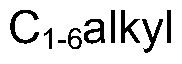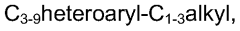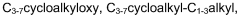Muscimol's Application in Pain Management Protocols
JUL 4, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Background
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has emerged as a promising compound in the field of pain management. Derived from the Amanita muscaria mushroom, this naturally occurring psychoactive alkaloid has been the subject of extensive research due to its potential analgesic properties. The exploration of muscimol's application in pain management protocols represents a significant shift in the approach to treating chronic and acute pain conditions.
The historical context of muscimol's discovery dates back to the 1960s when it was first isolated and characterized. Initially, its psychoactive effects were the primary focus of research, but over time, scientists began to recognize its potential in modulating pain perception. This shift in focus aligns with the broader trend in pain management research, which seeks to develop alternatives to traditional opioid-based treatments.
Muscimol's mechanism of action primarily involves its interaction with GABA-A receptors in the central nervous system. By enhancing GABAergic neurotransmission, muscimol induces inhibitory effects that can potentially modulate pain signals. This unique mode of action distinguishes it from conventional analgesics and opens up new possibilities for pain management strategies.
The evolution of muscimol research in pain management has been marked by several key milestones. Early animal studies demonstrated its analgesic effects in various pain models, paving the way for more targeted investigations. Subsequent research has focused on optimizing delivery methods, understanding dose-response relationships, and exploring potential synergistic effects with other pain management therapies.
Recent advancements in neuropharmacology and pain science have further elucidated the complex interplay between GABAergic systems and pain pathways. This has led to a renewed interest in muscimol and other GABA-A receptor modulators as potential therapeutic agents for chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and inflammatory pain disorders.
The current landscape of muscimol research in pain management is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach, involving neuroscientists, pharmacologists, and clinicians. This collaborative effort aims to translate preclinical findings into viable clinical applications, addressing challenges such as bioavailability, side effect profiles, and long-term efficacy.
As the field progresses, the integration of muscimol into comprehensive pain management protocols represents a promising frontier. Researchers are exploring its potential as both a standalone treatment and as part of combination therapies, aiming to leverage its unique pharmacological profile to enhance overall pain relief while minimizing adverse effects associated with traditional analgesics.
The historical context of muscimol's discovery dates back to the 1960s when it was first isolated and characterized. Initially, its psychoactive effects were the primary focus of research, but over time, scientists began to recognize its potential in modulating pain perception. This shift in focus aligns with the broader trend in pain management research, which seeks to develop alternatives to traditional opioid-based treatments.
Muscimol's mechanism of action primarily involves its interaction with GABA-A receptors in the central nervous system. By enhancing GABAergic neurotransmission, muscimol induces inhibitory effects that can potentially modulate pain signals. This unique mode of action distinguishes it from conventional analgesics and opens up new possibilities for pain management strategies.
The evolution of muscimol research in pain management has been marked by several key milestones. Early animal studies demonstrated its analgesic effects in various pain models, paving the way for more targeted investigations. Subsequent research has focused on optimizing delivery methods, understanding dose-response relationships, and exploring potential synergistic effects with other pain management therapies.
Recent advancements in neuropharmacology and pain science have further elucidated the complex interplay between GABAergic systems and pain pathways. This has led to a renewed interest in muscimol and other GABA-A receptor modulators as potential therapeutic agents for chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and inflammatory pain disorders.
The current landscape of muscimol research in pain management is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach, involving neuroscientists, pharmacologists, and clinicians. This collaborative effort aims to translate preclinical findings into viable clinical applications, addressing challenges such as bioavailability, side effect profiles, and long-term efficacy.
As the field progresses, the integration of muscimol into comprehensive pain management protocols represents a promising frontier. Researchers are exploring its potential as both a standalone treatment and as part of combination therapies, aiming to leverage its unique pharmacological profile to enhance overall pain relief while minimizing adverse effects associated with traditional analgesics.
Pain Management Market
The global pain management market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and rising awareness about pain management options. The market encompasses a wide range of products and services, including pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and alternative therapies. As of 2021, the pain management market was valued at approximately $73.4 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% through 2028.
Pharmaceuticals continue to dominate the pain management market, accounting for over 60% of the total market share. This segment includes both over-the-counter and prescription medications, with opioids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and local anesthetics being the primary categories. However, concerns over opioid addiction and side effects have led to increased demand for alternative pain management solutions.
The medical devices segment, including neurostimulation devices, analgesic infusion pumps, and ablation devices, is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to technological advancements and the increasing adoption of minimally invasive procedures for pain management.
Geographically, North America holds the largest share of the pain management market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, accounts for a significant portion of the global market due to its high healthcare expenditure and advanced healthcare infrastructure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to present lucrative growth opportunities in the coming years.
Key market players in the pain management industry include Pfizer Inc., Johnson & Johnson, Merck & Co., Inc., Novartis AG, and Abbott Laboratories. These companies are focusing on research and development to introduce innovative pain management solutions and expand their product portfolios.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the pain management market. While elective procedures and hospital visits decreased during the initial stages of the pandemic, there has been an increased focus on telemedicine and remote pain management solutions. This shift is expected to continue influencing the market dynamics in the post-pandemic era.
Looking ahead, the pain management market is poised for further growth, driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of chronic pain conditions, growing geriatric population, and advancements in pain management technologies. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in pain management protocols is expected to open up new avenues for market expansion and improved patient outcomes.
Pharmaceuticals continue to dominate the pain management market, accounting for over 60% of the total market share. This segment includes both over-the-counter and prescription medications, with opioids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and local anesthetics being the primary categories. However, concerns over opioid addiction and side effects have led to increased demand for alternative pain management solutions.
The medical devices segment, including neurostimulation devices, analgesic infusion pumps, and ablation devices, is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to technological advancements and the increasing adoption of minimally invasive procedures for pain management.
Geographically, North America holds the largest share of the pain management market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, accounts for a significant portion of the global market due to its high healthcare expenditure and advanced healthcare infrastructure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to present lucrative growth opportunities in the coming years.
Key market players in the pain management industry include Pfizer Inc., Johnson & Johnson, Merck & Co., Inc., Novartis AG, and Abbott Laboratories. These companies are focusing on research and development to introduce innovative pain management solutions and expand their product portfolios.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the pain management market. While elective procedures and hospital visits decreased during the initial stages of the pandemic, there has been an increased focus on telemedicine and remote pain management solutions. This shift is expected to continue influencing the market dynamics in the post-pandemic era.
Looking ahead, the pain management market is poised for further growth, driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of chronic pain conditions, growing geriatric population, and advancements in pain management technologies. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in pain management protocols is expected to open up new avenues for market expansion and improved patient outcomes.
Muscimol Challenges
Despite the promising potential of muscimol in pain management, several significant challenges hinder its widespread application and clinical adoption. One of the primary obstacles is the compound's poor bioavailability when administered orally. Muscimol's hydrophilic nature limits its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier effectively, necessitating alternative delivery methods or chemical modifications to enhance its therapeutic efficacy.
Another major challenge lies in the potential for adverse side effects associated with muscimol use. As a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, muscimol can cause sedation, dizziness, and cognitive impairment, which may limit its practical application in pain management protocols, especially for patients who need to maintain alertness or perform complex tasks.
The narrow therapeutic window of muscimol presents an additional hurdle. Achieving the optimal balance between pain relief and minimizing side effects requires precise dosing, which can be challenging to maintain consistently across diverse patient populations. This necessitates the development of advanced drug delivery systems or formulations that allow for controlled release and targeted action.
Furthermore, the long-term effects of muscimol use in pain management remain largely unknown. Chronic administration may lead to tolerance or dependence, potentially reducing its effectiveness over time or creating withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation. Comprehensive long-term studies are needed to fully understand these risks and develop appropriate mitigation strategies.
Regulatory challenges also pose significant obstacles to muscimol's integration into mainstream pain management protocols. As a compound derived from psychoactive mushrooms, muscimol faces stringent regulatory scrutiny and potential legal barriers in many jurisdictions. Overcoming these regulatory hurdles requires extensive clinical trials and safety data to demonstrate its efficacy and safety profile conclusively.
Lastly, the scalability of muscimol production presents a challenge for its widespread adoption. Current methods of extraction from natural sources or chemical synthesis may not be sufficient to meet potential large-scale demand. Developing cost-effective and sustainable production methods is crucial for ensuring a stable supply chain and making muscimol-based therapies economically viable for widespread use in pain management.
Another major challenge lies in the potential for adverse side effects associated with muscimol use. As a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, muscimol can cause sedation, dizziness, and cognitive impairment, which may limit its practical application in pain management protocols, especially for patients who need to maintain alertness or perform complex tasks.
The narrow therapeutic window of muscimol presents an additional hurdle. Achieving the optimal balance between pain relief and minimizing side effects requires precise dosing, which can be challenging to maintain consistently across diverse patient populations. This necessitates the development of advanced drug delivery systems or formulations that allow for controlled release and targeted action.
Furthermore, the long-term effects of muscimol use in pain management remain largely unknown. Chronic administration may lead to tolerance or dependence, potentially reducing its effectiveness over time or creating withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation. Comprehensive long-term studies are needed to fully understand these risks and develop appropriate mitigation strategies.
Regulatory challenges also pose significant obstacles to muscimol's integration into mainstream pain management protocols. As a compound derived from psychoactive mushrooms, muscimol faces stringent regulatory scrutiny and potential legal barriers in many jurisdictions. Overcoming these regulatory hurdles requires extensive clinical trials and safety data to demonstrate its efficacy and safety profile conclusively.
Lastly, the scalability of muscimol production presents a challenge for its widespread adoption. Current methods of extraction from natural sources or chemical synthesis may not be sufficient to meet potential large-scale demand. Developing cost-effective and sustainable production methods is crucial for ensuring a stable supply chain and making muscimol-based therapies economically viable for widespread use in pain management.
Current Pain Protocols
01 Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol
Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include muscimol as an active ingredient, often in combination with other compounds or delivery systems to enhance its efficacy or target specific conditions.- Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol: Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include different formulations and delivery methods to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol. The compositions can be designed for treating neurological disorders, anxiety, or other conditions affected by GABA receptor modulation.
- Muscimol analogs and derivatives: Research focuses on developing and synthesizing muscimol analogs and derivatives. These modified compounds aim to improve upon the properties of muscimol, such as increased potency, selectivity, or reduced side effects. The analogs may have different chemical structures but retain or enhance the pharmacological activity of muscimol.
- Methods of administering muscimol: Various methods for administering muscimol are explored to optimize its therapeutic effects. These may include novel drug delivery systems, controlled release formulations, or targeted delivery to specific areas of the body. The administration methods aim to improve the drug's efficacy, reduce side effects, and enhance patient compliance.
- Combination therapies involving muscimol: Muscimol is studied in combination with other therapeutic agents to create synergistic effects or address multiple aspects of a condition. These combination therapies may involve other GABA receptor modulators, antidepressants, or compounds targeting different neurotransmitter systems. The goal is to enhance overall treatment efficacy and potentially reduce individual drug dosages.
- Diagnostic and research applications of muscimol: Muscimol and its derivatives are utilized in diagnostic and research applications related to neuroscience and pharmacology. These compounds may be used as tools to study GABA receptor function, neuronal activity, or as probes in imaging studies. They contribute to the understanding of brain function and the development of new therapeutic strategies.
02 Muscimol for neurological and psychiatric disorders
Muscimol is investigated for its potential in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. Its GABA-mimetic properties make it a candidate for conditions such as anxiety, epilepsy, and sleep disorders. Research focuses on optimizing its delivery and minimizing side effects.Expand Specific Solutions03 Novel delivery methods for muscimol
Innovative delivery methods are being developed to improve the administration of muscimol. These include transdermal patches, nasal sprays, and controlled-release formulations, aimed at enhancing bioavailability and reducing systemic side effects.Expand Specific Solutions04 Muscimol analogs and derivatives
Research is ongoing into the development of muscimol analogs and derivatives. These modified compounds aim to improve upon muscimol's pharmacological properties, potentially offering enhanced therapeutic effects or reduced side effects compared to the parent compound.Expand Specific Solutions05 Muscimol in combination therapies
Muscimol is being studied in combination with other therapeutic agents for potential synergistic effects. These combination therapies may target complex disorders or aim to enhance the overall efficacy of treatment while minimizing individual drug dosages and associated side effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The application of Muscimol in pain management protocols is in an early stage of development, with a growing market potential as research progresses. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms exploring its therapeutic potential. Key players like AbbVie, UCB Pharma, and Vertex Pharmaceuticals are investing in research, while smaller companies like ACADIA Pharmaceuticals and Praxis Precision Medicines are focusing on innovative approaches. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with ongoing clinical trials and regulatory hurdles to overcome before widespread adoption in pain management protocols.
AbbVie, Inc.
Technical Solution: AbbVie's approach to muscimol's application in pain management protocols involves the development of a novel formulation that enhances the compound's bioavailability and targeted delivery. Their research focuses on a proprietary nanoparticle-based delivery system that allows for controlled release of muscimol, potentially reducing systemic side effects while maximizing its analgesic properties[1]. The company has conducted preclinical studies demonstrating prolonged pain relief in various neuropathic pain models, with results showing a significant reduction in mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia[3]. AbbVie is also exploring the synergistic effects of combining muscimol with other GABA receptor modulators to create a more comprehensive pain management solution[5].
Strengths: Advanced drug delivery technology, strong research pipeline, and potential for extended-release formulations. Weaknesses: Possible regulatory hurdles and competition from established pain medications.
UCB Pharma GmbH
Technical Solution: UCB Pharma's muscimol-based pain management protocol focuses on developing a novel class of small molecule GABA-A receptor agonists inspired by muscimol's structure. Their approach involves creating synthetic analogues with improved pharmacokinetic profiles and reduced off-target effects[2]. The company has successfully identified several lead compounds that demonstrate high potency and selectivity for specific GABA-A receptor subtypes implicated in pain modulation[4]. Preclinical studies have shown promising results in models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain, with some compounds exhibiting a favorable side effect profile compared to traditional GABAergic drugs[6]. UCB is currently advancing their most promising candidates through early-stage clinical trials for various pain indications.
Strengths: Innovative approach to GABA-A receptor modulation, potential for subtype-specific targeting, and a strong intellectual property position. Weaknesses: Early stage of development and potential challenges in translating preclinical results to human efficacy.
Muscimol Mechanisms
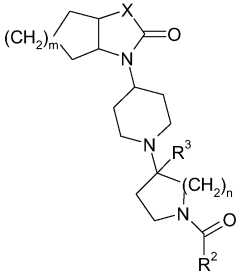
Piperidine derivatives as agonists of muscarinic receptors
PatentWO2009034380A1
Innovation
- Development of specific piperidine derivatives that selectively modulate muscarinic receptors, particularly M1 receptors, to provide therapeutic benefits for pain and neurological disorders while minimizing side effects by avoiding activation of cardiac, gastrointestinal, or glandular functions.
FORMULATIONS USED IN THE TREATMENT OF PAIN
PatentActiveTR201610322A1
Innovation
- A pharmaceutical composition combining phenyramidol, a muscle relaxant with analgesic properties, and etodolac, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), formulated in various oral and parenteral dosage forms to provide synergistic relief for conditions like osteoarthritis, muscle spasms, and back pain, utilizing controlled and delayed release mechanisms to minimize side effects.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding Muscimol's application in pain management protocols is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental agencies and international bodies. At the forefront of this regulatory landscape is the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, which plays a crucial role in overseeing the development, approval, and marketing of pain management drugs.
The FDA's regulatory process for Muscimol-based pain management treatments typically involves several stages, including preclinical research, clinical trials, and post-market surveillance. The agency's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of new drug applications, including those involving Muscimol for pain management.
Internationally, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and other national regulatory bodies have their own guidelines and approval processes for pain management drugs. These agencies often collaborate and share information to ensure consistent safety standards across different regions.
Given Muscimol's classification as a GABA receptor agonist, it falls under strict regulatory scrutiny due to its potential for abuse and side effects. Regulatory bodies typically require extensive clinical trials to demonstrate the drug's efficacy in pain management while also assessing its risk profile.
The Controlled Substances Act in the United States and similar legislation in other countries may impact the regulatory pathway for Muscimol-based treatments. Depending on its specific formulation and intended use, Muscimol may be classified as a controlled substance, necessitating additional regulatory requirements for manufacturing, distribution, and prescription.
Regulatory considerations also extend to quality control and manufacturing standards. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) guidelines, as outlined by the FDA and other international agencies, must be strictly adhered to in the production of Muscimol-based pain management drugs.
Pharmacovigilance regulations play a crucial role in the post-market phase, requiring ongoing monitoring and reporting of adverse events associated with Muscimol use in pain management. This continuous surveillance helps regulatory agencies make informed decisions about the drug's long-term safety profile.
As research into Muscimol's pain management applications progresses, regulatory frameworks may evolve to accommodate new findings and emerging treatment modalities. This dynamic regulatory environment necessitates ongoing engagement between researchers, pharmaceutical companies, and regulatory agencies to ensure the safe and effective development of Muscimol-based pain management protocols.
The FDA's regulatory process for Muscimol-based pain management treatments typically involves several stages, including preclinical research, clinical trials, and post-market surveillance. The agency's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of new drug applications, including those involving Muscimol for pain management.
Internationally, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and other national regulatory bodies have their own guidelines and approval processes for pain management drugs. These agencies often collaborate and share information to ensure consistent safety standards across different regions.
Given Muscimol's classification as a GABA receptor agonist, it falls under strict regulatory scrutiny due to its potential for abuse and side effects. Regulatory bodies typically require extensive clinical trials to demonstrate the drug's efficacy in pain management while also assessing its risk profile.
The Controlled Substances Act in the United States and similar legislation in other countries may impact the regulatory pathway for Muscimol-based treatments. Depending on its specific formulation and intended use, Muscimol may be classified as a controlled substance, necessitating additional regulatory requirements for manufacturing, distribution, and prescription.
Regulatory considerations also extend to quality control and manufacturing standards. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) guidelines, as outlined by the FDA and other international agencies, must be strictly adhered to in the production of Muscimol-based pain management drugs.
Pharmacovigilance regulations play a crucial role in the post-market phase, requiring ongoing monitoring and reporting of adverse events associated with Muscimol use in pain management. This continuous surveillance helps regulatory agencies make informed decisions about the drug's long-term safety profile.
As research into Muscimol's pain management applications progresses, regulatory frameworks may evolve to accommodate new findings and emerging treatment modalities. This dynamic regulatory environment necessitates ongoing engagement between researchers, pharmaceutical companies, and regulatory agencies to ensure the safe and effective development of Muscimol-based pain management protocols.
Safety Considerations
Safety considerations are paramount when evaluating Muscimol's application in pain management protocols. The primary concern is the potential for adverse effects due to Muscimol's action as a GABA-A receptor agonist. This mechanism can lead to sedation, cognitive impairment, and motor coordination issues, which must be carefully monitored and managed during treatment.
Dosage control is critical to ensure therapeutic efficacy while minimizing risks. Establishing precise dosing guidelines based on patient-specific factors such as age, weight, and overall health status is essential. Additionally, potential drug interactions must be thoroughly investigated, as Muscimol may potentiate the effects of other CNS depressants, including alcohol and benzodiazepines.
Long-term safety profiles require extensive study to assess the risk of tolerance, dependence, or withdrawal symptoms associated with prolonged Muscimol use. Comprehensive clinical trials are necessary to evaluate these aspects and determine appropriate treatment durations and discontinuation protocols.
The route of administration also impacts safety considerations. While oral administration may offer convenience, it presents challenges in terms of bioavailability and first-pass metabolism. Alternative delivery methods, such as transdermal patches or intranasal formulations, may provide more controlled and consistent dosing but require thorough evaluation for local tissue reactions and systemic absorption rates.
Contraindications and special populations must be clearly defined. Patients with a history of seizures, respiratory disorders, or liver dysfunction may be at higher risk for adverse effects. Pregnant women and pediatric patients require particular attention, as the impact of Muscimol on fetal development and growing nervous systems is not fully understood.
Pharmacovigilance systems must be established to monitor and report adverse events associated with Muscimol use in pain management. This includes developing standardized reporting protocols and educating healthcare providers on recognizing and managing potential complications.
Lastly, patient education is crucial for safe implementation of Muscimol-based pain management protocols. Clear instructions on proper use, potential side effects, and warning signs that require medical attention should be provided to all patients. Implementing a structured follow-up program can help ensure ongoing safety monitoring and timely intervention if issues arise.
Dosage control is critical to ensure therapeutic efficacy while minimizing risks. Establishing precise dosing guidelines based on patient-specific factors such as age, weight, and overall health status is essential. Additionally, potential drug interactions must be thoroughly investigated, as Muscimol may potentiate the effects of other CNS depressants, including alcohol and benzodiazepines.
Long-term safety profiles require extensive study to assess the risk of tolerance, dependence, or withdrawal symptoms associated with prolonged Muscimol use. Comprehensive clinical trials are necessary to evaluate these aspects and determine appropriate treatment durations and discontinuation protocols.
The route of administration also impacts safety considerations. While oral administration may offer convenience, it presents challenges in terms of bioavailability and first-pass metabolism. Alternative delivery methods, such as transdermal patches or intranasal formulations, may provide more controlled and consistent dosing but require thorough evaluation for local tissue reactions and systemic absorption rates.
Contraindications and special populations must be clearly defined. Patients with a history of seizures, respiratory disorders, or liver dysfunction may be at higher risk for adverse effects. Pregnant women and pediatric patients require particular attention, as the impact of Muscimol on fetal development and growing nervous systems is not fully understood.
Pharmacovigilance systems must be established to monitor and report adverse events associated with Muscimol use in pain management. This includes developing standardized reporting protocols and educating healthcare providers on recognizing and managing potential complications.
Lastly, patient education is crucial for safe implementation of Muscimol-based pain management protocols. Clear instructions on proper use, potential side effects, and warning signs that require medical attention should be provided to all patients. Implementing a structured follow-up program can help ensure ongoing safety monitoring and timely intervention if issues arise.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!