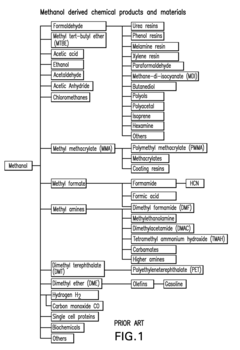
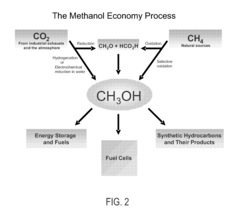
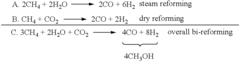
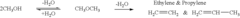How Dimethyl Ether Streamlines Fuel Distribution Networks?
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DME Fuel Evolution
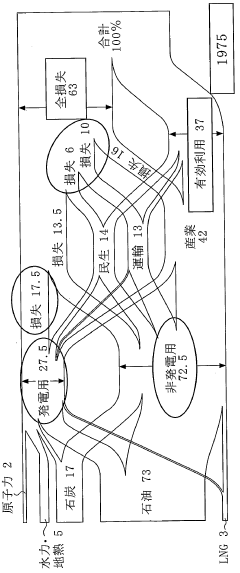
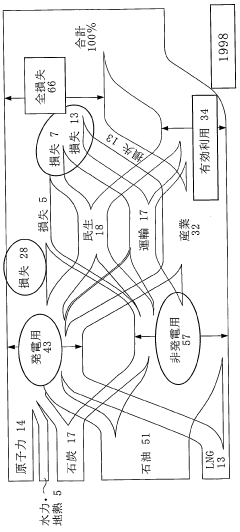
Dimethyl ether (DME) has emerged as a promising alternative fuel, revolutionizing the fuel distribution landscape. The evolution of DME as a fuel has been marked by significant milestones and technological advancements over the past few decades.
In the 1990s, researchers began exploring DME as a potential fuel source due to its clean-burning properties and ease of production. The initial focus was on developing efficient production methods, primarily through the dehydration of methanol or direct synthesis from syngas.
By the early 2000s, DME gained traction as a diesel substitute, particularly in Asia. Countries like Japan and China invested heavily in DME research and development, recognizing its potential to reduce dependence on conventional fossil fuels and improve air quality in urban areas.
The mid-2000s saw a surge in pilot projects and demonstration plants. These initiatives aimed to showcase DME's viability as a transportation fuel and its potential for use in power generation. Notably, Volvo Trucks conducted extensive field tests of DME-powered vehicles, demonstrating the fuel's compatibility with existing diesel engine technology.
From 2010 onwards, the focus shifted towards optimizing DME production processes and developing more efficient distribution networks. Advancements in catalysis and process engineering led to improved yields and reduced production costs, making DME more competitive with traditional fuels.
The past decade has witnessed a growing interest in bio-based DME production. This approach aligns with global sustainability goals, as DME can be produced from various renewable feedstocks, including biomass and waste materials. The development of small-scale, modular DME production units has further enhanced the fuel's potential for decentralized distribution.
Recent years have seen increased collaboration between industry players, research institutions, and governments to establish DME infrastructure. This includes the development of specialized storage and handling facilities, as well as the adaptation of existing fuel distribution networks to accommodate DME.
Looking ahead, the evolution of DME as a fuel is expected to continue, with a focus on further reducing production costs, expanding its application in various sectors, and integrating it into the broader renewable energy ecosystem. As environmental regulations become more stringent and the demand for cleaner fuels grows, DME is poised to play an increasingly important role in streamlining fuel distribution networks and supporting the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
In the 1990s, researchers began exploring DME as a potential fuel source due to its clean-burning properties and ease of production. The initial focus was on developing efficient production methods, primarily through the dehydration of methanol or direct synthesis from syngas.
By the early 2000s, DME gained traction as a diesel substitute, particularly in Asia. Countries like Japan and China invested heavily in DME research and development, recognizing its potential to reduce dependence on conventional fossil fuels and improve air quality in urban areas.
The mid-2000s saw a surge in pilot projects and demonstration plants. These initiatives aimed to showcase DME's viability as a transportation fuel and its potential for use in power generation. Notably, Volvo Trucks conducted extensive field tests of DME-powered vehicles, demonstrating the fuel's compatibility with existing diesel engine technology.
From 2010 onwards, the focus shifted towards optimizing DME production processes and developing more efficient distribution networks. Advancements in catalysis and process engineering led to improved yields and reduced production costs, making DME more competitive with traditional fuels.
The past decade has witnessed a growing interest in bio-based DME production. This approach aligns with global sustainability goals, as DME can be produced from various renewable feedstocks, including biomass and waste materials. The development of small-scale, modular DME production units has further enhanced the fuel's potential for decentralized distribution.
Recent years have seen increased collaboration between industry players, research institutions, and governments to establish DME infrastructure. This includes the development of specialized storage and handling facilities, as well as the adaptation of existing fuel distribution networks to accommodate DME.
Looking ahead, the evolution of DME as a fuel is expected to continue, with a focus on further reducing production costs, expanding its application in various sectors, and integrating it into the broader renewable energy ecosystem. As environmental regulations become more stringent and the demand for cleaner fuels grows, DME is poised to play an increasingly important role in streamlining fuel distribution networks and supporting the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
DME Market Analysis
The global dimethyl ether (DME) market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for clean and efficient alternative fuels. DME, with its favorable combustion properties and ease of handling, has emerged as a promising solution for streamlining fuel distribution networks. The market for DME is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a projected compound annual growth rate of over 9% from 2021 to 2026.
The primary driver of DME market growth is its potential as a cleaner alternative to conventional diesel fuel. DME offers reduced emissions of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and carbon monoxide, making it an attractive option for countries striving to meet stringent environmental regulations. This has led to increased adoption in various sectors, including transportation, power generation, and domestic fuel applications.
In the transportation sector, DME has gained traction as a substitute for diesel fuel in heavy-duty vehicles and long-haul trucks. Several major automotive manufacturers have shown interest in developing DME-compatible engines, recognizing its potential to reduce carbon footprint and improve air quality in urban areas. The ease of retrofitting existing diesel engines to run on DME has further accelerated its adoption in this sector.
The power generation industry has also embraced DME as a cleaner alternative to coal and oil-based fuels. DME-fired power plants have demonstrated improved efficiency and reduced emissions, making them an attractive option for countries seeking to diversify their energy mix and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. This trend is particularly evident in Asia-Pacific countries, where rapid industrialization and urbanization have created a pressing need for cleaner energy solutions.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the global DME market, with China leading in both production and consumption. The Chinese government's push for cleaner fuels and reduced dependence on imported oil has been a significant factor in driving DME adoption. Other key markets include Japan, South Korea, and India, where government initiatives and increasing environmental awareness have spurred demand for DME.
Europe and North America are also witnessing growing interest in DME, primarily driven by stringent emission regulations and the need for sustainable fuel alternatives. Several pilot projects and commercial-scale DME production facilities have been established in these regions, indicating a positive outlook for market growth.
The DME market is characterized by the presence of both established players and new entrants, leading to a competitive landscape. Key market players are focusing on expanding their production capacities, investing in research and development, and forming strategic partnerships to strengthen their market position. This competitive environment is expected to drive innovation and further improve the efficiency of DME production and distribution processes.
The primary driver of DME market growth is its potential as a cleaner alternative to conventional diesel fuel. DME offers reduced emissions of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and carbon monoxide, making it an attractive option for countries striving to meet stringent environmental regulations. This has led to increased adoption in various sectors, including transportation, power generation, and domestic fuel applications.
In the transportation sector, DME has gained traction as a substitute for diesel fuel in heavy-duty vehicles and long-haul trucks. Several major automotive manufacturers have shown interest in developing DME-compatible engines, recognizing its potential to reduce carbon footprint and improve air quality in urban areas. The ease of retrofitting existing diesel engines to run on DME has further accelerated its adoption in this sector.
The power generation industry has also embraced DME as a cleaner alternative to coal and oil-based fuels. DME-fired power plants have demonstrated improved efficiency and reduced emissions, making them an attractive option for countries seeking to diversify their energy mix and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. This trend is particularly evident in Asia-Pacific countries, where rapid industrialization and urbanization have created a pressing need for cleaner energy solutions.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the global DME market, with China leading in both production and consumption. The Chinese government's push for cleaner fuels and reduced dependence on imported oil has been a significant factor in driving DME adoption. Other key markets include Japan, South Korea, and India, where government initiatives and increasing environmental awareness have spurred demand for DME.
Europe and North America are also witnessing growing interest in DME, primarily driven by stringent emission regulations and the need for sustainable fuel alternatives. Several pilot projects and commercial-scale DME production facilities have been established in these regions, indicating a positive outlook for market growth.
The DME market is characterized by the presence of both established players and new entrants, leading to a competitive landscape. Key market players are focusing on expanding their production capacities, investing in research and development, and forming strategic partnerships to strengthen their market position. This competitive environment is expected to drive innovation and further improve the efficiency of DME production and distribution processes.
DME Tech Challenges
Despite the promising potential of Dimethyl Ether (DME) in streamlining fuel distribution networks, several technical challenges persist in its widespread adoption and implementation. These challenges span across production, storage, transportation, and end-use applications.
One of the primary hurdles lies in the production process of DME. While it can be synthesized from various feedstocks, including natural gas, coal, and biomass, optimizing the production efficiency and reducing costs remain significant challenges. The current production methods often involve energy-intensive processes, which can offset some of the environmental benefits of DME as a clean fuel alternative.
Storage and transportation of DME present another set of technical difficulties. DME has a lower energy density compared to conventional diesel fuel, necessitating larger storage tanks and more frequent refueling. This characteristic poses challenges in designing and implementing efficient storage and distribution infrastructure, particularly for long-distance transportation applications.
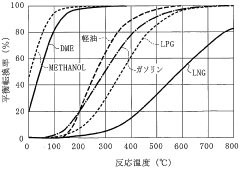
The compatibility of DME with existing fuel systems and engines is a crucial technical obstacle. While DME can be used in modified diesel engines, significant adaptations are required to accommodate its unique properties. These modifications include changes to fuel injection systems, seals, and gaskets, as DME has different lubricity and material compatibility characteristics compared to conventional diesel fuel.
Another challenge lies in the development of standardized fueling systems for DME. The lack of widespread infrastructure for DME distribution and refueling stations hinders its adoption in the transportation sector. Creating a network of DME fueling stations that can safely and efficiently handle the fuel requires substantial investment and technical innovation.
The purity and quality control of DME in the distribution network pose additional technical challenges. Ensuring consistent fuel quality across the supply chain is crucial for engine performance and longevity. Developing robust quality control measures and standards for DME production, storage, and distribution is essential to address these concerns.
Lastly, the integration of DME into existing energy systems and industrial processes presents technical hurdles. While DME shows promise as a clean-burning fuel and chemical feedstock, adapting current industrial processes and energy infrastructure to incorporate DME efficiently requires significant research and development efforts.
Addressing these technical challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of DME in streamlining fuel distribution networks. Overcoming these hurdles will require collaborative efforts from researchers, industry stakeholders, and policymakers to drive innovation and develop practical solutions for widespread DME adoption.
One of the primary hurdles lies in the production process of DME. While it can be synthesized from various feedstocks, including natural gas, coal, and biomass, optimizing the production efficiency and reducing costs remain significant challenges. The current production methods often involve energy-intensive processes, which can offset some of the environmental benefits of DME as a clean fuel alternative.
Storage and transportation of DME present another set of technical difficulties. DME has a lower energy density compared to conventional diesel fuel, necessitating larger storage tanks and more frequent refueling. This characteristic poses challenges in designing and implementing efficient storage and distribution infrastructure, particularly for long-distance transportation applications.
The compatibility of DME with existing fuel systems and engines is a crucial technical obstacle. While DME can be used in modified diesel engines, significant adaptations are required to accommodate its unique properties. These modifications include changes to fuel injection systems, seals, and gaskets, as DME has different lubricity and material compatibility characteristics compared to conventional diesel fuel.
Another challenge lies in the development of standardized fueling systems for DME. The lack of widespread infrastructure for DME distribution and refueling stations hinders its adoption in the transportation sector. Creating a network of DME fueling stations that can safely and efficiently handle the fuel requires substantial investment and technical innovation.
The purity and quality control of DME in the distribution network pose additional technical challenges. Ensuring consistent fuel quality across the supply chain is crucial for engine performance and longevity. Developing robust quality control measures and standards for DME production, storage, and distribution is essential to address these concerns.
Lastly, the integration of DME into existing energy systems and industrial processes presents technical hurdles. While DME shows promise as a clean-burning fuel and chemical feedstock, adapting current industrial processes and energy infrastructure to incorporate DME efficiently requires significant research and development efforts.
Addressing these technical challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of DME in streamlining fuel distribution networks. Overcoming these hurdles will require collaborative efforts from researchers, industry stakeholders, and policymakers to drive innovation and develop practical solutions for widespread DME adoption.
DME Network Solutions
01 Catalytic synthesis of dimethyl ether
Various catalytic processes are employed for the efficient synthesis of dimethyl ether. These processes often involve the use of specific catalysts, reaction conditions, and feedstocks to optimize the production of dimethyl ether. The catalytic synthesis methods aim to improve yield, selectivity, and energy efficiency in the production process.- Catalytic synthesis of dimethyl ether: Various catalytic processes are employed for the efficient synthesis of dimethyl ether. These methods often involve the use of specific catalysts and reaction conditions to optimize the conversion of feedstocks into dimethyl ether. The processes aim to improve yield, selectivity, and energy efficiency in the production of this important chemical compound.
- Dimethyl ether production from syngas: Syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, serves as a key feedstock for dimethyl ether production. The process typically involves the conversion of syngas to methanol, followed by methanol dehydration to form dimethyl ether. Various catalysts and process conditions are explored to enhance the efficiency and selectivity of this two-step or direct conversion process.
- Process optimization and energy efficiency: Efforts to streamline dimethyl ether production focus on optimizing process parameters and improving energy efficiency. This includes developing novel reactor designs, enhancing heat integration, and implementing advanced control strategies. The goal is to reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and increase overall process efficiency in dimethyl ether manufacturing.
- Innovative catalyst development: Research in catalyst development plays a crucial role in streamlining dimethyl ether production. Novel catalysts are designed to improve activity, selectivity, and stability in the conversion processes. This includes the exploration of bifunctional catalysts, nanostructured materials, and supported metal catalysts to enhance the efficiency of dimethyl ether synthesis from various feedstocks.
- Integration with renewable resources: To enhance sustainability, efforts are made to integrate dimethyl ether production with renewable resources. This includes the use of biomass-derived syngas, carbon dioxide utilization, and the development of bio-based processes. Such integration aims to reduce the carbon footprint of dimethyl ether production and align with circular economy principles.
02 Dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether
The dehydration of methanol is a common method for producing dimethyl ether. This process involves the removal of water from methanol molecules to form dimethyl ether. Various catalysts and reaction conditions are used to enhance the efficiency and selectivity of this dehydration process, aiming to maximize dimethyl ether yield while minimizing byproduct formation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Direct synthesis of dimethyl ether from syngas
Direct synthesis of dimethyl ether from syngas (a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen) is an alternative production method. This process aims to streamline dimethyl ether production by bypassing the intermediate methanol synthesis step. Various catalysts and process conditions are explored to improve the efficiency and selectivity of this direct synthesis route.Expand Specific Solutions04 Process optimization and energy efficiency
Efforts are made to optimize the dimethyl ether production process and improve energy efficiency. This includes developing novel reactor designs, improving heat integration, and implementing advanced process control strategies. The goal is to reduce energy consumption, increase productivity, and minimize waste in the dimethyl ether production process.Expand Specific Solutions05 Purification and separation of dimethyl ether
Various methods are employed for the purification and separation of dimethyl ether from reaction mixtures. These techniques aim to remove impurities and byproducts, ensuring high-purity dimethyl ether production. Distillation, adsorption, and membrane separation processes are among the methods used to achieve efficient purification and separation of dimethyl ether.Expand Specific Solutions
DME Industry Players
The dimethyl ether (DME) fuel distribution network market is in an early growth stage, with increasing interest due to DME's potential as a clean alternative fuel. The global market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, driven by environmental regulations and energy security concerns. While the technology is relatively mature, widespread adoption faces infrastructure challenges. Key players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. and Isuzu Motors are investing in DME research and development, focusing on engine compatibility and production scalability. Universities such as USC and Wuhan University of Science & Technology are contributing to technological advancements, while companies like Ford and Toshiba are exploring DME applications in various sectors, indicating a competitive and collaborative landscape.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative dimethyl ether (DME) production and distribution network to streamline fuel distribution. Their approach involves converting coal and natural gas to DME using advanced catalytic processes[1]. The company has implemented a large-scale DME production facility with a capacity of 1 million tons per year[2]. Sinopec's distribution network includes specialized DME storage tanks, dedicated pipelines, and modified fuel stations capable of dispensing DME alongside traditional fuels[3]. This integrated approach allows for efficient production, transportation, and end-use of DME as a clean alternative fuel.
Strengths: Established infrastructure, large-scale production capability, integrated supply chain. Weaknesses: Dependence on fossil fuel feedstocks, potential competition from other alternative fuels.
Isuzu Motors Ltd.
Technical Solution: Isuzu Motors has developed DME-powered vehicles to capitalize on the fuel's distribution advantages. Their technology includes modified diesel engines capable of running on DME, with specialized fuel injection systems and storage tanks[4]. Isuzu has conducted extensive field trials of DME trucks in various operating conditions, demonstrating fuel efficiency improvements of up to 10% compared to diesel[5]. The company has also collaborated with fuel suppliers to establish DME refueling stations, integrating seamlessly with existing distribution networks. Isuzu's approach focuses on the end-user perspective, ensuring that DME vehicles can be easily adopted without significant changes to logistics operations.
Strengths: Practical vehicle technology, proven field performance, collaboration with fuel suppliers. Weaknesses: Limited market penetration, dependence on DME infrastructure development.
DME Tech Innovations
Energy supply method and system
PatentWO2006004140A1
Innovation
- The introduction of Dimethyl Ether (DME) as a versatile energy circulation medium, which can be derived from biomass, waste, and petroleum residues, and used for power generation, transportation, and heating, allowing for efficient energy storage and distribution without relying on pipelines, and enabling the conversion of waste heat into usable energy.
Conversion of carbon dioxide to methanol and/or dimethyl ether using bi-reforming of methane or natural gas
PatentActiveUS7906559B2
Innovation
- A bi-reforming process combining steam and dry reforming of methane to achieve a specific CO/H2 molar ratio of 1:2, allowing for the efficient conversion of carbon dioxide and methane to methanol and dimethyl ether without producing CO2 or other by-products, using a catalyst such as V2O5 and NiO on a silica carrier.
DME Environmental Impact
Dimethyl ether (DME) has emerged as a promising alternative fuel with significant environmental benefits compared to conventional fossil fuels. As a clean-burning, non-toxic compound, DME offers substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants when used in place of diesel or other petroleum-based fuels.
One of the primary environmental advantages of DME is its lower carbon footprint. When produced from renewable sources such as biomass or waste materials, DME can achieve near-zero or even negative carbon emissions on a lifecycle basis. Even when derived from natural gas, DME still results in lower CO2 emissions compared to diesel fuel due to its higher hydrogen-to-carbon ratio and more efficient combustion properties.
DME combustion produces virtually no particulate matter or sulfur oxides, which are major contributors to air pollution and respiratory health issues in urban areas. The reduction in these harmful emissions can lead to improved air quality and public health outcomes, particularly in densely populated regions heavily reliant on diesel-powered vehicles and equipment.
Furthermore, DME is non-toxic and rapidly biodegradable, posing minimal risk to soil and water resources in the event of spills or leaks. This characteristic makes DME safer to handle and transport compared to conventional fuels, reducing the potential for environmental contamination throughout the distribution network.
The adoption of DME as a fuel can also contribute to the mitigation of ozone depletion and smog formation. Unlike some alternative fuels, DME has a low ozone-forming potential and does not contribute significantly to the formation of ground-level ozone or photochemical smog.
In terms of infrastructure impact, DME's compatibility with existing LPG handling and distribution systems means that its introduction requires minimal modifications to current fuel networks. This reduces the need for extensive new infrastructure development, which can have its own environmental consequences in terms of land use and resource consumption.
However, it is important to note that the full environmental benefits of DME are contingent on its production methods. While DME derived from renewable sources offers the greatest environmental advantages, production from fossil fuels may still result in some greenhouse gas emissions, albeit lower than those associated with conventional fuels.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of DME in fuel distribution networks is largely positive, offering significant reductions in emissions, improved air quality, and enhanced safety profiles compared to traditional fossil fuels. As production methods continue to evolve towards more sustainable practices, DME's role in creating cleaner and more environmentally friendly fuel distribution systems is likely to expand.
One of the primary environmental advantages of DME is its lower carbon footprint. When produced from renewable sources such as biomass or waste materials, DME can achieve near-zero or even negative carbon emissions on a lifecycle basis. Even when derived from natural gas, DME still results in lower CO2 emissions compared to diesel fuel due to its higher hydrogen-to-carbon ratio and more efficient combustion properties.
DME combustion produces virtually no particulate matter or sulfur oxides, which are major contributors to air pollution and respiratory health issues in urban areas. The reduction in these harmful emissions can lead to improved air quality and public health outcomes, particularly in densely populated regions heavily reliant on diesel-powered vehicles and equipment.
Furthermore, DME is non-toxic and rapidly biodegradable, posing minimal risk to soil and water resources in the event of spills or leaks. This characteristic makes DME safer to handle and transport compared to conventional fuels, reducing the potential for environmental contamination throughout the distribution network.
The adoption of DME as a fuel can also contribute to the mitigation of ozone depletion and smog formation. Unlike some alternative fuels, DME has a low ozone-forming potential and does not contribute significantly to the formation of ground-level ozone or photochemical smog.
In terms of infrastructure impact, DME's compatibility with existing LPG handling and distribution systems means that its introduction requires minimal modifications to current fuel networks. This reduces the need for extensive new infrastructure development, which can have its own environmental consequences in terms of land use and resource consumption.
However, it is important to note that the full environmental benefits of DME are contingent on its production methods. While DME derived from renewable sources offers the greatest environmental advantages, production from fossil fuels may still result in some greenhouse gas emissions, albeit lower than those associated with conventional fuels.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of DME in fuel distribution networks is largely positive, offering significant reductions in emissions, improved air quality, and enhanced safety profiles compared to traditional fossil fuels. As production methods continue to evolve towards more sustainable practices, DME's role in creating cleaner and more environmentally friendly fuel distribution systems is likely to expand.
DME Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework for dimethyl ether (DME) plays a crucial role in shaping its adoption and integration into fuel distribution networks. As DME gains traction as a cleaner alternative fuel, governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are developing and refining policies to ensure its safe production, storage, transportation, and use.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has recognized DME as an alternative fuel under the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program. This classification allows DME producers to generate Renewable Identification Numbers (RINs), providing economic incentives for its production and use. Additionally, the Department of Energy (DOE) has included DME in its alternative fuel vehicle programs, further supporting its integration into the transportation sector.
The European Union has also taken steps to promote DME as a sustainable fuel option. The Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) includes DME as an eligible renewable fuel, encouraging its production from renewable sources. Furthermore, the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) has developed specific standards for DME as a fuel, ensuring consistency and safety across member states.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have implemented supportive regulatory frameworks for DME. China has included DME in its national energy strategy, offering tax incentives and subsidies for DME production and utilization. Japan has established technical standards for DME fuel and vehicles, facilitating its adoption in the transportation sector.
Safety regulations are a critical component of the DME regulatory framework. Organizations such as the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) in the United States have developed guidelines for the safe handling and storage of DME. These regulations address issues such as fire protection, equipment specifications, and emergency response procedures.
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has also recognized DME as a potential marine fuel, developing guidelines for its use in shipping. This opens up new opportunities for DME in the maritime sector, potentially streamlining fuel distribution networks across global shipping routes.
As DME continues to gain prominence, regulatory bodies are working to harmonize standards and regulations across borders. International collaborations, such as the International DME Association, are facilitating knowledge sharing and promoting consistent regulatory approaches worldwide. This harmonization effort aims to reduce barriers to DME adoption and create a more streamlined global market for this alternative fuel.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has recognized DME as an alternative fuel under the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program. This classification allows DME producers to generate Renewable Identification Numbers (RINs), providing economic incentives for its production and use. Additionally, the Department of Energy (DOE) has included DME in its alternative fuel vehicle programs, further supporting its integration into the transportation sector.
The European Union has also taken steps to promote DME as a sustainable fuel option. The Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) includes DME as an eligible renewable fuel, encouraging its production from renewable sources. Furthermore, the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) has developed specific standards for DME as a fuel, ensuring consistency and safety across member states.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have implemented supportive regulatory frameworks for DME. China has included DME in its national energy strategy, offering tax incentives and subsidies for DME production and utilization. Japan has established technical standards for DME fuel and vehicles, facilitating its adoption in the transportation sector.
Safety regulations are a critical component of the DME regulatory framework. Organizations such as the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) in the United States have developed guidelines for the safe handling and storage of DME. These regulations address issues such as fire protection, equipment specifications, and emergency response procedures.
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has also recognized DME as a potential marine fuel, developing guidelines for its use in shipping. This opens up new opportunities for DME in the maritime sector, potentially streamlining fuel distribution networks across global shipping routes.
As DME continues to gain prominence, regulatory bodies are working to harmonize standards and regulations across borders. International collaborations, such as the International DME Association, are facilitating knowledge sharing and promoting consistent regulatory approaches worldwide. This harmonization effort aims to reduce barriers to DME adoption and create a more streamlined global market for this alternative fuel.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!