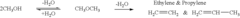How Dimethyl Ether Simplifies Large-Scale Energy Deployments?
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DME Technology Background and Objectives
Dimethyl ether (DME) has emerged as a promising alternative fuel and energy carrier, attracting significant attention in the quest for sustainable and efficient large-scale energy deployments. The technology behind DME production and utilization has evolved over several decades, with its roots tracing back to the early 20th century when it was first synthesized as a chemical compound.
Initially, DME was primarily used in aerosol propellants and as a precursor in chemical synthesis. However, its potential as a clean-burning fuel began to gain recognition in the 1990s, particularly in Asia and Europe. This shift in focus marked the beginning of a new era for DME technology, with researchers and industry experts exploring its applications in various energy sectors.
The primary objective of DME technology development has been to create a versatile, environmentally friendly alternative to conventional fossil fuels. DME's unique properties, including its high cetane number, low emissions, and ease of handling, have made it an attractive option for simplifying large-scale energy deployments across multiple sectors.
One of the key goals in DME technology advancement has been to optimize production processes, focusing on improving efficiency and reducing costs. This has led to the development of various production methods, including the traditional two-step process from syngas and the more recent single-step process directly from methanol. These advancements have significantly contributed to making DME a more viable option for large-scale energy applications.
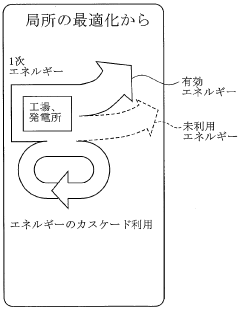
Another crucial objective has been to expand DME's applicability in different energy sectors. Research and development efforts have focused on adapting existing infrastructure and technologies to accommodate DME, particularly in transportation, power generation, and domestic fuel applications. This adaptability is a critical factor in simplifying large-scale energy deployments, as it reduces the need for extensive and costly infrastructure overhauls.
The environmental benefits of DME have also been a driving force behind its technological development. As global concerns about climate change and air pollution have intensified, the pursuit of cleaner-burning fuels has become increasingly important. DME's low emissions profile, particularly its near-zero particulate matter emissions and reduced NOx and SOx emissions compared to conventional diesel, aligns well with stringent environmental regulations and sustainability goals.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of DME technology is aimed at further enhancing its production efficiency, expanding its applications, and integrating it into the broader energy transition landscape. Researchers are exploring innovative catalysts and process designs to improve DME synthesis, while also investigating its potential role in renewable energy storage and distribution systems. These ongoing efforts underscore the technology's evolving nature and its potential to play a significant role in simplifying and decarbonizing large-scale energy deployments in the coming decades.
Initially, DME was primarily used in aerosol propellants and as a precursor in chemical synthesis. However, its potential as a clean-burning fuel began to gain recognition in the 1990s, particularly in Asia and Europe. This shift in focus marked the beginning of a new era for DME technology, with researchers and industry experts exploring its applications in various energy sectors.
The primary objective of DME technology development has been to create a versatile, environmentally friendly alternative to conventional fossil fuels. DME's unique properties, including its high cetane number, low emissions, and ease of handling, have made it an attractive option for simplifying large-scale energy deployments across multiple sectors.
One of the key goals in DME technology advancement has been to optimize production processes, focusing on improving efficiency and reducing costs. This has led to the development of various production methods, including the traditional two-step process from syngas and the more recent single-step process directly from methanol. These advancements have significantly contributed to making DME a more viable option for large-scale energy applications.
Another crucial objective has been to expand DME's applicability in different energy sectors. Research and development efforts have focused on adapting existing infrastructure and technologies to accommodate DME, particularly in transportation, power generation, and domestic fuel applications. This adaptability is a critical factor in simplifying large-scale energy deployments, as it reduces the need for extensive and costly infrastructure overhauls.
The environmental benefits of DME have also been a driving force behind its technological development. As global concerns about climate change and air pollution have intensified, the pursuit of cleaner-burning fuels has become increasingly important. DME's low emissions profile, particularly its near-zero particulate matter emissions and reduced NOx and SOx emissions compared to conventional diesel, aligns well with stringent environmental regulations and sustainability goals.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of DME technology is aimed at further enhancing its production efficiency, expanding its applications, and integrating it into the broader energy transition landscape. Researchers are exploring innovative catalysts and process designs to improve DME synthesis, while also investigating its potential role in renewable energy storage and distribution systems. These ongoing efforts underscore the technology's evolving nature and its potential to play a significant role in simplifying and decarbonizing large-scale energy deployments in the coming decades.
Market Demand Analysis for DME Energy Solutions
The market demand for Dimethyl Ether (DME) energy solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by the global push for cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. DME, a clean-burning, non-toxic fuel, is gaining traction as a viable alternative to traditional fossil fuels in large-scale energy deployments.
The transportation sector represents a substantial market for DME, particularly in heavy-duty vehicles and long-haul trucking. As governments worldwide implement stricter emissions regulations, fleet operators are seeking cleaner fuel options. DME's compatibility with existing diesel engine infrastructure makes it an attractive choice for this market segment.
In the power generation sector, DME is emerging as a promising fuel for gas turbines and combined cycle power plants. Its low emissions profile and high energy density make it suitable for both centralized and distributed power generation systems. This versatility opens up opportunities in both developed markets looking to reduce their carbon footprint and developing regions seeking reliable, clean energy solutions.
The industrial sector presents another significant market for DME energy solutions. As a clean-burning fuel and chemical feedstock, DME can be used in various industrial processes, including heating, drying, and as a propellant. This versatility expands its potential market reach across multiple industries.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to be a key growth market for DME energy solutions. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are investing heavily in DME technology and infrastructure to address air quality concerns and reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels. Europe and North America are also showing increasing interest in DME as part of their renewable energy strategies.
The market demand for DME is further bolstered by its potential as a hydrogen carrier. As the hydrogen economy gains momentum, DME's ability to store and transport hydrogen efficiently could drive additional demand in the energy storage and distribution sectors.
However, the market faces challenges, including the need for infrastructure development and regulatory support. The success of DME energy solutions will depend on continued technological advancements, cost reductions, and supportive policy frameworks to encourage adoption.
In conclusion, the market demand for DME energy solutions is poised for growth across multiple sectors and regions. Its versatility, clean-burning properties, and potential to simplify large-scale energy deployments position DME as a promising component of the global transition to sustainable energy systems.
The transportation sector represents a substantial market for DME, particularly in heavy-duty vehicles and long-haul trucking. As governments worldwide implement stricter emissions regulations, fleet operators are seeking cleaner fuel options. DME's compatibility with existing diesel engine infrastructure makes it an attractive choice for this market segment.
In the power generation sector, DME is emerging as a promising fuel for gas turbines and combined cycle power plants. Its low emissions profile and high energy density make it suitable for both centralized and distributed power generation systems. This versatility opens up opportunities in both developed markets looking to reduce their carbon footprint and developing regions seeking reliable, clean energy solutions.
The industrial sector presents another significant market for DME energy solutions. As a clean-burning fuel and chemical feedstock, DME can be used in various industrial processes, including heating, drying, and as a propellant. This versatility expands its potential market reach across multiple industries.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to be a key growth market for DME energy solutions. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are investing heavily in DME technology and infrastructure to address air quality concerns and reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels. Europe and North America are also showing increasing interest in DME as part of their renewable energy strategies.
The market demand for DME is further bolstered by its potential as a hydrogen carrier. As the hydrogen economy gains momentum, DME's ability to store and transport hydrogen efficiently could drive additional demand in the energy storage and distribution sectors.
However, the market faces challenges, including the need for infrastructure development and regulatory support. The success of DME energy solutions will depend on continued technological advancements, cost reductions, and supportive policy frameworks to encourage adoption.
In conclusion, the market demand for DME energy solutions is poised for growth across multiple sectors and regions. Its versatility, clean-burning properties, and potential to simplify large-scale energy deployments position DME as a promising component of the global transition to sustainable energy systems.
Current State and Challenges of DME Technology
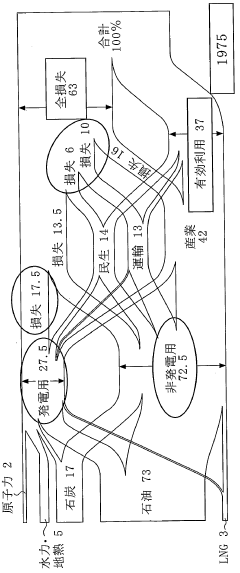
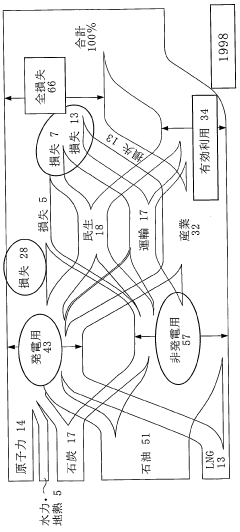
Dimethyl ether (DME) technology has made significant strides in recent years, positioning itself as a promising alternative fuel for large-scale energy deployments. The current state of DME technology is characterized by a growing interest in its potential to simplify energy systems and reduce environmental impact. DME can be produced from various feedstocks, including natural gas, coal, and biomass, making it a versatile energy carrier.
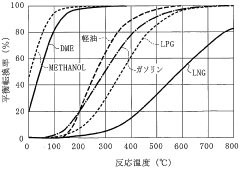
One of the key advantages of DME is its similarity to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) in terms of physical properties. This allows for the use of existing LPG infrastructure with minimal modifications, significantly reducing the costs associated with large-scale energy deployments. DME's high cetane number and clean-burning characteristics make it an attractive alternative to diesel fuel in compression ignition engines, potentially simplifying the transition to cleaner transportation fuels.
However, despite these advantages, DME technology faces several challenges that hinder its widespread adoption. One of the primary obstacles is the limited production capacity of DME on a global scale. While there are several commercial-scale DME plants in operation, particularly in Asia, the overall production volume remains relatively low compared to conventional fuels. This limited supply chain presents a significant barrier to large-scale implementation.
Another challenge lies in the need for specialized equipment and infrastructure modifications. Although DME can utilize much of the existing LPG infrastructure, some components, such as seals and gaskets, may require replacement due to DME's different chemical properties. This necessitates additional investment and technical expertise, which can be a deterrent for some potential adopters.
The regulatory landscape surrounding DME also presents challenges. In many regions, fuel standards and regulations are not yet fully developed for DME, creating uncertainty for investors and slowing down market penetration. The lack of clear policy support and incentives in some countries further complicates the adoption of DME technology on a large scale.
From a technical perspective, ongoing research is focused on improving DME production efficiency and reducing costs. Current production methods, while effective, still have room for optimization in terms of energy consumption and overall process efficiency. Additionally, efforts are being made to enhance DME's energy density, which is lower than that of conventional diesel fuel, requiring larger fuel tanks for equivalent range in vehicle applications.
Lastly, public awareness and acceptance of DME as an alternative fuel remain limited. The lack of familiarity with DME among end-users and policymakers can lead to hesitation in embracing this technology. Overcoming this challenge requires concerted efforts in education, demonstration projects, and public outreach to showcase the benefits and safety of DME in various applications.
One of the key advantages of DME is its similarity to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) in terms of physical properties. This allows for the use of existing LPG infrastructure with minimal modifications, significantly reducing the costs associated with large-scale energy deployments. DME's high cetane number and clean-burning characteristics make it an attractive alternative to diesel fuel in compression ignition engines, potentially simplifying the transition to cleaner transportation fuels.
However, despite these advantages, DME technology faces several challenges that hinder its widespread adoption. One of the primary obstacles is the limited production capacity of DME on a global scale. While there are several commercial-scale DME plants in operation, particularly in Asia, the overall production volume remains relatively low compared to conventional fuels. This limited supply chain presents a significant barrier to large-scale implementation.
Another challenge lies in the need for specialized equipment and infrastructure modifications. Although DME can utilize much of the existing LPG infrastructure, some components, such as seals and gaskets, may require replacement due to DME's different chemical properties. This necessitates additional investment and technical expertise, which can be a deterrent for some potential adopters.
The regulatory landscape surrounding DME also presents challenges. In many regions, fuel standards and regulations are not yet fully developed for DME, creating uncertainty for investors and slowing down market penetration. The lack of clear policy support and incentives in some countries further complicates the adoption of DME technology on a large scale.
From a technical perspective, ongoing research is focused on improving DME production efficiency and reducing costs. Current production methods, while effective, still have room for optimization in terms of energy consumption and overall process efficiency. Additionally, efforts are being made to enhance DME's energy density, which is lower than that of conventional diesel fuel, requiring larger fuel tanks for equivalent range in vehicle applications.
Lastly, public awareness and acceptance of DME as an alternative fuel remain limited. The lack of familiarity with DME among end-users and policymakers can lead to hesitation in embracing this technology. Overcoming this challenge requires concerted efforts in education, demonstration projects, and public outreach to showcase the benefits and safety of DME in various applications.
Existing DME Deployment Solutions
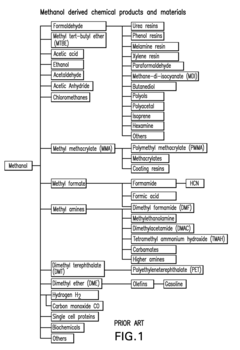
01 Catalytic synthesis of dimethyl ether
Various catalytic processes are employed for the synthesis of dimethyl ether. These methods often involve the dehydration of methanol or the direct conversion of syngas. Catalysts such as zeolites, metal oxides, or supported metals are used to enhance the reaction efficiency and selectivity. The process conditions, including temperature, pressure, and catalyst composition, are optimized to improve yield and reduce byproduct formation.- Catalytic synthesis of dimethyl ether: Various catalytic processes are employed for the synthesis of dimethyl ether. These methods often involve the dehydration of methanol or the direct conversion of syngas. Catalysts such as zeolites, metal oxides, or supported metals are used to facilitate the reaction and improve selectivity. The choice of catalyst and reaction conditions significantly influences the efficiency and yield of dimethyl ether production.
- Purification and separation techniques: Efficient purification and separation methods are crucial for obtaining high-purity dimethyl ether. These techniques may include distillation, adsorption, or membrane separation processes. The removal of impurities and by-products is essential for meeting product specifications and ensuring the quality of the final dimethyl ether product.
- Process optimization and energy efficiency: Improving the energy efficiency of dimethyl ether production is a key focus area. This involves optimizing reaction conditions, heat integration, and process design to reduce energy consumption and improve overall process economics. Advanced control strategies and process intensification techniques are employed to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs.
- Alternative feedstocks and production routes: Research into alternative feedstocks and production routes for dimethyl ether aims to diversify raw material sources and improve sustainability. This includes exploring biomass-derived feedstocks, waste materials, or novel synthesis pathways. The development of these alternative routes can potentially reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease the environmental impact of dimethyl ether production.
- Applications and formulations: Dimethyl ether finds applications in various fields, including as a propellant, fuel additive, or refrigerant. Research focuses on developing new formulations and applications that leverage the unique properties of dimethyl ether. This includes studying its performance in different fuel blends, exploring its potential as a green solvent, or investigating its use in chemical synthesis as a versatile building block.
02 Purification and separation of dimethyl ether
Techniques for purifying and separating dimethyl ether from reaction mixtures are crucial for obtaining high-quality product. These methods may include distillation, adsorption, membrane separation, or cryogenic processes. The choice of separation technique depends on the composition of the reaction mixture and the desired purity of the final product. Efficient separation processes help to simplify the overall production of dimethyl ether.Expand Specific Solutions03 Process intensification for dimethyl ether production
Process intensification strategies are employed to simplify and improve the efficiency of dimethyl ether production. These may include the use of novel reactor designs, such as microreactors or multifunctional reactors, which combine reaction and separation steps. Other approaches involve the development of more active and selective catalysts, optimization of heat integration, and the use of advanced process control systems to enhance overall process performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Alternative feedstocks for dimethyl ether synthesis
Research is ongoing to explore alternative feedstocks for dimethyl ether production, aiming to simplify the process and reduce reliance on traditional fossil fuel sources. These feedstocks may include biomass, waste materials, or carbon dioxide. The use of alternative raw materials often requires the development of new catalysts and process conditions tailored to the specific feedstock characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions05 Direct synthesis of dimethyl ether from syngas
Direct synthesis of dimethyl ether from syngas (a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen) is an approach to simplify the production process by eliminating the intermediate methanol synthesis step. This method requires the development of bifunctional catalysts that can perform both the synthesis of methanol and its subsequent dehydration to dimethyl ether in a single reactor. Optimizing reaction conditions and catalyst formulations is crucial for improving the efficiency of this direct synthesis route.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in DME Energy Industry
The dimethyl ether (DME) market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for clean energy alternatives. The global DME market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 10%. Technologically, DME production is relatively mature, with established processes for synthesis from various feedstocks. Key players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., SK Energy, and Linde GmbH are actively developing and commercializing DME technologies. Research institutions such as the University of Southern California and Chinese Academy of Sciences are advancing novel DME applications. While challenges remain in large-scale deployment, ongoing R&D efforts by companies like Toshiba and JFE Holdings are improving DME's viability as a versatile energy carrier for power generation, transportation, and industrial uses.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a comprehensive dimethyl ether (DME) production and utilization strategy. Their approach involves large-scale DME synthesis from coal and natural gas, utilizing advanced catalysts and reactor designs. Sinopec has implemented a two-step process: first, syngas production through coal gasification or natural gas reforming, followed by DME synthesis using Cu-ZnO-Al2O3 catalysts[1]. This method achieves high conversion rates and selectivity. Sinopec has also pioneered DME as a clean-burning fuel for power generation and transportation, with pilot projects demonstrating its feasibility in diesel engine modifications and LPG blending[2]. Their research extends to DME as a hydrogen carrier for fuel cells, potentially simplifying hydrogen storage and transport in energy systems[3].
Strengths: Vertically integrated production chain, from feedstock to end-use applications. Extensive R&D capabilities and pilot project experience. Weaknesses: Heavy reliance on coal-based DME production may face environmental scrutiny. Limited international market presence compared to global energy giants.
Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Processing
Technical Solution: The Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Processing has focused on optimizing DME production processes and exploring novel applications. They have developed a single-step DME synthesis technology that directly converts syngas to DME, improving efficiency and reducing capital costs[1]. This process utilizes a bifunctional catalyst that combines methanol synthesis and dehydration functions. The institute has also made significant progress in DME purification techniques, achieving high-purity DME suitable for various applications[2]. Their research extends to using DME as a chemical feedstock for producing olefins and aromatics, potentially revolutionizing the petrochemical industry[3]. Additionally, they have conducted extensive studies on DME's combustion characteristics and emissions profile, supporting its use as a clean alternative fuel in various energy deployments[4].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research in DME synthesis and applications. Strong integration with Sinopec's industrial capabilities. Weaknesses: May face challenges in commercializing research findings. Potential overlap with other Sinopec subsidiaries' research efforts.
Core Innovations in DME Technology
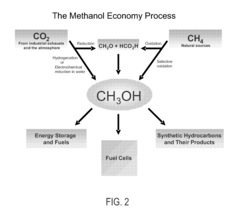
Energy supply method and system
PatentWO2006004140A1
Innovation
- The introduction of Dimethyl Ether (DME) as a versatile energy circulation medium, which can be derived from biomass, waste, and petroleum residues, and used for power generation, transportation, and heating, allowing for efficient energy storage and distribution without relying on pipelines, and enabling the conversion of waste heat into usable energy.
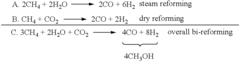
Conversion of carbon dioxide to methanol and/or dimethyl ether using bi-reforming of methane or natural gas
PatentActiveUS7906559B2
Innovation
- A bi-reforming process combining steam and dry reforming of methane to achieve a specific CO/H2 molar ratio of 1:2, allowing for the efficient conversion of carbon dioxide and methane to methanol and dimethyl ether without producing CO2 or other by-products, using a catalyst such as V2O5 and NiO on a silica carrier.
Environmental Impact of DME Deployments
The environmental impact of Dimethyl Ether (DME) deployments in large-scale energy systems is a critical consideration for sustainable development. DME, as a clean-burning fuel, offers several environmental advantages over traditional fossil fuels, particularly in terms of reduced emissions and improved air quality.
One of the primary environmental benefits of DME is its low carbon footprint. When produced from renewable sources such as biomass or captured CO2, DME can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fossil fuels. This characteristic makes DME an attractive option for countries and organizations aiming to meet their climate change mitigation targets and transition towards a low-carbon economy.
In terms of air quality, DME combustion produces negligible particulate matter and sulfur dioxide emissions. This is particularly important in urban areas where air pollution from transportation and industrial activities poses severe health risks. The deployment of DME-based energy systems can contribute to improved air quality, potentially reducing respiratory illnesses and associated healthcare costs.
Water conservation is another environmental advantage of DME deployments. Unlike some other alternative fuels, DME production does not require significant water resources, making it suitable for implementation in water-stressed regions. This characteristic can help mitigate the environmental stress on local water supplies, particularly in areas where water scarcity is a growing concern.
However, the environmental impact of DME deployments also depends on the production methods and feedstock used. While DME can be produced from renewable sources, it is currently often derived from natural gas or coal. In these cases, the environmental benefits may be partially offset by the upstream emissions associated with fossil fuel extraction and processing.
Land use changes and biodiversity impacts should also be considered, especially if large-scale biomass production is required for DME synthesis. Careful management and sustainable practices in feedstock cultivation are essential to minimize negative effects on ecosystems and maintain biodiversity.
The lifecycle assessment of DME deployments reveals potential environmental trade-offs. While DME offers clear benefits in terms of reduced emissions and improved air quality at the point of use, the overall environmental impact depends on factors such as production efficiency, transportation, and end-use applications. Comprehensive lifecycle analyses are crucial for accurately evaluating the net environmental impact of DME deployments in different contexts.
In conclusion, DME deployments have the potential to significantly reduce environmental impacts compared to conventional energy systems, particularly in terms of emissions and air quality. However, realizing these benefits requires careful consideration of production methods, feedstock sources, and lifecycle impacts to ensure that DME implementations truly contribute to sustainable energy solutions.
One of the primary environmental benefits of DME is its low carbon footprint. When produced from renewable sources such as biomass or captured CO2, DME can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fossil fuels. This characteristic makes DME an attractive option for countries and organizations aiming to meet their climate change mitigation targets and transition towards a low-carbon economy.
In terms of air quality, DME combustion produces negligible particulate matter and sulfur dioxide emissions. This is particularly important in urban areas where air pollution from transportation and industrial activities poses severe health risks. The deployment of DME-based energy systems can contribute to improved air quality, potentially reducing respiratory illnesses and associated healthcare costs.
Water conservation is another environmental advantage of DME deployments. Unlike some other alternative fuels, DME production does not require significant water resources, making it suitable for implementation in water-stressed regions. This characteristic can help mitigate the environmental stress on local water supplies, particularly in areas where water scarcity is a growing concern.
However, the environmental impact of DME deployments also depends on the production methods and feedstock used. While DME can be produced from renewable sources, it is currently often derived from natural gas or coal. In these cases, the environmental benefits may be partially offset by the upstream emissions associated with fossil fuel extraction and processing.
Land use changes and biodiversity impacts should also be considered, especially if large-scale biomass production is required for DME synthesis. Careful management and sustainable practices in feedstock cultivation are essential to minimize negative effects on ecosystems and maintain biodiversity.
The lifecycle assessment of DME deployments reveals potential environmental trade-offs. While DME offers clear benefits in terms of reduced emissions and improved air quality at the point of use, the overall environmental impact depends on factors such as production efficiency, transportation, and end-use applications. Comprehensive lifecycle analyses are crucial for accurately evaluating the net environmental impact of DME deployments in different contexts.
In conclusion, DME deployments have the potential to significantly reduce environmental impacts compared to conventional energy systems, particularly in terms of emissions and air quality. However, realizing these benefits requires careful consideration of production methods, feedstock sources, and lifecycle impacts to ensure that DME implementations truly contribute to sustainable energy solutions.
DME Infrastructure Requirements
The implementation of Dimethyl Ether (DME) as a large-scale energy solution requires specific infrastructure considerations to ensure efficient and safe deployment. DME's unique properties as a clean-burning, easily transportable fuel necessitate adaptations to existing energy infrastructure systems.
Storage facilities for DME must be designed to accommodate its physical properties. Unlike natural gas, DME can be liquefied at relatively low pressures, similar to propane. This characteristic allows for more compact storage solutions, reducing the overall footprint of storage facilities. However, specialized tanks capable of maintaining the required pressure and temperature conditions are essential to prevent leakage and ensure long-term storage stability.
Transportation infrastructure for DME can leverage existing LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) networks with minimal modifications. Pipelines, trucks, and rail systems currently used for propane transport can be adapted for DME distribution. This compatibility significantly reduces the initial investment required for large-scale DME deployment, as it allows for the utilization of established logistics networks.
Fueling stations for DME-powered vehicles require specific equipment designed to handle its unique properties. While similar to LPG fueling systems, DME stations need dedicated dispensers, storage tanks, and safety systems. The installation of these specialized components is crucial for the widespread adoption of DME as a transportation fuel.
Power generation facilities utilizing DME as a fuel source must be equipped with appropriate combustion systems. DME's clean-burning nature allows for the use of simpler emission control systems compared to traditional fossil fuels. However, burners and turbines may require modifications to optimize performance and efficiency when operating with DME.
Safety infrastructure is a critical component of DME deployment. While DME is non-toxic and environmentally benign, it is flammable and requires proper handling. Leak detection systems, emergency shut-off valves, and firefighting equipment specifically designed for DME must be integrated into all stages of the supply chain, from production facilities to end-user applications.
Regulatory compliance and standardization play a vital role in DME infrastructure development. Establishing clear guidelines for DME handling, storage, and use is essential for ensuring consistent safety standards across the industry. Collaboration between government agencies, industry stakeholders, and international organizations is necessary to develop and implement these regulations effectively.
In conclusion, the infrastructure requirements for large-scale DME deployment are significant but largely achievable through adaptations of existing systems. The compatibility with LPG infrastructure provides a substantial advantage, reducing the overall cost and complexity of implementation. As DME continues to gain traction as a clean energy solution, ongoing investment in specialized infrastructure will be crucial to support its widespread adoption and maximize its potential as a versatile, sustainable fuel source.
Storage facilities for DME must be designed to accommodate its physical properties. Unlike natural gas, DME can be liquefied at relatively low pressures, similar to propane. This characteristic allows for more compact storage solutions, reducing the overall footprint of storage facilities. However, specialized tanks capable of maintaining the required pressure and temperature conditions are essential to prevent leakage and ensure long-term storage stability.
Transportation infrastructure for DME can leverage existing LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) networks with minimal modifications. Pipelines, trucks, and rail systems currently used for propane transport can be adapted for DME distribution. This compatibility significantly reduces the initial investment required for large-scale DME deployment, as it allows for the utilization of established logistics networks.
Fueling stations for DME-powered vehicles require specific equipment designed to handle its unique properties. While similar to LPG fueling systems, DME stations need dedicated dispensers, storage tanks, and safety systems. The installation of these specialized components is crucial for the widespread adoption of DME as a transportation fuel.
Power generation facilities utilizing DME as a fuel source must be equipped with appropriate combustion systems. DME's clean-burning nature allows for the use of simpler emission control systems compared to traditional fossil fuels. However, burners and turbines may require modifications to optimize performance and efficiency when operating with DME.
Safety infrastructure is a critical component of DME deployment. While DME is non-toxic and environmentally benign, it is flammable and requires proper handling. Leak detection systems, emergency shut-off valves, and firefighting equipment specifically designed for DME must be integrated into all stages of the supply chain, from production facilities to end-user applications.
Regulatory compliance and standardization play a vital role in DME infrastructure development. Establishing clear guidelines for DME handling, storage, and use is essential for ensuring consistent safety standards across the industry. Collaboration between government agencies, industry stakeholders, and international organizations is necessary to develop and implement these regulations effectively.
In conclusion, the infrastructure requirements for large-scale DME deployment are significant but largely achievable through adaptations of existing systems. The compatibility with LPG infrastructure provides a substantial advantage, reducing the overall cost and complexity of implementation. As DME continues to gain traction as a clean energy solution, ongoing investment in specialized infrastructure will be crucial to support its widespread adoption and maximize its potential as a versatile, sustainable fuel source.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!