Cultural Significance of Muscimol in Mythology
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Origins
Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in various species of mushrooms, particularly those belonging to the Amanita genus, has a rich and complex history deeply intertwined with human culture and mythology. The origins of muscimol's cultural significance can be traced back thousands of years, with evidence of its use in shamanic and religious practices across diverse civilizations.
The earliest known references to muscimol-containing mushrooms date back to ancient Siberian and North American indigenous cultures. These societies recognized the potent effects of Amanita muscaria, commonly known as the fly agaric mushroom, and incorporated it into their spiritual and medicinal practices. The distinctive red cap with white spots of the fly agaric became an iconic symbol in folklore and artistic representations.
In Siberian shamanic traditions, the consumption of Amanita muscaria played a crucial role in religious ceremonies and vision quests. Shamans would ingest the mushroom to induce altered states of consciousness, believing it allowed them to communicate with spirits and access higher realms of knowledge. This practice was deeply embedded in their cosmology and understanding of the natural world.
The cultural significance of muscimol spread beyond Siberia, influencing mythologies and religious practices in other parts of the world. In Norse mythology, some scholars suggest that the berserker warriors' legendary fury may have been induced by the consumption of Amanita muscaria. The mushroom's association with divine inspiration and supernatural abilities became a recurring theme in various cultural narratives.
In Central American cultures, particularly among the Mazatec people of Mexico, muscimol-containing mushrooms were revered as sacred and used in religious rituals. While the primary psychoactive compound in these mushrooms was psilocybin rather than muscimol, the cultural importance of entheogenic fungi shares similarities with the Amanita traditions of other regions.
The cultural significance of muscimol extended to artistic and literary expressions. Depictions of mushrooms resembling Amanita muscaria can be found in various forms of art, from ancient cave paintings to medieval European religious iconography. Some researchers have even proposed connections between muscimol-induced visions and certain mythological creatures or supernatural experiences described in folklore.
As human societies evolved, the role of muscimol in cultural practices underwent transformations. In some cases, its use became more secretive or was supplanted by other substances. However, the legacy of muscimol in mythology and cultural memory persisted, often manifesting in symbolic representations and allegorical references in literature and art.
The earliest known references to muscimol-containing mushrooms date back to ancient Siberian and North American indigenous cultures. These societies recognized the potent effects of Amanita muscaria, commonly known as the fly agaric mushroom, and incorporated it into their spiritual and medicinal practices. The distinctive red cap with white spots of the fly agaric became an iconic symbol in folklore and artistic representations.
In Siberian shamanic traditions, the consumption of Amanita muscaria played a crucial role in religious ceremonies and vision quests. Shamans would ingest the mushroom to induce altered states of consciousness, believing it allowed them to communicate with spirits and access higher realms of knowledge. This practice was deeply embedded in their cosmology and understanding of the natural world.
The cultural significance of muscimol spread beyond Siberia, influencing mythologies and religious practices in other parts of the world. In Norse mythology, some scholars suggest that the berserker warriors' legendary fury may have been induced by the consumption of Amanita muscaria. The mushroom's association with divine inspiration and supernatural abilities became a recurring theme in various cultural narratives.
In Central American cultures, particularly among the Mazatec people of Mexico, muscimol-containing mushrooms were revered as sacred and used in religious rituals. While the primary psychoactive compound in these mushrooms was psilocybin rather than muscimol, the cultural importance of entheogenic fungi shares similarities with the Amanita traditions of other regions.
The cultural significance of muscimol extended to artistic and literary expressions. Depictions of mushrooms resembling Amanita muscaria can be found in various forms of art, from ancient cave paintings to medieval European religious iconography. Some researchers have even proposed connections between muscimol-induced visions and certain mythological creatures or supernatural experiences described in folklore.
As human societies evolved, the role of muscimol in cultural practices underwent transformations. In some cases, its use became more secretive or was supplanted by other substances. However, the legacy of muscimol in mythology and cultural memory persisted, often manifesting in symbolic representations and allegorical references in literature and art.
Cultural Demand
The cultural demand for muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, particularly Amanita muscaria, has deep roots in mythology and traditional practices across various cultures. This demand is driven by the compound's ability to induce altered states of consciousness, which have been historically associated with spiritual experiences and divine communication.
In many indigenous cultures, particularly in Siberia and parts of North America, the use of muscimol-containing mushrooms has been an integral part of shamanic rituals and religious ceremonies. These practices have created a sustained cultural demand for the substance, as it is believed to facilitate communication with the spirit world and provide insights into the nature of reality.
The mythological significance of muscimol has also contributed to its cultural demand in literature, art, and popular culture. References to the distinctive red and white spotted Amanita muscaria mushroom can be found in various folktales, fairy stories, and artistic depictions, often associated with magical or otherworldly themes. This has led to a broader cultural fascination with the mushroom and its effects, extending beyond traditional ritualistic use.
In modern times, there has been a resurgence of interest in traditional plant medicines and psychoactive substances, driven by a combination of factors including the search for alternative healing modalities, spiritual exploration, and academic research into consciousness. This trend has reignited cultural demand for muscimol and its associated mythology, particularly among those seeking to connect with ancient wisdom traditions or explore altered states of consciousness.
The cultural demand for muscimol is also reflected in the growing field of ethnomycology, which studies the historical and cultural relationships between humans and fungi. Researchers and enthusiasts in this field have shown increasing interest in understanding the role of muscimol-containing mushrooms in various mythologies and cultural practices, further fueling demand for knowledge and experiences related to this compound.
However, it is important to note that the cultural demand for muscimol exists in tension with legal and safety considerations. Many countries have restrictions on the use and possession of Amanita muscaria and other muscimol-containing substances, which has led to the development of underground or fringe communities dedicated to preserving and exploring these cultural practices.
In conclusion, the cultural demand for muscimol in mythology remains significant, driven by its historical use in spiritual practices, its presence in folklore and art, and contemporary interest in traditional plant medicines and consciousness exploration. This demand continues to shape cultural narratives and practices, even as it navigates the complexities of modern legal and societal norms.
In many indigenous cultures, particularly in Siberia and parts of North America, the use of muscimol-containing mushrooms has been an integral part of shamanic rituals and religious ceremonies. These practices have created a sustained cultural demand for the substance, as it is believed to facilitate communication with the spirit world and provide insights into the nature of reality.
The mythological significance of muscimol has also contributed to its cultural demand in literature, art, and popular culture. References to the distinctive red and white spotted Amanita muscaria mushroom can be found in various folktales, fairy stories, and artistic depictions, often associated with magical or otherworldly themes. This has led to a broader cultural fascination with the mushroom and its effects, extending beyond traditional ritualistic use.
In modern times, there has been a resurgence of interest in traditional plant medicines and psychoactive substances, driven by a combination of factors including the search for alternative healing modalities, spiritual exploration, and academic research into consciousness. This trend has reignited cultural demand for muscimol and its associated mythology, particularly among those seeking to connect with ancient wisdom traditions or explore altered states of consciousness.
The cultural demand for muscimol is also reflected in the growing field of ethnomycology, which studies the historical and cultural relationships between humans and fungi. Researchers and enthusiasts in this field have shown increasing interest in understanding the role of muscimol-containing mushrooms in various mythologies and cultural practices, further fueling demand for knowledge and experiences related to this compound.
However, it is important to note that the cultural demand for muscimol exists in tension with legal and safety considerations. Many countries have restrictions on the use and possession of Amanita muscaria and other muscimol-containing substances, which has led to the development of underground or fringe communities dedicated to preserving and exploring these cultural practices.
In conclusion, the cultural demand for muscimol in mythology remains significant, driven by its historical use in spiritual practices, its presence in folklore and art, and contemporary interest in traditional plant medicines and consciousness exploration. This demand continues to shape cultural narratives and practices, even as it navigates the complexities of modern legal and societal norms.
Current Research
Current research on the cultural significance of muscimol in mythology has been expanding rapidly, with interdisciplinary approaches shedding new light on this fascinating topic. Anthropologists and ethnobotanists have been collaborating to explore the historical use of Amanita muscaria mushrooms in various cultures, particularly in Siberian and North American indigenous traditions.
Recent studies have focused on the neurological effects of muscimol, the primary psychoactive compound in Amanita muscaria. Researchers are investigating how these effects may have influenced religious and spiritual experiences, potentially explaining the mushroom's prominence in mythological narratives. Advanced neuroimaging techniques are being employed to map brain activity during muscimol-induced altered states of consciousness.
Linguistic analysis of ancient texts and oral traditions has revealed recurring themes and symbols associated with muscimol-containing mushrooms across different cultures. This comparative approach is helping scholars identify common motifs and archetypes in mythology that may be linked to the mushroom's psychoactive properties.
Archaeologists have been uncovering new evidence of Amanita muscaria use in prehistoric societies. Recent excavations in Europe and Asia have yielded artifacts and rock art that potentially depict mushroom-related rituals, providing tangible links between mythology and historical practices.
Ethnomycologists are conducting field studies in regions where traditional mushroom use persists, documenting contemporary practices and their connections to ancient mythological narratives. This research is crucial for understanding the evolution and preservation of muscimol-related cultural practices.
In the field of comparative religion, scholars are reexamining creation myths and cosmological narratives through the lens of entheogen use. The role of muscimol in shaping religious experiences and belief systems is being reevaluated, challenging previous interpretations of mythological texts.
Biochemists and pharmacologists are investigating the molecular mechanisms of muscimol's action on the brain, seeking to understand how its unique properties may have influenced the development of spiritual and mythological concepts. This research is bridging the gap between neuroscience and cultural studies.
Environmental scientists are studying the ecological relationships between Amanita muscaria and its habitat, exploring how climate change and human activity may impact the mushroom's distribution and, consequently, its cultural significance in affected regions.
The integration of virtual reality and augmented reality technologies is opening new avenues for experiencing and studying muscimol-induced states in controlled settings. This innovative approach allows researchers to recreate and analyze mythological narratives in immersive environments.
As research progresses, ethical considerations surrounding the study and potential modern applications of muscimol are becoming increasingly important. Scholars are engaging in discussions about the responsible exploration of traditional knowledge and the potential implications of reviving ancient practices in contemporary contexts.
Recent studies have focused on the neurological effects of muscimol, the primary psychoactive compound in Amanita muscaria. Researchers are investigating how these effects may have influenced religious and spiritual experiences, potentially explaining the mushroom's prominence in mythological narratives. Advanced neuroimaging techniques are being employed to map brain activity during muscimol-induced altered states of consciousness.
Linguistic analysis of ancient texts and oral traditions has revealed recurring themes and symbols associated with muscimol-containing mushrooms across different cultures. This comparative approach is helping scholars identify common motifs and archetypes in mythology that may be linked to the mushroom's psychoactive properties.
Archaeologists have been uncovering new evidence of Amanita muscaria use in prehistoric societies. Recent excavations in Europe and Asia have yielded artifacts and rock art that potentially depict mushroom-related rituals, providing tangible links between mythology and historical practices.
Ethnomycologists are conducting field studies in regions where traditional mushroom use persists, documenting contemporary practices and their connections to ancient mythological narratives. This research is crucial for understanding the evolution and preservation of muscimol-related cultural practices.
In the field of comparative religion, scholars are reexamining creation myths and cosmological narratives through the lens of entheogen use. The role of muscimol in shaping religious experiences and belief systems is being reevaluated, challenging previous interpretations of mythological texts.
Biochemists and pharmacologists are investigating the molecular mechanisms of muscimol's action on the brain, seeking to understand how its unique properties may have influenced the development of spiritual and mythological concepts. This research is bridging the gap between neuroscience and cultural studies.
Environmental scientists are studying the ecological relationships between Amanita muscaria and its habitat, exploring how climate change and human activity may impact the mushroom's distribution and, consequently, its cultural significance in affected regions.
The integration of virtual reality and augmented reality technologies is opening new avenues for experiencing and studying muscimol-induced states in controlled settings. This innovative approach allows researchers to recreate and analyze mythological narratives in immersive environments.
As research progresses, ethical considerations surrounding the study and potential modern applications of muscimol are becoming increasingly important. Scholars are engaging in discussions about the responsible exploration of traditional knowledge and the potential implications of reviving ancient practices in contemporary contexts.
Muscimol Extraction
01 Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol
Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include muscimol as an active ingredient, often in combination with other compounds or excipients. The formulations can be designed for different routes of administration and may target specific conditions or disorders.- Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol: Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include different formulations and delivery methods to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol. The compositions can be designed for treating neurological disorders, anxiety, or other conditions affected by GABA receptor modulation.
- Muscimol analogs and derivatives: Research focuses on developing and synthesizing muscimol analogs and derivatives. These modified compounds aim to improve upon the properties of muscimol, such as increased potency, selectivity, or reduced side effects. The analogs may have different chemical structures but retain or enhance the pharmacological activity of muscimol.
- Methods of administering muscimol: Various methods for administering muscimol are explored to optimize its therapeutic effects. These may include novel drug delivery systems, controlled release formulations, or targeted delivery approaches. The administration methods aim to improve the drug's bioavailability, reduce side effects, and enhance patient compliance.
- Combination therapies involving muscimol: Muscimol is studied in combination with other therapeutic agents to achieve synergistic effects or address multiple aspects of a condition. These combination therapies may involve other GABA receptor modulators, neurotransmitter regulators, or compounds targeting different biological pathways to enhance overall treatment efficacy.
- Muscimol in neurological and psychiatric applications: Muscimol is investigated for its potential in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders. Its action as a GABA receptor agonist is explored in conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, sleep disturbances, and neurodegenerative diseases. Research focuses on understanding its mechanisms of action and optimizing its use in these therapeutic areas.
02 Muscimol for neurological and psychiatric disorders
Muscimol is investigated for its potential in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. It may be used in therapies targeting conditions such as anxiety, depression, epilepsy, and neurodegenerative diseases. The compound's action on GABA receptors is believed to contribute to its therapeutic effects in these areas.Expand Specific Solutions03 Synthesis and production methods for muscimol
Various methods for synthesizing and producing muscimol are developed to improve yield, purity, and efficiency. These may include chemical synthesis routes, biotechnological approaches, or extraction methods from natural sources. The focus is on creating scalable and cost-effective production processes for pharmaceutical-grade muscimol.Expand Specific Solutions04 Muscimol analogs and derivatives
Research is conducted on muscimol analogs and derivatives to enhance its pharmacological properties or reduce side effects. These modified compounds may have improved bioavailability, selectivity, or potency compared to the parent molecule. Structure-activity relationship studies guide the development of these novel muscimol-based compounds.Expand Specific Solutions05 Drug delivery systems for muscimol
Innovative drug delivery systems are developed to optimize the administration of muscimol. These may include controlled release formulations, targeted delivery mechanisms, or novel routes of administration. The aim is to improve the efficacy and safety profile of muscimol-based therapies by enhancing its pharmacokinetics and reducing systemic exposure.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Mythological Figures
The cultural significance of muscimol in mythology represents a niche field at the intersection of ethnobotany, anthropology, and pharmacology. The market for this research is relatively small but growing, driven by increasing interest in traditional plant-based medicines and psychoactive compounds. Companies like Psyched Wellness Ltd. and CaaMTech LLC are at the forefront, developing health supplements and engineered psychedelic drugs respectively. Academic institutions such as Georgetown University School of Medicine and Jilin Agricultural University contribute to the knowledge base. The technology is still in its early stages, with ongoing research into safety, efficacy, and potential applications. As regulatory frameworks evolve, larger pharmaceutical companies like Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. may become more involved, potentially expanding the market and accelerating technological advancements.
Psyched Wellness Ltd.
Technical Solution: Psyched Wellness Ltd. has developed a proprietary extraction and purification process for Amanita muscaria mushrooms, focusing on the safe and controlled extraction of muscimol. Their approach involves careful harvesting, drying, and processing of the mushrooms to isolate muscimol while removing potentially harmful compounds. The company has created a line of functional mushroom products, including tinctures and capsules, that harness the potential benefits of muscimol while emphasizing safety and standardization[1][2]. Their research also explores the cultural and historical significance of Amanita muscaria in various mythologies, incorporating this knowledge into their product development and marketing strategies.
Strengths: Specialized focus on Amanita muscaria and muscimol, proprietary extraction process, emphasis on safety and standardization. Weaknesses: Limited scope compared to broader psychedelic research companies, potential regulatory challenges due to muscimol's legal status in some regions.
CaaMTech LLC
Technical Solution: CaaMTech LLC has developed a comprehensive approach to studying the cultural significance of muscimol in mythology, combining chemical analysis with anthropological research. Their technology involves advanced spectrometry techniques to identify and quantify muscimol and related compounds in historical artifacts and traditional preparations. CaaMTech has created a database linking chemical profiles to specific cultural practices and mythological narratives across different societies[3]. This interdisciplinary approach allows for a more nuanced understanding of how the pharmacological properties of muscimol may have influenced its role in various mythologies and religious practices throughout history.
Strengths: Interdisciplinary approach combining chemistry and anthropology, comprehensive database of muscimol-related cultural practices. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in accurately analyzing ancient samples, reliance on interpretation of historical data.
Pharmacological Effects
Amanita muscaria compounds
PatentPendingUS20240050502A1
Innovation
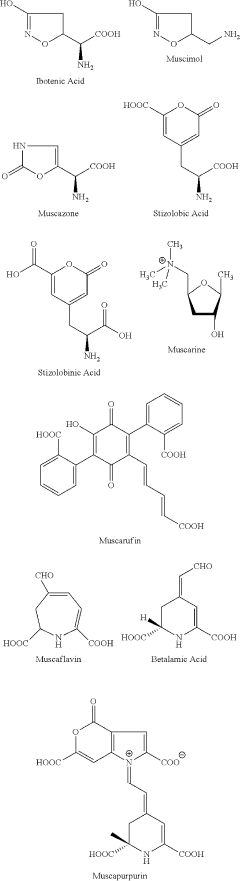
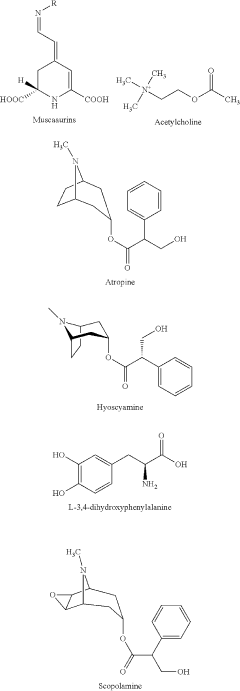
- Development of purified Amanita muscaria compound compositions and formulations comprising specific ratios of ibotenic acid, muscimol, and other compounds, which are structurally distinct and free from other Amanita muscaria compounds, combined with excipients and serotonergic drugs, psilocybin derivatives, or cannabinoids to create pharmaceutical formulations for therapeutic use.
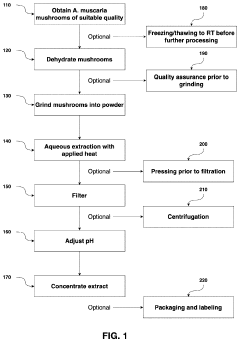
Processes for Extracting Muscimol from Amanita Muscaria
PatentPendingUS20240165180A1
Innovation
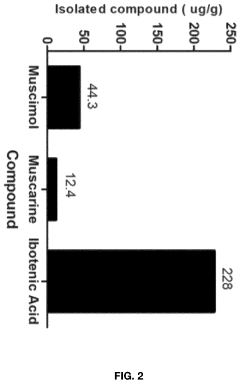
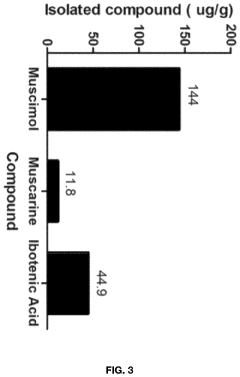
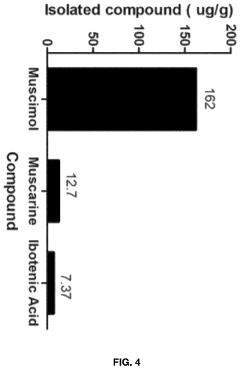
- Aqueous extraction of Amanita muscaria biomass is performed with heat, followed by pH reduction between 2.0 to 4.0 and concentration through distillation or refluxing, which decreases ibotenic acid content and increases muscimol content, resulting in a muscimol-rich extract with enhanced purity.
Legal Considerations
The legal considerations surrounding muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, are complex and multifaceted. In many jurisdictions, the possession, distribution, and use of muscimol-containing mushrooms are strictly regulated or prohibited due to their hallucinogenic properties. The legal status of these substances often falls under controlled substance laws, which vary significantly from country to country.
In the United States, for instance, Amanita muscaria mushrooms, which contain muscimol, are not specifically scheduled under the Controlled Substances Act. However, the extracted compound muscimol itself is classified as a Schedule III controlled substance. This creates a legal gray area where the mushrooms may be legal to possess in some states, but their use for psychoactive purposes could potentially be prosecuted under analog laws.
Many European countries have similarly ambiguous legal frameworks regarding muscimol-containing mushrooms. In the United Kingdom, fresh mushrooms containing muscimol were legal until the Drugs Act of 2005, which criminalized their possession and sale. Other European nations have varying degrees of regulation, with some allowing limited personal use or cultivation for traditional or religious purposes.
The legal landscape becomes even more complex when considering the cultural and historical significance of muscimol in certain indigenous traditions. Some countries have enacted laws that protect the use of psychoactive substances in traditional religious or spiritual practices. For example, the United States Supreme Court has ruled in favor of certain Native American groups using peyote in religious ceremonies, despite its status as a controlled substance.
This precedent raises questions about the potential for legal protections for traditional uses of muscimol-containing mushrooms in cultures where they have played a significant mythological or spiritual role. However, such protections are not universally recognized and can be subject to intense legal debate and scrutiny.
From a research perspective, the legal status of muscimol can impact scientific studies on its potential therapeutic applications. Researchers must navigate a complex regulatory environment to obtain permits for studying controlled substances, which can hinder the advancement of knowledge in this field.
As societal attitudes towards psychoactive substances evolve, there is ongoing discussion about potential reforms to drug laws. Some advocates argue for a more nuanced approach that distinguishes between harmful narcotics and substances with potential cultural or medicinal value. However, any changes to the legal status of muscimol would likely require significant shifts in policy and public perception.
In the United States, for instance, Amanita muscaria mushrooms, which contain muscimol, are not specifically scheduled under the Controlled Substances Act. However, the extracted compound muscimol itself is classified as a Schedule III controlled substance. This creates a legal gray area where the mushrooms may be legal to possess in some states, but their use for psychoactive purposes could potentially be prosecuted under analog laws.
Many European countries have similarly ambiguous legal frameworks regarding muscimol-containing mushrooms. In the United Kingdom, fresh mushrooms containing muscimol were legal until the Drugs Act of 2005, which criminalized their possession and sale. Other European nations have varying degrees of regulation, with some allowing limited personal use or cultivation for traditional or religious purposes.
The legal landscape becomes even more complex when considering the cultural and historical significance of muscimol in certain indigenous traditions. Some countries have enacted laws that protect the use of psychoactive substances in traditional religious or spiritual practices. For example, the United States Supreme Court has ruled in favor of certain Native American groups using peyote in religious ceremonies, despite its status as a controlled substance.
This precedent raises questions about the potential for legal protections for traditional uses of muscimol-containing mushrooms in cultures where they have played a significant mythological or spiritual role. However, such protections are not universally recognized and can be subject to intense legal debate and scrutiny.
From a research perspective, the legal status of muscimol can impact scientific studies on its potential therapeutic applications. Researchers must navigate a complex regulatory environment to obtain permits for studying controlled substances, which can hinder the advancement of knowledge in this field.
As societal attitudes towards psychoactive substances evolve, there is ongoing discussion about potential reforms to drug laws. Some advocates argue for a more nuanced approach that distinguishes between harmful narcotics and substances with potential cultural or medicinal value. However, any changes to the legal status of muscimol would likely require significant shifts in policy and public perception.
Preservation Efforts
Preservation efforts for the cultural significance of muscimol in mythology have become increasingly important as traditional knowledge and practices face the risk of being lost in the modern world. These efforts span various domains, including ethnobotany, anthropology, and cultural heritage conservation.
One key aspect of preservation involves documenting and recording the oral traditions and mythological narratives associated with muscimol-containing plants, such as Amanita muscaria. Researchers and cultural anthropologists are working closely with indigenous communities to capture these stories, rituals, and beliefs before they fade from collective memory. This process often involves audio and video recordings, as well as written transcriptions, to ensure a comprehensive record for future generations.
Digital archiving has emerged as a crucial tool in preservation efforts. Online databases and virtual museums are being developed to store and showcase information about muscimol's role in various mythologies. These digital platforms not only serve as repositories of knowledge but also provide accessible educational resources for scholars, students, and the general public interested in this aspect of cultural heritage.
Efforts are also being made to preserve the physical artifacts associated with muscimol use in traditional contexts. This includes the conservation of ceremonial objects, artwork, and historical texts that reference the substance or depict its use. Museums and cultural institutions are developing specialized conservation techniques to maintain these delicate items, ensuring their longevity for future study and exhibition.
In situ conservation of muscimol-containing plants and their habitats is another critical component of preservation efforts. This involves protecting natural areas where these plants grow and supporting sustainable harvesting practices among communities that traditionally use them. Such initiatives aim to maintain the ecological and cultural contexts in which these plants have significance.
Educational programs and community engagement initiatives play a vital role in preserving the cultural significance of muscimol. These programs focus on raising awareness about the historical and cultural importance of the substance, particularly among younger generations. They often include workshops, seminars, and cultural events that promote understanding and respect for traditional knowledge systems.
Lastly, legal and policy frameworks are being developed to protect the intellectual property rights of indigenous communities regarding their traditional knowledge of muscimol and related practices. These efforts aim to prevent the exploitation of this cultural heritage and ensure that any benefits derived from its study or use are shared equitably with the communities of origin.
One key aspect of preservation involves documenting and recording the oral traditions and mythological narratives associated with muscimol-containing plants, such as Amanita muscaria. Researchers and cultural anthropologists are working closely with indigenous communities to capture these stories, rituals, and beliefs before they fade from collective memory. This process often involves audio and video recordings, as well as written transcriptions, to ensure a comprehensive record for future generations.
Digital archiving has emerged as a crucial tool in preservation efforts. Online databases and virtual museums are being developed to store and showcase information about muscimol's role in various mythologies. These digital platforms not only serve as repositories of knowledge but also provide accessible educational resources for scholars, students, and the general public interested in this aspect of cultural heritage.
Efforts are also being made to preserve the physical artifacts associated with muscimol use in traditional contexts. This includes the conservation of ceremonial objects, artwork, and historical texts that reference the substance or depict its use. Museums and cultural institutions are developing specialized conservation techniques to maintain these delicate items, ensuring their longevity for future study and exhibition.
In situ conservation of muscimol-containing plants and their habitats is another critical component of preservation efforts. This involves protecting natural areas where these plants grow and supporting sustainable harvesting practices among communities that traditionally use them. Such initiatives aim to maintain the ecological and cultural contexts in which these plants have significance.
Educational programs and community engagement initiatives play a vital role in preserving the cultural significance of muscimol. These programs focus on raising awareness about the historical and cultural importance of the substance, particularly among younger generations. They often include workshops, seminars, and cultural events that promote understanding and respect for traditional knowledge systems.
Lastly, legal and policy frameworks are being developed to protect the intellectual property rights of indigenous communities regarding their traditional knowledge of muscimol and related practices. These efforts aim to prevent the exploitation of this cultural heritage and ensure that any benefits derived from its study or use are shared equitably with the communities of origin.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!