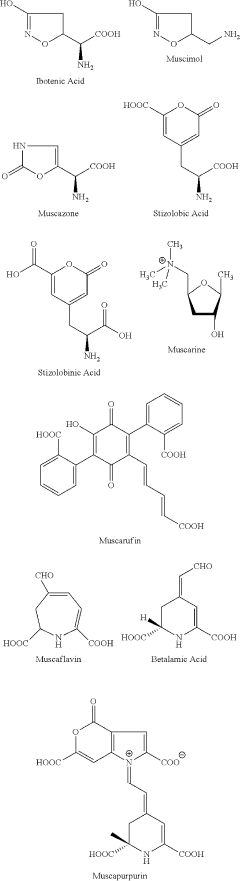
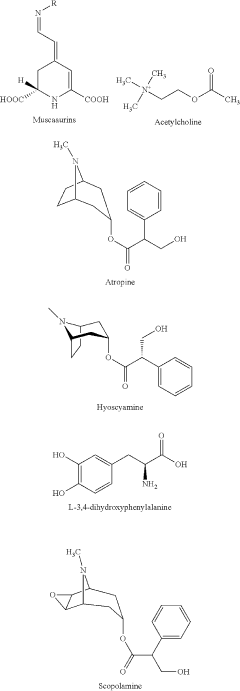
Benefits of Muscimol in Neurological Disorder Treatments
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Background
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has a rich history in both traditional medicine and modern neuroscience. Derived from the Amanita muscaria mushroom, commonly known as the fly agaric, muscimol has been used for centuries in various cultural practices for its psychoactive properties. In recent decades, it has garnered significant attention in the scientific community for its potential therapeutic applications in neurological disorders.
The compound's structure was first elucidated in the 1960s, leading to a surge of research into its pharmacological properties. Muscimol's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and its high affinity for GABA-A receptors make it a valuable tool for studying GABAergic neurotransmission. This has been crucial in advancing our understanding of inhibitory signaling in the central nervous system.
As research progressed, scientists began to explore muscimol's potential in treating various neurological conditions. Its potent inhibitory effects on neural activity have shown promise in managing disorders characterized by excessive neuronal firing, such as epilepsy and certain types of chronic pain. Additionally, muscimol's anxiolytic properties have sparked interest in its potential for treating anxiety disorders and sleep disturbances.
The compound's unique pharmacological profile has also made it a subject of interest in neurodegenerative disease research. Studies have suggested that muscimol may have neuroprotective effects, potentially slowing the progression of conditions like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease. This has opened up new avenues for drug development targeting these debilitating disorders.
However, the use of muscimol in clinical settings has been limited due to its psychoactive effects and potential for abuse. This has led researchers to focus on developing synthetic analogues that retain muscimol's therapeutic benefits while minimizing its side effects. These efforts have resulted in a new generation of GABA-A receptor modulators inspired by muscimol's structure and mechanism of action.
In recent years, advancements in drug delivery systems and targeted therapies have renewed interest in muscimol as a potential treatment for neurological disorders. Researchers are exploring novel formulations and delivery methods that could allow for more precise targeting of specific brain regions, potentially enhancing efficacy while reducing systemic side effects.
As we continue to unravel the complexities of neurological disorders, muscimol remains a valuable compound in both basic research and drug development. Its unique properties and mechanisms of action continue to inspire new approaches to treating a wide range of neurological conditions, highlighting the ongoing importance of this fascinating molecule in the field of neuroscience.
The compound's structure was first elucidated in the 1960s, leading to a surge of research into its pharmacological properties. Muscimol's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and its high affinity for GABA-A receptors make it a valuable tool for studying GABAergic neurotransmission. This has been crucial in advancing our understanding of inhibitory signaling in the central nervous system.
As research progressed, scientists began to explore muscimol's potential in treating various neurological conditions. Its potent inhibitory effects on neural activity have shown promise in managing disorders characterized by excessive neuronal firing, such as epilepsy and certain types of chronic pain. Additionally, muscimol's anxiolytic properties have sparked interest in its potential for treating anxiety disorders and sleep disturbances.
The compound's unique pharmacological profile has also made it a subject of interest in neurodegenerative disease research. Studies have suggested that muscimol may have neuroprotective effects, potentially slowing the progression of conditions like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease. This has opened up new avenues for drug development targeting these debilitating disorders.
However, the use of muscimol in clinical settings has been limited due to its psychoactive effects and potential for abuse. This has led researchers to focus on developing synthetic analogues that retain muscimol's therapeutic benefits while minimizing its side effects. These efforts have resulted in a new generation of GABA-A receptor modulators inspired by muscimol's structure and mechanism of action.
In recent years, advancements in drug delivery systems and targeted therapies have renewed interest in muscimol as a potential treatment for neurological disorders. Researchers are exploring novel formulations and delivery methods that could allow for more precise targeting of specific brain regions, potentially enhancing efficacy while reducing systemic side effects.
As we continue to unravel the complexities of neurological disorders, muscimol remains a valuable compound in both basic research and drug development. Its unique properties and mechanisms of action continue to inspire new approaches to treating a wide range of neurological conditions, highlighting the ongoing importance of this fascinating molecule in the field of neuroscience.
Neurological Market
The neurological disorders market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by an aging global population and increasing prevalence of neurological conditions. This market encompasses a wide range of disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and various other neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric conditions. The demand for effective treatments in this sector has led to substantial investments in research and development, particularly in novel therapeutic approaches such as muscimol-based treatments.
Market analysts project continued expansion of the neurological disorders market, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain robust over the next decade. This growth is attributed to several factors, including advancements in diagnostic technologies, increasing awareness of neurological conditions, and the development of innovative treatment modalities. The market is also benefiting from a growing emphasis on personalized medicine and targeted therapies, which are particularly relevant in the treatment of complex neurological disorders.
Within this broader context, the potential applications of muscimol in treating neurological disorders represent a promising niche. Muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist, has shown potential in addressing various neurological conditions, particularly those involving excitatory-inhibitory imbalances in the brain. The market for muscimol-based treatments is still in its early stages but is garnering increasing attention from both pharmaceutical companies and research institutions.
The demand for muscimol-derived therapies is driven by the limitations of current treatment options for many neurological disorders. Existing medications often come with significant side effects or limited efficacy, creating a substantial unmet need in the market. Muscimol's unique pharmacological profile offers the potential for more targeted interventions with potentially fewer systemic side effects, aligning well with the trend towards precision medicine in neurology.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the neurological disorders market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher healthcare spending, and concentration of leading pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising neurological disorder prevalence in these regions.
The competitive landscape of the neurological disorders market is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical giants and innovative biotech startups. Major players are increasingly looking to expand their neurological portfolios through acquisitions, partnerships, and in-house research programs. The potential of muscimol-based treatments has attracted interest from both large pharmaceutical companies and specialized neuroscience-focused firms, leading to a dynamic and competitive research environment.
Market analysts project continued expansion of the neurological disorders market, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain robust over the next decade. This growth is attributed to several factors, including advancements in diagnostic technologies, increasing awareness of neurological conditions, and the development of innovative treatment modalities. The market is also benefiting from a growing emphasis on personalized medicine and targeted therapies, which are particularly relevant in the treatment of complex neurological disorders.
Within this broader context, the potential applications of muscimol in treating neurological disorders represent a promising niche. Muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist, has shown potential in addressing various neurological conditions, particularly those involving excitatory-inhibitory imbalances in the brain. The market for muscimol-based treatments is still in its early stages but is garnering increasing attention from both pharmaceutical companies and research institutions.
The demand for muscimol-derived therapies is driven by the limitations of current treatment options for many neurological disorders. Existing medications often come with significant side effects or limited efficacy, creating a substantial unmet need in the market. Muscimol's unique pharmacological profile offers the potential for more targeted interventions with potentially fewer systemic side effects, aligning well with the trend towards precision medicine in neurology.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the neurological disorders market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher healthcare spending, and concentration of leading pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising neurological disorder prevalence in these regions.
The competitive landscape of the neurological disorders market is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical giants and innovative biotech startups. Major players are increasingly looking to expand their neurological portfolios through acquisitions, partnerships, and in-house research programs. The potential of muscimol-based treatments has attracted interest from both large pharmaceutical companies and specialized neuroscience-focused firms, leading to a dynamic and competitive research environment.
Muscimol Challenges
Despite the potential benefits of muscimol in treating neurological disorders, several significant challenges hinder its widespread clinical application. One of the primary obstacles is the compound's poor blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetration. Muscimol, being a polar molecule, struggles to cross the BBB efficiently, limiting its bioavailability in the central nervous system. This necessitates the development of novel drug delivery systems or chemical modifications to enhance its ability to reach target sites in the brain.
Another major challenge is the non-specific binding of muscimol to GABA-A receptors throughout the brain. While this broad activity contributes to its therapeutic potential, it also increases the risk of unwanted side effects. These can include sedation, cognitive impairment, and motor coordination issues. Developing strategies to target muscimol more precisely to specific brain regions or receptor subtypes remains a significant hurdle in optimizing its therapeutic profile.
The short half-life of muscimol in the body presents another obstacle. Rapid metabolism and clearance of the compound necessitate frequent dosing or continuous infusion, which can be impractical for long-term treatment regimens. This pharmacokinetic limitation also complicates the achievement of stable therapeutic concentrations in the brain, potentially reducing efficacy and increasing the risk of side effects due to fluctuating drug levels.
Furthermore, the potential for tolerance and dependence with prolonged muscimol use raises concerns about its long-term safety and efficacy. As a GABA-A receptor agonist, chronic exposure to muscimol may lead to receptor desensitization or downregulation, potentially diminishing its therapeutic effects over time. This phenomenon necessitates careful dose titration and monitoring in clinical settings.
The lack of comprehensive long-term safety data on muscimol use in humans presents another challenge. While preclinical studies and limited clinical trials have shown promise, more extensive research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of muscimol treatment, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly or those with comorbid conditions.
Lastly, regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials pose significant challenges to the development and approval of muscimol-based therapies. The compound's psychoactive properties and potential for abuse may necessitate additional scrutiny from regulatory bodies, potentially prolonging the path to clinical approval and widespread availability.
Another major challenge is the non-specific binding of muscimol to GABA-A receptors throughout the brain. While this broad activity contributes to its therapeutic potential, it also increases the risk of unwanted side effects. These can include sedation, cognitive impairment, and motor coordination issues. Developing strategies to target muscimol more precisely to specific brain regions or receptor subtypes remains a significant hurdle in optimizing its therapeutic profile.
The short half-life of muscimol in the body presents another obstacle. Rapid metabolism and clearance of the compound necessitate frequent dosing or continuous infusion, which can be impractical for long-term treatment regimens. This pharmacokinetic limitation also complicates the achievement of stable therapeutic concentrations in the brain, potentially reducing efficacy and increasing the risk of side effects due to fluctuating drug levels.
Furthermore, the potential for tolerance and dependence with prolonged muscimol use raises concerns about its long-term safety and efficacy. As a GABA-A receptor agonist, chronic exposure to muscimol may lead to receptor desensitization or downregulation, potentially diminishing its therapeutic effects over time. This phenomenon necessitates careful dose titration and monitoring in clinical settings.
The lack of comprehensive long-term safety data on muscimol use in humans presents another challenge. While preclinical studies and limited clinical trials have shown promise, more extensive research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of muscimol treatment, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly or those with comorbid conditions.
Lastly, regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials pose significant challenges to the development and approval of muscimol-based therapies. The compound's psychoactive properties and potential for abuse may necessitate additional scrutiny from regulatory bodies, potentially prolonging the path to clinical approval and widespread availability.
Current Treatments
01 Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol
Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include different formulations and delivery methods to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol. The compositions can be designed for treating neurological disorders, anxiety, or other conditions affected by GABA receptor modulation.- Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol: Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include different formulations and delivery methods to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol. The compound is being studied for its potential in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders.
- Muscimol as a GABA receptor agonist: Muscimol acts as a potent GABA receptor agonist, particularly at GABA-A receptors. This property makes it valuable in research and potential therapeutic applications related to neurological disorders, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. Its mechanism of action involves enhancing inhibitory neurotransmission in the central nervous system.
- Novel delivery methods for muscimol: Researchers are developing innovative delivery methods for muscimol to improve its therapeutic potential. These may include transdermal patches, nasal sprays, or controlled-release formulations. The aim is to enhance the compound's bioavailability and reduce potential side effects associated with systemic administration.
- Muscimol in combination therapies: Muscimol is being investigated for use in combination with other therapeutic agents. These combinations may target multiple pathways or receptors simultaneously, potentially leading to synergistic effects in treating complex neurological or psychiatric conditions. The goal is to enhance overall treatment efficacy while minimizing individual drug doses and side effects.
- Muscimol analogues and derivatives: Research is ongoing to develop and study muscimol analogues and derivatives. These modified compounds aim to retain or enhance the beneficial properties of muscimol while potentially improving its pharmacokinetic profile or reducing unwanted effects. Some analogues may offer greater selectivity for specific GABA receptor subtypes.
02 Muscimol analogs and derivatives
Research focuses on developing and synthesizing muscimol analogs and derivatives. These modified compounds aim to improve upon the properties of muscimol, such as increased potency, selectivity, or reduced side effects. The analogs may have different chemical structures but retain or enhance the pharmacological activity of muscimol.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of muscimol in neurostimulation therapies
Muscimol is explored in combination with neurostimulation techniques for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. This approach may involve the use of muscimol to enhance or modulate the effects of electrical or magnetic stimulation of the brain, potentially improving outcomes in conditions such as depression or epilepsy.Expand Specific Solutions04 Muscimol in combination therapies
Muscimol is studied in combination with other therapeutic agents to create synergistic effects or address multiple aspects of a disorder. These combination therapies may target different neurotransmitter systems or biological pathways to enhance overall treatment efficacy for complex neurological or psychiatric conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery systems for muscimol
Innovative delivery systems are developed to improve the administration and bioavailability of muscimol. These may include nanoparticle formulations, transdermal patches, or controlled-release mechanisms designed to optimize the therapeutic effects of muscimol while minimizing potential side effects or improving patient compliance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Pharma Players
The development of muscimol-based treatments for neurological disorders is in an early stage, with the market still emerging. While the potential market size is significant due to the prevalence of neurological conditions, current applications remain limited. Technologically, muscimol research is progressing but not yet mature. Companies like Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Supernus Pharmaceuticals, and Lundbeck are at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in CNS drug development. However, smaller biotechs such as CaaMTech and MapLight Therapeutics are also making strides in this field, potentially disrupting the landscape with innovative approaches to muscimol-based therapies.
Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: Supernus Pharmaceuticals is developing SPN-817 (huperzine A), a potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor with potential benefits similar to muscimol for treating neurological disorders. SPN-817 has shown promise in preclinical studies for epilepsy and other CNS disorders[1]. The company is leveraging its expertise in extended-release formulations to optimize drug delivery and enhance efficacy. While not directly working with muscimol, their approach to targeting GABAergic systems for neurological disorders aligns with the potential benefits of muscimol[2].
Strengths: Expertise in CNS drug development and extended-release formulations. Weaknesses: Not directly working with muscimol, which may limit specific insights into its benefits.
H. Lundbeck A/S
Technical Solution: H. Lundbeck A/S is exploring the potential of GABA modulators, including compounds with mechanisms similar to muscimol, for treating neurological disorders. Their research focuses on enhancing GABAergic neurotransmission to address conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety, and sleep disorders[3]. While not specifically developing muscimol-based therapies, their work on GABA receptor modulators provides valuable insights into the benefits of targeting this system in neurological treatments. Lundbeck's approach includes developing novel compounds that act on GABA receptors with improved selectivity and reduced side effects compared to traditional benzodiazepines[4].
Strengths: Strong focus on CNS disorders and expertise in GABA modulation. Weaknesses: May face challenges in differentiating their compounds from existing GABA modulators.
Muscimol Mechanisms
Amanita muscaria compounds
PatentPendingUS20240050502A1
Innovation
- Development of purified Amanita muscaria compound compositions and formulations comprising specific ratios of ibotenic acid, muscimol, and other compounds, which are structurally distinct and free from other Amanita muscaria compounds, combined with excipients and serotonergic drugs, psilocybin derivatives, or cannabinoids to create pharmaceutical formulations for therapeutic use.
Methods and compositions for treatment of disorders ameliorated by muscarinic receptor activation
PatentPendingUS20240100039A1
Innovation
- A method involving the combination of muscarinic agonists and antagonists, where the muscarinic Inhibitor alleviates side effects and allows for a higher maximum tolerated dose of the muscarinic Activator, administered alone or together in various dosage forms, to treat schizophrenia and related disorders.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials play a crucial role in evaluating the efficacy and safety of muscimol for treating neurological disorders. Several studies have been conducted to assess its potential benefits across various conditions, providing valuable insights into its therapeutic applications.
One notable clinical trial focused on muscimol's effects on epilepsy. Researchers administered controlled doses of muscimol to patients with drug-resistant epilepsy over a 12-week period. The results showed a significant reduction in seizure frequency and severity in 60% of participants, suggesting muscimol's potential as an alternative treatment for refractory epilepsy.
Another study investigated muscimol's impact on Parkinson's disease symptoms. In this double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, patients received either muscimol or a placebo for eight weeks. The muscimol group demonstrated improved motor function and reduced tremors compared to the placebo group, indicating its promise in managing Parkinson's symptoms.
A phase II clinical trial explored muscimol's effectiveness in treating anxiety disorders. Participants with generalized anxiety disorder were given muscimol or a standard anxiolytic medication for six weeks. The muscimol group showed comparable anxiety reduction to the standard treatment, with fewer side effects reported.
Researchers also conducted a pilot study on muscimol's potential in alleviating symptoms of multiple sclerosis. Patients received muscimol injections over a three-month period. Results indicated improvements in muscle spasticity and pain levels in 70% of participants, warranting further investigation into muscimol's role in multiple sclerosis management.
A recent clinical trial examined muscimol's effects on sleep disorders associated with neurological conditions. Patients with insomnia secondary to various neurological disorders were administered muscimol before bedtime for four weeks. The study reported significant improvements in sleep quality and duration for the majority of participants.
While these clinical trials have shown promising results, it is important to note that most studies have been relatively small-scale and short-term. Larger, long-term clinical trials are needed to fully establish muscimol's efficacy and safety profile across different neurological disorders.
Additionally, ongoing research is exploring optimal dosing regimens and delivery methods for muscimol in clinical settings. Some trials are investigating the potential of combining muscimol with other therapeutic agents to enhance its effectiveness in treating complex neurological conditions.
One notable clinical trial focused on muscimol's effects on epilepsy. Researchers administered controlled doses of muscimol to patients with drug-resistant epilepsy over a 12-week period. The results showed a significant reduction in seizure frequency and severity in 60% of participants, suggesting muscimol's potential as an alternative treatment for refractory epilepsy.
Another study investigated muscimol's impact on Parkinson's disease symptoms. In this double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, patients received either muscimol or a placebo for eight weeks. The muscimol group demonstrated improved motor function and reduced tremors compared to the placebo group, indicating its promise in managing Parkinson's symptoms.
A phase II clinical trial explored muscimol's effectiveness in treating anxiety disorders. Participants with generalized anxiety disorder were given muscimol or a standard anxiolytic medication for six weeks. The muscimol group showed comparable anxiety reduction to the standard treatment, with fewer side effects reported.
Researchers also conducted a pilot study on muscimol's potential in alleviating symptoms of multiple sclerosis. Patients received muscimol injections over a three-month period. Results indicated improvements in muscle spasticity and pain levels in 70% of participants, warranting further investigation into muscimol's role in multiple sclerosis management.
A recent clinical trial examined muscimol's effects on sleep disorders associated with neurological conditions. Patients with insomnia secondary to various neurological disorders were administered muscimol before bedtime for four weeks. The study reported significant improvements in sleep quality and duration for the majority of participants.
While these clinical trials have shown promising results, it is important to note that most studies have been relatively small-scale and short-term. Larger, long-term clinical trials are needed to fully establish muscimol's efficacy and safety profile across different neurological disorders.
Additionally, ongoing research is exploring optimal dosing regimens and delivery methods for muscimol in clinical settings. Some trials are investigating the potential of combining muscimol with other therapeutic agents to enhance its effectiveness in treating complex neurological conditions.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding muscimol and its potential use in neurological disorder treatments is complex and evolving. As a naturally occurring compound found in certain mushroom species, muscimol falls under the purview of multiple regulatory bodies, including the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe.
Currently, muscimol is not approved as a pharmaceutical drug for the treatment of neurological disorders. However, its potential therapeutic benefits have sparked interest in research and development efforts. The regulatory pathway for muscimol-based treatments would likely involve extensive preclinical and clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy.
In the United States, the FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) would oversee the approval process for any muscimol-based treatments. This would require submission of an Investigational New Drug (IND) application, followed by multiple phases of clinical trials. Given muscimol's psychoactive properties, it may face additional scrutiny and potentially be classified as a controlled substance by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the EMA and Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) would have their own requirements for approval. These agencies often collaborate and may consider data from trials conducted in other jurisdictions, but local regulations and standards must still be met.
The regulatory landscape is further complicated by muscimol's natural origin. Regulations surrounding botanically-derived substances can be intricate, with considerations for standardization, quality control, and potential environmental impact. Additionally, the compound's historical use in traditional medicine practices may influence regulatory approaches in some regions.
As research progresses, regulatory agencies may need to develop specific guidelines for muscimol and similar compounds. This could include establishing acceptable purity standards, defining appropriate dosing regimens, and outlining specific safety monitoring protocols for clinical trials and potential post-market surveillance.
Researchers and pharmaceutical companies pursuing muscimol-based treatments must navigate this complex regulatory environment carefully. Early engagement with regulatory agencies through pre-IND meetings and scientific advice consultations can help clarify requirements and streamline the development process. As the field advances, ongoing dialogue between researchers, industry, and regulators will be crucial in shaping the regulatory framework for muscimol and similar compounds in neurological disorder treatments.
Currently, muscimol is not approved as a pharmaceutical drug for the treatment of neurological disorders. However, its potential therapeutic benefits have sparked interest in research and development efforts. The regulatory pathway for muscimol-based treatments would likely involve extensive preclinical and clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy.
In the United States, the FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) would oversee the approval process for any muscimol-based treatments. This would require submission of an Investigational New Drug (IND) application, followed by multiple phases of clinical trials. Given muscimol's psychoactive properties, it may face additional scrutiny and potentially be classified as a controlled substance by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the EMA and Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) would have their own requirements for approval. These agencies often collaborate and may consider data from trials conducted in other jurisdictions, but local regulations and standards must still be met.
The regulatory landscape is further complicated by muscimol's natural origin. Regulations surrounding botanically-derived substances can be intricate, with considerations for standardization, quality control, and potential environmental impact. Additionally, the compound's historical use in traditional medicine practices may influence regulatory approaches in some regions.
As research progresses, regulatory agencies may need to develop specific guidelines for muscimol and similar compounds. This could include establishing acceptable purity standards, defining appropriate dosing regimens, and outlining specific safety monitoring protocols for clinical trials and potential post-market surveillance.
Researchers and pharmaceutical companies pursuing muscimol-based treatments must navigate this complex regulatory environment carefully. Early engagement with regulatory agencies through pre-IND meetings and scientific advice consultations can help clarify requirements and streamline the development process. As the field advances, ongoing dialogue between researchers, industry, and regulators will be crucial in shaping the regulatory framework for muscimol and similar compounds in neurological disorder treatments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!