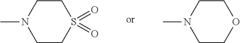Muscimol Integration in Emerging Therapeutic Practices
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Background and Research Objectives
Muscimol, a naturally occurring psychoactive compound found in various species of mushrooms, particularly Amanita muscaria, has a rich history in traditional medicine and shamanic practices. This GABA receptor agonist has recently garnered significant attention in the scientific community for its potential therapeutic applications. The evolution of muscimol research has progressed from ethnobotanical studies to advanced neuropharmacological investigations, marking a shift in our understanding of its mechanisms and potential benefits.
The primary objective of this research is to explore the integration of muscimol into emerging therapeutic practices, with a focus on its potential applications in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. This encompasses a comprehensive examination of muscimol's pharmacological properties, its interactions with the GABAergic system, and its effects on neural circuits implicated in various pathological conditions.
Current research trends indicate a growing interest in muscimol's anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and neuroprotective properties. The compound's ability to modulate GABA receptors presents promising avenues for treating conditions such as anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, its potential in pain management and as an alternative to traditional anesthetics is being actively investigated.
The technological advancements in drug delivery systems and neuroimaging techniques have significantly contributed to the progress in muscimol research. These developments allow for more precise targeting of specific brain regions and real-time monitoring of muscimol's effects on neural activity, enhancing our understanding of its therapeutic mechanisms.
One of the key challenges in muscimol research is optimizing its pharmacokinetic profile to enhance its therapeutic efficacy while minimizing potential side effects. This includes developing novel formulations and delivery methods to improve its bioavailability and target specificity. Furthermore, elucidating the long-term effects of muscimol use and its potential for addiction or tolerance development remains a critical area of investigation.
The integration of muscimol into emerging therapeutic practices also necessitates a thorough examination of regulatory frameworks and ethical considerations. As research progresses, it is crucial to establish guidelines for its clinical use, ensuring patient safety and efficacy in therapeutic applications.
In conclusion, the research on muscimol integration in emerging therapeutic practices aims to bridge the gap between traditional knowledge and modern medicine, leveraging advanced scientific methodologies to unlock the full potential of this compound. The outcomes of this research could potentially revolutionize treatment approaches for a wide range of neurological and psychiatric disorders, offering new hope for patients and expanding the toolkit of therapeutic options available to healthcare providers.
The primary objective of this research is to explore the integration of muscimol into emerging therapeutic practices, with a focus on its potential applications in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. This encompasses a comprehensive examination of muscimol's pharmacological properties, its interactions with the GABAergic system, and its effects on neural circuits implicated in various pathological conditions.
Current research trends indicate a growing interest in muscimol's anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and neuroprotective properties. The compound's ability to modulate GABA receptors presents promising avenues for treating conditions such as anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, its potential in pain management and as an alternative to traditional anesthetics is being actively investigated.
The technological advancements in drug delivery systems and neuroimaging techniques have significantly contributed to the progress in muscimol research. These developments allow for more precise targeting of specific brain regions and real-time monitoring of muscimol's effects on neural activity, enhancing our understanding of its therapeutic mechanisms.
One of the key challenges in muscimol research is optimizing its pharmacokinetic profile to enhance its therapeutic efficacy while minimizing potential side effects. This includes developing novel formulations and delivery methods to improve its bioavailability and target specificity. Furthermore, elucidating the long-term effects of muscimol use and its potential for addiction or tolerance development remains a critical area of investigation.
The integration of muscimol into emerging therapeutic practices also necessitates a thorough examination of regulatory frameworks and ethical considerations. As research progresses, it is crucial to establish guidelines for its clinical use, ensuring patient safety and efficacy in therapeutic applications.
In conclusion, the research on muscimol integration in emerging therapeutic practices aims to bridge the gap between traditional knowledge and modern medicine, leveraging advanced scientific methodologies to unlock the full potential of this compound. The outcomes of this research could potentially revolutionize treatment approaches for a wide range of neurological and psychiatric disorders, offering new hope for patients and expanding the toolkit of therapeutic options available to healthcare providers.
Market Analysis for Muscimol-Based Therapies
The market for muscimol-based therapies is experiencing significant growth and attracting increasing attention from pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and investors. This emerging sector is driven by the growing interest in alternative treatments for neurological and psychiatric disorders, as well as the potential applications in pain management and addiction treatment.
Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain species of mushrooms, has shown promising results in preclinical and early clinical studies for various conditions. The global market for neurological disorder treatments, which includes potential muscimol applications, is projected to expand substantially in the coming years. This growth is fueled by an aging population, increasing prevalence of mental health disorders, and a shift towards more personalized and targeted therapies.
The demand for novel treatments in psychiatry and neurology is particularly strong, as many existing medications have limited efficacy or significant side effects. Muscimol-based therapies offer a potential alternative with a unique mechanism of action, targeting GABA receptors in the brain. This approach has garnered interest for conditions such as anxiety, depression, epilepsy, and certain neurodegenerative diseases.
In the field of pain management, muscimol-based treatments are being explored as a potential non-opioid alternative, addressing the urgent need for effective pain relief without the risk of addiction. This aligns with the global efforts to combat the opioid crisis and develop safer pain management options.
The market for addiction treatment is another area where muscimol-based therapies show promise. With the increasing recognition of addiction as a chronic brain disease, there is a growing demand for innovative treatments that can address the underlying neurological aspects of addiction.
Geographically, North America and Europe are expected to be the leading markets for muscimol-based therapies, due to their advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher healthcare spending, and more favorable regulatory environments for novel treatments. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are also showing increasing interest, driven by rising healthcare expenditure and growing awareness of mental health issues.
Despite the promising outlook, the market for muscimol-based therapies faces several challenges. These include regulatory hurdles, as psychoactive compounds often face stringent approval processes. Additionally, there is a need for more extensive clinical trials to establish the safety and efficacy of muscimol-based treatments across various indications. Public perception and potential stigma associated with psychoactive compounds derived from mushrooms may also need to be addressed through education and awareness campaigns.
Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain species of mushrooms, has shown promising results in preclinical and early clinical studies for various conditions. The global market for neurological disorder treatments, which includes potential muscimol applications, is projected to expand substantially in the coming years. This growth is fueled by an aging population, increasing prevalence of mental health disorders, and a shift towards more personalized and targeted therapies.
The demand for novel treatments in psychiatry and neurology is particularly strong, as many existing medications have limited efficacy or significant side effects. Muscimol-based therapies offer a potential alternative with a unique mechanism of action, targeting GABA receptors in the brain. This approach has garnered interest for conditions such as anxiety, depression, epilepsy, and certain neurodegenerative diseases.
In the field of pain management, muscimol-based treatments are being explored as a potential non-opioid alternative, addressing the urgent need for effective pain relief without the risk of addiction. This aligns with the global efforts to combat the opioid crisis and develop safer pain management options.
The market for addiction treatment is another area where muscimol-based therapies show promise. With the increasing recognition of addiction as a chronic brain disease, there is a growing demand for innovative treatments that can address the underlying neurological aspects of addiction.
Geographically, North America and Europe are expected to be the leading markets for muscimol-based therapies, due to their advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher healthcare spending, and more favorable regulatory environments for novel treatments. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are also showing increasing interest, driven by rising healthcare expenditure and growing awareness of mental health issues.
Despite the promising outlook, the market for muscimol-based therapies faces several challenges. These include regulatory hurdles, as psychoactive compounds often face stringent approval processes. Additionally, there is a need for more extensive clinical trials to establish the safety and efficacy of muscimol-based treatments across various indications. Public perception and potential stigma associated with psychoactive compounds derived from mushrooms may also need to be addressed through education and awareness campaigns.
Current Challenges in Muscimol Integration
The integration of muscimol into emerging therapeutic practices faces several significant challenges that require careful consideration and innovative solutions. One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of muscimol's long-term effects on the human brain and body. While short-term studies have shown promising results, the lack of comprehensive longitudinal research hinders its widespread adoption in clinical settings.
Another critical challenge lies in the precise dosing and administration of muscimol. Given its potent psychoactive properties, determining the optimal therapeutic dose that balances efficacy and safety remains a complex task. This is further complicated by individual variations in metabolism and sensitivity to the compound, necessitating personalized treatment approaches.
The regulatory landscape presents a formidable barrier to muscimol integration. As a Schedule III controlled substance in many jurisdictions, its use in therapeutic practices is subject to strict regulations and oversight. Navigating these legal complexities and obtaining necessary approvals for clinical trials and eventual therapeutic use requires significant time, resources, and expertise.
Standardization of muscimol production and quality control poses another challenge. Ensuring consistent purity and potency across different batches is crucial for reliable therapeutic outcomes. The development of standardized extraction and synthesis methods, as well as rigorous quality assurance protocols, is essential to address this issue.
The potential for adverse interactions with other medications and substances is a concern that demands thorough investigation. As muscimol affects GABAergic neurotransmission, its interaction with other drugs that modulate brain activity must be carefully studied to prevent unforeseen complications in patients undergoing multiple treatments.
Public perception and stigma associated with psychoactive compounds present a social and educational challenge. Overcoming misconceptions and fostering acceptance of muscimol as a legitimate therapeutic agent requires extensive public education and awareness campaigns.
Lastly, the development of targeted delivery systems for muscimol presents a technological hurdle. Optimizing its bioavailability and ensuring it reaches specific brain regions while minimizing systemic exposure is crucial for maximizing therapeutic benefits and reducing potential side effects. This may involve exploring novel drug delivery technologies or formulations tailored to muscimol's unique properties.
Another critical challenge lies in the precise dosing and administration of muscimol. Given its potent psychoactive properties, determining the optimal therapeutic dose that balances efficacy and safety remains a complex task. This is further complicated by individual variations in metabolism and sensitivity to the compound, necessitating personalized treatment approaches.
The regulatory landscape presents a formidable barrier to muscimol integration. As a Schedule III controlled substance in many jurisdictions, its use in therapeutic practices is subject to strict regulations and oversight. Navigating these legal complexities and obtaining necessary approvals for clinical trials and eventual therapeutic use requires significant time, resources, and expertise.
Standardization of muscimol production and quality control poses another challenge. Ensuring consistent purity and potency across different batches is crucial for reliable therapeutic outcomes. The development of standardized extraction and synthesis methods, as well as rigorous quality assurance protocols, is essential to address this issue.
The potential for adverse interactions with other medications and substances is a concern that demands thorough investigation. As muscimol affects GABAergic neurotransmission, its interaction with other drugs that modulate brain activity must be carefully studied to prevent unforeseen complications in patients undergoing multiple treatments.
Public perception and stigma associated with psychoactive compounds present a social and educational challenge. Overcoming misconceptions and fostering acceptance of muscimol as a legitimate therapeutic agent requires extensive public education and awareness campaigns.
Lastly, the development of targeted delivery systems for muscimol presents a technological hurdle. Optimizing its bioavailability and ensuring it reaches specific brain regions while minimizing systemic exposure is crucial for maximizing therapeutic benefits and reducing potential side effects. This may involve exploring novel drug delivery technologies or formulations tailored to muscimol's unique properties.
Current Muscimol Integration Methods
01 Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol
Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include different formulations and delivery methods to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol. The compositions can be designed for treating neurological disorders, anxiety, or other conditions affected by GABA receptor modulation.- Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol: Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include different formulations and delivery methods to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol. The compositions can be designed for treating neurological disorders, anxiety, or other conditions affected by GABA receptor modulation.
- Muscimol analogs and derivatives: Research focuses on developing and synthesizing muscimol analogs and derivatives. These modified compounds aim to improve upon the properties of muscimol, such as increased potency, selectivity, or reduced side effects. The analogs may have different chemical structures but retain or enhance the pharmacological activity of muscimol.
- Methods of administering muscimol: Various methods for administering muscimol are explored to optimize its therapeutic effects. These may include novel drug delivery systems, controlled release formulations, or specific routes of administration such as transdermal, intranasal, or intravenous. The goal is to improve the drug's bioavailability and target specific areas of the body or brain.
- Muscimol in combination therapies: Muscimol is studied in combination with other active compounds to create synergistic therapeutic effects. These combination therapies may target multiple pathways or receptors simultaneously, potentially enhancing the overall efficacy of the treatment. The combinations are explored for various indications, including neurological and psychiatric disorders.
- Muscimol production and purification methods: Techniques for the production and purification of muscimol are developed to improve yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness. These methods may involve novel synthetic routes, biotechnological approaches, or extraction techniques from natural sources. Purification processes are optimized to ensure high-quality muscimol for pharmaceutical use.
02 Muscimol analogs and derivatives
Research focuses on developing and synthesizing muscimol analogs and derivatives. These modified compounds aim to improve upon the properties of muscimol, such as enhanced selectivity, potency, or reduced side effects. The analogs may be designed to target specific GABA receptor subtypes or to have improved pharmacokinetic profiles.Expand Specific Solutions03 Methods of administering muscimol
Various methods for administering muscimol are explored to optimize its therapeutic effects. These may include novel drug delivery systems, such as transdermal patches, intranasal sprays, or controlled-release formulations. The administration methods aim to improve bioavailability, reduce side effects, and enhance patient compliance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination therapies involving muscimol
Muscimol is investigated in combination with other therapeutic agents to create synergistic effects or address multiple aspects of a condition. These combination therapies may target complex disorders or aim to reduce the required dosage of individual components, potentially minimizing side effects while maintaining or improving efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions05 Muscimol in neurological and psychiatric treatments
Muscimol's potential in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders is a significant area of research. Its GABA-mimetic properties are explored for conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Studies focus on understanding its mechanism of action in the central nervous system and optimizing its therapeutic applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Muscimol Research
The research on Muscimol Integration in Emerging Therapeutic Practices is in its early stages, with the market still developing. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms. Key players like Vertex Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, and ACADIA Pharmaceuticals are investing in this area, leveraging their R&D capabilities. The market size is relatively small but growing, driven by increasing interest in novel therapeutic approaches. Technologically, the field is still evolving, with companies at various stages of development, from preclinical research to early clinical trials. This nascent stage presents opportunities for innovation and potential breakthroughs in muscimol-based therapies.
Glaxo Group Ltd.
Technical Solution: Glaxo Group Ltd., part of GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), has been investigating muscimol integration in the context of neuropsychiatric disorders. Their research focuses on developing a controlled-release formulation of muscimol for the treatment of anxiety and sleep disorders. GSK's approach involves encapsulating muscimol in a proprietary polymer matrix that allows for sustained release over 24 hours, potentially improving patient compliance and reducing dosing frequency[7]. Preclinical studies have demonstrated prolonged anxiolytic effects and improved sleep quality in rodent models[8]. The company is also exploring the potential of muscimol in combination with other GABA modulators to create a more comprehensive treatment for complex neuropsychiatric conditions. GSK has recently initiated a Phase I clinical trial to evaluate the pharmacokinetics and safety profile of their sustained-release muscimol formulation in healthy volunteers[9].
Strengths: Sustained-release formulation for improved patient compliance; Potential for combination therapies. Weaknesses: Limited to specific neuropsychiatric indications; Potential for tolerance development with long-term use.
Theravance Biopharma R&D IP LLC
Technical Solution: Theravance Biopharma has been exploring muscimol integration in the context of gastrointestinal disorders, particularly focusing on irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Their innovative approach involves developing a gut-restricted formulation of muscimol that targets GABA-A receptors in the enteric nervous system without systemic absorption. This localized action aims to modulate gut motility and reduce visceral hypersensitivity associated with IBS and IBD[13]. Preclinical studies have demonstrated significant improvements in abdominal pain scores and stool consistency in animal models of IBS[14]. Theravance is also investigating the potential anti-inflammatory effects of their muscimol formulation in the gut, which could provide additional benefits for IBD patients. The company has recently completed a Phase I clinical trial assessing the safety and pharmacokinetics of their gut-restricted muscimol formulation in healthy volunteers, with plans to initiate Phase II studies in IBS patients in the near future[15].
Strengths: Gut-restricted formulation for targeted action; Potential for treating both IBS and IBD. Weaknesses: Limited to gastrointestinal applications; Potential for local side effects in the gut.
Breakthrough Studies in Muscimol Therapeutics
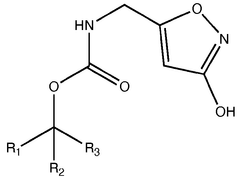
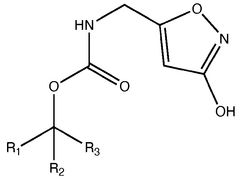
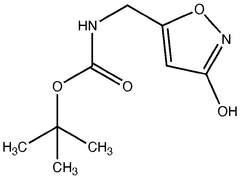
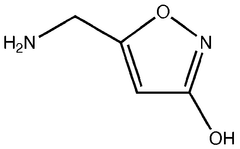
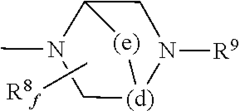
Pharmaceutical intermediates and methods for preparing the same in the synthesis of muscimol and congeners and derivatives thereof
PatentWO2025128106A1
Innovation
- A novel method for preparing muscimol mono-BOC and muscimol hydrochloride that avoids the use of ion exchange chromatography by modifying the original synthetic route to include a flow reactor for the cyclization step and using BOC anhydride to purify the muscimol, thereby stabilizing the product and improving yields.
Biphenyl compounds useful as muscarinic receptor antagonists
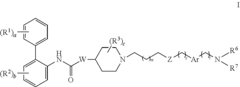
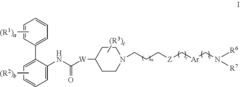
PatentInactiveUS20110281851A1
Innovation
- Development of novel biphenyl compounds with muscarinic receptor antagonist activity, designed for inhalation to provide high potency and reduced systemic side effects, with a long duration of action to enable once-daily or weekly dosing.
Regulatory Framework for Muscimol Use
The regulatory framework for muscimol use is a complex and evolving landscape that requires careful consideration. As muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, gains attention for its potential therapeutic applications, regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with how to classify and control its use.
In the United States, muscimol is not specifically scheduled under the Controlled Substances Act. However, its source, Amanita muscaria mushrooms, falls into a legal gray area. While the mushrooms themselves are not controlled substances, the extraction and concentration of muscimol may be interpreted as manufacturing a controlled substance analog, potentially leading to legal complications.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved any muscimol-based products for medical use. This means that any therapeutic applications are currently considered experimental and subject to strict research protocols. Clinical trials involving muscimol must adhere to rigorous FDA guidelines, including obtaining Investigational New Drug (IND) approval.
Internationally, the regulatory status of muscimol varies. Some countries have explicitly banned Amanita muscaria and its compounds, while others maintain ambiguous positions. The United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances does not list muscimol, leaving individual nations to determine their own regulatory approaches.
As research into muscimol's therapeutic potential progresses, there is growing pressure on regulatory bodies to establish clear guidelines. This includes defining acceptable purity standards, dosage limits, and administration protocols for clinical use. Additionally, regulators must consider the potential for abuse and implement appropriate safeguards.
The emerging therapeutic practices involving muscimol necessitate a balanced approach to regulation. On one hand, overly restrictive policies could hinder valuable research and potential medical breakthroughs. On the other, insufficient oversight could lead to safety risks and misuse. Regulatory frameworks must evolve to accommodate the unique properties of muscimol while ensuring public safety and promoting scientific advancement.
Moving forward, collaboration between researchers, healthcare professionals, and regulatory agencies will be crucial in developing appropriate guidelines. This may involve creating new categories for natural psychoactive compounds with therapeutic potential, distinct from traditional pharmaceutical regulations. Such an approach could facilitate responsible research while maintaining necessary controls.
In the United States, muscimol is not specifically scheduled under the Controlled Substances Act. However, its source, Amanita muscaria mushrooms, falls into a legal gray area. While the mushrooms themselves are not controlled substances, the extraction and concentration of muscimol may be interpreted as manufacturing a controlled substance analog, potentially leading to legal complications.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved any muscimol-based products for medical use. This means that any therapeutic applications are currently considered experimental and subject to strict research protocols. Clinical trials involving muscimol must adhere to rigorous FDA guidelines, including obtaining Investigational New Drug (IND) approval.
Internationally, the regulatory status of muscimol varies. Some countries have explicitly banned Amanita muscaria and its compounds, while others maintain ambiguous positions. The United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances does not list muscimol, leaving individual nations to determine their own regulatory approaches.
As research into muscimol's therapeutic potential progresses, there is growing pressure on regulatory bodies to establish clear guidelines. This includes defining acceptable purity standards, dosage limits, and administration protocols for clinical use. Additionally, regulators must consider the potential for abuse and implement appropriate safeguards.
The emerging therapeutic practices involving muscimol necessitate a balanced approach to regulation. On one hand, overly restrictive policies could hinder valuable research and potential medical breakthroughs. On the other, insufficient oversight could lead to safety risks and misuse. Regulatory frameworks must evolve to accommodate the unique properties of muscimol while ensuring public safety and promoting scientific advancement.
Moving forward, collaboration between researchers, healthcare professionals, and regulatory agencies will be crucial in developing appropriate guidelines. This may involve creating new categories for natural psychoactive compounds with therapeutic potential, distinct from traditional pharmaceutical regulations. Such an approach could facilitate responsible research while maintaining necessary controls.
Safety and Ethical Considerations
The integration of muscimol into emerging therapeutic practices necessitates a thorough examination of safety and ethical considerations. Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, presents unique challenges in clinical applications due to its potent effects on the central nervous system.
From a safety perspective, the primary concern is the potential for adverse reactions and interactions with other medications. Muscimol's GABAergic properties can lead to sedation, cognitive impairment, and altered perception, which may be problematic in certain patient populations. Rigorous dosing protocols and careful patient screening are essential to mitigate these risks.
Long-term effects of muscimol use in therapeutic settings remain largely unknown, necessitating extensive longitudinal studies to assess potential neurological impacts. Additionally, the risk of psychological dependence or misuse must be carefully evaluated, particularly in patients with a history of substance abuse disorders.
Ethical considerations surrounding muscimol integration are multifaceted. The use of psychoactive substances in therapy raises questions about informed consent and patient autonomy. Ensuring that patients fully understand the nature of the treatment and its potential risks is paramount. This includes addressing cultural and religious sensitivities that may arise from the use of substances traditionally associated with spiritual practices.
The potential for off-label use and recreational misuse of muscimol-based therapies presents another ethical challenge. Strict regulatory frameworks and prescribing guidelines must be established to prevent diversion and maintain the integrity of therapeutic applications.
Privacy and confidentiality concerns are heightened in muscimol-based treatments due to the deeply personal nature of psychedelic experiences. Protecting patient data and maintaining appropriate boundaries between therapists and patients becomes even more critical in these contexts.
Equitable access to muscimol-based therapies is an important ethical consideration. As research progresses, ensuring that these treatments are available to diverse populations and not limited by socioeconomic factors will be crucial for ethical implementation.
Lastly, the ethical implications of altering consciousness for therapeutic purposes must be carefully considered. This includes addressing concerns about the potential for psychological manipulation and ensuring that therapists are adequately trained to guide patients through altered states of consciousness safely and ethically.
From a safety perspective, the primary concern is the potential for adverse reactions and interactions with other medications. Muscimol's GABAergic properties can lead to sedation, cognitive impairment, and altered perception, which may be problematic in certain patient populations. Rigorous dosing protocols and careful patient screening are essential to mitigate these risks.
Long-term effects of muscimol use in therapeutic settings remain largely unknown, necessitating extensive longitudinal studies to assess potential neurological impacts. Additionally, the risk of psychological dependence or misuse must be carefully evaluated, particularly in patients with a history of substance abuse disorders.
Ethical considerations surrounding muscimol integration are multifaceted. The use of psychoactive substances in therapy raises questions about informed consent and patient autonomy. Ensuring that patients fully understand the nature of the treatment and its potential risks is paramount. This includes addressing cultural and religious sensitivities that may arise from the use of substances traditionally associated with spiritual practices.
The potential for off-label use and recreational misuse of muscimol-based therapies presents another ethical challenge. Strict regulatory frameworks and prescribing guidelines must be established to prevent diversion and maintain the integrity of therapeutic applications.
Privacy and confidentiality concerns are heightened in muscimol-based treatments due to the deeply personal nature of psychedelic experiences. Protecting patient data and maintaining appropriate boundaries between therapists and patients becomes even more critical in these contexts.
Equitable access to muscimol-based therapies is an important ethical consideration. As research progresses, ensuring that these treatments are available to diverse populations and not limited by socioeconomic factors will be crucial for ethical implementation.
Lastly, the ethical implications of altering consciousness for therapeutic purposes must be carefully considered. This includes addressing concerns about the potential for psychological manipulation and ensuring that therapists are adequately trained to guide patients through altered states of consciousness safely and ethically.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!