Muscimol's Role in Modulating Mood Disorders
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Background
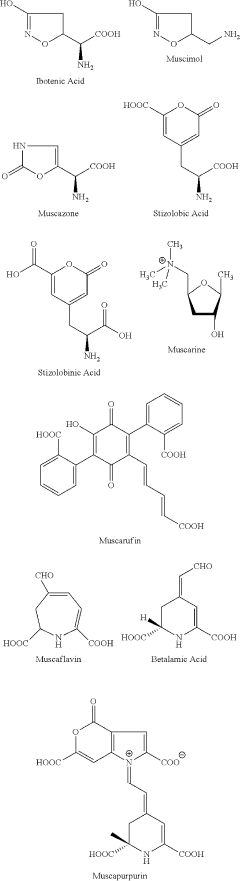
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has been the subject of extensive research in the field of neuroscience and psychopharmacology. This naturally occurring psychoactive compound is primarily found in various species of mushrooms, most notably Amanita muscaria. Historically, these mushrooms have been used in traditional medicine and shamanic practices across different cultures, particularly in Siberia and parts of Northern Europe.
The scientific interest in muscimol began in the mid-20th century when researchers started investigating the chemical composition of Amanita muscaria. In 1964, muscimol was first isolated and identified as one of the primary psychoactive components of these mushrooms. This discovery marked the beginning of a new era in understanding the neurochemical basis of mood regulation and the potential therapeutic applications of GABA-ergic compounds.
Muscimol's molecular structure closely resembles that of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. This structural similarity allows muscimol to bind to GABA-A receptors with high affinity, leading to enhanced inhibitory neurotransmission. The compound's ability to modulate GABAergic signaling has made it a valuable tool in neuroscience research, particularly in studies exploring the role of inhibitory neurotransmission in mood regulation.
Over the past few decades, the understanding of muscimol's pharmacological properties has evolved significantly. Research has revealed that muscimol's effects extend beyond simple GABA-A receptor activation. It has been found to influence various neurotransmitter systems, including dopamine and serotonin, which are crucial in mood regulation. This complex interaction with multiple neurotransmitter systems has sparked interest in muscimol's potential as a therapeutic agent for mood disorders.
The exploration of muscimol's role in mood modulation has been driven by the increasing prevalence of mood disorders worldwide and the limitations of current treatment options. Traditional antidepressants and mood stabilizers often have delayed onset of action and significant side effects, prompting the search for novel therapeutic approaches. Muscimol's rapid and potent effects on neural signaling have positioned it as a promising candidate for developing new treatments for conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder.
Recent advancements in neuroimaging and electrophysiological techniques have allowed researchers to gain deeper insights into muscimol's effects on brain function. These studies have revealed that muscimol can modulate neural activity in key brain regions associated with mood regulation, including the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus. This growing body of evidence has further strengthened the rationale for investigating muscimol's therapeutic potential in mood disorders.
The scientific interest in muscimol began in the mid-20th century when researchers started investigating the chemical composition of Amanita muscaria. In 1964, muscimol was first isolated and identified as one of the primary psychoactive components of these mushrooms. This discovery marked the beginning of a new era in understanding the neurochemical basis of mood regulation and the potential therapeutic applications of GABA-ergic compounds.
Muscimol's molecular structure closely resembles that of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. This structural similarity allows muscimol to bind to GABA-A receptors with high affinity, leading to enhanced inhibitory neurotransmission. The compound's ability to modulate GABAergic signaling has made it a valuable tool in neuroscience research, particularly in studies exploring the role of inhibitory neurotransmission in mood regulation.
Over the past few decades, the understanding of muscimol's pharmacological properties has evolved significantly. Research has revealed that muscimol's effects extend beyond simple GABA-A receptor activation. It has been found to influence various neurotransmitter systems, including dopamine and serotonin, which are crucial in mood regulation. This complex interaction with multiple neurotransmitter systems has sparked interest in muscimol's potential as a therapeutic agent for mood disorders.
The exploration of muscimol's role in mood modulation has been driven by the increasing prevalence of mood disorders worldwide and the limitations of current treatment options. Traditional antidepressants and mood stabilizers often have delayed onset of action and significant side effects, prompting the search for novel therapeutic approaches. Muscimol's rapid and potent effects on neural signaling have positioned it as a promising candidate for developing new treatments for conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder.
Recent advancements in neuroimaging and electrophysiological techniques have allowed researchers to gain deeper insights into muscimol's effects on brain function. These studies have revealed that muscimol can modulate neural activity in key brain regions associated with mood regulation, including the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus. This growing body of evidence has further strengthened the rationale for investigating muscimol's therapeutic potential in mood disorders.
Market Analysis
The market for mood disorder treatments has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of mental health issues and the rising prevalence of mood disorders worldwide. Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, has emerged as a potential therapeutic agent for modulating mood disorders, attracting attention from both pharmaceutical companies and mental health professionals.
The global mood disorders treatment market is projected to expand substantially in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to exceed 5% through 2027. This growth is fueled by factors such as the increasing incidence of depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorders, as well as the growing acceptance of mental health treatments in developing countries. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, as lockdowns and social isolation have led to a surge in mental health issues globally.
Within this broader market, there is a growing interest in novel therapeutic approaches, including psychedelic-based treatments. Muscimol, with its unique pharmacological properties, has the potential to carve out a niche within this emerging segment. The compound's ability to modulate GABA receptors, which play a crucial role in regulating mood and anxiety, positions it as a promising candidate for mood disorder treatments.
Several pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are actively exploring muscimol's potential in clinical settings. Early-stage clinical trials have shown promising results in treating anxiety and depression, with fewer side effects compared to traditional antidepressants. This has sparked interest from both established pharmaceutical giants and innovative biotech startups, leading to increased investment in muscimol-based drug development programs.
The market demand for muscimol-based treatments is likely to be driven by patients seeking alternatives to conventional mood disorder medications, which often come with significant side effects and variable efficacy. Additionally, healthcare providers are increasingly open to exploring novel therapeutic options, particularly for treatment-resistant cases of depression and anxiety.
However, the market for muscimol-based treatments faces several challenges. Regulatory hurdles remain significant, as psychoactive compounds often face stringent approval processes. Public perception and potential stigma associated with mushroom-derived compounds may also impact market acceptance. Furthermore, competition from other emerging psychedelic-based therapies, such as psilocybin and ketamine, could influence muscimol's market share.
Despite these challenges, the potential market for muscimol in mood disorder treatment remains substantial. As research progresses and clinical evidence accumulates, muscimol-based therapies could capture a significant portion of the mood disorder treatment market, particularly in treatment-resistant cases or as part of combination therapies. The compound's unique mechanism of action and potential for fewer side effects position it as a valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal against mood disorders, potentially improving outcomes for millions of patients worldwide.
The global mood disorders treatment market is projected to expand substantially in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to exceed 5% through 2027. This growth is fueled by factors such as the increasing incidence of depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorders, as well as the growing acceptance of mental health treatments in developing countries. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, as lockdowns and social isolation have led to a surge in mental health issues globally.
Within this broader market, there is a growing interest in novel therapeutic approaches, including psychedelic-based treatments. Muscimol, with its unique pharmacological properties, has the potential to carve out a niche within this emerging segment. The compound's ability to modulate GABA receptors, which play a crucial role in regulating mood and anxiety, positions it as a promising candidate for mood disorder treatments.
Several pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are actively exploring muscimol's potential in clinical settings. Early-stage clinical trials have shown promising results in treating anxiety and depression, with fewer side effects compared to traditional antidepressants. This has sparked interest from both established pharmaceutical giants and innovative biotech startups, leading to increased investment in muscimol-based drug development programs.
The market demand for muscimol-based treatments is likely to be driven by patients seeking alternatives to conventional mood disorder medications, which often come with significant side effects and variable efficacy. Additionally, healthcare providers are increasingly open to exploring novel therapeutic options, particularly for treatment-resistant cases of depression and anxiety.
However, the market for muscimol-based treatments faces several challenges. Regulatory hurdles remain significant, as psychoactive compounds often face stringent approval processes. Public perception and potential stigma associated with mushroom-derived compounds may also impact market acceptance. Furthermore, competition from other emerging psychedelic-based therapies, such as psilocybin and ketamine, could influence muscimol's market share.
Despite these challenges, the potential market for muscimol in mood disorder treatment remains substantial. As research progresses and clinical evidence accumulates, muscimol-based therapies could capture a significant portion of the mood disorder treatment market, particularly in treatment-resistant cases or as part of combination therapies. The compound's unique mechanism of action and potential for fewer side effects position it as a valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal against mood disorders, potentially improving outcomes for millions of patients worldwide.
Current Challenges
Despite the promising potential of muscimol in modulating mood disorders, several significant challenges currently hinder its widespread application and clinical adoption. These challenges span across various domains, including pharmacological, neurobiological, and clinical aspects.
One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of muscimol's precise mechanisms of action in mood regulation. While its role as a GABA-A receptor agonist is well-established, the complex interplay between GABAergic signaling and mood disorders remains incompletely elucidated. This knowledge gap impedes the development of targeted therapeutic strategies and optimal dosing regimens.
The pharmacokinetic properties of muscimol present another hurdle. Its poor blood-brain barrier penetration and rapid metabolism in the body limit its bioavailability and duration of action. These factors necessitate frequent dosing or alternative delivery methods, which can impact patient compliance and treatment efficacy.
Side effects and safety concerns also pose significant challenges. Muscimol's potent GABAergic activity can lead to sedation, cognitive impairment, and motor coordination issues. Balancing therapeutic efficacy with an acceptable side effect profile remains a critical challenge in its development as a mood disorder treatment.
The heterogeneity of mood disorders further complicates the application of muscimol-based therapies. Different subtypes of depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder may respond differently to GABAergic modulation, necessitating a more nuanced approach to patient selection and treatment protocols.
Regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials represent another set of challenges. As a naturally occurring compound with psychoactive properties, muscimol faces stringent regulatory scrutiny. Demonstrating its safety and efficacy in large-scale, controlled clinical trials is essential but time-consuming and costly.
The potential for drug interactions and contraindications with existing mood disorder treatments also requires careful consideration. Muscimol's effects on neurotransmitter systems may interact with commonly prescribed antidepressants, mood stabilizers, or anxiolytics, necessitating comprehensive drug interaction studies.
Lastly, the development of synthetic analogues or delivery systems to overcome muscimol's pharmacokinetic limitations presents both opportunities and challenges. While such approaches may enhance its therapeutic potential, they introduce additional complexities in terms of drug development, manufacturing, and regulatory approval processes.
Addressing these multifaceted challenges requires a coordinated effort across various scientific disciplines, including neuropharmacology, clinical psychiatry, and drug development. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for realizing the full potential of muscimol in the treatment of mood disorders and improving patient outcomes in mental health care.
One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of muscimol's precise mechanisms of action in mood regulation. While its role as a GABA-A receptor agonist is well-established, the complex interplay between GABAergic signaling and mood disorders remains incompletely elucidated. This knowledge gap impedes the development of targeted therapeutic strategies and optimal dosing regimens.
The pharmacokinetic properties of muscimol present another hurdle. Its poor blood-brain barrier penetration and rapid metabolism in the body limit its bioavailability and duration of action. These factors necessitate frequent dosing or alternative delivery methods, which can impact patient compliance and treatment efficacy.
Side effects and safety concerns also pose significant challenges. Muscimol's potent GABAergic activity can lead to sedation, cognitive impairment, and motor coordination issues. Balancing therapeutic efficacy with an acceptable side effect profile remains a critical challenge in its development as a mood disorder treatment.
The heterogeneity of mood disorders further complicates the application of muscimol-based therapies. Different subtypes of depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder may respond differently to GABAergic modulation, necessitating a more nuanced approach to patient selection and treatment protocols.
Regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials represent another set of challenges. As a naturally occurring compound with psychoactive properties, muscimol faces stringent regulatory scrutiny. Demonstrating its safety and efficacy in large-scale, controlled clinical trials is essential but time-consuming and costly.
The potential for drug interactions and contraindications with existing mood disorder treatments also requires careful consideration. Muscimol's effects on neurotransmitter systems may interact with commonly prescribed antidepressants, mood stabilizers, or anxiolytics, necessitating comprehensive drug interaction studies.
Lastly, the development of synthetic analogues or delivery systems to overcome muscimol's pharmacokinetic limitations presents both opportunities and challenges. While such approaches may enhance its therapeutic potential, they introduce additional complexities in terms of drug development, manufacturing, and regulatory approval processes.
Addressing these multifaceted challenges requires a coordinated effort across various scientific disciplines, including neuropharmacology, clinical psychiatry, and drug development. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for realizing the full potential of muscimol in the treatment of mood disorders and improving patient outcomes in mental health care.
Therapeutic Approaches
01 Muscimol as a mood enhancer
Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushrooms, is being investigated for its potential mood-enhancing properties. Research suggests it may have anxiolytic and antidepressant effects, possibly by modulating GABA receptors in the brain. Studies are exploring its use in treating various mood disorders and improving overall emotional well-being.- Muscimol as a mood enhancer: Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushrooms, is being investigated for its potential mood-enhancing properties. Research suggests it may have anxiolytic and antidepressant effects, possibly by modulating GABA receptors in the brain. Studies are exploring its use in treating various mood disorders and improving overall emotional well-being.
- Delivery methods for muscimol: Various delivery methods are being developed to administer muscimol effectively. These include oral formulations, transdermal patches, and novel drug delivery systems. Researchers are focusing on improving bioavailability and controlling the release of the compound to optimize its mood-altering effects while minimizing potential side effects.
- Combination therapies with muscimol: Researchers are exploring the potential of combining muscimol with other compounds or therapies to enhance its mood-altering effects. This includes investigating synergistic interactions with other natural or synthetic substances, as well as integrating muscimol use with psychotherapy or other treatment modalities for mood disorders.
- Biosynthesis and production of muscimol: Advancements in biotechnology are being applied to develop more efficient methods for producing muscimol. This includes genetic engineering of organisms to synthesize the compound, as well as optimizing extraction and purification processes from natural sources. The goal is to ensure a stable and high-quality supply of muscimol for research and potential therapeutic applications.
- Safety and regulatory considerations: As research into muscimol's mood-altering properties progresses, there is a focus on establishing safety profiles and addressing regulatory requirements. This includes conducting toxicology studies, determining appropriate dosages, and developing guidelines for its use. Researchers are also exploring ways to mitigate potential risks and side effects associated with muscimol consumption.
02 Delivery methods for muscimol
Various delivery methods are being developed to optimize the administration of muscimol for mood-related applications. These include oral formulations, transdermal patches, and novel drug delivery systems designed to enhance bioavailability and control release rates. Researchers are also exploring combination therapies with other compounds to potentiate muscimol's effects.Expand Specific Solutions03 Muscimol in neurological research
Muscimol is being used as a tool in neurological research to study brain function and mood regulation. Its specific action on GABA receptors allows researchers to investigate the role of GABAergic signaling in emotional processing and mood disorders. This research may lead to new insights into the neurobiology of mood and potential therapeutic targets.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety and regulatory considerations
As research into muscimol's mood-altering effects progresses, there is increasing focus on safety assessments and regulatory considerations. Studies are being conducted to evaluate potential side effects, determine optimal dosages, and establish safety profiles for various applications. Regulatory bodies are closely monitoring developments to ensure appropriate guidelines for potential therapeutic use.Expand Specific Solutions05 Muscimol analogues and derivatives
Research is ongoing to develop and evaluate muscimol analogues and derivatives that may offer improved mood-enhancing effects or better pharmacokinetic profiles. These modified compounds aim to retain or enhance the beneficial properties of muscimol while potentially reducing unwanted side effects or improving targeted delivery to specific brain regions involved in mood regulation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The field of muscimol's role in modulating mood disorders is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as research progresses. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with companies like ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Karuna Therapeutics, and H. Lundbeck A/S leading the way in neuropsychiatric drug development. While not directly focused on muscimol, these firms are advancing related compounds for mood disorders. Academic institutions such as Yale University and the University of Bonn are contributing fundamental research, potentially paving the way for future clinical applications. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms, indicating a dynamic and promising area for innovation in mental health treatments.
ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: ACADIA Pharmaceuticals is exploring muscimol's potential in treating mood disorders through its selective GABA-A receptor modulation approach. The company has developed a proprietary platform that allows for the fine-tuning of GABA-A receptor subtype selectivity, potentially enhancing muscimol's therapeutic effects while minimizing side effects[4]. ACADIA's research focuses on developing muscimol derivatives that exhibit improved blood-brain barrier penetration and extended half-life[5]. They have conducted phase I clinical trials evaluating the safety and pharmacokinetics of their lead muscimol-based compound in healthy volunteers, with promising initial results showing good tolerability and target engagement[6].
Strengths: Specialized focus on CNS disorders, innovative GABA-A receptor modulation platform, and progress in clinical development. Weaknesses: Smaller company with potentially limited resources compared to big pharma, and dependence on success of lead compounds.
Karuna Therapeutics, Inc.
Technical Solution: Karuna Therapeutics is investigating muscimol's role in mood disorders as part of their broader neuroscience pipeline. Their approach combines muscimol with other neuromodulators to create novel therapeutic combinations for treatment-resistant depression and anxiety disorders. The company has developed a proprietary muscimol prodrug that aims to improve its oral bioavailability and duration of action[7]. Karuna's research also explores the potential of muscimol in targeting specific neural circuits involved in mood regulation, using advanced neuroimaging techniques to guide their drug development process[8]. Preclinical studies have shown promising results in animal models of depression, with their muscimol-based compound demonstrating rapid onset of antidepressant effects[9].
Strengths: Innovative approach combining muscimol with other neuromodulators, focus on treatment-resistant populations, and use of advanced neuroimaging techniques. Weaknesses: Early stage of development for muscimol-based compounds and potential challenges in demonstrating superiority over existing treatments.
Pharmacological Insights
Amanita muscaria compounds
PatentPendingUS20240050502A1
Innovation
- Development of purified Amanita muscaria compound compositions and formulations comprising specific ratios of ibotenic acid, muscimol, and other compounds, which are structurally distinct and free from other Amanita muscaria compounds, combined with excipients and serotonergic drugs, psilocybin derivatives, or cannabinoids to create pharmaceutical formulations for therapeutic use.
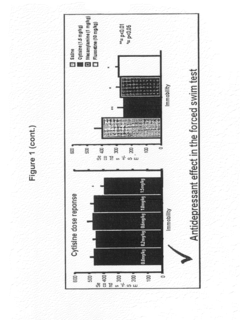
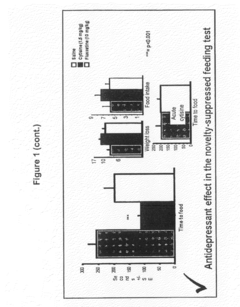
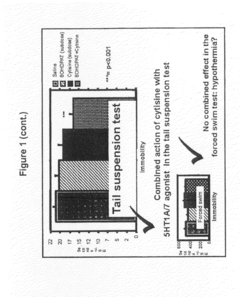
Cytisine and Acetylcholine Analogs and Methods of Treating Mood Disorders
PatentInactiveUS20090318491A1
Innovation
- Development of compounds that act as partial agonists or antagonists of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, specifically targeting α4β2, α3β4, and α7 subtypes, which can be used to treat mood disorders by interfering with endogenous acetylcholine signaling, potentially offering antidepressant-like responses.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding muscimol and its potential use in treating mood disorders is complex and multifaceted. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the development and approval of new drugs, including those targeting mood disorders. Muscimol, as a GABA receptor agonist, falls under strict regulatory scrutiny due to its psychoactive properties and potential for abuse.
Currently, muscimol is classified as a Schedule III controlled substance by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), which imposes significant restrictions on its research, manufacture, and distribution. This classification presents challenges for researchers and pharmaceutical companies interested in exploring muscimol's therapeutic potential for mood disorders.
The regulatory pathway for muscimol-based treatments would likely involve extensive preclinical studies, followed by rigorous clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. The FDA's Investigational New Drug (IND) application process would be a critical step, requiring comprehensive data on the compound's pharmacology, toxicology, and proposed clinical protocol.
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) would have their own requirements for approving muscimol-based therapies. These agencies often collaborate with the FDA, but may have distinct criteria and processes for drug approval.
Given the potential for abuse and side effects associated with GABA receptor agonists, post-marketing surveillance and risk evaluation and mitigation strategies (REMS) would likely be mandated by regulatory authorities. This would involve ongoing monitoring of safety data and potential restrictions on prescribing and dispensing practices.
The regulatory landscape for psychoactive substances is evolving, particularly in light of recent developments in psychedelic-assisted therapies. This shift may influence future regulatory approaches to muscimol and similar compounds. However, any changes would need to balance the potential therapeutic benefits with public health and safety concerns.
Researchers and pharmaceutical companies pursuing muscimol-based treatments for mood disorders must navigate this complex regulatory environment. Engagement with regulatory agencies early in the development process, through pre-IND meetings and scientific advice procedures, can help clarify requirements and streamline the path to approval.
Currently, muscimol is classified as a Schedule III controlled substance by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), which imposes significant restrictions on its research, manufacture, and distribution. This classification presents challenges for researchers and pharmaceutical companies interested in exploring muscimol's therapeutic potential for mood disorders.
The regulatory pathway for muscimol-based treatments would likely involve extensive preclinical studies, followed by rigorous clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. The FDA's Investigational New Drug (IND) application process would be a critical step, requiring comprehensive data on the compound's pharmacology, toxicology, and proposed clinical protocol.
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) would have their own requirements for approving muscimol-based therapies. These agencies often collaborate with the FDA, but may have distinct criteria and processes for drug approval.
Given the potential for abuse and side effects associated with GABA receptor agonists, post-marketing surveillance and risk evaluation and mitigation strategies (REMS) would likely be mandated by regulatory authorities. This would involve ongoing monitoring of safety data and potential restrictions on prescribing and dispensing practices.
The regulatory landscape for psychoactive substances is evolving, particularly in light of recent developments in psychedelic-assisted therapies. This shift may influence future regulatory approaches to muscimol and similar compounds. However, any changes would need to balance the potential therapeutic benefits with public health and safety concerns.
Researchers and pharmaceutical companies pursuing muscimol-based treatments for mood disorders must navigate this complex regulatory environment. Engagement with regulatory agencies early in the development process, through pre-IND meetings and scientific advice procedures, can help clarify requirements and streamline the path to approval.
Safety Considerations
When considering the use of muscimol in modulating mood disorders, safety considerations are paramount. Muscimol, a potent GABA agonist, has shown promise in preclinical studies for its potential therapeutic effects on mood disorders. However, its use in clinical settings requires careful evaluation of potential risks and side effects.
One primary safety concern is the risk of excessive sedation and cognitive impairment. Muscimol's strong activation of GABA receptors can lead to drowsiness, confusion, and impaired motor coordination. These effects may be particularly pronounced in elderly patients or those with pre-existing cognitive impairments. Careful dosing and monitoring protocols must be established to mitigate these risks.
Another critical safety consideration is the potential for drug interactions. Muscimol may interact with other medications that affect the GABAergic system, such as benzodiazepines or barbiturates. These interactions could lead to enhanced sedative effects or respiratory depression. Comprehensive medication reviews and drug interaction screenings are essential for patients considering muscimol-based treatments.
The risk of tolerance and dependence is also a significant concern. Prolonged use of muscimol may lead to the development of tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve the same therapeutic effect. This could potentially increase the risk of adverse effects. Additionally, there is a possibility of physical dependence, which could result in withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation of the treatment.
Muscimol's effects on the cardiovascular system must also be carefully monitored. Some studies have reported changes in blood pressure and heart rate associated with muscimol administration. Patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions may require additional screening and monitoring during treatment.
The potential for paradoxical reactions is another safety consideration. In some cases, GABAergic compounds can produce unexpected excitatory effects, particularly in individuals with certain neurological conditions. This underscores the need for careful patient selection and close monitoring during the initial stages of treatment.
Long-term safety data for muscimol in the treatment of mood disorders is currently limited. Comprehensive long-term studies are needed to assess the potential for cumulative toxicity or delayed-onset adverse effects. This includes evaluating the impact on cognitive function, neuroplasticity, and overall brain health with prolonged use.
Lastly, the risk of accidental overdose must be addressed through proper storage, handling, and patient education protocols. Given muscimol's potency, even small dosing errors could lead to significant adverse effects. Implementing robust safety measures and patient education programs is crucial to minimize this risk.
One primary safety concern is the risk of excessive sedation and cognitive impairment. Muscimol's strong activation of GABA receptors can lead to drowsiness, confusion, and impaired motor coordination. These effects may be particularly pronounced in elderly patients or those with pre-existing cognitive impairments. Careful dosing and monitoring protocols must be established to mitigate these risks.
Another critical safety consideration is the potential for drug interactions. Muscimol may interact with other medications that affect the GABAergic system, such as benzodiazepines or barbiturates. These interactions could lead to enhanced sedative effects or respiratory depression. Comprehensive medication reviews and drug interaction screenings are essential for patients considering muscimol-based treatments.
The risk of tolerance and dependence is also a significant concern. Prolonged use of muscimol may lead to the development of tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve the same therapeutic effect. This could potentially increase the risk of adverse effects. Additionally, there is a possibility of physical dependence, which could result in withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation of the treatment.
Muscimol's effects on the cardiovascular system must also be carefully monitored. Some studies have reported changes in blood pressure and heart rate associated with muscimol administration. Patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions may require additional screening and monitoring during treatment.
The potential for paradoxical reactions is another safety consideration. In some cases, GABAergic compounds can produce unexpected excitatory effects, particularly in individuals with certain neurological conditions. This underscores the need for careful patient selection and close monitoring during the initial stages of treatment.
Long-term safety data for muscimol in the treatment of mood disorders is currently limited. Comprehensive long-term studies are needed to assess the potential for cumulative toxicity or delayed-onset adverse effects. This includes evaluating the impact on cognitive function, neuroplasticity, and overall brain health with prolonged use.
Lastly, the risk of accidental overdose must be addressed through proper storage, handling, and patient education protocols. Given muscimol's potency, even small dosing errors could lead to significant adverse effects. Implementing robust safety measures and patient education programs is crucial to minimize this risk.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!