates tasks between high-performance and low-power cores, optimizing battery usage for different signal processing workloads[6].
Strengths: Wide adoption in mobile devices, comprehensive power management solutions, strong integration with cellular technologies. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on mobile applications, may have limitations in other domains.
CMOS Battery Innovations
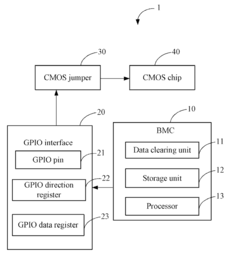
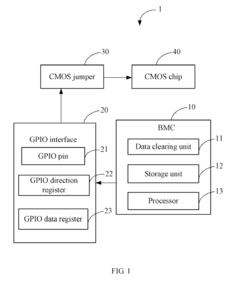
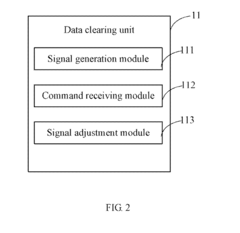
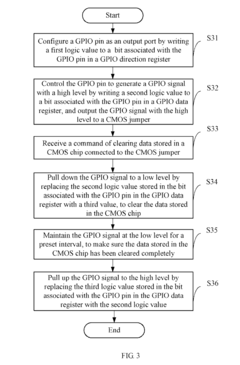
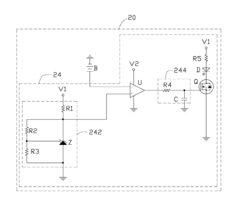
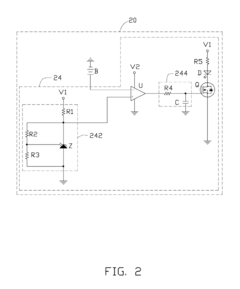
Computing device and method for clearing data stored in complementary metal-oxide semiconductor chip
PatentInactiveUS20120047307A1
Innovation
- A computing device with a data clearing unit that uses a GPIO interface to configure a CMOS jumper, generating a high-level signal to maintain data and then pulling it down to clear data stored in the CMOS chip, allowing for safe and controlled data reset.
Host computer
PatentInactiveUS20120043993A1
Innovation
- Incorporating a voltage detection circuit within the host computer that includes a comparator, electronic switch, alarm unit, reference voltage generating circuit, and delay circuit to detect and alert the user when the battery voltage falls below a certain threshold, using a light emitting diode as an alarm unit.
Power Management Strategies
Power management strategies play a crucial role in optimizing the performance and longevity of CMOS batteries in signal processing systems. These strategies are designed to balance the power requirements of the system with the limited energy capacity of the CMOS battery, ensuring reliable operation and extended battery life.
One key approach is dynamic voltage scaling (DVS), which adjusts the operating voltage of the system based on its current workload. By reducing the voltage during periods of low activity, DVS significantly decreases power consumption without compromising system functionality. This technique is particularly effective in signal processing systems that experience varying computational demands.
Another important strategy is clock gating, which selectively disables clock signals to inactive circuit blocks. This prevents unnecessary switching activity and reduces dynamic power consumption. In signal processing systems, where different components may be active at different times, clock gating can lead to substantial energy savings.
Power gating is a more aggressive technique that completely shuts off power to unused circuit blocks. While this approach offers greater power savings than clock gating, it requires careful implementation to manage the associated wake-up latency and potential data loss. In signal processing systems, power gating can be applied to specific processing units or memory blocks when they are not in use.
Adaptive body biasing (ABB) is a technique that adjusts the threshold voltage of transistors to optimize the trade-off between performance and leakage power. By dynamically controlling the body bias voltage, ABB can reduce leakage current during idle periods while maintaining high performance during active operation. This is particularly beneficial in CMOS-based signal processing systems that require both high-speed operation and low standby power.
Task scheduling and workload distribution strategies also play a significant role in power management. By intelligently allocating tasks across available processing resources and optimizing the execution order, these strategies can minimize power consumption while meeting performance requirements. This is especially relevant in multi-core signal processing systems where workload balancing can lead to more efficient energy utilization.
The implementation of low-power design techniques at the circuit and architecture levels is another critical aspect of power management. This includes the use of low-power logic families, optimized memory hierarchies, and efficient interconnect structures. In signal processing systems, these techniques can be tailored to the specific computational patterns and data flow requirements of the application.
Lastly, the integration of power-aware algorithms and software optimization techniques can further enhance the effectiveness of hardware-based power management strategies. By considering power consumption as a key metric during algorithm design and software development, significant energy savings can be achieved at the system level.
One key approach is dynamic voltage scaling (DVS), which adjusts the operating voltage of the system based on its current workload. By reducing the voltage during periods of low activity, DVS significantly decreases power consumption without compromising system functionality. This technique is particularly effective in signal processing systems that experience varying computational demands.
Another important strategy is clock gating, which selectively disables clock signals to inactive circuit blocks. This prevents unnecessary switching activity and reduces dynamic power consumption. In signal processing systems, where different components may be active at different times, clock gating can lead to substantial energy savings.
Power gating is a more aggressive technique that completely shuts off power to unused circuit blocks. While this approach offers greater power savings than clock gating, it requires careful implementation to manage the associated wake-up latency and potential data loss. In signal processing systems, power gating can be applied to specific processing units or memory blocks when they are not in use.
Adaptive body biasing (ABB) is a technique that adjusts the threshold voltage of transistors to optimize the trade-off between performance and leakage power. By dynamically controlling the body bias voltage, ABB can reduce leakage current during idle periods while maintaining high performance during active operation. This is particularly beneficial in CMOS-based signal processing systems that require both high-speed operation and low standby power.
Task scheduling and workload distribution strategies also play a significant role in power management. By intelligently allocating tasks across available processing resources and optimizing the execution order, these strategies can minimize power consumption while meeting performance requirements. This is especially relevant in multi-core signal processing systems where workload balancing can lead to more efficient energy utilization.
The implementation of low-power design techniques at the circuit and architecture levels is another critical aspect of power management. This includes the use of low-power logic families, optimized memory hierarchies, and efficient interconnect structures. In signal processing systems, these techniques can be tailored to the specific computational patterns and data flow requirements of the application.
Lastly, the integration of power-aware algorithms and software optimization techniques can further enhance the effectiveness of hardware-based power management strategies. By considering power consumption as a key metric during algorithm design and software development, significant energy savings can be achieved at the system level.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of CMOS batteries in signal processing systems is a critical consideration in the broader context of electronic waste management and sustainable technology development. CMOS batteries, while small in size, can have significant cumulative effects on the environment due to their widespread use in various electronic devices and systems.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with CMOS batteries is their disposal. These batteries contain potentially harmful materials, including lithium, which can pose risks to ecosystems if not properly managed. When CMOS batteries are discarded with general electronic waste, they may end up in landfills, where their components can leach into soil and groundwater, potentially contaminating local environments and affecting wildlife.
The manufacturing process of CMOS batteries also contributes to their environmental footprint. The production of these batteries involves the extraction and processing of raw materials, which can lead to habitat destruction, energy consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the chemical processes used in battery manufacturing may generate hazardous waste that requires careful handling and disposal.
From a lifecycle perspective, the frequent replacement of CMOS batteries in signal processing systems adds to the overall electronic waste stream. While these batteries are designed to last for several years, their eventual failure necessitates replacement, contributing to the growing problem of e-waste. This issue is particularly relevant in the context of obsolescence and the rapid turnover of electronic devices.
However, it is important to note that advancements in CMOS battery technology are addressing some of these environmental concerns. Manufacturers are developing more environmentally friendly battery chemistries and exploring ways to improve battery lifespan, which could reduce the frequency of replacements and associated waste. Additionally, efforts to enhance the recyclability of CMOS batteries and improve e-waste management practices are helping to mitigate their environmental impact.
The energy efficiency of CMOS batteries in signal processing systems also plays a role in their environmental impact. By providing stable power to maintain critical system settings and real-time clocks, these batteries contribute to the overall energy efficiency of electronic devices. This efficiency can lead to reduced power consumption and, consequently, lower carbon emissions associated with device operation.
In conclusion, while CMOS batteries are essential components in signal processing systems, their environmental impact necessitates ongoing research and development to minimize negative effects. Balancing the technological benefits with environmental considerations remains a key challenge for the electronics industry, driving innovation in battery design, manufacturing processes, and recycling technologies.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with CMOS batteries is their disposal. These batteries contain potentially harmful materials, including lithium, which can pose risks to ecosystems if not properly managed. When CMOS batteries are discarded with general electronic waste, they may end up in landfills, where their components can leach into soil and groundwater, potentially contaminating local environments and affecting wildlife.
The manufacturing process of CMOS batteries also contributes to their environmental footprint. The production of these batteries involves the extraction and processing of raw materials, which can lead to habitat destruction, energy consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the chemical processes used in battery manufacturing may generate hazardous waste that requires careful handling and disposal.
From a lifecycle perspective, the frequent replacement of CMOS batteries in signal processing systems adds to the overall electronic waste stream. While these batteries are designed to last for several years, their eventual failure necessitates replacement, contributing to the growing problem of e-waste. This issue is particularly relevant in the context of obsolescence and the rapid turnover of electronic devices.
However, it is important to note that advancements in CMOS battery technology are addressing some of these environmental concerns. Manufacturers are developing more environmentally friendly battery chemistries and exploring ways to improve battery lifespan, which could reduce the frequency of replacements and associated waste. Additionally, efforts to enhance the recyclability of CMOS batteries and improve e-waste management practices are helping to mitigate their environmental impact.
The energy efficiency of CMOS batteries in signal processing systems also plays a role in their environmental impact. By providing stable power to maintain critical system settings and real-time clocks, these batteries contribute to the overall energy efficiency of electronic devices. This efficiency can lead to reduced power consumption and, consequently, lower carbon emissions associated with device operation.
In conclusion, while CMOS batteries are essential components in signal processing systems, their environmental impact necessitates ongoing research and development to minimize negative effects. Balancing the technological benefits with environmental considerations remains a key challenge for the electronics industry, driving innovation in battery design, manufacturing processes, and recycling technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!