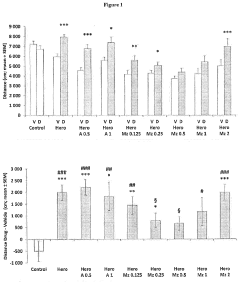
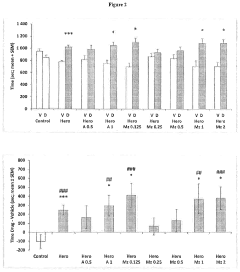
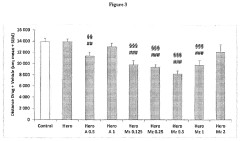
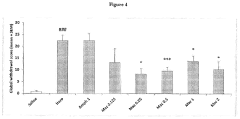
The Role of Muscimol in Substance Dependence Treatments
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Background
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has emerged as a compound of significant interest in the field of substance dependence treatments. This naturally occurring psychoactive compound is primarily found in various species of mushrooms, most notably in Amanita muscaria. Historically, these mushrooms have been used in traditional medicine and shamanic practices across different cultures, particularly in Siberia and parts of Europe.
The scientific exploration of muscimol began in the mid-20th century when it was first isolated and characterized. Its chemical structure, C4H6N2O2, was elucidated, revealing it to be a zwitterionic amino acid derivative. This discovery paved the way for further research into its pharmacological properties and potential therapeutic applications.
Muscimol's mechanism of action primarily involves its high affinity for GABA-A receptors in the central nervous system. By binding to these receptors, it enhances inhibitory neurotransmission, leading to various physiological and psychological effects. These effects include sedation, muscle relaxation, and alterations in mood and perception, which have sparked interest in its potential for treating various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
In the context of substance dependence, muscimol's ability to modulate GABAergic transmission has drawn attention from researchers. The GABAergic system plays a crucial role in the neurobiological processes underlying addiction, including reward processing, stress response, and withdrawal symptoms. This connection has led to investigations into muscimol's potential as a therapeutic agent for managing substance dependence disorders.
Early studies on muscimol focused primarily on its psychoactive properties and potential risks. However, as understanding of neurotransmitter systems and their role in addiction has advanced, research has shifted towards exploring its therapeutic potential. Preclinical studies have shown promising results in animal models of addiction, particularly in reducing drug-seeking behavior and mitigating withdrawal symptoms for various substances of abuse.
The growing interest in muscimol for substance dependence treatments is part of a broader trend in addiction research, which seeks to identify novel compounds that can target specific neural pathways involved in addiction. This approach aims to develop more effective and targeted therapies with potentially fewer side effects compared to traditional treatments.
As research progresses, the focus has expanded to include not only muscimol itself but also synthetic analogues and derivatives that may offer improved pharmacological profiles. These efforts aim to harness the beneficial effects of muscimol while minimizing potential adverse effects or abuse liability.
The scientific exploration of muscimol began in the mid-20th century when it was first isolated and characterized. Its chemical structure, C4H6N2O2, was elucidated, revealing it to be a zwitterionic amino acid derivative. This discovery paved the way for further research into its pharmacological properties and potential therapeutic applications.
Muscimol's mechanism of action primarily involves its high affinity for GABA-A receptors in the central nervous system. By binding to these receptors, it enhances inhibitory neurotransmission, leading to various physiological and psychological effects. These effects include sedation, muscle relaxation, and alterations in mood and perception, which have sparked interest in its potential for treating various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
In the context of substance dependence, muscimol's ability to modulate GABAergic transmission has drawn attention from researchers. The GABAergic system plays a crucial role in the neurobiological processes underlying addiction, including reward processing, stress response, and withdrawal symptoms. This connection has led to investigations into muscimol's potential as a therapeutic agent for managing substance dependence disorders.
Early studies on muscimol focused primarily on its psychoactive properties and potential risks. However, as understanding of neurotransmitter systems and their role in addiction has advanced, research has shifted towards exploring its therapeutic potential. Preclinical studies have shown promising results in animal models of addiction, particularly in reducing drug-seeking behavior and mitigating withdrawal symptoms for various substances of abuse.
The growing interest in muscimol for substance dependence treatments is part of a broader trend in addiction research, which seeks to identify novel compounds that can target specific neural pathways involved in addiction. This approach aims to develop more effective and targeted therapies with potentially fewer side effects compared to traditional treatments.
As research progresses, the focus has expanded to include not only muscimol itself but also synthetic analogues and derivatives that may offer improved pharmacological profiles. These efforts aim to harness the beneficial effects of muscimol while minimizing potential adverse effects or abuse liability.
Market Analysis
The market for substance dependence treatments has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of addiction issues and the need for effective interventions. Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, has emerged as a potential candidate for novel treatment approaches in this field.
The global substance abuse treatment market was valued at approximately $16.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $27.9 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 6.7% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the rising prevalence of substance abuse disorders, particularly opioid addiction, and the increasing focus on developing innovative treatment options.
Within this broader market, there is a growing interest in psychedelic-assisted therapies, including those utilizing compounds like muscimol. The psychedelic drug market, which encompasses muscimol and related substances, is expected to witness rapid expansion, with some estimates suggesting a CAGR of over 16% from 2020 to 2027.
The potential application of muscimol in substance dependence treatments aligns with the current trend towards personalized medicine and targeted therapies. As traditional treatment methods often face challenges in terms of efficacy and patient compliance, there is a significant unmet need for novel approaches that can address the complex nature of addiction.
Geographically, North America dominates the substance abuse treatment market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is primarily due to the high prevalence of substance abuse disorders in the region, coupled with advanced healthcare infrastructure and favorable reimbursement policies. Europe follows as the second-largest market, while Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years.
The market demand for muscimol-based treatments is likely to be influenced by several factors, including regulatory approvals, clinical trial outcomes, and shifts in healthcare policies. As research in this area progresses, there is potential for muscimol to carve out a niche within the broader substance dependence treatment market, particularly if it demonstrates efficacy in addressing treatment-resistant cases or offers advantages over existing therapies.
However, it is important to note that the market for muscimol-based treatments is still in its nascent stages. Regulatory hurdles, potential side effects, and the need for extensive clinical trials may impact the speed of market penetration. Additionally, public perception and acceptance of psychedelic-derived treatments will play a crucial role in shaping market demand.
As the field of addiction medicine continues to evolve, the role of muscimol in substance dependence treatments represents an area of significant market potential. Its success will depend on a combination of scientific validation, regulatory support, and strategic positioning within the competitive landscape of addiction therapeutics.
The global substance abuse treatment market was valued at approximately $16.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $27.9 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 6.7% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the rising prevalence of substance abuse disorders, particularly opioid addiction, and the increasing focus on developing innovative treatment options.
Within this broader market, there is a growing interest in psychedelic-assisted therapies, including those utilizing compounds like muscimol. The psychedelic drug market, which encompasses muscimol and related substances, is expected to witness rapid expansion, with some estimates suggesting a CAGR of over 16% from 2020 to 2027.
The potential application of muscimol in substance dependence treatments aligns with the current trend towards personalized medicine and targeted therapies. As traditional treatment methods often face challenges in terms of efficacy and patient compliance, there is a significant unmet need for novel approaches that can address the complex nature of addiction.
Geographically, North America dominates the substance abuse treatment market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is primarily due to the high prevalence of substance abuse disorders in the region, coupled with advanced healthcare infrastructure and favorable reimbursement policies. Europe follows as the second-largest market, while Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years.
The market demand for muscimol-based treatments is likely to be influenced by several factors, including regulatory approvals, clinical trial outcomes, and shifts in healthcare policies. As research in this area progresses, there is potential for muscimol to carve out a niche within the broader substance dependence treatment market, particularly if it demonstrates efficacy in addressing treatment-resistant cases or offers advantages over existing therapies.
However, it is important to note that the market for muscimol-based treatments is still in its nascent stages. Regulatory hurdles, potential side effects, and the need for extensive clinical trials may impact the speed of market penetration. Additionally, public perception and acceptance of psychedelic-derived treatments will play a crucial role in shaping market demand.
As the field of addiction medicine continues to evolve, the role of muscimol in substance dependence treatments represents an area of significant market potential. Its success will depend on a combination of scientific validation, regulatory support, and strategic positioning within the competitive landscape of addiction therapeutics.
Current Challenges
The current challenges in utilizing muscimol for substance dependence treatments are multifaceted and complex. One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of muscimol's precise mechanisms of action in the context of addiction. While its GABA-A receptor agonist properties are well-established, the intricate neurobiological pathways through which it may influence addictive behaviors remain unclear.
Another significant challenge lies in the potential side effects associated with muscimol administration. As a potent GABA-A agonist, muscimol can cause sedation, cognitive impairment, and motor incoordination. These effects could potentially interfere with patients' daily functioning and adherence to treatment protocols, necessitating careful dosage optimization and monitoring.
The pharmacokinetics of muscimol present additional hurdles. Its short half-life and poor oral bioavailability limit its therapeutic potential in its current form. Developing suitable formulations or delivery methods that can maintain effective concentrations in the brain while minimizing systemic exposure is a critical challenge that researchers must address.
Moreover, the regulatory landscape surrounding muscimol as a potential treatment for substance dependence is complex. As a naturally occurring psychoactive compound, muscimol faces stringent regulatory scrutiny. Navigating the regulatory pathways for clinical trials and potential approval as a therapeutic agent requires substantial resources and time.
The heterogeneity of substance use disorders poses another challenge in muscimol research. Different substances of abuse have distinct neurobiological underpinnings, and the efficacy of muscimol may vary across different types of addiction. Tailoring treatment approaches and identifying the most suitable patient populations for muscimol-based interventions remain significant challenges.
Additionally, the potential for abuse or misuse of muscimol itself is a concern that needs careful consideration. As a compound with psychoactive properties, there is a risk that it could be diverted or misused, potentially complicating its development as a therapeutic agent for substance dependence.
Lastly, the current lack of large-scale, long-term clinical studies on muscimol's efficacy and safety in treating substance dependence is a significant barrier. Conducting such studies requires substantial funding, time, and coordination among research institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and regulatory bodies. Overcoming these logistical and financial challenges is crucial for advancing muscimol as a viable treatment option for substance dependence.
Another significant challenge lies in the potential side effects associated with muscimol administration. As a potent GABA-A agonist, muscimol can cause sedation, cognitive impairment, and motor incoordination. These effects could potentially interfere with patients' daily functioning and adherence to treatment protocols, necessitating careful dosage optimization and monitoring.
The pharmacokinetics of muscimol present additional hurdles. Its short half-life and poor oral bioavailability limit its therapeutic potential in its current form. Developing suitable formulations or delivery methods that can maintain effective concentrations in the brain while minimizing systemic exposure is a critical challenge that researchers must address.
Moreover, the regulatory landscape surrounding muscimol as a potential treatment for substance dependence is complex. As a naturally occurring psychoactive compound, muscimol faces stringent regulatory scrutiny. Navigating the regulatory pathways for clinical trials and potential approval as a therapeutic agent requires substantial resources and time.
The heterogeneity of substance use disorders poses another challenge in muscimol research. Different substances of abuse have distinct neurobiological underpinnings, and the efficacy of muscimol may vary across different types of addiction. Tailoring treatment approaches and identifying the most suitable patient populations for muscimol-based interventions remain significant challenges.
Additionally, the potential for abuse or misuse of muscimol itself is a concern that needs careful consideration. As a compound with psychoactive properties, there is a risk that it could be diverted or misused, potentially complicating its development as a therapeutic agent for substance dependence.
Lastly, the current lack of large-scale, long-term clinical studies on muscimol's efficacy and safety in treating substance dependence is a significant barrier. Conducting such studies requires substantial funding, time, and coordination among research institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and regulatory bodies. Overcoming these logistical and financial challenges is crucial for advancing muscimol as a viable treatment option for substance dependence.
Treatment Approaches
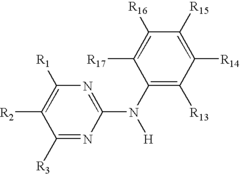
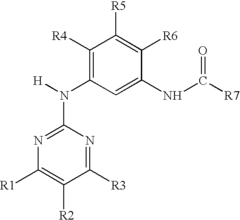
01 Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol
Muscimol is used in various pharmaceutical compositions for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. These formulations may include specific dosage forms, delivery methods, and combinations with other active ingredients to enhance therapeutic effects or reduce side effects.- Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol: Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include muscimol as an active ingredient, often in combination with other compounds or excipients. The formulations can be designed for different routes of administration and may target specific conditions or disorders.
- Muscimol for neurological and psychiatric disorders: Muscimol is investigated for its potential in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. It may be used in therapies targeting conditions such as anxiety, depression, epilepsy, and other central nervous system disorders. Research focuses on its GABA-ergic properties and potential neuroprotective effects.
- Synthesis and production methods for muscimol: Various methods for synthesizing and producing muscimol are developed. These may include chemical synthesis routes, biotechnological approaches, or extraction methods from natural sources. The focus is on improving yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness of muscimol production for research and pharmaceutical applications.
- Muscimol analogs and derivatives: Research into muscimol analogs and derivatives aims to develop compounds with improved pharmacological properties. These modified versions may have enhanced potency, selectivity, or reduced side effects compared to muscimol. Structure-activity relationship studies guide the design of these novel compounds.
- Drug delivery systems for muscimol: Innovative drug delivery systems are developed to improve the administration and efficacy of muscimol. These may include controlled release formulations, targeted delivery methods, or novel routes of administration. The goal is to enhance bioavailability, reduce side effects, and improve patient compliance.
02 Muscimol derivatives and analogs
Research focuses on developing muscimol derivatives and analogs with improved pharmacological properties. These modified compounds aim to enhance efficacy, reduce side effects, or alter the pharmacokinetic profile of muscimol for specific therapeutic applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Methods of synthesizing muscimol
Various methods for synthesizing muscimol and its derivatives are developed to improve yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness. These synthetic routes may involve novel catalysts, reaction conditions, or precursor compounds to optimize the production process.Expand Specific Solutions04 Muscimol in combination therapies
Muscimol is explored in combination with other therapeutic agents for synergistic effects in treating various conditions. These combinations may target multiple pathways or mechanisms to enhance overall treatment efficacy or address complex disorders.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery systems for muscimol
Innovative delivery systems are developed to improve the administration and bioavailability of muscimol. These may include transdermal patches, nanoparticle formulations, or targeted delivery mechanisms to enhance the compound's therapeutic potential and reduce systemic side effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The field of muscimol in substance dependence treatments is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as research progresses. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with various companies and institutions exploring its applications. Key players like McLean Hospital and PureTech Health are conducting pioneering research, while pharmaceutical companies such as Zambon Group and Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma are showing interest in potential drug development. Academic institutions like Louisiana State University and Trinity College Dublin are contributing to the fundamental understanding of muscimol's mechanisms. The involvement of diverse entities, from research hospitals to biotech firms, indicates a competitive landscape with significant potential for breakthroughs in addiction treatment.
McLean Hospital, Inc.
Technical Solution: McLean Hospital has been conducting extensive research on muscimol's potential in substance dependence treatments. Their approach involves using muscimol, a GABA-A receptor agonist, to modulate neural circuits implicated in addiction. The hospital's researchers have developed a novel drug delivery system that allows for targeted administration of muscimol to specific brain regions associated with addiction[1]. This method aims to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms in patients with substance use disorders. Additionally, McLean Hospital has initiated clinical trials combining muscimol with cognitive behavioral therapy to enhance treatment outcomes[3]. Their research also explores the potential of muscimol in treating alcohol use disorder, showing promising results in reducing alcohol consumption in animal models[5].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research combining pharmacological and behavioral approaches. Access to advanced neuroimaging facilities for monitoring treatment effects. Weaknesses: Limited long-term data on muscimol's efficacy and potential side effects in humans. Regulatory hurdles for novel drug delivery methods.
PureTech Health LLC
Technical Solution: PureTech Health has developed an innovative approach to utilizing muscimol in substance dependence treatments. Their proprietary technology, LYT-300, is an oral form of allopregnanolone that leverages muscimol's GABA-A receptor modulation properties[2]. This formulation is designed to overcome the poor oral bioavailability of allopregnanolone, potentially offering a more convenient and effective treatment option for substance use disorders. PureTech's research focuses on muscimol's ability to reduce anxiety and stress, which are often triggers for substance abuse. The company has conducted preclinical studies demonstrating LYT-300's efficacy in reducing alcohol consumption and drug-seeking behaviors[4]. Furthermore, PureTech is exploring the potential of combining muscimol-based treatments with digital therapeutics to provide comprehensive care for patients struggling with addiction[6].
Strengths: Innovative drug delivery system improving bioavailability. Potential for a more patient-friendly oral treatment. Weaknesses: Early-stage development with limited human trial data. Potential competition from established addiction treatments.
Pharmacological Insights
Mazindol treatment for heroin dependence and substance use disorder
PatentActiveUS20210161865A1
Innovation
- Mazindol, administered in a multi-layer matrix-type tablet with both immediate and sustained release layers, reduces opioid rewarding effects and withdrawal symptoms, providing a prolonged therapeutic effect and improved compliance through controlled release.
Use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors for treating substance use disorders
PatentInactiveUS20050203098A1
Innovation
- Administering tyrosine kinase inhibitors, particularly non-toxic and selective c-kit inhibitors, to deplete mast cells, thereby alleviating drug dependence and withdrawal symptoms by inhibiting mast cell proliferation and activation.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding the use of muscimol in substance dependence treatments is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental agencies and international bodies. At the forefront of this regulatory landscape is the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, which plays a crucial role in overseeing the development, testing, and approval of new pharmaceutical treatments. The FDA's rigorous approval process for new drugs includes multiple phases of clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy.
In the context of muscimol, its classification as a GABA receptor agonist places it under strict regulatory scrutiny. The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) also has a significant role in regulating muscimol due to its psychoactive properties. Currently, muscimol is classified as a Schedule III controlled substance in the United States, which impacts its research and potential therapeutic applications.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines on the use of psychoactive substances in medical treatments. These guidelines influence national policies and regulations across member states. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees similar regulatory processes within the European Union, ensuring that potential muscimol-based treatments meet stringent safety and efficacy standards.
Research institutions and pharmaceutical companies must navigate this complex regulatory environment when investigating muscimol's potential in substance dependence treatments. This includes obtaining necessary permits and approvals for conducting research, adhering to Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and ensuring compliance with ethical guidelines for human subject research.
The regulatory framework also encompasses post-market surveillance and pharmacovigilance requirements. Once approved, any muscimol-based treatments would be subject to ongoing monitoring for adverse effects and long-term safety. This involves reporting systems for healthcare providers and patients to document any unexpected side effects or complications.
Ethical considerations form another critical aspect of the regulatory landscape. Given the nature of substance dependence and the vulnerable populations involved, there are stringent ethical guidelines governing clinical trials and treatment protocols. Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) play a crucial role in ensuring that research protocols meet ethical standards and protect participants' rights and welfare.
As research into muscimol's potential for treating substance dependence progresses, regulatory bodies may need to adapt their frameworks to accommodate new scientific findings. This could involve reassessing the scheduling of muscimol or developing new guidelines specific to its use in addiction treatment. The evolving nature of drug policy and the increasing focus on alternative treatments for substance dependence may also influence future regulatory approaches to muscimol-based therapies.
In the context of muscimol, its classification as a GABA receptor agonist places it under strict regulatory scrutiny. The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) also has a significant role in regulating muscimol due to its psychoactive properties. Currently, muscimol is classified as a Schedule III controlled substance in the United States, which impacts its research and potential therapeutic applications.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines on the use of psychoactive substances in medical treatments. These guidelines influence national policies and regulations across member states. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees similar regulatory processes within the European Union, ensuring that potential muscimol-based treatments meet stringent safety and efficacy standards.
Research institutions and pharmaceutical companies must navigate this complex regulatory environment when investigating muscimol's potential in substance dependence treatments. This includes obtaining necessary permits and approvals for conducting research, adhering to Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and ensuring compliance with ethical guidelines for human subject research.
The regulatory framework also encompasses post-market surveillance and pharmacovigilance requirements. Once approved, any muscimol-based treatments would be subject to ongoing monitoring for adverse effects and long-term safety. This involves reporting systems for healthcare providers and patients to document any unexpected side effects or complications.
Ethical considerations form another critical aspect of the regulatory landscape. Given the nature of substance dependence and the vulnerable populations involved, there are stringent ethical guidelines governing clinical trials and treatment protocols. Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) play a crucial role in ensuring that research protocols meet ethical standards and protect participants' rights and welfare.
As research into muscimol's potential for treating substance dependence progresses, regulatory bodies may need to adapt their frameworks to accommodate new scientific findings. This could involve reassessing the scheduling of muscimol or developing new guidelines specific to its use in addiction treatment. The evolving nature of drug policy and the increasing focus on alternative treatments for substance dependence may also influence future regulatory approaches to muscimol-based therapies.
Ethical Considerations
The use of muscimol in substance dependence treatments raises several important ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. One primary concern is the potential for abuse or misuse of muscimol itself, given its psychoactive properties. Researchers and clinicians must implement strict protocols to ensure that the administration of muscimol is tightly controlled and monitored to prevent any unintended consequences or development of new dependencies.
Another critical ethical issue is the informed consent process. Patients must be fully informed about the experimental nature of muscimol-based treatments, including potential risks, side effects, and the current state of scientific knowledge regarding its efficacy. This transparency is crucial for maintaining patient autonomy and trust in the medical community.
The long-term effects of muscimol on brain function and overall health are not yet fully understood. Ethical research practices demand ongoing monitoring and follow-up studies to assess any potential negative impacts on patients' cognitive abilities, mental health, or quality of life. This longitudinal approach is essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals undergoing muscimol-based treatments.
Equity and access to treatment are also significant ethical considerations. As research progresses and if muscimol-based therapies prove effective, there may be disparities in access due to cost or availability. Ensuring fair distribution and accessibility of these treatments across different socioeconomic groups is crucial to avoid exacerbating existing healthcare inequalities.
Privacy and confidentiality concerns must be rigorously addressed, particularly given the sensitive nature of substance dependence treatments. Proper safeguards must be in place to protect patient data and prevent stigmatization or discrimination based on participation in muscimol-based treatment programs.
The ethical implications of using a substance with psychoactive properties to treat addiction also warrant careful consideration. This approach may challenge traditional views on substance use and addiction treatment, necessitating ongoing dialogue with patients, healthcare providers, and the broader public to address concerns and misconceptions.
Lastly, the potential for off-label use or self-medication with muscimol presents significant ethical challenges. Clear guidelines and regulations must be established to prevent misuse and ensure that muscimol-based treatments are only administered under proper medical supervision. Public education and awareness campaigns may be necessary to mitigate risks associated with unsupervised use or attempts to recreate treatments outside of clinical settings.
Another critical ethical issue is the informed consent process. Patients must be fully informed about the experimental nature of muscimol-based treatments, including potential risks, side effects, and the current state of scientific knowledge regarding its efficacy. This transparency is crucial for maintaining patient autonomy and trust in the medical community.
The long-term effects of muscimol on brain function and overall health are not yet fully understood. Ethical research practices demand ongoing monitoring and follow-up studies to assess any potential negative impacts on patients' cognitive abilities, mental health, or quality of life. This longitudinal approach is essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals undergoing muscimol-based treatments.
Equity and access to treatment are also significant ethical considerations. As research progresses and if muscimol-based therapies prove effective, there may be disparities in access due to cost or availability. Ensuring fair distribution and accessibility of these treatments across different socioeconomic groups is crucial to avoid exacerbating existing healthcare inequalities.
Privacy and confidentiality concerns must be rigorously addressed, particularly given the sensitive nature of substance dependence treatments. Proper safeguards must be in place to protect patient data and prevent stigmatization or discrimination based on participation in muscimol-based treatment programs.
The ethical implications of using a substance with psychoactive properties to treat addiction also warrant careful consideration. This approach may challenge traditional views on substance use and addiction treatment, necessitating ongoing dialogue with patients, healthcare providers, and the broader public to address concerns and misconceptions.
Lastly, the potential for off-label use or self-medication with muscimol presents significant ethical challenges. Clear guidelines and regulations must be established to prevent misuse and ensure that muscimol-based treatments are only administered under proper medical supervision. Public education and awareness campaigns may be necessary to mitigate risks associated with unsupervised use or attempts to recreate treatments outside of clinical settings.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!