Industrial Challenges in Dimethyl Ether Value Chain
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DME Industry Background and Objectives
Dimethyl ether (DME) has emerged as a promising alternative fuel and chemical feedstock, gaining significant attention in recent years due to its clean-burning properties and versatile applications. The DME industry has evolved from its initial focus on aerosol propellants to encompass a wide range of uses, including power generation, transportation fuel, and chemical synthesis.
The development of the DME industry can be traced back to the 1960s when it was primarily used as a propellant. However, the true potential of DME as a sustainable energy source and chemical building block was not fully realized until the late 1990s and early 2000s. This shift in perception was driven by growing environmental concerns and the need for cleaner fuel alternatives.
In recent years, the DME industry has experienced rapid growth, particularly in Asia, where countries like China and Japan have been at the forefront of DME production and utilization. The global DME market is projected to expand significantly in the coming decades, driven by increasing demand for clean-burning fuels and stringent environmental regulations.
The primary objective of the DME industry is to establish a robust and sustainable value chain that can compete with traditional fossil fuels and petrochemical feedstocks. This involves addressing challenges across the entire lifecycle of DME, from production and distribution to end-use applications. Key goals include improving production efficiency, reducing costs, and expanding infrastructure for DME distribution and utilization.
One of the main technological trends in the DME industry is the development of more efficient and cost-effective production methods. Traditional DME production relies on methanol dehydration, but newer technologies are exploring direct synthesis from syngas or biomass, potentially offering significant cost and energy savings. Additionally, there is a growing focus on renewable DME production, using biomass or captured CO2 as feedstock, to further enhance the environmental benefits of DME.
The DME industry also aims to expand its market presence in various sectors. In the transportation sector, DME is being explored as a low-emission alternative to diesel fuel, particularly for heavy-duty vehicles. In the power generation sector, DME is considered a potential replacement for liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and a complement to natural gas in remote areas. The chemical industry is investigating DME as a versatile intermediate for the production of various chemicals, including olefins and aromatics.
As the DME industry continues to evolve, it faces several challenges that need to be addressed to realize its full potential. These include scaling up production capacity, developing dedicated infrastructure for DME distribution and storage, and overcoming regulatory barriers in different markets. The industry also needs to focus on improving public awareness and acceptance of DME as a clean and safe alternative fuel.
The development of the DME industry can be traced back to the 1960s when it was primarily used as a propellant. However, the true potential of DME as a sustainable energy source and chemical building block was not fully realized until the late 1990s and early 2000s. This shift in perception was driven by growing environmental concerns and the need for cleaner fuel alternatives.
In recent years, the DME industry has experienced rapid growth, particularly in Asia, where countries like China and Japan have been at the forefront of DME production and utilization. The global DME market is projected to expand significantly in the coming decades, driven by increasing demand for clean-burning fuels and stringent environmental regulations.
The primary objective of the DME industry is to establish a robust and sustainable value chain that can compete with traditional fossil fuels and petrochemical feedstocks. This involves addressing challenges across the entire lifecycle of DME, from production and distribution to end-use applications. Key goals include improving production efficiency, reducing costs, and expanding infrastructure for DME distribution and utilization.
One of the main technological trends in the DME industry is the development of more efficient and cost-effective production methods. Traditional DME production relies on methanol dehydration, but newer technologies are exploring direct synthesis from syngas or biomass, potentially offering significant cost and energy savings. Additionally, there is a growing focus on renewable DME production, using biomass or captured CO2 as feedstock, to further enhance the environmental benefits of DME.
The DME industry also aims to expand its market presence in various sectors. In the transportation sector, DME is being explored as a low-emission alternative to diesel fuel, particularly for heavy-duty vehicles. In the power generation sector, DME is considered a potential replacement for liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and a complement to natural gas in remote areas. The chemical industry is investigating DME as a versatile intermediate for the production of various chemicals, including olefins and aromatics.
As the DME industry continues to evolve, it faces several challenges that need to be addressed to realize its full potential. These include scaling up production capacity, developing dedicated infrastructure for DME distribution and storage, and overcoming regulatory barriers in different markets. The industry also needs to focus on improving public awareness and acceptance of DME as a clean and safe alternative fuel.
DME Market Demand Analysis
The global dimethyl ether (DME) market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for clean-burning alternative fuels and the expansion of its applications in various industries. DME's versatility as a fuel and chemical feedstock has positioned it as a promising solution to address environmental concerns and energy security issues.
In the transportation sector, DME has gained traction as a potential replacement for diesel fuel, particularly in heavy-duty vehicles. Its high cetane number and clean combustion properties make it an attractive option for reducing emissions and improving air quality in urban areas. Several countries, including China, Japan, and Sweden, have conducted pilot projects and trials to assess the feasibility of DME as a transportation fuel, demonstrating growing interest in its adoption.
The industrial sector represents another significant market for DME, where it is used as a propellant in aerosol products, a refrigerant, and a blowing agent for foam insulation. The shift towards more environmentally friendly propellants has led to increased demand for DME in the personal care and household products industries. Additionally, DME's potential as a chemical feedstock for the production of olefins and other valuable chemicals has attracted attention from petrochemical companies looking to diversify their product portfolios.
In the energy sector, DME has shown promise as a clean-burning fuel for power generation and domestic cooking. Its ability to be easily liquefied and transported makes it an attractive option for remote areas lacking access to natural gas infrastructure. This has led to growing interest in DME as a solution for rural electrification and clean cooking initiatives in developing countries.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is expected to be the fastest-growing market for DME. This growth is primarily driven by government initiatives to reduce air pollution and promote cleaner energy sources. In China, policies supporting the use of DME as a transportation fuel and cooking gas have significantly boosted market demand.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in scaling up DME production and distribution infrastructure. The current global production capacity is limited, and significant investments are required to establish a robust supply chain. Additionally, the market faces competition from other alternative fuels and technologies, such as electric vehicles and hydrogen fuel cells, which may impact long-term demand projections.
To fully realize the potential of DME, continued research and development efforts are needed to improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and expand its applications. Collaboration between industry stakeholders, policymakers, and research institutions will be crucial in addressing these challenges and driving market growth.
In the transportation sector, DME has gained traction as a potential replacement for diesel fuel, particularly in heavy-duty vehicles. Its high cetane number and clean combustion properties make it an attractive option for reducing emissions and improving air quality in urban areas. Several countries, including China, Japan, and Sweden, have conducted pilot projects and trials to assess the feasibility of DME as a transportation fuel, demonstrating growing interest in its adoption.
The industrial sector represents another significant market for DME, where it is used as a propellant in aerosol products, a refrigerant, and a blowing agent for foam insulation. The shift towards more environmentally friendly propellants has led to increased demand for DME in the personal care and household products industries. Additionally, DME's potential as a chemical feedstock for the production of olefins and other valuable chemicals has attracted attention from petrochemical companies looking to diversify their product portfolios.
In the energy sector, DME has shown promise as a clean-burning fuel for power generation and domestic cooking. Its ability to be easily liquefied and transported makes it an attractive option for remote areas lacking access to natural gas infrastructure. This has led to growing interest in DME as a solution for rural electrification and clean cooking initiatives in developing countries.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is expected to be the fastest-growing market for DME. This growth is primarily driven by government initiatives to reduce air pollution and promote cleaner energy sources. In China, policies supporting the use of DME as a transportation fuel and cooking gas have significantly boosted market demand.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in scaling up DME production and distribution infrastructure. The current global production capacity is limited, and significant investments are required to establish a robust supply chain. Additionally, the market faces competition from other alternative fuels and technologies, such as electric vehicles and hydrogen fuel cells, which may impact long-term demand projections.
To fully realize the potential of DME, continued research and development efforts are needed to improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and expand its applications. Collaboration between industry stakeholders, policymakers, and research institutions will be crucial in addressing these challenges and driving market growth.
DME Production Challenges
The production of dimethyl ether (DME) faces several significant challenges that impact its widespread adoption as an alternative fuel and chemical feedstock. One of the primary hurdles is the high capital cost associated with DME production facilities. The infrastructure required for large-scale DME production, including synthesis reactors, separation units, and storage systems, demands substantial initial investment, which can deter potential producers and investors.
Another critical challenge lies in the energy efficiency of the DME production process. While DME can be synthesized from various feedstocks, including natural gas, coal, and biomass, the conversion processes often involve multiple steps and energy-intensive operations. This results in a relatively low overall energy efficiency, which can affect the economic viability of DME production, especially when compared to conventional fuels.
The purity requirements for DME production also present technical difficulties. DME must meet stringent quality standards for use as a fuel or chemical intermediate, necessitating advanced purification techniques. Impurities in the final product can lead to performance issues in engines or affect downstream chemical processes, making efficient and cost-effective purification a crucial aspect of production.
Catalyst performance and longevity pose additional challenges in DME synthesis. The catalysts used in the production process are subject to deactivation and fouling, which can reduce conversion rates and product yield over time. Developing more robust and efficient catalysts that can withstand the harsh reaction conditions while maintaining high activity is an ongoing area of research and development.
Feedstock flexibility is another important consideration in DME production. While DME can be produced from various sources, optimizing the production process for different feedstocks requires significant engineering efforts. Each feedstock type presents unique challenges in terms of pretreatment, conversion efficiency, and impurity management, necessitating tailored production strategies.
Scaling up DME production to meet potential market demand also presents logistical and technical challenges. As production volumes increase, issues related to heat management, reactor design, and product handling become more complex. Ensuring consistent product quality and maintaining operational stability at larger scales requires sophisticated process control systems and engineering solutions.
Lastly, the integration of DME production with existing industrial infrastructure poses challenges. Retrofitting existing plants or designing new facilities that can efficiently produce DME alongside other products requires careful planning and significant investment. The need for specialized storage and transportation infrastructure for DME adds another layer of complexity to its production and distribution chain.
Another critical challenge lies in the energy efficiency of the DME production process. While DME can be synthesized from various feedstocks, including natural gas, coal, and biomass, the conversion processes often involve multiple steps and energy-intensive operations. This results in a relatively low overall energy efficiency, which can affect the economic viability of DME production, especially when compared to conventional fuels.
The purity requirements for DME production also present technical difficulties. DME must meet stringent quality standards for use as a fuel or chemical intermediate, necessitating advanced purification techniques. Impurities in the final product can lead to performance issues in engines or affect downstream chemical processes, making efficient and cost-effective purification a crucial aspect of production.
Catalyst performance and longevity pose additional challenges in DME synthesis. The catalysts used in the production process are subject to deactivation and fouling, which can reduce conversion rates and product yield over time. Developing more robust and efficient catalysts that can withstand the harsh reaction conditions while maintaining high activity is an ongoing area of research and development.
Feedstock flexibility is another important consideration in DME production. While DME can be produced from various sources, optimizing the production process for different feedstocks requires significant engineering efforts. Each feedstock type presents unique challenges in terms of pretreatment, conversion efficiency, and impurity management, necessitating tailored production strategies.
Scaling up DME production to meet potential market demand also presents logistical and technical challenges. As production volumes increase, issues related to heat management, reactor design, and product handling become more complex. Ensuring consistent product quality and maintaining operational stability at larger scales requires sophisticated process control systems and engineering solutions.
Lastly, the integration of DME production with existing industrial infrastructure poses challenges. Retrofitting existing plants or designing new facilities that can efficiently produce DME alongside other products requires careful planning and significant investment. The need for specialized storage and transportation infrastructure for DME adds another layer of complexity to its production and distribution chain.
Current DME Production Methods
01 Production of dimethyl ether
Various methods for producing dimethyl ether are described, including catalytic dehydration of methanol, direct synthesis from syngas, and conversion of hydrocarbons. These processes often involve specific catalysts and reaction conditions to optimize yield and selectivity.- Production of dimethyl ether: Various methods for producing dimethyl ether are described, including catalytic dehydration of methanol, direct synthesis from syngas, and conversion of other hydrocarbons. These processes often involve specific catalysts and reaction conditions to optimize yield and selectivity.
- Catalysts for dimethyl ether synthesis: Different types of catalysts are used in the production of dimethyl ether, including zeolites, metal oxides, and composite catalysts. The choice and preparation of catalysts significantly influence the efficiency and selectivity of the dimethyl ether synthesis process.
- Applications of dimethyl ether: Dimethyl ether has various applications, including use as a fuel additive, aerosol propellant, and refrigerant. It is also being explored as an alternative clean fuel for diesel engines and power generation due to its favorable combustion properties.
- Purification and separation of dimethyl ether: Methods for purifying and separating dimethyl ether from reaction mixtures or other compounds are described. These processes often involve distillation, adsorption, or membrane separation techniques to obtain high-purity dimethyl ether.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Research on the environmental impact and safety aspects of dimethyl ether production and use is ongoing. This includes studies on emissions reduction, storage safety, and handling procedures to ensure the sustainable and safe utilization of dimethyl ether in various applications.
02 Catalysts for dimethyl ether synthesis
Different types of catalysts are used in the production of dimethyl ether, including zeolites, metal oxides, and composite catalysts. The choice of catalyst can significantly affect the reaction efficiency, product selectivity, and overall process economics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of dimethyl ether
Dimethyl ether has various applications, including use as a fuel additive, aerosol propellant, and refrigerant. It is also being explored as a potential alternative fuel for diesel engines due to its clean-burning properties and high cetane number.Expand Specific Solutions04 Purification and separation of dimethyl ether
Methods for purifying and separating dimethyl ether from reaction mixtures or other compounds are described. These processes may involve distillation, adsorption, or membrane separation techniques to obtain high-purity dimethyl ether for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of dimethyl ether production and use. This includes developing more efficient production processes, reducing emissions, and ensuring safe handling and storage of the compound.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in DME Industry
The industrial challenges in the Dimethyl Ether (DME) value chain are characterized by a competitive landscape in various stages of development. The market is experiencing growth, driven by increasing demand for clean energy alternatives. Key players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., BASF, and Linde GmbH are investing in research and development to improve production efficiency and expand applications. The technology is maturing, with companies such as Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Processing and Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics leading innovations in catalysis and process optimization. However, the industry still faces challenges in scaling up production and establishing widespread infrastructure for DME distribution and utilization.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an advanced dimethyl ether (DME) production process using syngas derived from coal or natural gas. Their technology employs a single-step synthesis method, integrating methanol synthesis and dehydration into one reactor [1]. This process achieves higher conversion rates and energy efficiency compared to traditional two-step methods. Sinopec has also implemented a large-scale DME production facility with an annual capacity of 1 million tons, demonstrating the commercial viability of their technology [2]. Additionally, they have made progress in DME application as a clean fuel alternative, particularly in heavy-duty vehicles and power generation, addressing industrial challenges in the DME value chain [3].
Strengths: Integrated single-step synthesis process, large-scale production capabilities, and progress in DME applications. Weaknesses: Dependence on coal or natural gas feedstock, which may face environmental scrutiny.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed innovative catalysts for DME production, focusing on improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Their proprietary catalyst technology enables direct synthesis of DME from syngas, bypassing the methanol intermediate step [4]. This process results in higher yields and lower energy consumption. BASF has also made advancements in DME purification techniques, addressing the challenge of removing impurities that can affect fuel quality and engine performance [5]. Furthermore, they have explored the use of bio-based feedstocks for DME production, aligning with sustainability goals and potentially opening new market opportunities in the biofuels sector [6].
Strengths: Advanced catalyst technology, direct DME synthesis process, and progress in bio-based DME production. Weaknesses: May face competition in catalyst market and potential scalability challenges for bio-based processes.
DME Catalyst Innovations
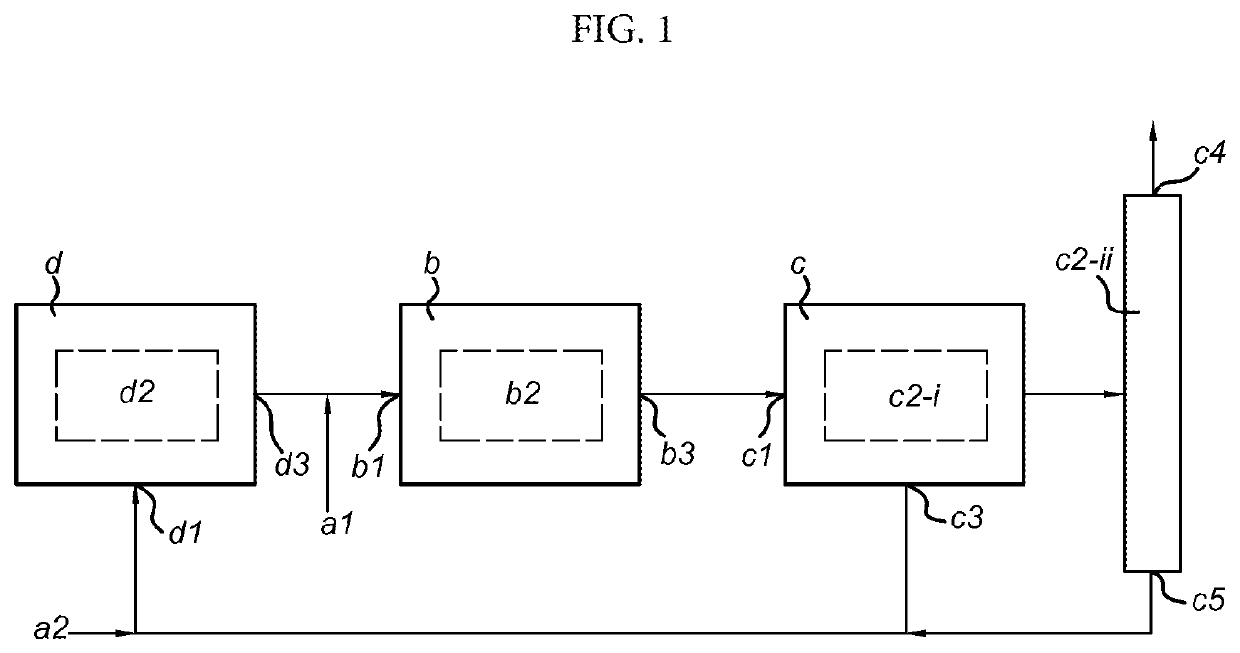
Process and system for producing dimethyl ether
PatentActiveUS11897839B2
Innovation
- A process combining conventional DME synthesis with a separation-enhanced reverse water gas shift reaction, allowing for flexible feedstock composition and reducing the need for CO2 recycles by converting CO2 to CO, thereby improving yield and reducing costs.
Process and system for producing dimethyl ether
PatentActiveUS20200399195A1
Innovation
- A process combining conventional DME synthesis with a separation-enhanced reverse water gas shift reaction, allowing for efficient DME production using any carbon oxide species, reducing the need for CO2 recycles, and minimizing methanol recycles, while utilizing a catalyst system capable of converting synthesis gas to DME.
DME Environmental Impact
Dimethyl ether (DME) has gained attention as a potential alternative fuel due to its clean-burning properties and versatile production methods. However, its environmental impact throughout the value chain requires careful consideration. The production of DME primarily involves the dehydration of methanol or direct synthesis from syngas, both of which have associated environmental implications.
In terms of greenhouse gas emissions, DME production can offer advantages over conventional fossil fuels when derived from renewable sources. Biomass-based DME production, for instance, can potentially achieve near-carbon neutrality, as the carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by the CO2 absorbed during biomass growth. However, when produced from fossil fuels, the overall carbon footprint may be comparable to or slightly lower than that of conventional diesel fuel, depending on the specific production process and energy sources used.
Water consumption and potential contamination are important environmental factors to consider in DME production. The methanol dehydration process requires significant amounts of water, and proper wastewater management is crucial to prevent the release of harmful chemicals into local ecosystems. Additionally, the use of catalysts in DME synthesis may introduce trace contaminants that need to be carefully managed and disposed of.
Air quality impacts of DME use are generally positive compared to conventional diesel fuel. DME combustion produces lower levels of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur oxides, contributing to reduced smog formation and improved urban air quality. This characteristic makes DME particularly attractive for use in heavy-duty vehicles and industrial applications in densely populated areas.
Land use changes associated with DME production, especially when derived from biomass feedstocks, can have significant environmental implications. Large-scale cultivation of energy crops for DME production may lead to deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and competition with food crops. Sustainable land management practices and careful selection of feedstock sources are essential to mitigate these potential negative impacts.
The transportation and storage of DME also present environmental considerations. While DME has a lower global warming potential as a greenhouse gas compared to methane, accidental releases during handling and distribution could still contribute to atmospheric warming. However, DME's properties allow for easier handling and storage compared to some other alternative fuels, potentially reducing the risk of spills and associated environmental contamination.
In conclusion, while DME offers several environmental benefits, particularly in terms of air quality and potential carbon neutrality, its overall environmental impact depends heavily on the production methods, feedstock sources, and management practices employed throughout the value chain. Continued research and development efforts are needed to optimize DME production processes, improve energy efficiency, and minimize environmental impacts to fully realize its potential as a sustainable alternative fuel.
In terms of greenhouse gas emissions, DME production can offer advantages over conventional fossil fuels when derived from renewable sources. Biomass-based DME production, for instance, can potentially achieve near-carbon neutrality, as the carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by the CO2 absorbed during biomass growth. However, when produced from fossil fuels, the overall carbon footprint may be comparable to or slightly lower than that of conventional diesel fuel, depending on the specific production process and energy sources used.
Water consumption and potential contamination are important environmental factors to consider in DME production. The methanol dehydration process requires significant amounts of water, and proper wastewater management is crucial to prevent the release of harmful chemicals into local ecosystems. Additionally, the use of catalysts in DME synthesis may introduce trace contaminants that need to be carefully managed and disposed of.
Air quality impacts of DME use are generally positive compared to conventional diesel fuel. DME combustion produces lower levels of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur oxides, contributing to reduced smog formation and improved urban air quality. This characteristic makes DME particularly attractive for use in heavy-duty vehicles and industrial applications in densely populated areas.
Land use changes associated with DME production, especially when derived from biomass feedstocks, can have significant environmental implications. Large-scale cultivation of energy crops for DME production may lead to deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and competition with food crops. Sustainable land management practices and careful selection of feedstock sources are essential to mitigate these potential negative impacts.
The transportation and storage of DME also present environmental considerations. While DME has a lower global warming potential as a greenhouse gas compared to methane, accidental releases during handling and distribution could still contribute to atmospheric warming. However, DME's properties allow for easier handling and storage compared to some other alternative fuels, potentially reducing the risk of spills and associated environmental contamination.
In conclusion, while DME offers several environmental benefits, particularly in terms of air quality and potential carbon neutrality, its overall environmental impact depends heavily on the production methods, feedstock sources, and management practices employed throughout the value chain. Continued research and development efforts are needed to optimize DME production processes, improve energy efficiency, and minimize environmental impacts to fully realize its potential as a sustainable alternative fuel.
DME Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework for dimethyl ether (DME) plays a crucial role in shaping its value chain and addressing industrial challenges. As DME gains traction as a clean alternative fuel, governments worldwide are developing and refining regulations to ensure its safe production, storage, transportation, and use.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has included DME in its Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program, recognizing its potential as a renewable fuel. This inclusion provides incentives for DME production from renewable sources, encouraging investment in the sector. Additionally, the Department of Energy (DOE) has supported research and development efforts to advance DME technology and its applications.
The European Union has also taken steps to promote DME as a sustainable fuel option. The Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) includes DME as an eligible renewable fuel, setting targets for its use in the transportation sector. This regulatory support has spurred interest in DME production and utilization across EU member states.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have implemented policies to support DME adoption. China has included DME in its national energy strategy, offering tax incentives and subsidies for DME production and use. Japan has established safety standards for DME handling and storage, facilitating its integration into the existing energy infrastructure.
Safety regulations for DME handling and storage are critical components of the regulatory framework. International standards, such as those developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), provide guidelines for the safe handling, storage, and transportation of DME. These standards help harmonize practices across different regions and ensure consistent safety measures throughout the value chain.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in shaping the DME industry. Emissions standards for DME production facilities and end-use applications are being developed and refined to minimize environmental impact. Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies are being employed to evaluate the overall environmental footprint of DME, influencing policy decisions and market acceptance.
The regulatory landscape for DME is still evolving, with ongoing efforts to address gaps and harmonize standards across different jurisdictions. Industry stakeholders are actively engaging with regulatory bodies to provide input and shape policies that support the growth of the DME market while ensuring safety and environmental protection.
As the DME value chain continues to develop, regulatory frameworks will need to adapt to address emerging challenges and opportunities. This may include updating fuel quality standards, refining safety protocols for new applications, and developing incentives to promote DME adoption in various sectors.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has included DME in its Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program, recognizing its potential as a renewable fuel. This inclusion provides incentives for DME production from renewable sources, encouraging investment in the sector. Additionally, the Department of Energy (DOE) has supported research and development efforts to advance DME technology and its applications.
The European Union has also taken steps to promote DME as a sustainable fuel option. The Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) includes DME as an eligible renewable fuel, setting targets for its use in the transportation sector. This regulatory support has spurred interest in DME production and utilization across EU member states.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have implemented policies to support DME adoption. China has included DME in its national energy strategy, offering tax incentives and subsidies for DME production and use. Japan has established safety standards for DME handling and storage, facilitating its integration into the existing energy infrastructure.
Safety regulations for DME handling and storage are critical components of the regulatory framework. International standards, such as those developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), provide guidelines for the safe handling, storage, and transportation of DME. These standards help harmonize practices across different regions and ensure consistent safety measures throughout the value chain.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in shaping the DME industry. Emissions standards for DME production facilities and end-use applications are being developed and refined to minimize environmental impact. Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies are being employed to evaluate the overall environmental footprint of DME, influencing policy decisions and market acceptance.
The regulatory landscape for DME is still evolving, with ongoing efforts to address gaps and harmonize standards across different jurisdictions. Industry stakeholders are actively engaging with regulatory bodies to provide input and shape policies that support the growth of the DME market while ensuring safety and environmental protection.
As the DME value chain continues to develop, regulatory frameworks will need to adapt to address emerging challenges and opportunities. This may include updating fuel quality standards, refining safety protocols for new applications, and developing incentives to promote DME adoption in various sectors.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!