Muscimol's Interaction with Modern Antidepressants
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol and Antidepressants: Background and Objectives
Muscimol, a naturally occurring psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, has recently garnered attention in the field of neuropharmacology for its potential interactions with modern antidepressants. This research aims to explore the complex interplay between muscimol and contemporary antidepressant medications, with the ultimate goal of uncovering novel therapeutic approaches for treating depression and related mood disorders.
The evolution of antidepressant treatments has seen significant advancements over the past few decades, from the introduction of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) to the development of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). Despite these improvements, many patients still experience inadequate responses or intolerable side effects, highlighting the need for innovative treatment strategies.
Muscimol, as a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, presents an intriguing avenue for investigation due to its unique mechanism of action. Unlike traditional antidepressants that primarily target monoamine neurotransmitter systems, muscimol's effects on the GABAergic system may offer complementary or synergistic benefits when combined with existing antidepressant therapies.
The primary objective of this research is to elucidate the pharmacological interactions between muscimol and various classes of modern antidepressants. This includes examining potential synergistic effects, identifying any adverse interactions, and exploring the possibility of muscimol as an adjunctive treatment to enhance the efficacy of current antidepressant regimens.
Furthermore, this study aims to investigate the neurobiological mechanisms underlying these interactions. By understanding how muscimol's GABAergic activity influences the monoaminergic systems targeted by conventional antidepressants, we may uncover new insights into the pathophysiology of depression and identify novel targets for therapeutic intervention.
Another crucial aspect of this research is to assess the potential for muscimol to address treatment-resistant depression. Given that a significant proportion of patients do not respond adequately to current antidepressant therapies, exploring muscimol's capacity to augment or provide an alternative treatment option could have substantial clinical implications.
Additionally, this study will examine the safety profile of combining muscimol with modern antidepressants, focusing on both short-term and long-term effects. This includes evaluating potential drug-drug interactions, assessing the risk of adverse events, and determining optimal dosing strategies to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing side effects.
By comprehensively investigating muscimol's interaction with modern antidepressants, this research aims to contribute to the development of more effective, personalized treatment approaches for depression. The findings from this study may pave the way for innovative combination therapies, potentially revolutionizing the management of mood disorders and improving outcomes for patients who have not found relief with existing treatment options.
The evolution of antidepressant treatments has seen significant advancements over the past few decades, from the introduction of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) to the development of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). Despite these improvements, many patients still experience inadequate responses or intolerable side effects, highlighting the need for innovative treatment strategies.
Muscimol, as a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, presents an intriguing avenue for investigation due to its unique mechanism of action. Unlike traditional antidepressants that primarily target monoamine neurotransmitter systems, muscimol's effects on the GABAergic system may offer complementary or synergistic benefits when combined with existing antidepressant therapies.
The primary objective of this research is to elucidate the pharmacological interactions between muscimol and various classes of modern antidepressants. This includes examining potential synergistic effects, identifying any adverse interactions, and exploring the possibility of muscimol as an adjunctive treatment to enhance the efficacy of current antidepressant regimens.
Furthermore, this study aims to investigate the neurobiological mechanisms underlying these interactions. By understanding how muscimol's GABAergic activity influences the monoaminergic systems targeted by conventional antidepressants, we may uncover new insights into the pathophysiology of depression and identify novel targets for therapeutic intervention.
Another crucial aspect of this research is to assess the potential for muscimol to address treatment-resistant depression. Given that a significant proportion of patients do not respond adequately to current antidepressant therapies, exploring muscimol's capacity to augment or provide an alternative treatment option could have substantial clinical implications.
Additionally, this study will examine the safety profile of combining muscimol with modern antidepressants, focusing on both short-term and long-term effects. This includes evaluating potential drug-drug interactions, assessing the risk of adverse events, and determining optimal dosing strategies to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing side effects.
By comprehensively investigating muscimol's interaction with modern antidepressants, this research aims to contribute to the development of more effective, personalized treatment approaches for depression. The findings from this study may pave the way for innovative combination therapies, potentially revolutionizing the management of mood disorders and improving outcomes for patients who have not found relief with existing treatment options.
Market Analysis of Muscimol-Based Therapies
The market for muscimol-based therapies is experiencing significant growth potential, driven by the increasing prevalence of depression and the need for more effective treatment options. As traditional antidepressants often come with side effects and limited efficacy for some patients, there is a growing demand for alternative approaches. Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, has shown promise in preclinical studies for its potential antidepressant effects.
The global antidepressant market is substantial, valued at over $14 billion in 2020 and expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% through 2027. Within this market, there is an emerging niche for novel therapies that can address treatment-resistant depression or offer faster-acting relief. Muscimol-based therapies could potentially capture a portion of this market, especially if they demonstrate improved efficacy or reduced side effects compared to existing treatments.
Consumer interest in natural and plant-based remedies has been on the rise, which could benefit muscimol-based therapies derived from mushrooms. This trend aligns with the growing acceptance of psychedelic-assisted therapies in mental health treatment, creating a more receptive environment for muscimol-based products.
However, the market for muscimol-based therapies faces several challenges. Regulatory hurdles remain significant, as muscimol is classified as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions. Obtaining approval for clinical use will require extensive research and clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. Additionally, public perception and potential stigma associated with psychoactive compounds may need to be addressed through education and awareness campaigns.
Competition in the antidepressant market is intense, with established pharmaceutical companies dominating the landscape. Muscimol-based therapies would need to demonstrate clear advantages over existing treatments to gain market share. Pricing strategies will also be crucial, as new therapies often command premium prices, which could limit accessibility and adoption.
The potential market for muscimol-based therapies extends beyond depression. Research suggests possible applications in anxiety disorders, PTSD, and other neurological conditions. This versatility could expand the total addressable market and create multiple revenue streams for companies developing muscimol-based products.
Partnerships between pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are likely to play a crucial role in advancing muscimol-based therapies. These collaborations can accelerate research and development, leveraging expertise in drug development, clinical trials, and regulatory navigation.
In conclusion, while the market for muscimol-based therapies is still in its infancy, it shows promise for growth. Success will depend on overcoming regulatory challenges, demonstrating clear clinical benefits, and effectively positioning these therapies within the broader mental health treatment landscape. As research progresses and clinical data accumulates, the market potential for muscimol-based therapies is expected to become clearer, potentially offering new hope for patients struggling with depression and related disorders.
The global antidepressant market is substantial, valued at over $14 billion in 2020 and expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% through 2027. Within this market, there is an emerging niche for novel therapies that can address treatment-resistant depression or offer faster-acting relief. Muscimol-based therapies could potentially capture a portion of this market, especially if they demonstrate improved efficacy or reduced side effects compared to existing treatments.
Consumer interest in natural and plant-based remedies has been on the rise, which could benefit muscimol-based therapies derived from mushrooms. This trend aligns with the growing acceptance of psychedelic-assisted therapies in mental health treatment, creating a more receptive environment for muscimol-based products.
However, the market for muscimol-based therapies faces several challenges. Regulatory hurdles remain significant, as muscimol is classified as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions. Obtaining approval for clinical use will require extensive research and clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. Additionally, public perception and potential stigma associated with psychoactive compounds may need to be addressed through education and awareness campaigns.
Competition in the antidepressant market is intense, with established pharmaceutical companies dominating the landscape. Muscimol-based therapies would need to demonstrate clear advantages over existing treatments to gain market share. Pricing strategies will also be crucial, as new therapies often command premium prices, which could limit accessibility and adoption.
The potential market for muscimol-based therapies extends beyond depression. Research suggests possible applications in anxiety disorders, PTSD, and other neurological conditions. This versatility could expand the total addressable market and create multiple revenue streams for companies developing muscimol-based products.
Partnerships between pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are likely to play a crucial role in advancing muscimol-based therapies. These collaborations can accelerate research and development, leveraging expertise in drug development, clinical trials, and regulatory navigation.
In conclusion, while the market for muscimol-based therapies is still in its infancy, it shows promise for growth. Success will depend on overcoming regulatory challenges, demonstrating clear clinical benefits, and effectively positioning these therapies within the broader mental health treatment landscape. As research progresses and clinical data accumulates, the market potential for muscimol-based therapies is expected to become clearer, potentially offering new hope for patients struggling with depression and related disorders.
Current Challenges in Muscimol-Antidepressant Interactions
The interaction between muscimol and modern antidepressants presents several significant challenges in both research and clinical applications. One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which muscimol, a GABA-A receptor agonist, interacts with the diverse array of antidepressant medications currently in use.
The complexity of neurotransmitter systems involved in depression and the action of antidepressants further complicates this research. While most modern antidepressants target monoamine systems, particularly serotonin and norepinephrine, muscimol's primary action on the GABAergic system introduces a new layer of complexity in understanding potential interactions and effects.
Another challenge lies in the potential for adverse effects when combining muscimol with antidepressants. The GABAergic system's role in regulating neural excitability means that muscimol could potentially alter the efficacy or side effect profile of antidepressants in unpredictable ways. This raises concerns about safety and efficacy in clinical settings, particularly given the variability in individual patient responses to both antidepressants and GABAergic compounds.
The lack of standardized protocols for studying muscimol-antidepressant interactions poses a significant hurdle. Researchers face difficulties in designing studies that can accurately assess the combined effects of these compounds across different antidepressant classes and patient populations. This challenge is compounded by the ethical considerations of conducting such studies in human subjects, particularly given the potential risks involved.
From a pharmacokinetic perspective, understanding how muscimol and antidepressants interact at the level of drug metabolism and distribution presents another challenge. The potential for drug-drug interactions, including alterations in absorption, distribution, metabolism, or excretion of either compound, needs thorough investigation to ensure patient safety and optimize therapeutic outcomes.
The long-term effects of combining muscimol with antidepressants remain largely unknown, presenting a significant gap in our understanding. This includes potential impacts on neuroplasticity, cognitive function, and the overall trajectory of depressive disorders. Longitudinal studies are needed but face challenges in terms of duration, cost, and participant retention.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of muscimol, particularly in combination with established antidepressants, presents hurdles for both researchers and clinicians. Navigating the complex approval processes for novel combination therapies, especially those involving compounds with psychoactive properties like muscimol, requires significant time and resources.
The complexity of neurotransmitter systems involved in depression and the action of antidepressants further complicates this research. While most modern antidepressants target monoamine systems, particularly serotonin and norepinephrine, muscimol's primary action on the GABAergic system introduces a new layer of complexity in understanding potential interactions and effects.
Another challenge lies in the potential for adverse effects when combining muscimol with antidepressants. The GABAergic system's role in regulating neural excitability means that muscimol could potentially alter the efficacy or side effect profile of antidepressants in unpredictable ways. This raises concerns about safety and efficacy in clinical settings, particularly given the variability in individual patient responses to both antidepressants and GABAergic compounds.
The lack of standardized protocols for studying muscimol-antidepressant interactions poses a significant hurdle. Researchers face difficulties in designing studies that can accurately assess the combined effects of these compounds across different antidepressant classes and patient populations. This challenge is compounded by the ethical considerations of conducting such studies in human subjects, particularly given the potential risks involved.
From a pharmacokinetic perspective, understanding how muscimol and antidepressants interact at the level of drug metabolism and distribution presents another challenge. The potential for drug-drug interactions, including alterations in absorption, distribution, metabolism, or excretion of either compound, needs thorough investigation to ensure patient safety and optimize therapeutic outcomes.
The long-term effects of combining muscimol with antidepressants remain largely unknown, presenting a significant gap in our understanding. This includes potential impacts on neuroplasticity, cognitive function, and the overall trajectory of depressive disorders. Longitudinal studies are needed but face challenges in terms of duration, cost, and participant retention.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of muscimol, particularly in combination with established antidepressants, presents hurdles for both researchers and clinicians. Navigating the complex approval processes for novel combination therapies, especially those involving compounds with psychoactive properties like muscimol, requires significant time and resources.
Existing Protocols for Muscimol-Antidepressant Co-administration
01 Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol
Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include different formulations and delivery methods to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol. The compositions can be designed for treating neurological disorders, anxiety, or other conditions affected by GABA receptor modulation.- Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol: Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include different formulations and delivery methods to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol. The compositions can be designed for treating neurological disorders, anxiety, or other conditions affected by GABA receptor modulation.
- Muscimol analogs and derivatives: Research involves the development and use of muscimol analogs and derivatives. These compounds are designed to have similar or enhanced pharmacological properties compared to muscimol, potentially offering improved therapeutic effects or reduced side effects. The analogs may be synthesized through various chemical modifications of the muscimol structure.
- Muscimol in combination therapies: Muscimol is explored in combination with other active ingredients for synergistic therapeutic effects. These combinations may target multiple pathways or receptors simultaneously, potentially enhancing the overall treatment efficacy for complex disorders. The combinations are studied for various conditions, including neurological and psychiatric disorders.
- Muscimol delivery systems: Novel delivery systems are developed for muscimol to improve its administration and bioavailability. These may include transdermal patches, nanoparticle formulations, or controlled-release mechanisms. The aim is to optimize the drug's pharmacokinetics and reduce potential side effects associated with systemic administration.
- Muscimol in neurodegenerative disease treatment: Muscimol and its derivatives are investigated for their potential in treating neurodegenerative diseases. The compound's GABA-mimetic properties are explored for neuroprotective effects and symptom management in conditions such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and other related disorders. Research focuses on understanding the mechanism of action and optimizing treatment protocols.
02 Muscimol analogs and derivatives
Research focuses on developing muscimol analogs and derivatives with improved pharmacological properties. These modified compounds aim to enhance therapeutic effects, reduce side effects, or improve drug delivery. Synthetic methods for creating these analogs are explored to optimize their potential as pharmaceutical agents.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of muscimol in neurological treatments
Muscimol and its derivatives are investigated for their potential in treating various neurological conditions. This includes applications in epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, and other disorders affecting the central nervous system. Research explores different administration methods and dosage regimens to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing adverse effects.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination therapies involving muscimol
Muscimol is studied in combination with other active ingredients to create synergistic therapeutic effects. These combination therapies may target multiple pathways or receptors simultaneously, potentially enhancing overall treatment efficacy for complex neurological or psychiatric disorders.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery systems for muscimol
Innovative delivery systems are developed to improve the administration and bioavailability of muscimol. These may include transdermal patches, nanoparticle formulations, or controlled-release mechanisms. The goal is to enhance drug efficacy, reduce dosing frequency, and minimize systemic side effects through targeted delivery.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Muscimol Research and Antidepressant Industry
The research on muscimol's interaction with modern antidepressants is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential due to the increasing prevalence of depression worldwide. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical giants like Pfizer, Novartis, and Boehringer Ingelheim, alongside specialized biotech firms such as ACADIA Pharmaceuticals and NeuShen Therapeutics. While the technology is still emerging, companies are investing in R&D to explore muscimol's potential as a novel therapeutic approach. The market is expected to evolve rapidly as clinical trials progress and regulatory pathways become clearer, with collaborations between academia and industry playing a crucial role in advancing the field.
Pfizer Inc.
Technical Solution: Pfizer's research on muscimol's interaction with modern antidepressants focuses on developing novel combination therapies. They are exploring the potential synergistic effects of muscimol, a GABA-A receptor agonist, with SSRIs and SNRIs. Their approach involves using advanced neuroimaging techniques to map brain activity changes when muscimol is co-administered with antidepressants[1]. Pfizer is also investigating the role of muscimol in modulating neurotransmitter systems beyond GABA, particularly its indirect effects on serotonin and norepinephrine pathways[3]. Their preclinical studies have shown promising results in enhancing the efficacy of traditional antidepressants while potentially reducing side effects[5].
Strengths: Extensive R&D resources, global clinical trial network, and established market presence in antidepressant medications. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory hurdles in combining established drugs with novel compounds, and the need for long-term safety data.
ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: ACADIA Pharmaceuticals is pioneering research on muscimol's interaction with modern antidepressants, focusing on its potential to enhance treatment-resistant depression. Their approach combines muscimol with their proprietary selective serotonin inverse agonist technology[2]. ACADIA's research explores how muscimol's GABA-A receptor activation may complement the modulation of serotonin receptors, potentially offering a dual-action antidepressant effect. They are conducting preclinical studies to evaluate the impact of this combination on neural plasticity and stress resilience[4]. Additionally, ACADIA is investigating the potential of muscimol to mitigate side effects commonly associated with traditional antidepressants, such as sexual dysfunction and weight gain[6].
Strengths: Specialized focus on CNS disorders, innovative approach to receptor targeting. Weaknesses: Smaller company with limited resources compared to big pharma, potentially longer development timeline.
Breakthrough Studies on Muscimol-Antidepressant Synergies
Methods of using muscarinic antagonists in the treatment of depression
PatentWO2020206410A1
Innovation
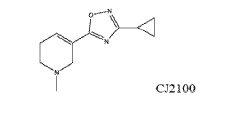
- Development of muscarinic antagonists, such as CJ2100, which separate antidepressant activity from cognitive impairment, allowing for effective depression treatment without disrupting learning, memory, or attention processes.
Peptide for regulating reactivity to serotonin reuptake inhibitorbased antidepressant, and use thereof
PatentActiveUS20210269481A1
Innovation
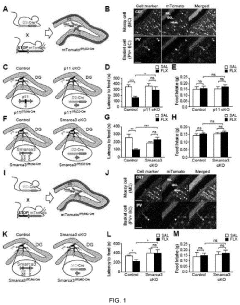
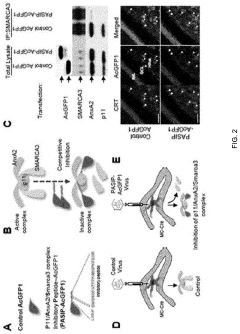
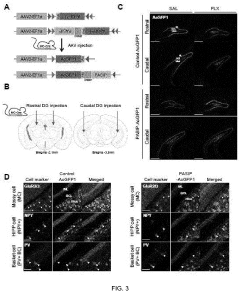
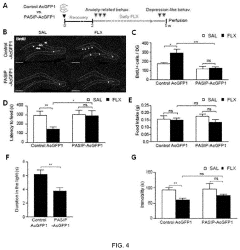
- A peptide with a specific amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 1) that inhibits the functional assembly of the p11/AnxA2/SMARCA3 complex in hippocampal mossy cells, thereby controlling reactivity to serotonin reuptake inhibitors, is developed. This peptide can be delivered via vectors or pharmaceutical compositions to target specific neural regions, reducing side effects and enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
Regulatory Framework for Novel Psychoactive Substances
The regulatory framework for novel psychoactive substances (NPS) plays a crucial role in the research and development of muscimol's interaction with modern antidepressants. As muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, gains attention for its potential therapeutic applications, it falls under the scrutiny of regulatory bodies worldwide.
In many jurisdictions, muscimol is classified as a controlled substance due to its psychoactive properties. This classification presents significant challenges for researchers investigating its potential synergistic effects with modern antidepressants. The regulatory landscape often requires extensive documentation, stringent safety protocols, and rigorous clinical trial designs to obtain approval for such studies.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have established specific guidelines for researching novel psychoactive substances in combination with existing medications. These guidelines emphasize the importance of comprehensive preclinical studies to assess potential drug interactions, toxicity profiles, and mechanisms of action before progressing to human trials.
Researchers must navigate complex approval processes, including obtaining licenses for handling controlled substances and securing ethical approvals from institutional review boards. The regulatory framework also mandates strict protocols for storage, handling, and disposal of muscimol and related compounds to prevent misuse or diversion.
International cooperation and harmonization efforts are underway to streamline the regulatory processes for NPS research. Organizations such as the International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) and the World Health Organization (WHO) play pivotal roles in shaping global policies and facilitating cross-border research collaborations.
The evolving nature of NPS regulations presents both challenges and opportunities for muscimol research. While stringent controls aim to protect public health and safety, they can also impede scientific progress. Regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the need for balanced approaches that maintain safety standards while fostering innovation in psychopharmacology.
As research on muscimol's interaction with modern antidepressants progresses, it is likely to influence future regulatory frameworks. Positive findings may lead to more flexible regulations for specific research purposes, while adverse outcomes could result in tighter controls. The dynamic interplay between scientific discoveries and regulatory adaptations will continue to shape the landscape of NPS research and development.
In many jurisdictions, muscimol is classified as a controlled substance due to its psychoactive properties. This classification presents significant challenges for researchers investigating its potential synergistic effects with modern antidepressants. The regulatory landscape often requires extensive documentation, stringent safety protocols, and rigorous clinical trial designs to obtain approval for such studies.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have established specific guidelines for researching novel psychoactive substances in combination with existing medications. These guidelines emphasize the importance of comprehensive preclinical studies to assess potential drug interactions, toxicity profiles, and mechanisms of action before progressing to human trials.
Researchers must navigate complex approval processes, including obtaining licenses for handling controlled substances and securing ethical approvals from institutional review boards. The regulatory framework also mandates strict protocols for storage, handling, and disposal of muscimol and related compounds to prevent misuse or diversion.
International cooperation and harmonization efforts are underway to streamline the regulatory processes for NPS research. Organizations such as the International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) and the World Health Organization (WHO) play pivotal roles in shaping global policies and facilitating cross-border research collaborations.
The evolving nature of NPS regulations presents both challenges and opportunities for muscimol research. While stringent controls aim to protect public health and safety, they can also impede scientific progress. Regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the need for balanced approaches that maintain safety standards while fostering innovation in psychopharmacology.
As research on muscimol's interaction with modern antidepressants progresses, it is likely to influence future regulatory frameworks. Positive findings may lead to more flexible regulations for specific research purposes, while adverse outcomes could result in tighter controls. The dynamic interplay between scientific discoveries and regulatory adaptations will continue to shape the landscape of NPS research and development.
Pharmacokinetic Profiling of Muscimol-Antidepressant Combinations
The pharmacokinetic profiling of muscimol-antidepressant combinations is a critical aspect of understanding the potential interactions between these compounds. This analysis involves studying the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) processes of both muscimol and various modern antidepressants when administered together.
Absorption studies focus on how the presence of muscimol affects the uptake of antidepressants and vice versa. Researchers investigate changes in absorption rates, bioavailability, and potential alterations in the gastrointestinal environment that may influence drug absorption. These studies often employ in vitro models and in vivo animal experiments to elucidate the mechanisms involved.
Distribution analyses examine how muscimol and antidepressants are transported throughout the body when co-administered. This includes assessing changes in plasma protein binding, tissue distribution, and blood-brain barrier penetration. Advanced imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are utilized to track the distribution of these compounds in real-time.
Metabolism studies are crucial for identifying potential drug-drug interactions at the enzymatic level. Researchers investigate whether muscimol affects the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes responsible for metabolizing many antidepressants. Conversely, the impact of antidepressants on muscimol metabolism is also examined. In vitro assays using human liver microsomes and hepatocytes are commonly employed for these investigations.
Excretion analyses focus on how the combination of muscimol and antidepressants affects their elimination from the body. This includes studying changes in renal clearance, hepatic clearance, and potential alterations in drug transporter activity. Researchers use both in vitro and in vivo models to assess these parameters and identify any significant deviations from the individual pharmacokinetic profiles.
Pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation techniques play a crucial role in integrating data from various studies to predict the overall impact of muscimol-antidepressant combinations. These models help researchers estimate drug concentrations over time, identify potential drug-drug interactions, and optimize dosing regimens for clinical studies.
The results of these pharmacokinetic profiling studies are essential for determining the safety and efficacy of combining muscimol with modern antidepressants. They provide valuable insights into potential drug interactions, guide the design of clinical trials, and inform healthcare professionals about the appropriate use of these combinations in patient care.
Absorption studies focus on how the presence of muscimol affects the uptake of antidepressants and vice versa. Researchers investigate changes in absorption rates, bioavailability, and potential alterations in the gastrointestinal environment that may influence drug absorption. These studies often employ in vitro models and in vivo animal experiments to elucidate the mechanisms involved.
Distribution analyses examine how muscimol and antidepressants are transported throughout the body when co-administered. This includes assessing changes in plasma protein binding, tissue distribution, and blood-brain barrier penetration. Advanced imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are utilized to track the distribution of these compounds in real-time.
Metabolism studies are crucial for identifying potential drug-drug interactions at the enzymatic level. Researchers investigate whether muscimol affects the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes responsible for metabolizing many antidepressants. Conversely, the impact of antidepressants on muscimol metabolism is also examined. In vitro assays using human liver microsomes and hepatocytes are commonly employed for these investigations.
Excretion analyses focus on how the combination of muscimol and antidepressants affects their elimination from the body. This includes studying changes in renal clearance, hepatic clearance, and potential alterations in drug transporter activity. Researchers use both in vitro and in vivo models to assess these parameters and identify any significant deviations from the individual pharmacokinetic profiles.
Pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation techniques play a crucial role in integrating data from various studies to predict the overall impact of muscimol-antidepressant combinations. These models help researchers estimate drug concentrations over time, identify potential drug-drug interactions, and optimize dosing regimens for clinical studies.
The results of these pharmacokinetic profiling studies are essential for determining the safety and efficacy of combining muscimol with modern antidepressants. They provide valuable insights into potential drug interactions, guide the design of clinical trials, and inform healthcare professionals about the appropriate use of these combinations in patient care.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!