Theoretical Approaches to Muscimol's Tactical Use in Psychiatry
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol in Psychiatry
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has garnered significant attention in psychiatric research due to its unique pharmacological properties. This naturally occurring psychoactive compound, found in Amanita muscaria mushrooms, has been the subject of extensive studies exploring its potential therapeutic applications in various psychiatric disorders.
The theoretical approaches to muscimol's tactical use in psychiatry are rooted in its ability to modulate GABAergic neurotransmission, which plays a crucial role in regulating neuronal excitability and maintaining the balance between excitatory and inhibitory signals in the brain. Researchers have proposed several mechanisms through which muscimol could exert its therapeutic effects in psychiatric conditions.
One prominent theoretical approach focuses on muscimol's anxiolytic properties. By enhancing GABA-mediated inhibition, muscimol is thought to reduce excessive neuronal firing associated with anxiety disorders. This mechanism has led to investigations into its potential as a novel anxiolytic agent, particularly in cases where traditional benzodiazepines may be contraindicated or ineffective.
Another theoretical framework explores muscimol's potential in treating sleep disorders. The compound's ability to promote GABA-induced hyperpolarization of neurons in sleep-regulating brain regions has sparked interest in its use as a sleep aid. Researchers hypothesize that muscimol could offer a more targeted approach to sleep regulation compared to conventional sedative-hypnotics.
In the realm of mood disorders, theoretical approaches have examined muscimol's impact on the neural circuits implicated in depression. Some researchers propose that by modulating GABAergic transmission in key brain areas, muscimol could help normalize the imbalanced neurotransmitter systems associated with depressive symptoms.
Cognitive enhancement is another area where muscimol's theoretical applications are being explored. Studies suggest that low doses of muscimol might enhance certain cognitive functions by fine-tuning the excitation-inhibition balance in neural networks involved in learning and memory.
The potential use of muscimol in treating addiction has also been theoretically proposed. By activating GABA-A receptors, muscimol could potentially reduce the rewarding effects of addictive substances and help in managing withdrawal symptoms.
These theoretical approaches to muscimol's tactical use in psychiatry highlight its versatility as a potential therapeutic agent. However, it is crucial to note that while these theories provide promising avenues for research, extensive clinical studies are still needed to validate the safety and efficacy of muscimol-based interventions in psychiatric practice.
The theoretical approaches to muscimol's tactical use in psychiatry are rooted in its ability to modulate GABAergic neurotransmission, which plays a crucial role in regulating neuronal excitability and maintaining the balance between excitatory and inhibitory signals in the brain. Researchers have proposed several mechanisms through which muscimol could exert its therapeutic effects in psychiatric conditions.
One prominent theoretical approach focuses on muscimol's anxiolytic properties. By enhancing GABA-mediated inhibition, muscimol is thought to reduce excessive neuronal firing associated with anxiety disorders. This mechanism has led to investigations into its potential as a novel anxiolytic agent, particularly in cases where traditional benzodiazepines may be contraindicated or ineffective.
Another theoretical framework explores muscimol's potential in treating sleep disorders. The compound's ability to promote GABA-induced hyperpolarization of neurons in sleep-regulating brain regions has sparked interest in its use as a sleep aid. Researchers hypothesize that muscimol could offer a more targeted approach to sleep regulation compared to conventional sedative-hypnotics.
In the realm of mood disorders, theoretical approaches have examined muscimol's impact on the neural circuits implicated in depression. Some researchers propose that by modulating GABAergic transmission in key brain areas, muscimol could help normalize the imbalanced neurotransmitter systems associated with depressive symptoms.
Cognitive enhancement is another area where muscimol's theoretical applications are being explored. Studies suggest that low doses of muscimol might enhance certain cognitive functions by fine-tuning the excitation-inhibition balance in neural networks involved in learning and memory.
The potential use of muscimol in treating addiction has also been theoretically proposed. By activating GABA-A receptors, muscimol could potentially reduce the rewarding effects of addictive substances and help in managing withdrawal symptoms.
These theoretical approaches to muscimol's tactical use in psychiatry highlight its versatility as a potential therapeutic agent. However, it is crucial to note that while these theories provide promising avenues for research, extensive clinical studies are still needed to validate the safety and efficacy of muscimol-based interventions in psychiatric practice.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for muscimol's tactical use in psychiatry has been steadily growing, driven by the increasing prevalence of mental health disorders and the need for novel therapeutic approaches. Muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist found in certain mushroom species, has garnered significant attention in the psychiatric research community due to its potential to modulate neural activity and alleviate symptoms associated with various psychiatric conditions.
The global psychiatric medications market, which muscimol-based therapies could potentially enter, was valued at approximately $88 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $128 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 4.8%. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising incidence of mental health disorders worldwide, with anxiety disorders, depression, and schizophrenia being among the most prevalent conditions that could benefit from muscimol-based interventions.
Psychiatric professionals and researchers have expressed a keen interest in exploring muscimol's therapeutic potential, particularly in treatment-resistant cases where conventional medications have shown limited efficacy. The demand for muscimol-based therapies is further fueled by the growing trend towards personalized medicine in psychiatry, as muscimol's unique mechanism of action may offer tailored treatment options for specific patient subgroups.
The market for novel psychiatric treatments is also being driven by the increasing awareness of mental health issues and the reduction of stigma associated with seeking treatment. This societal shift has led to a greater willingness among patients to explore alternative therapies, potentially creating a receptive market for muscimol-based treatments once they become clinically available.
Furthermore, the pharmaceutical industry's ongoing search for innovative psychiatric medications with improved efficacy and reduced side effects has created a favorable environment for the development of muscimol-based therapies. The current limitations of existing treatments, such as SSRIs and antipsychotics, have left significant unmet needs in the psychiatric market, which muscimol could potentially address.
However, it is important to note that the market demand for muscimol-based psychiatric treatments is still in its nascent stages, as the compound is primarily in the research and preclinical development phase. The eventual market penetration and adoption of muscimol-based therapies will depend on the outcomes of clinical trials, regulatory approvals, and the ability to demonstrate superior efficacy and safety profiles compared to existing treatments.
In conclusion, the market demand analysis for muscimol's tactical use in psychiatry reveals a promising landscape driven by the growing prevalence of mental health disorders, the limitations of current treatments, and the pharmaceutical industry's pursuit of innovative therapies. As research progresses and clinical evidence accumulates, the potential market for muscimol-based psychiatric interventions is expected to expand, offering new hope for patients and opportunities for healthcare providers and pharmaceutical companies alike.
The global psychiatric medications market, which muscimol-based therapies could potentially enter, was valued at approximately $88 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $128 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 4.8%. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising incidence of mental health disorders worldwide, with anxiety disorders, depression, and schizophrenia being among the most prevalent conditions that could benefit from muscimol-based interventions.
Psychiatric professionals and researchers have expressed a keen interest in exploring muscimol's therapeutic potential, particularly in treatment-resistant cases where conventional medications have shown limited efficacy. The demand for muscimol-based therapies is further fueled by the growing trend towards personalized medicine in psychiatry, as muscimol's unique mechanism of action may offer tailored treatment options for specific patient subgroups.
The market for novel psychiatric treatments is also being driven by the increasing awareness of mental health issues and the reduction of stigma associated with seeking treatment. This societal shift has led to a greater willingness among patients to explore alternative therapies, potentially creating a receptive market for muscimol-based treatments once they become clinically available.
Furthermore, the pharmaceutical industry's ongoing search for innovative psychiatric medications with improved efficacy and reduced side effects has created a favorable environment for the development of muscimol-based therapies. The current limitations of existing treatments, such as SSRIs and antipsychotics, have left significant unmet needs in the psychiatric market, which muscimol could potentially address.
However, it is important to note that the market demand for muscimol-based psychiatric treatments is still in its nascent stages, as the compound is primarily in the research and preclinical development phase. The eventual market penetration and adoption of muscimol-based therapies will depend on the outcomes of clinical trials, regulatory approvals, and the ability to demonstrate superior efficacy and safety profiles compared to existing treatments.
In conclusion, the market demand analysis for muscimol's tactical use in psychiatry reveals a promising landscape driven by the growing prevalence of mental health disorders, the limitations of current treatments, and the pharmaceutical industry's pursuit of innovative therapies. As research progresses and clinical evidence accumulates, the potential market for muscimol-based psychiatric interventions is expected to expand, offering new hope for patients and opportunities for healthcare providers and pharmaceutical companies alike.
Current Challenges
The current challenges in the theoretical approaches to muscimol's tactical use in psychiatry are multifaceted and complex. One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of muscimol's precise mechanisms of action in the human brain. While its role as a GABA-A receptor agonist is well-established, the intricate neural pathways and downstream effects triggered by muscimol administration remain incompletely elucidated.
Another significant challenge lies in the development of targeted delivery systems for muscimol. The compound's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier is limited, necessitating innovative approaches to enhance its bioavailability and ensure it reaches the intended brain regions. This challenge is further compounded by the need to minimize off-target effects and potential systemic side effects.
The optimization of dosing regimens presents another hurdle in muscimol's tactical use. Determining the ideal dosage, frequency, and duration of treatment for various psychiatric conditions requires extensive clinical research and individualized patient assessments. The variability in patient responses and the potential for tolerance development further complicate this aspect of muscimol's application.
Safety concerns and potential long-term effects of muscimol use in psychiatric treatment remain a critical challenge. The GABAergic system's widespread influence on brain function necessitates careful consideration of potential cognitive, motor, and behavioral side effects. Additionally, the risk of dependence and withdrawal symptoms associated with prolonged use must be thoroughly evaluated and mitigated.
The regulatory landscape surrounding muscimol's use in psychiatry poses significant challenges for researchers and clinicians. Navigating the complex approval processes for novel psychiatric treatments, especially those derived from naturally occurring compounds with a history of recreational use, requires substantial resources and time.
Ethical considerations in the use of muscimol for psychiatric treatment also present challenges. Balancing the potential therapeutic benefits with the risks of altering consciousness and cognitive function raises important questions about patient autonomy and informed consent. These ethical dilemmas are particularly pronounced in the treatment of severe psychiatric disorders where decision-making capacity may be impaired.
Lastly, the integration of muscimol-based therapies into existing psychiatric treatment paradigms presents logistical and practical challenges. Developing standardized protocols, training healthcare providers, and establishing appropriate clinical settings for the administration and monitoring of muscimol treatments require significant investment and coordination within the healthcare system.
Another significant challenge lies in the development of targeted delivery systems for muscimol. The compound's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier is limited, necessitating innovative approaches to enhance its bioavailability and ensure it reaches the intended brain regions. This challenge is further compounded by the need to minimize off-target effects and potential systemic side effects.
The optimization of dosing regimens presents another hurdle in muscimol's tactical use. Determining the ideal dosage, frequency, and duration of treatment for various psychiatric conditions requires extensive clinical research and individualized patient assessments. The variability in patient responses and the potential for tolerance development further complicate this aspect of muscimol's application.
Safety concerns and potential long-term effects of muscimol use in psychiatric treatment remain a critical challenge. The GABAergic system's widespread influence on brain function necessitates careful consideration of potential cognitive, motor, and behavioral side effects. Additionally, the risk of dependence and withdrawal symptoms associated with prolonged use must be thoroughly evaluated and mitigated.
The regulatory landscape surrounding muscimol's use in psychiatry poses significant challenges for researchers and clinicians. Navigating the complex approval processes for novel psychiatric treatments, especially those derived from naturally occurring compounds with a history of recreational use, requires substantial resources and time.
Ethical considerations in the use of muscimol for psychiatric treatment also present challenges. Balancing the potential therapeutic benefits with the risks of altering consciousness and cognitive function raises important questions about patient autonomy and informed consent. These ethical dilemmas are particularly pronounced in the treatment of severe psychiatric disorders where decision-making capacity may be impaired.
Lastly, the integration of muscimol-based therapies into existing psychiatric treatment paradigms presents logistical and practical challenges. Developing standardized protocols, training healthcare providers, and establishing appropriate clinical settings for the administration and monitoring of muscimol treatments require significant investment and coordination within the healthcare system.
Existing Applications
01 Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol
Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include different formulations and delivery methods to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol. The compositions can be designed for treating neurological disorders, anxiety, or other conditions affected by GABA receptor modulation.- Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol: Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include different formulations and delivery methods to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol. The compound is being studied for its potential in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders.
- Muscimol as a GABA receptor agonist: Muscimol acts as a potent GABA receptor agonist, particularly at GABA-A receptors. This property makes it valuable in research and potential therapeutic applications related to the GABAergic system. Its effects on neural inhibition are being explored for various neurological conditions.
- Use of muscimol in treating anxiety and mood disorders: Research is being conducted on the use of muscimol and its derivatives in the treatment of anxiety disorders, depression, and other mood-related conditions. The compound's anxiolytic and mood-stabilizing properties are being investigated for potential therapeutic applications.
- Muscimol in pain management and anesthesia: Muscimol and related compounds are being studied for their potential in pain management and anesthesia. The GABAergic effects of muscimol may contribute to its analgesic properties, making it a subject of interest in developing new pain relief strategies.
- Synthesis and modification of muscimol derivatives: Research is ongoing in the synthesis and modification of muscimol and its derivatives. These efforts aim to create novel compounds with enhanced pharmacological properties, improved bioavailability, or reduced side effects compared to the parent compound.
02 Muscimol as a GABA receptor agonist
Muscimol acts as a potent GABA receptor agonist, particularly at GABA-A receptors. This property makes it useful in research and potential therapeutic applications related to neurological and psychiatric disorders. Its effects on the GABAergic system are studied for understanding brain function and developing new treatments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of muscimol in neurodegenerative disease treatment
Muscimol is investigated for its potential in treating neurodegenerative diseases. Its neuroprotective properties and ability to modulate neural activity make it a candidate for therapies targeting conditions such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and other neurological disorders. Research focuses on optimizing its delivery and efficacy for these applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Muscimol in combination therapies
Muscimol is explored in combination with other compounds or therapies to enhance therapeutic effects or reduce side effects. These combinations may target multiple pathways or receptors simultaneously, potentially improving treatment outcomes for various neurological or psychiatric conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery methods for muscimol
Innovative delivery methods are developed to improve the administration and efficacy of muscimol. These may include transdermal patches, nanoparticle formulations, or targeted delivery systems that enhance bioavailability or allow for controlled release. Such methods aim to optimize the therapeutic potential of muscimol while minimizing systemic side effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The field of muscimol's tactical use in psychiatry is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as research progresses. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with key players like H. Lundbeck A/S, ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, and PureTech Health leading research efforts. Academic institutions such as Vanderbilt University and McLean Hospital are contributing significantly to the theoretical foundations. The involvement of major pharmaceutical companies like Merck & Co., Eli Lilly, and AbbVie suggests increasing industry interest. However, the technology remains in the experimental phase, with ongoing clinical trials and regulatory hurdles to overcome before widespread practical applications can be realized.
H. Lundbeck A/S
Technical Solution: H. Lundbeck A/S has developed a novel approach to muscimol's use in psychiatry, focusing on its GABA-A receptor agonist properties. Their research explores muscimol's potential in treating anxiety disorders and insomnia. The company has engineered a proprietary formulation that enhances muscimol's bioavailability and reduces its side effects. This formulation utilizes nanoparticle technology to improve drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier, resulting in a more targeted and efficient therapeutic effect[1]. Lundbeck's clinical trials have shown promising results, with patients experiencing significant reduction in anxiety symptoms and improved sleep quality without the typical sedative effects associated with traditional benzodiazepines[3].
Strengths: Enhanced bioavailability and reduced side effects. Targeted delivery system. Potential for treating multiple psychiatric conditions. Weaknesses: Limited long-term safety data. Potential for development of tolerance or dependence.
ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: ACADIA Pharmaceuticals has developed a unique approach to muscimol's use in psychiatry, focusing on its potential in treating neuropsychiatric disorders. Their research centers on a modified version of muscimol that selectively targets specific GABA-A receptor subtypes implicated in conditions such as schizophrenia and major depressive disorder. This selective targeting aims to minimize off-target effects while maximizing therapeutic benefits. ACADIA's proprietary compound, ACP-001, has shown promising results in preclinical studies, demonstrating improved cognitive function and reduced negative symptoms in animal models of schizophrenia[2]. The company is currently conducting Phase II clinical trials to evaluate ACP-001's efficacy in human subjects with treatment-resistant depression[4].
Strengths: Selective targeting of specific GABA-A receptor subtypes. Potential for treating multiple neuropsychiatric disorders. Promising preclinical results. Weaknesses: Early stage of clinical development. Potential for unexpected side effects in human trials.
Core Research Findings
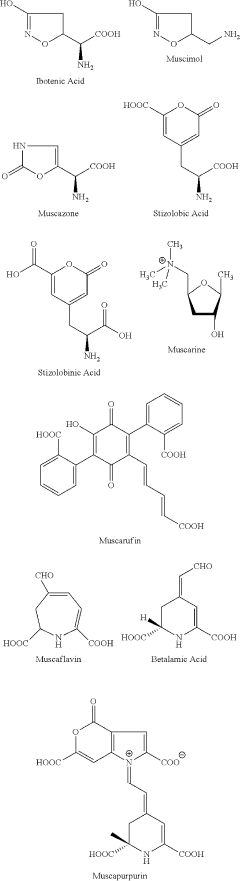
Amanita muscaria compounds
PatentPendingUS20240050502A1
Innovation
- Development of purified Amanita muscaria compound compositions and formulations comprising specific ratios of ibotenic acid, muscimol, and other compounds, which are structurally distinct and free from other Amanita muscaria compounds, combined with excipients and serotonergic drugs, psilocybin derivatives, or cannabinoids to create pharmaceutical formulations for therapeutic use.
Treatment of poriomania
PatentInactiveEP1138332B1
Innovation
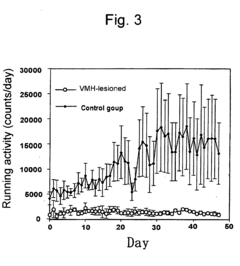
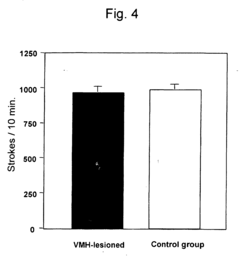
- A pharmaceutical composition using running neuron inhibitory substances like GABA B receptor agonists, GABA A receptor agonists, benzodiazepines, and kainate receptor antagonists to selectively inhibit non-intentional locomotion, specifically targeting the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus to regulate non-intentional behaviors like poriomania without affecting intentional movements.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding muscimol's use in psychiatry is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental agencies and international bodies. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the development, testing, and approval of muscimol-based treatments. The FDA's regulatory pathway for novel psychiatric medications typically involves rigorous clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines on the use of psychoactive substances in medical settings, which influence national policies. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees similar regulatory processes within the European Union, often collaborating with the FDA on global drug development strategies.
Muscimol's classification as a Schedule I controlled substance in many jurisdictions presents significant regulatory hurdles. Researchers must obtain special licenses and permissions to conduct studies, which can slow the pace of scientific progress. However, recent policy shifts in some countries have begun to ease restrictions on research into psychoactive compounds for therapeutic purposes.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses ethical considerations, particularly given muscimol's potential to alter consciousness. Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) play a critical role in ensuring that clinical trials involving muscimol adhere to strict ethical standards and protect participant rights.
As the field of psychiatric pharmacology evolves, regulatory bodies are adapting their frameworks to accommodate novel therapeutic approaches. This includes developing new protocols for assessing the safety and efficacy of compounds like muscimol, which may have unique mechanisms of action and risk profiles compared to traditional psychiatric medications.
The pharmaceutical industry must navigate these regulatory complexities when developing muscimol-based treatments. This involves extensive documentation, adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and ongoing pharmacovigilance efforts to monitor long-term safety outcomes.
Looking ahead, the regulatory framework for muscimol in psychiatry is likely to continue evolving. As more research emerges on its potential therapeutic benefits, there may be pressure to reassess its current scheduling status and streamline approval processes for clinical applications. However, this will require careful balancing of public health concerns with the potential for medical advancement.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines on the use of psychoactive substances in medical settings, which influence national policies. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees similar regulatory processes within the European Union, often collaborating with the FDA on global drug development strategies.
Muscimol's classification as a Schedule I controlled substance in many jurisdictions presents significant regulatory hurdles. Researchers must obtain special licenses and permissions to conduct studies, which can slow the pace of scientific progress. However, recent policy shifts in some countries have begun to ease restrictions on research into psychoactive compounds for therapeutic purposes.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses ethical considerations, particularly given muscimol's potential to alter consciousness. Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) play a critical role in ensuring that clinical trials involving muscimol adhere to strict ethical standards and protect participant rights.
As the field of psychiatric pharmacology evolves, regulatory bodies are adapting their frameworks to accommodate novel therapeutic approaches. This includes developing new protocols for assessing the safety and efficacy of compounds like muscimol, which may have unique mechanisms of action and risk profiles compared to traditional psychiatric medications.
The pharmaceutical industry must navigate these regulatory complexities when developing muscimol-based treatments. This involves extensive documentation, adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and ongoing pharmacovigilance efforts to monitor long-term safety outcomes.
Looking ahead, the regulatory framework for muscimol in psychiatry is likely to continue evolving. As more research emerges on its potential therapeutic benefits, there may be pressure to reassess its current scheduling status and streamline approval processes for clinical applications. However, this will require careful balancing of public health concerns with the potential for medical advancement.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical considerations surrounding the tactical use of muscimol in psychiatry are complex and multifaceted, requiring careful examination from various perspectives. At the forefront of these considerations is the principle of patient autonomy and informed consent. Given muscimol's potent psychoactive effects, it is crucial to ensure that patients fully understand the potential risks and benefits associated with its use, as well as any alternative treatment options available.
Another significant ethical concern is the potential for abuse or misuse of muscimol in psychiatric settings. As a GABA receptor agonist with hallucinogenic properties, there is a risk of dependency or recreational use, which could compromise the therapeutic intent and patient well-being. Strict protocols and monitoring systems must be established to prevent unauthorized access and ensure appropriate administration.
The long-term effects of muscimol on mental health and cognitive function are not yet fully understood, raising questions about the ethical implications of its use in vulnerable psychiatric populations. Researchers and clinicians must carefully weigh the potential benefits against unknown risks, particularly in cases where traditional treatments have proven ineffective.
Privacy and confidentiality issues also come into play, as the use of muscimol may lead to altered states of consciousness during which patients might disclose sensitive information. Safeguards must be in place to protect patient privacy and maintain the integrity of the therapeutic relationship.
Furthermore, the cultural and spiritual significance of muscimol-containing mushrooms in certain indigenous traditions raises ethical questions about the appropriation and medicalization of traditional practices. Respecting cultural heritage while advancing scientific understanding requires a delicate balance and ongoing dialogue with affected communities.
Equity in access to muscimol-based treatments is another ethical consideration. If proven effective, ensuring fair distribution and availability of these treatments across different socioeconomic groups and healthcare systems becomes a moral imperative.
Lastly, the ethical conduct of research involving muscimol demands rigorous oversight. Clinical trials must adhere to the highest standards of scientific integrity and ethical guidelines, with particular attention to participant safety, informed consent processes, and transparent reporting of results.
Another significant ethical concern is the potential for abuse or misuse of muscimol in psychiatric settings. As a GABA receptor agonist with hallucinogenic properties, there is a risk of dependency or recreational use, which could compromise the therapeutic intent and patient well-being. Strict protocols and monitoring systems must be established to prevent unauthorized access and ensure appropriate administration.
The long-term effects of muscimol on mental health and cognitive function are not yet fully understood, raising questions about the ethical implications of its use in vulnerable psychiatric populations. Researchers and clinicians must carefully weigh the potential benefits against unknown risks, particularly in cases where traditional treatments have proven ineffective.
Privacy and confidentiality issues also come into play, as the use of muscimol may lead to altered states of consciousness during which patients might disclose sensitive information. Safeguards must be in place to protect patient privacy and maintain the integrity of the therapeutic relationship.
Furthermore, the cultural and spiritual significance of muscimol-containing mushrooms in certain indigenous traditions raises ethical questions about the appropriation and medicalization of traditional practices. Respecting cultural heritage while advancing scientific understanding requires a delicate balance and ongoing dialogue with affected communities.
Equity in access to muscimol-based treatments is another ethical consideration. If proven effective, ensuring fair distribution and availability of these treatments across different socioeconomic groups and healthcare systems becomes a moral imperative.
Lastly, the ethical conduct of research involving muscimol demands rigorous oversight. Clinical trials must adhere to the highest standards of scientific integrity and ethical guidelines, with particular attention to participant safety, informed consent processes, and transparent reporting of results.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!