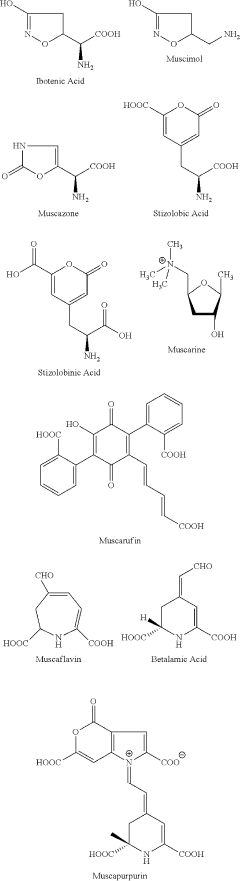
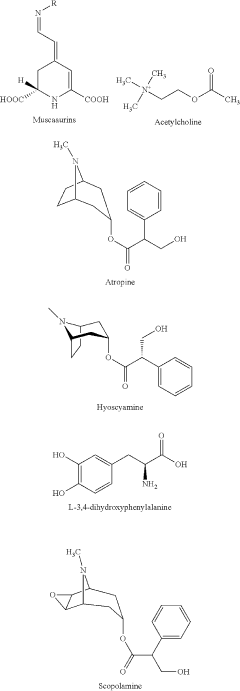
Muscimol and Its Psychoactive Properties
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Background and Research Objectives
Muscimol, a potent psychoactive compound found in various species of mushrooms, particularly those belonging to the Amanita genus, has been a subject of scientific interest for decades. This naturally occurring alkaloid has a rich history of traditional use in shamanic practices and religious rituals across different cultures. The primary objective of this research is to comprehensively explore muscimol's psychoactive properties and its potential applications in modern medicine and neuroscience.
The evolution of muscimol research can be traced back to the mid-20th century when scientists first isolated and identified the compound. Since then, significant advancements have been made in understanding its chemical structure, pharmacological properties, and mechanisms of action. Muscimol's ability to act as a selective GABA-A receptor agonist has positioned it as a valuable tool in neuroscience research and a potential therapeutic agent for various neurological disorders.
Recent technological developments in neuroimaging and molecular biology have enabled researchers to gain deeper insights into muscimol's effects on brain function and neural networks. These advancements have paved the way for more targeted investigations into its potential therapeutic applications, particularly in the treatment of anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and neurodegenerative diseases.
The current research landscape surrounding muscimol is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from pharmacology, neuroscience, psychology, and medicinal chemistry. This collaborative effort aims to unlock the full potential of muscimol and its derivatives in both basic research and clinical applications.
Key research objectives in the field of muscimol studies include:
1. Elucidating the precise mechanisms by which muscimol interacts with GABA-A receptors and modulates neural activity.
2. Investigating the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
3. Exploring the structure-activity relationships of muscimol and its analogs to develop more potent and selective compounds.
4. Assessing the long-term effects and safety profile of muscimol use in both experimental and clinical settings.
5. Developing novel drug delivery methods to enhance the bioavailability and targeted action of muscimol-based therapies.
As research in this field progresses, it is anticipated that new insights into muscimol's psychoactive properties will emerge, potentially leading to breakthrough treatments for a range of neurological conditions. The ongoing exploration of this fascinating compound continues to push the boundaries of our understanding of brain function and the potential of naturally derived psychoactive substances in modern medicine.
The evolution of muscimol research can be traced back to the mid-20th century when scientists first isolated and identified the compound. Since then, significant advancements have been made in understanding its chemical structure, pharmacological properties, and mechanisms of action. Muscimol's ability to act as a selective GABA-A receptor agonist has positioned it as a valuable tool in neuroscience research and a potential therapeutic agent for various neurological disorders.
Recent technological developments in neuroimaging and molecular biology have enabled researchers to gain deeper insights into muscimol's effects on brain function and neural networks. These advancements have paved the way for more targeted investigations into its potential therapeutic applications, particularly in the treatment of anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and neurodegenerative diseases.
The current research landscape surrounding muscimol is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from pharmacology, neuroscience, psychology, and medicinal chemistry. This collaborative effort aims to unlock the full potential of muscimol and its derivatives in both basic research and clinical applications.
Key research objectives in the field of muscimol studies include:
1. Elucidating the precise mechanisms by which muscimol interacts with GABA-A receptors and modulates neural activity.
2. Investigating the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
3. Exploring the structure-activity relationships of muscimol and its analogs to develop more potent and selective compounds.
4. Assessing the long-term effects and safety profile of muscimol use in both experimental and clinical settings.
5. Developing novel drug delivery methods to enhance the bioavailability and targeted action of muscimol-based therapies.
As research in this field progresses, it is anticipated that new insights into muscimol's psychoactive properties will emerge, potentially leading to breakthrough treatments for a range of neurological conditions. The ongoing exploration of this fascinating compound continues to push the boundaries of our understanding of brain function and the potential of naturally derived psychoactive substances in modern medicine.
Market Analysis for Psychoactive Compounds
The market for psychoactive compounds has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing interest in mental health treatments, recreational use, and potential therapeutic applications. Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, particularly Amanita muscaria, has garnered attention for its unique properties and potential applications.
The global psychedelic drugs market, which includes muscimol and related compounds, was valued at approximately $2 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $6.8 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 16.3% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising prevalence of mental health disorders, increasing acceptance of psychedelic drugs for therapeutic purposes, and ongoing research into their potential benefits.
In the context of muscimol specifically, the market is still relatively niche but showing promising signs of expansion. The compound's GABA-mimetic properties have attracted interest from pharmaceutical companies and researchers exploring its potential in treating anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and sleep disturbances. Additionally, the traditional use of Amanita muscaria in certain cultures has sparked curiosity in the wellness and alternative medicine sectors.
The market for muscimol-based products can be segmented into pharmaceutical applications, nutraceuticals, and research chemicals. Pharmaceutical applications currently represent the largest market share, with several clinical trials underway to investigate muscimol's therapeutic potential. The nutraceutical segment, while smaller, is experiencing rapid growth as consumers seek natural alternatives for stress relief and cognitive enhancement.
Geographically, North America dominates the psychoactive compounds market, followed by Europe. These regions benefit from advanced healthcare infrastructure, favorable regulatory environments for research, and growing acceptance of alternative therapies. However, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing mental health awareness and rising disposable incomes.
Key market players in the broader psychoactive compounds space include Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, and Compass Pathways. While these companies primarily focus on other psychedelics like psilocybin and MDMA, their research and development efforts contribute to the overall growth and legitimacy of the psychoactive compounds market, potentially benefiting muscimol research indirectly.
Challenges in the muscimol market include regulatory hurdles, as the compound is classified as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions. This classification complicates research efforts and limits commercial applications. Additionally, public perception and stigma surrounding psychoactive compounds pose barriers to market growth, necessitating educational initiatives and responsible marketing strategies.
The global psychedelic drugs market, which includes muscimol and related compounds, was valued at approximately $2 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $6.8 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 16.3% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising prevalence of mental health disorders, increasing acceptance of psychedelic drugs for therapeutic purposes, and ongoing research into their potential benefits.
In the context of muscimol specifically, the market is still relatively niche but showing promising signs of expansion. The compound's GABA-mimetic properties have attracted interest from pharmaceutical companies and researchers exploring its potential in treating anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and sleep disturbances. Additionally, the traditional use of Amanita muscaria in certain cultures has sparked curiosity in the wellness and alternative medicine sectors.
The market for muscimol-based products can be segmented into pharmaceutical applications, nutraceuticals, and research chemicals. Pharmaceutical applications currently represent the largest market share, with several clinical trials underway to investigate muscimol's therapeutic potential. The nutraceutical segment, while smaller, is experiencing rapid growth as consumers seek natural alternatives for stress relief and cognitive enhancement.
Geographically, North America dominates the psychoactive compounds market, followed by Europe. These regions benefit from advanced healthcare infrastructure, favorable regulatory environments for research, and growing acceptance of alternative therapies. However, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing mental health awareness and rising disposable incomes.
Key market players in the broader psychoactive compounds space include Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, and Compass Pathways. While these companies primarily focus on other psychedelics like psilocybin and MDMA, their research and development efforts contribute to the overall growth and legitimacy of the psychoactive compounds market, potentially benefiting muscimol research indirectly.
Challenges in the muscimol market include regulatory hurdles, as the compound is classified as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions. This classification complicates research efforts and limits commercial applications. Additionally, public perception and stigma surrounding psychoactive compounds pose barriers to market growth, necessitating educational initiatives and responsible marketing strategies.
Current State of Muscimol Research
Muscimol research has made significant strides in recent years, with a growing body of scientific literature exploring its psychoactive properties and potential therapeutic applications. Current studies focus on understanding the compound's mechanism of action, its effects on the central nervous system, and its potential use in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Researchers have identified muscimol as a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, which explains its sedative, anxiolytic, and muscle relaxant effects. This understanding has led to increased interest in its potential as a novel therapeutic agent for conditions such as anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and insomnia. Preclinical studies have shown promising results in animal models, demonstrating muscimol's ability to reduce seizure activity and alleviate anxiety-like behaviors.
The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of muscimol are now better understood, with studies revealing its rapid absorption and distribution in the brain. This knowledge has implications for dosing strategies and potential drug delivery methods. Researchers are exploring various administration routes, including oral, intranasal, and transdermal applications, to optimize its therapeutic potential while minimizing side effects.
Neuroimaging studies have provided insights into muscimol's effects on brain activity and connectivity. Functional MRI and PET scans have revealed alterations in neural networks associated with cognition, emotion, and sensory processing following muscimol administration. These findings contribute to our understanding of the compound's psychoactive properties and its potential impact on various brain functions.
Safety and toxicology studies are ongoing, with researchers investigating the long-term effects of muscimol use and potential interactions with other medications. While initial results suggest a favorable safety profile compared to some existing psychoactive drugs, more comprehensive clinical trials are needed to establish its safety and efficacy in human subjects.
Synthetic chemistry efforts have focused on developing novel muscimol analogs with enhanced pharmacological properties. These modified compounds aim to improve selectivity, potency, and bioavailability while reducing unwanted side effects. Some promising candidates have emerged from these studies, potentially expanding the therapeutic applications of muscimol-like compounds.
The current state of muscimol research also includes investigations into its potential use in treating neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Preliminary studies suggest that muscimol's neuroprotective properties may help slow disease progression and alleviate symptoms, though more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Researchers have identified muscimol as a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, which explains its sedative, anxiolytic, and muscle relaxant effects. This understanding has led to increased interest in its potential as a novel therapeutic agent for conditions such as anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and insomnia. Preclinical studies have shown promising results in animal models, demonstrating muscimol's ability to reduce seizure activity and alleviate anxiety-like behaviors.
The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of muscimol are now better understood, with studies revealing its rapid absorption and distribution in the brain. This knowledge has implications for dosing strategies and potential drug delivery methods. Researchers are exploring various administration routes, including oral, intranasal, and transdermal applications, to optimize its therapeutic potential while minimizing side effects.
Neuroimaging studies have provided insights into muscimol's effects on brain activity and connectivity. Functional MRI and PET scans have revealed alterations in neural networks associated with cognition, emotion, and sensory processing following muscimol administration. These findings contribute to our understanding of the compound's psychoactive properties and its potential impact on various brain functions.
Safety and toxicology studies are ongoing, with researchers investigating the long-term effects of muscimol use and potential interactions with other medications. While initial results suggest a favorable safety profile compared to some existing psychoactive drugs, more comprehensive clinical trials are needed to establish its safety and efficacy in human subjects.
Synthetic chemistry efforts have focused on developing novel muscimol analogs with enhanced pharmacological properties. These modified compounds aim to improve selectivity, potency, and bioavailability while reducing unwanted side effects. Some promising candidates have emerged from these studies, potentially expanding the therapeutic applications of muscimol-like compounds.
The current state of muscimol research also includes investigations into its potential use in treating neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Preliminary studies suggest that muscimol's neuroprotective properties may help slow disease progression and alleviate symptoms, though more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Existing Muscimol Extraction Methods
01 Psychoactive effects of muscimol
Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushrooms, exhibits potent GABA-A receptor agonist properties. It induces various psychoactive effects, including sedation, hallucinations, and altered states of consciousness. Research focuses on understanding its mechanism of action and potential therapeutic applications in neurological disorders.- Psychoactive effects of muscimol: Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushrooms, exhibits potent GABA-A receptor agonist properties. It produces various psychoactive effects including sedation, hallucinations, and altered perception. Research has focused on understanding its mechanism of action and potential therapeutic applications in neurological disorders.
- Formulation and delivery methods for muscimol: Various formulation and delivery methods have been developed to optimize the administration of muscimol for therapeutic purposes. These include oral, transdermal, and intranasal formulations, as well as controlled-release systems to modulate its psychoactive effects and improve its pharmacokinetic profile.
- Therapeutic applications of muscimol: Research has explored the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol's psychoactive properties. Studies have investigated its use in treating anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and sleep disturbances. The compound's ability to modulate GABA neurotransmission has also been studied for its neuroprotective effects in various neurological conditions.
- Synthetic analogs and derivatives of muscimol: Efforts have been made to develop synthetic analogs and derivatives of muscimol with enhanced pharmacological properties. These modified compounds aim to retain the beneficial psychoactive effects while reducing potential side effects or improving specific therapeutic outcomes. Structure-activity relationship studies have guided the design of these novel molecules.
- Detection and quantification methods for muscimol: Various analytical techniques have been developed to detect and quantify muscimol in biological samples and pharmaceutical preparations. These methods are crucial for studying the compound's pharmacokinetics, ensuring quality control in drug formulations, and monitoring potential misuse. Techniques include chromatography, mass spectrometry, and immunoassays.
02 Muscimol analogs and derivatives
Development of muscimol analogs and derivatives aims to enhance its psychoactive properties or modify its effects. These compounds are designed to improve pharmacokinetics, increase potency, or reduce side effects. Synthetic approaches and structure-activity relationship studies are employed to create novel molecules with targeted psychoactive profiles.Expand Specific Solutions03 Formulation and delivery methods
Various formulation and delivery methods are explored to optimize the psychoactive properties of muscimol. These include oral, transdermal, and intranasal formulations, as well as controlled-release systems. The goal is to enhance bioavailability, improve onset of action, and maintain desired psychoactive effects while minimizing adverse reactions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Therapeutic applications of muscimol
Research investigates the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol's psychoactive properties. Areas of interest include anxiety disorders, sleep disorders, and certain neurological conditions. Studies focus on harnessing its GABA-ergic effects while managing potential risks and side effects associated with its psychoactive nature.Expand Specific Solutions05 Detection and analysis methods
Development of advanced detection and analysis methods for muscimol and its metabolites is crucial for understanding its psychoactive properties. These techniques include high-performance liquid chromatography, mass spectrometry, and immunoassays. Improved analytical methods aid in pharmacokinetic studies, toxicology assessments, and quality control of muscimol-containing products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Psychoactive Research
The research on muscimol and its psychoactive properties is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential due to increased interest in psychedelic compounds for therapeutic applications. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms. Key players like ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, DemeRx, and CaaMTech are actively exploring muscimol's potential, leveraging their expertise in neuroscience and drug development. The technology is still evolving, with companies focusing on optimizing muscimol's pharmacological profile and delivery methods. As the field progresses, collaborations between academic institutions and industry partners are likely to accelerate research and development efforts.
ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: ACADIA Pharmaceuticals is investigating muscimol and related GABA-A receptor agonists for their potential in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders. Their research focuses on developing novel small molecule compounds that modulate GABA-A receptors, similar to muscimol's mechanism of action. ACADIA's approach involves creating more selective and potent GABA-A receptor modulators, aiming to enhance therapeutic effects while minimizing side effects. The company has conducted preclinical studies on compounds that target specific GABA-A receptor subtypes, showing promise in models of anxiety, depression, and cognitive disorders[4][5]. This research builds upon the understanding of muscimol's psychoactive properties to develop next-generation therapeutics.
Strengths: Extensive experience in CNS drug development. Advanced research capabilities in receptor pharmacology. Weaknesses: Competitive field with many players in GABA receptor research. Potential for off-target effects with GABA modulators.
DemeRx, Inc.
Technical Solution: DemeRx is exploring muscimol and related compounds as part of their research into novel treatments for addiction and other neuropsychiatric disorders. Their approach involves investigating the potential of GABA-A receptor modulators, including muscimol analogs, for their ability to influence addictive behaviors and neural plasticity. DemeRx's research focuses on understanding how muscimol-like compounds can affect the brain's reward system and stress responses, which are key factors in addiction. The company is developing proprietary formulations and delivery methods to optimize the therapeutic potential of these compounds while minimizing psychoactive side effects[6]. Their studies include both preclinical models and early-phase clinical trials to assess safety and efficacy in human subjects[7].
Strengths: Specialized focus on addiction treatment, an area with high unmet medical need. Innovative approach to modulating GABA systems for addiction therapy. Weaknesses: Challenges in translating preclinical findings to human efficacy. Potential for abuse or misuse of compounds with psychoactive properties.
Core Innovations in Muscimol Synthesis
Amanita muscaria compounds
PatentPendingUS20240050502A1
Innovation
- Development of purified Amanita muscaria compound compositions and formulations comprising specific ratios of ibotenic acid, muscimol, and other compounds, which are structurally distinct and free from other Amanita muscaria compounds, combined with excipients and serotonergic drugs, psilocybin derivatives, or cannabinoids to create pharmaceutical formulations for therapeutic use.
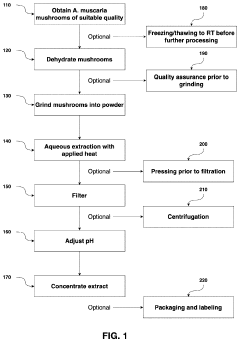
Processes for Extracting Muscimol from Amanita Muscaria
PatentPendingUS20240165180A1
Innovation
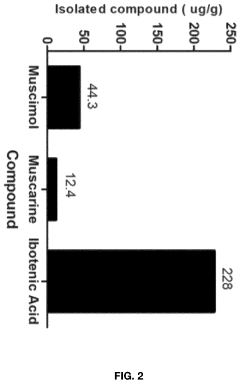
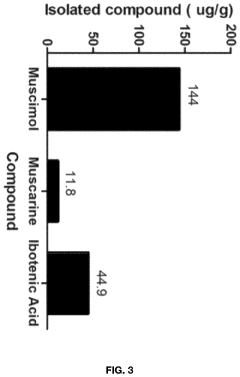
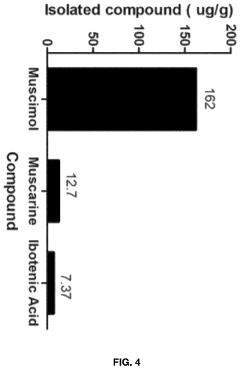
- Aqueous extraction of Amanita muscaria biomass is performed with heat, followed by pH reduction between 2.0 to 4.0 and concentration through distillation or refluxing, which decreases ibotenic acid content and increases muscimol content, resulting in a muscimol-rich extract with enhanced purity.
Regulatory Framework for Psychoactive Substances
The regulatory framework for psychoactive substances, including muscimol, is complex and varies significantly across different jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) play crucial roles in regulating these substances. The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) categorizes psychoactive compounds into schedules based on their potential for abuse, medical use, and safety profile.
Muscimol, while not explicitly scheduled under the CSA, falls under regulatory scrutiny due to its psychoactive properties. The FDA has authority over any potential medical applications, requiring rigorous clinical trials and safety assessments before approval. Research on muscimol and similar compounds often requires special licenses and adherence to strict protocols to ensure compliance with federal regulations.
Internationally, the United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances provides a framework for global control of psychoactive substances. However, muscimol is not currently listed in any of the convention's schedules, leading to varied approaches in different countries. Some nations have implemented specific laws to regulate muscimol-containing fungi or synthetic analogues.
The regulatory landscape is further complicated by the natural occurrence of muscimol in certain mushroom species, particularly Amanita muscaria. This raises questions about the regulation of naturally occurring psychoactive compounds versus their synthetic counterparts. Many countries have separate regulations for plant-based psychoactive substances, which may impact research and potential therapeutic applications of muscimol.
Recent trends in psychedelic research have led to discussions about potential reclassification of certain psychoactive substances. This could potentially affect the regulatory status of muscimol and similar compounds. Some jurisdictions are exploring more nuanced approaches to regulation, considering the potential therapeutic benefits alongside the risks associated with psychoactive substances.
Researchers working with muscimol must navigate a complex web of regulations, including obtaining necessary permits, ensuring proper storage and handling, and adhering to strict reporting requirements. These regulatory hurdles can significantly impact the pace and scope of research into muscimol's psychoactive properties and potential therapeutic applications.
As the field of psychoactive substance research evolves, there is ongoing debate about the need for regulatory reform to balance public safety concerns with the potential for scientific advancement and therapeutic breakthroughs. This dynamic regulatory environment underscores the importance of staying informed about current and proposed legislation affecting psychoactive substance research.
Muscimol, while not explicitly scheduled under the CSA, falls under regulatory scrutiny due to its psychoactive properties. The FDA has authority over any potential medical applications, requiring rigorous clinical trials and safety assessments before approval. Research on muscimol and similar compounds often requires special licenses and adherence to strict protocols to ensure compliance with federal regulations.
Internationally, the United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances provides a framework for global control of psychoactive substances. However, muscimol is not currently listed in any of the convention's schedules, leading to varied approaches in different countries. Some nations have implemented specific laws to regulate muscimol-containing fungi or synthetic analogues.
The regulatory landscape is further complicated by the natural occurrence of muscimol in certain mushroom species, particularly Amanita muscaria. This raises questions about the regulation of naturally occurring psychoactive compounds versus their synthetic counterparts. Many countries have separate regulations for plant-based psychoactive substances, which may impact research and potential therapeutic applications of muscimol.
Recent trends in psychedelic research have led to discussions about potential reclassification of certain psychoactive substances. This could potentially affect the regulatory status of muscimol and similar compounds. Some jurisdictions are exploring more nuanced approaches to regulation, considering the potential therapeutic benefits alongside the risks associated with psychoactive substances.
Researchers working with muscimol must navigate a complex web of regulations, including obtaining necessary permits, ensuring proper storage and handling, and adhering to strict reporting requirements. These regulatory hurdles can significantly impact the pace and scope of research into muscimol's psychoactive properties and potential therapeutic applications.
As the field of psychoactive substance research evolves, there is ongoing debate about the need for regulatory reform to balance public safety concerns with the potential for scientific advancement and therapeutic breakthroughs. This dynamic regulatory environment underscores the importance of staying informed about current and proposed legislation affecting psychoactive substance research.
Safety and Ethical Considerations
The research on muscimol and its psychoactive properties necessitates careful consideration of safety and ethical aspects. Given the potent nature of this compound, strict safety protocols must be implemented in laboratory settings to protect researchers and subjects. This includes proper handling, storage, and disposal procedures for muscimol, as well as rigorous safety training for all personnel involved in the studies.
Ethical considerations are paramount when conducting human trials involving psychoactive substances. Informed consent processes must be thorough, ensuring participants fully understand the potential risks and effects of muscimol. Researchers must adhere to stringent ethical guidelines, such as those outlined by institutional review boards and international research ethics committees.
The potential for abuse and misuse of muscimol outside of controlled research environments raises significant ethical concerns. As research progresses, it is crucial to consider the societal implications of increased knowledge about muscimol's psychoactive properties. This includes addressing potential recreational use and developing strategies to mitigate associated risks.
Long-term safety assessments are essential, as the effects of repeated muscimol exposure are not fully understood. Researchers must design longitudinal studies to evaluate potential physiological and psychological impacts over extended periods. Additionally, the development of standardized dosing protocols is critical to ensure consistency and safety across different research studies.
Ethical considerations extend to the sourcing of muscimol. While it can be synthesized in laboratories, it is also found naturally in certain mushroom species. Researchers must ensure that any natural sources are obtained legally and sustainably, without endangering ecosystems or violating international regulations on psychoactive substances.
The potential therapeutic applications of muscimol, such as in treating anxiety or neurological disorders, present a complex ethical landscape. Balancing the potential benefits against the risks of psychoactive effects requires careful deliberation. Researchers must work closely with medical ethicists to navigate these challenges and ensure that any potential treatments prioritize patient safety and well-being.
Transparency in research findings is crucial from an ethical standpoint. All results, including negative outcomes or unexpected side effects, should be fully disclosed to the scientific community and relevant regulatory bodies. This commitment to openness helps build trust and ensures that future research can build upon a comprehensive understanding of muscimol's properties and effects.
Ethical considerations are paramount when conducting human trials involving psychoactive substances. Informed consent processes must be thorough, ensuring participants fully understand the potential risks and effects of muscimol. Researchers must adhere to stringent ethical guidelines, such as those outlined by institutional review boards and international research ethics committees.
The potential for abuse and misuse of muscimol outside of controlled research environments raises significant ethical concerns. As research progresses, it is crucial to consider the societal implications of increased knowledge about muscimol's psychoactive properties. This includes addressing potential recreational use and developing strategies to mitigate associated risks.
Long-term safety assessments are essential, as the effects of repeated muscimol exposure are not fully understood. Researchers must design longitudinal studies to evaluate potential physiological and psychological impacts over extended periods. Additionally, the development of standardized dosing protocols is critical to ensure consistency and safety across different research studies.
Ethical considerations extend to the sourcing of muscimol. While it can be synthesized in laboratories, it is also found naturally in certain mushroom species. Researchers must ensure that any natural sources are obtained legally and sustainably, without endangering ecosystems or violating international regulations on psychoactive substances.
The potential therapeutic applications of muscimol, such as in treating anxiety or neurological disorders, present a complex ethical landscape. Balancing the potential benefits against the risks of psychoactive effects requires careful deliberation. Researchers must work closely with medical ethicists to navigate these challenges and ensure that any potential treatments prioritize patient safety and well-being.
Transparency in research findings is crucial from an ethical standpoint. All results, including negative outcomes or unexpected side effects, should be fully disclosed to the scientific community and relevant regulatory bodies. This commitment to openness helps build trust and ensures that future research can build upon a comprehensive understanding of muscimol's properties and effects.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!