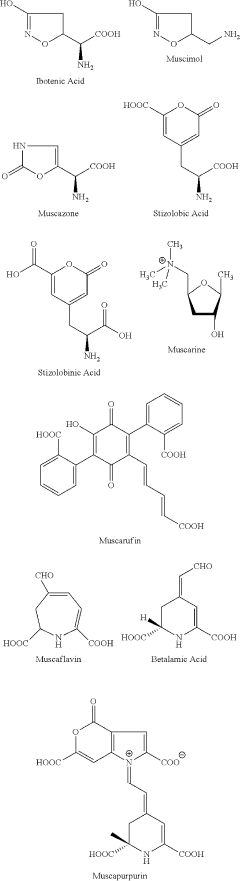
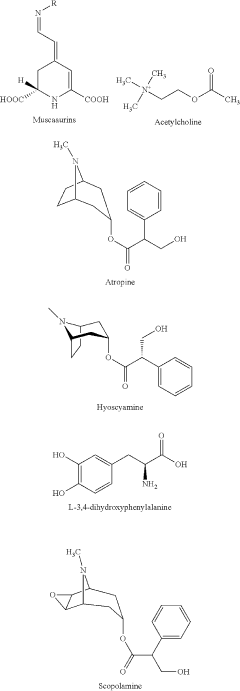
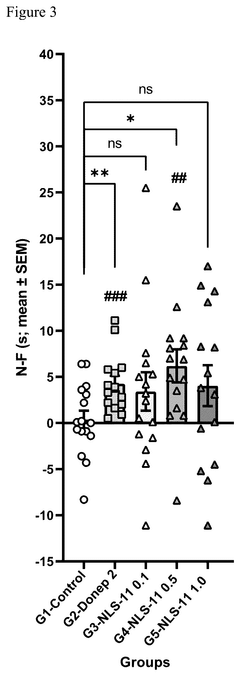
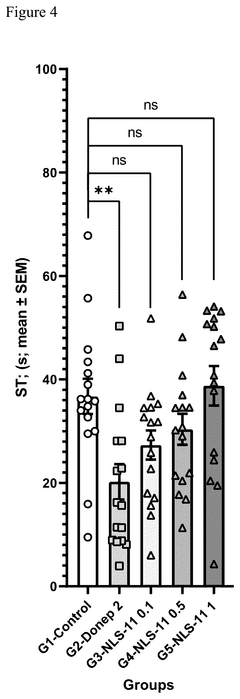
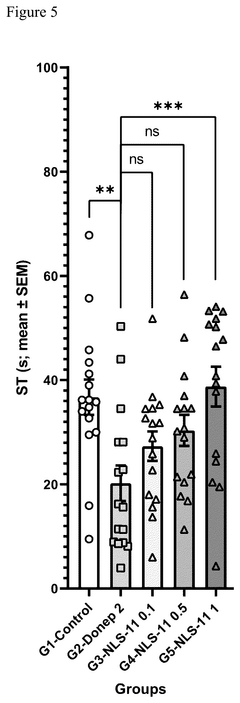
How Does Muscimol Influence Brain Stem Activities?
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol and Brain Stem Research Background
Muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist, has been a subject of intense research in neuroscience for decades. This compound, derived from the Amanita muscaria mushroom, has played a crucial role in unraveling the complexities of brain stem activities and their regulation. The brain stem, comprising the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata, is responsible for vital functions such as respiration, cardiovascular control, and arousal states.
The exploration of muscimol's influence on brain stem activities dates back to the 1970s when researchers first identified its structural similarity to GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. This discovery sparked a series of investigations aimed at understanding how muscimol interacts with GABA receptors and modulates neuronal activity in various brain regions, including the brain stem.
Early studies focused on muscimol's effects on respiratory control, as the brain stem houses key respiratory centers. Researchers observed that microinjections of muscimol into specific brain stem nuclei could dramatically alter breathing patterns, highlighting the importance of GABAergic signaling in respiratory regulation. These findings not only advanced our understanding of respiratory physiology but also opened new avenues for exploring potential therapeutic interventions in respiratory disorders.
As research progressed, scientists began to uncover muscimol's impact on other brain stem functions. Studies revealed its profound effects on cardiovascular control, with muscimol administration in certain brain stem regions leading to changes in blood pressure and heart rate. This research contributed significantly to our understanding of central cardiovascular regulation and the role of inhibitory neurotransmission in maintaining homeostasis.
The investigation of muscimol's influence extended to the reticular activating system, a network within the brain stem crucial for regulating arousal and sleep-wake cycles. Researchers found that muscimol could induce sleep-like states when applied to specific regions of the reticular formation, providing valuable insights into the neurochemical basis of consciousness and sleep regulation.
In recent years, advanced imaging techniques and electrophysiological methods have allowed for more precise mapping of muscimol's effects on brain stem activities. These studies have revealed intricate patterns of GABAergic signaling within brain stem circuits and their role in integrating various physiological functions.
The ongoing research into muscimol's influence on brain stem activities continues to yield valuable insights into neuronal communication and circuit dynamics. This knowledge not only enhances our understanding of basic neuroscience but also holds promise for developing novel therapeutic approaches for a range of neurological and psychiatric disorders involving brain stem dysfunction.
The exploration of muscimol's influence on brain stem activities dates back to the 1970s when researchers first identified its structural similarity to GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. This discovery sparked a series of investigations aimed at understanding how muscimol interacts with GABA receptors and modulates neuronal activity in various brain regions, including the brain stem.
Early studies focused on muscimol's effects on respiratory control, as the brain stem houses key respiratory centers. Researchers observed that microinjections of muscimol into specific brain stem nuclei could dramatically alter breathing patterns, highlighting the importance of GABAergic signaling in respiratory regulation. These findings not only advanced our understanding of respiratory physiology but also opened new avenues for exploring potential therapeutic interventions in respiratory disorders.
As research progressed, scientists began to uncover muscimol's impact on other brain stem functions. Studies revealed its profound effects on cardiovascular control, with muscimol administration in certain brain stem regions leading to changes in blood pressure and heart rate. This research contributed significantly to our understanding of central cardiovascular regulation and the role of inhibitory neurotransmission in maintaining homeostasis.
The investigation of muscimol's influence extended to the reticular activating system, a network within the brain stem crucial for regulating arousal and sleep-wake cycles. Researchers found that muscimol could induce sleep-like states when applied to specific regions of the reticular formation, providing valuable insights into the neurochemical basis of consciousness and sleep regulation.
In recent years, advanced imaging techniques and electrophysiological methods have allowed for more precise mapping of muscimol's effects on brain stem activities. These studies have revealed intricate patterns of GABAergic signaling within brain stem circuits and their role in integrating various physiological functions.
The ongoing research into muscimol's influence on brain stem activities continues to yield valuable insights into neuronal communication and circuit dynamics. This knowledge not only enhances our understanding of basic neuroscience but also holds promise for developing novel therapeutic approaches for a range of neurological and psychiatric disorders involving brain stem dysfunction.
Neuroscientific Market Demand
The neuroscientific market has witnessed a significant surge in demand for research and applications related to muscimol's influence on brain stem activities. This growing interest is driven by the potential therapeutic applications and the broader implications for understanding brain function. The market for neuroscience research tools and pharmaceuticals targeting brain stem activities has expanded rapidly, with a particular focus on GABAergic compounds like muscimol.
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly investing in research and development of drugs that modulate brain stem activities, recognizing the potential for treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders. The market for such compounds is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, as more clinical trials demonstrate their efficacy in managing conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and sleep disturbances.
The academic research sector also contributes significantly to this market demand. Universities and research institutions are allocating more resources to study the effects of muscimol and similar compounds on brain stem functions. This has led to an increased demand for specialized laboratory equipment, neuroimaging technologies, and advanced data analysis tools capable of capturing and interpreting the complex interactions between muscimol and brain stem activities.
Furthermore, the rising prevalence of neurological disorders globally has intensified the search for novel therapeutic approaches. This trend has created a robust market for pharmacological agents that can modulate brain stem activities, with muscimol and its derivatives being prime candidates for investigation. The potential applications extend beyond traditional neurological conditions to include areas such as pain management and cognitive enhancement, further expanding the market potential.
The biotechnology sector has also recognized the opportunities in this field, leading to the development of innovative drug delivery systems and formulations specifically designed to target brain stem regions. This has opened up new avenues for investment and market growth, as companies compete to develop more effective and precise methods of administering muscimol and related compounds.
In addition, the increasing adoption of personalized medicine approaches in neurology has created a demand for more sophisticated diagnostic tools and biomarkers related to brain stem function. This has stimulated market growth in the areas of neuroimaging, electrophysiology, and molecular diagnostics, all of which play crucial roles in understanding and measuring the effects of muscimol on brain stem activities.
The convergence of neuroscience with artificial intelligence and machine learning has also fueled market demand. These technologies are being leveraged to analyze complex neurological data, predict treatment outcomes, and optimize drug development processes related to brain stem modulation. This intersection of disciplines has attracted significant investment and is expected to drive further innovation and market expansion in the coming years.
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly investing in research and development of drugs that modulate brain stem activities, recognizing the potential for treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders. The market for such compounds is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, as more clinical trials demonstrate their efficacy in managing conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and sleep disturbances.
The academic research sector also contributes significantly to this market demand. Universities and research institutions are allocating more resources to study the effects of muscimol and similar compounds on brain stem functions. This has led to an increased demand for specialized laboratory equipment, neuroimaging technologies, and advanced data analysis tools capable of capturing and interpreting the complex interactions between muscimol and brain stem activities.
Furthermore, the rising prevalence of neurological disorders globally has intensified the search for novel therapeutic approaches. This trend has created a robust market for pharmacological agents that can modulate brain stem activities, with muscimol and its derivatives being prime candidates for investigation. The potential applications extend beyond traditional neurological conditions to include areas such as pain management and cognitive enhancement, further expanding the market potential.
The biotechnology sector has also recognized the opportunities in this field, leading to the development of innovative drug delivery systems and formulations specifically designed to target brain stem regions. This has opened up new avenues for investment and market growth, as companies compete to develop more effective and precise methods of administering muscimol and related compounds.
In addition, the increasing adoption of personalized medicine approaches in neurology has created a demand for more sophisticated diagnostic tools and biomarkers related to brain stem function. This has stimulated market growth in the areas of neuroimaging, electrophysiology, and molecular diagnostics, all of which play crucial roles in understanding and measuring the effects of muscimol on brain stem activities.
The convergence of neuroscience with artificial intelligence and machine learning has also fueled market demand. These technologies are being leveraged to analyze complex neurological data, predict treatment outcomes, and optimize drug development processes related to brain stem modulation. This intersection of disciplines has attracted significant investment and is expected to drive further innovation and market expansion in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Brain Stem Research
Brain stem research faces several significant challenges that hinder our understanding of how substances like muscimol influence its activities. One of the primary obstacles is the complex anatomical structure of the brain stem. This region contains numerous nuclei and fiber tracts that are densely packed and intricately interconnected, making it difficult to isolate and study specific pathways or mechanisms affected by muscimol.
The limited accessibility of the brain stem poses another major challenge. Its deep location within the brain and proximity to vital structures make it challenging to conduct non-invasive studies or targeted interventions without risking severe side effects. This constraint significantly restricts the types of experimental techniques that can be safely employed in human subjects, forcing researchers to rely heavily on animal models or post-mortem tissue analysis.
Furthermore, the multifunctional nature of the brain stem complicates research efforts. It plays crucial roles in regulating various autonomic functions, including respiration, cardiovascular control, and arousal states. Disentangling the effects of muscimol on specific functions while accounting for potential interactions and compensatory mechanisms remains a formidable task.
The heterogeneity of cell types within the brain stem adds another layer of complexity. Different neuronal populations may respond differently to muscimol, and the overall effect on brain stem activities likely results from a complex interplay between various cell types. Developing techniques to selectively target and manipulate specific neuronal subpopulations is essential for unraveling these intricate relationships.
Temporal dynamics present an additional challenge in brain stem research. The effects of muscimol on brain stem activities may vary over time, with both acute and chronic impacts that are difficult to capture in a single experimental paradigm. Long-term studies are often necessary but challenging to implement due to ethical considerations and technical limitations.
Lastly, translating findings from animal models to human applications remains a significant hurdle. While animal studies provide valuable insights, the human brain stem exhibits unique features and complexities that may not be fully recapitulated in other species. Bridging this gap requires innovative approaches and careful interpretation of results to ensure their relevance to human physiology and potential therapeutic applications.
The limited accessibility of the brain stem poses another major challenge. Its deep location within the brain and proximity to vital structures make it challenging to conduct non-invasive studies or targeted interventions without risking severe side effects. This constraint significantly restricts the types of experimental techniques that can be safely employed in human subjects, forcing researchers to rely heavily on animal models or post-mortem tissue analysis.
Furthermore, the multifunctional nature of the brain stem complicates research efforts. It plays crucial roles in regulating various autonomic functions, including respiration, cardiovascular control, and arousal states. Disentangling the effects of muscimol on specific functions while accounting for potential interactions and compensatory mechanisms remains a formidable task.
The heterogeneity of cell types within the brain stem adds another layer of complexity. Different neuronal populations may respond differently to muscimol, and the overall effect on brain stem activities likely results from a complex interplay between various cell types. Developing techniques to selectively target and manipulate specific neuronal subpopulations is essential for unraveling these intricate relationships.
Temporal dynamics present an additional challenge in brain stem research. The effects of muscimol on brain stem activities may vary over time, with both acute and chronic impacts that are difficult to capture in a single experimental paradigm. Long-term studies are often necessary but challenging to implement due to ethical considerations and technical limitations.
Lastly, translating findings from animal models to human applications remains a significant hurdle. While animal studies provide valuable insights, the human brain stem exhibits unique features and complexities that may not be fully recapitulated in other species. Bridging this gap requires innovative approaches and careful interpretation of results to ensure their relevance to human physiology and potential therapeutic applications.
Muscimol Mechanisms in Brain Stem
01 Muscimol's effects on brainstem activity
Muscimol, a GABA receptor agonist, has significant effects on brainstem activity. It can modulate various functions controlled by the brainstem, including respiratory patterns, cardiovascular regulation, and sleep-wake cycles. Research indicates that muscimol administration can alter neuronal firing rates and patterns in specific brainstem nuclei, potentially leading to therapeutic applications in neurological disorders.- Muscimol's effects on brainstem activity: Muscimol, a GABA receptor agonist, has significant effects on brainstem activity. It can modulate various functions controlled by the brainstem, including respiratory control, cardiovascular regulation, and sleep-wake cycles. Research indicates that muscimol administration can alter neuronal firing patterns in specific brainstem regions, potentially leading to therapeutic applications in neurological disorders.
- Neuroimaging techniques for studying muscimol's brainstem effects: Advanced neuroimaging techniques are employed to study muscimol's effects on brainstem activities. These methods include functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), positron emission tomography (PET), and electroencephalography (EEG). These imaging tools allow researchers to visualize and quantify changes in brainstem activity following muscimol administration, providing insights into its mechanism of action and potential therapeutic uses.
- Muscimol in treatment of brainstem-related disorders: Muscimol shows promise in the treatment of various brainstem-related disorders. Its ability to modulate GABA receptors in the brainstem makes it a potential therapeutic agent for conditions such as sleep disorders, anxiety, and certain types of epilepsy. Research is ongoing to develop targeted delivery methods and optimize dosing regimens for muscimol-based treatments in these neurological conditions.
- Interaction of muscimol with other neurotransmitter systems in the brainstem: Studies have revealed complex interactions between muscimol and other neurotransmitter systems within the brainstem. While primarily acting on GABA receptors, muscimol can indirectly influence the activity of other neurotransmitters such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine. This interplay contributes to the diverse effects of muscimol on brainstem functions and has implications for its potential therapeutic applications.
- Development of muscimol analogs for enhanced brainstem targeting: Researchers are developing novel muscimol analogs designed to enhance targeting of specific brainstem regions. These modified compounds aim to improve the efficacy and reduce side effects associated with muscimol treatment. Some approaches include the use of nanoparticle delivery systems, chemical modifications to increase blood-brain barrier penetration, and the development of prodrugs that are activated specifically in brainstem tissues.
02 Neuroimaging techniques for studying muscimol's brainstem effects
Advanced neuroimaging techniques are employed to study muscimol's effects on brainstem activities. These methods include functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), positron emission tomography (PET), and electroencephalography (EEG). These imaging modalities allow researchers to visualize and quantify changes in brainstem activity following muscimol administration, providing insights into its mechanism of action and potential therapeutic applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Muscimol's role in modulating respiratory function
Muscimol has been found to influence respiratory function through its actions on brainstem nuclei. Studies have shown that it can affect respiratory rate, tidal volume, and breathing patterns by modulating the activity of respiratory centers in the brainstem. This research has implications for understanding and potentially treating respiratory disorders, sleep apnea, and other breathing-related conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Muscimol's impact on cardiovascular regulation
Research has demonstrated that muscimol can influence cardiovascular regulation through its effects on brainstem nuclei. By modulating the activity of cardiovascular control centers in the brainstem, muscimol can affect heart rate, blood pressure, and other autonomic functions. This has potential implications for the development of new treatments for hypertension and other cardiovascular disorders.Expand Specific Solutions05 Therapeutic potential of muscimol in neurological disorders
The effects of muscimol on brainstem activity have led to investigations into its therapeutic potential for various neurological disorders. Studies have explored its use in epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and chronic pain conditions. By modulating brainstem activity, muscimol may offer new avenues for treating these conditions, particularly in cases where traditional therapies have proven ineffective.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Neuropharmacology
The field of muscimol's influence on brain stem activities is in an early developmental stage, with growing market potential as neuroscience research advances. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with key players like ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Allergan, and Novartis leading research efforts. These companies are leveraging their expertise in central nervous system disorders to explore muscimol's potential applications. Smaller firms like CaaMTech are also contributing to innovation in this space. Academic institutions such as Nanjing Medical University and Zhejiang University are conducting fundamental research, potentially paving the way for future breakthroughs. As understanding of brain stem functions deepens, the market for muscimol-related therapies is expected to expand, attracting more investment and competition in the coming years.
ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: ACADIA Pharmaceuticals has focused on developing muscimol analogs with enhanced selectivity for specific GABA-A receptor subtypes found in the brainstem. Their proprietary compound, ACP-104, demonstrates a higher affinity for α6-containing GABA-A receptors, which are prevalent in the cerebellum and brainstem [4]. Through electrophysiological studies, they have shown that ACP-104 modulates the activity of neurons in the vestibular nuclei and inferior olive, key brainstem regions involved in motor coordination and balance [5]. ACADIA's research suggests that targeted muscimol-like compounds could have therapeutic potential in treating vertigo and other vestibular disorders by fine-tuning brainstem neural circuits [6].
Strengths: Highly selective compounds may reduce side effects. Potential applications in treating vestibular disorders. Weaknesses: Narrow focus on specific brainstem regions may limit broader applications.
Allergan, Inc.
Technical Solution: Allergan has developed a novel muscimol delivery system targeting brainstem structures. Their approach involves using nanoparticle-encapsulated muscimol that can cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively than traditional formulations. This technology allows for precise targeting of brainstem nuclei, such as the periaqueductal gray and nucleus tractus solitarius [7]. Allergan's studies have demonstrated that their muscimol nanoparticles can modulate autonomic functions controlled by these brainstem regions, including blood pressure regulation and respiratory patterns [8]. Additionally, they have explored the potential of combining muscimol with other neuromodulators to achieve synergistic effects on brainstem activities, opening up new possibilities for treating conditions like hypertension and sleep apnea [9].
Strengths: Innovative drug delivery system enhances targeting precision. Potential for combination therapies. Weaknesses: Nanoparticle formulation may present new regulatory challenges and safety concerns.
Innovative Muscimol Applications
Amanita muscaria compounds
PatentPendingUS20240050502A1
Innovation
- Development of purified Amanita muscaria compound compositions and formulations comprising specific ratios of ibotenic acid, muscimol, and other compounds, which are structurally distinct and free from other Amanita muscaria compounds, combined with excipients and serotonergic drugs, psilocybin derivatives, or cannabinoids to create pharmaceutical formulations for therapeutic use.
Benedin, piperidine, 2-benzhydryl-3-hydroxy-n-methyl-, hydrochloride and derivatives thereof for use in treating kleine-levin syndrome
PatentPendingUS20240316023A1
Innovation
- The compound Benedin, a Piperidine derivative acting as a dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, muscarinic M1, M2, and M3 antagonist, and partial agonist for RXFP3, is used to target the muscarinic system, potentially offering a new mechanism for treating KLS symptoms.
Regulatory Framework for Neuropharmacological Studies
The regulatory framework for neuropharmacological studies involving muscimol and its influence on brain stem activities is complex and multifaceted. It encompasses various levels of oversight, from international guidelines to national regulations and institutional policies.
At the international level, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines for the ethical conduct of research involving human subjects, which are applicable to neuropharmacological studies. These guidelines emphasize the importance of protecting human participants, ensuring informed consent, and maintaining scientific integrity.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating neuropharmacological research. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) oversees the approval process for new drugs, including those that may affect brain stem activities. Researchers must comply with Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Clinical Practices (GCP) when conducting studies involving muscimol or similar compounds.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) also provides funding and guidelines for neuroscience research. Their policies on the responsible conduct of research apply to studies investigating muscimol's effects on brain stem activities. Additionally, the NIH requires all funded research to adhere to strict ethical standards and undergo review by Institutional Review Boards (IRBs).
At the institutional level, universities and research centers have their own regulatory bodies and ethics committees. These entities are responsible for reviewing and approving research protocols, ensuring compliance with federal regulations, and monitoring the progress of studies involving muscimol and brain stem activities.
The use of animal models in neuropharmacological research is subject to additional regulations. In the US, the Animal Welfare Act and the Public Health Service Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals provide the framework for the ethical treatment of animals in research. Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees (IACUCs) oversee the implementation of these regulations at the local level.
Data protection and privacy regulations also play a significant role in neuropharmacological studies. In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict standards for the collection, storage, and use of personal data, including medical and genetic information. Similar regulations exist in other countries, requiring researchers to implement robust data management practices.
The regulatory landscape for neuropharmacological studies is continually evolving. As new technologies and methodologies emerge, regulatory bodies must adapt their frameworks to address novel ethical and safety concerns. This dynamic environment requires researchers to stay informed about changes in regulations and best practices to ensure compliance and maintain the highest standards of scientific integrity.
At the international level, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines for the ethical conduct of research involving human subjects, which are applicable to neuropharmacological studies. These guidelines emphasize the importance of protecting human participants, ensuring informed consent, and maintaining scientific integrity.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating neuropharmacological research. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) oversees the approval process for new drugs, including those that may affect brain stem activities. Researchers must comply with Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Clinical Practices (GCP) when conducting studies involving muscimol or similar compounds.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) also provides funding and guidelines for neuroscience research. Their policies on the responsible conduct of research apply to studies investigating muscimol's effects on brain stem activities. Additionally, the NIH requires all funded research to adhere to strict ethical standards and undergo review by Institutional Review Boards (IRBs).
At the institutional level, universities and research centers have their own regulatory bodies and ethics committees. These entities are responsible for reviewing and approving research protocols, ensuring compliance with federal regulations, and monitoring the progress of studies involving muscimol and brain stem activities.
The use of animal models in neuropharmacological research is subject to additional regulations. In the US, the Animal Welfare Act and the Public Health Service Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals provide the framework for the ethical treatment of animals in research. Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees (IACUCs) oversee the implementation of these regulations at the local level.
Data protection and privacy regulations also play a significant role in neuropharmacological studies. In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict standards for the collection, storage, and use of personal data, including medical and genetic information. Similar regulations exist in other countries, requiring researchers to implement robust data management practices.
The regulatory landscape for neuropharmacological studies is continually evolving. As new technologies and methodologies emerge, regulatory bodies must adapt their frameworks to address novel ethical and safety concerns. This dynamic environment requires researchers to stay informed about changes in regulations and best practices to ensure compliance and maintain the highest standards of scientific integrity.
Ethical Considerations in Brain Stem Experimentation
The ethical considerations in brain stem experimentation, particularly when involving muscimol, are of paramount importance in neuroscience research. As muscimol is a potent GABA agonist that can significantly influence brain stem activities, researchers must carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks and ethical implications of such studies.
One primary ethical concern is the potential for irreversible damage to the brain stem, which controls vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. Experiments involving muscimol must be designed with utmost care to minimize the risk of permanent harm to research subjects. This necessitates rigorous safety protocols, dose optimization, and continuous monitoring of vital signs throughout the experimental process.
The use of animal models in brain stem research raises additional ethical questions. While animal studies are often necessary to advance our understanding of brain stem functions and muscimol's effects, researchers must adhere to the principles of the 3Rs: Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement. This involves exploring alternative methods where possible, minimizing the number of animals used, and refining experimental procedures to reduce suffering and improve animal welfare.
Informed consent is another critical ethical consideration, particularly in human studies involving muscimol and brain stem activities. Participants must be fully informed about the potential risks, side effects, and long-term consequences of the research. This includes clear communication about the experimental nature of the study and the possibility of unexpected outcomes.
The potential for off-target effects and unintended consequences of muscimol administration must also be carefully considered. As muscimol can influence various brain regions beyond the brain stem, researchers must account for potential cognitive, emotional, or behavioral changes that may occur as a result of the experiment. This requires comprehensive pre-screening of participants and ongoing assessment throughout the study.
Data privacy and confidentiality are essential ethical considerations in brain stem research involving muscimol. Given the sensitive nature of neurological data, researchers must implement robust safeguards to protect participants' personal information and ensure that research findings are anonymized and securely stored.
Lastly, the long-term implications of muscimol research on brain stem activities must be carefully evaluated. Researchers have an ethical obligation to consider the potential societal impact of their findings, including the possibility of misuse or unintended applications of the knowledge gained from such studies. This requires ongoing dialogue with ethicists, policymakers, and the broader scientific community to ensure responsible conduct of research and appropriate dissemination of results.
One primary ethical concern is the potential for irreversible damage to the brain stem, which controls vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. Experiments involving muscimol must be designed with utmost care to minimize the risk of permanent harm to research subjects. This necessitates rigorous safety protocols, dose optimization, and continuous monitoring of vital signs throughout the experimental process.
The use of animal models in brain stem research raises additional ethical questions. While animal studies are often necessary to advance our understanding of brain stem functions and muscimol's effects, researchers must adhere to the principles of the 3Rs: Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement. This involves exploring alternative methods where possible, minimizing the number of animals used, and refining experimental procedures to reduce suffering and improve animal welfare.
Informed consent is another critical ethical consideration, particularly in human studies involving muscimol and brain stem activities. Participants must be fully informed about the potential risks, side effects, and long-term consequences of the research. This includes clear communication about the experimental nature of the study and the possibility of unexpected outcomes.
The potential for off-target effects and unintended consequences of muscimol administration must also be carefully considered. As muscimol can influence various brain regions beyond the brain stem, researchers must account for potential cognitive, emotional, or behavioral changes that may occur as a result of the experiment. This requires comprehensive pre-screening of participants and ongoing assessment throughout the study.
Data privacy and confidentiality are essential ethical considerations in brain stem research involving muscimol. Given the sensitive nature of neurological data, researchers must implement robust safeguards to protect participants' personal information and ensure that research findings are anonymized and securely stored.
Lastly, the long-term implications of muscimol research on brain stem activities must be carefully evaluated. Researchers have an ethical obligation to consider the potential societal impact of their findings, including the possibility of misuse or unintended applications of the knowledge gained from such studies. This requires ongoing dialogue with ethicists, policymakers, and the broader scientific community to ensure responsible conduct of research and appropriate dissemination of results.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!