Cultural Traditions Centered on Muscimol Consumption
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Consumption History and Research Objectives
Muscimol consumption has a rich history dating back thousands of years, with evidence of its use in various cultures around the world. This psychoactive compound, found primarily in Amanita muscaria mushrooms, has played a significant role in religious, spiritual, and medicinal practices across different societies.
The earliest documented use of muscimol-containing mushrooms can be traced to Siberian shamanic traditions, where they were used in religious ceremonies and for divination purposes. These practices spread to other parts of Northern Europe and Asia, influencing local customs and beliefs. In North America, indigenous cultures also incorporated muscimol-containing mushrooms into their spiritual practices, although the extent and duration of use varied among different tribes.
Throughout history, the consumption of muscimol has been associated with altered states of consciousness, visions, and spiritual experiences. This has led to its integration into various mythologies and folklore, such as the theory that Amanita muscaria may have inspired the iconic red-and-white spotted mushrooms in popular culture.
In more recent times, scientific interest in muscimol has grown significantly. Researchers have begun to explore its potential therapeutic applications, particularly in the field of neuroscience. Studies have investigated muscimol's effects on the GABA neurotransmitter system, which plays a crucial role in regulating neuronal excitability in the central nervous system.
The objectives of current research on muscimol consumption traditions are multifaceted. One primary goal is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the historical and cultural contexts in which muscimol has been used. This includes documenting traditional preparation methods, consumption rituals, and the social and spiritual significance attributed to the experience across different cultures.
Another important research objective is to investigate the pharmacological properties of muscimol and its potential medical applications. This includes studying its effects on brain function, exploring its possible use in treating neurological disorders, and assessing its safety profile for potential therapeutic use.
Furthermore, researchers aim to examine the ecological and environmental factors that influence the production of muscimol in Amanita muscaria and related species. This includes studying the mushroom's lifecycle, habitat requirements, and the impact of climate change on its distribution and chemical composition.
Lastly, there is a growing interest in exploring the intersection of traditional knowledge and modern scientific understanding. Researchers seek to bridge the gap between ancient wisdom and contemporary medical practices, potentially uncovering new insights that could benefit both fields of study.
The earliest documented use of muscimol-containing mushrooms can be traced to Siberian shamanic traditions, where they were used in religious ceremonies and for divination purposes. These practices spread to other parts of Northern Europe and Asia, influencing local customs and beliefs. In North America, indigenous cultures also incorporated muscimol-containing mushrooms into their spiritual practices, although the extent and duration of use varied among different tribes.
Throughout history, the consumption of muscimol has been associated with altered states of consciousness, visions, and spiritual experiences. This has led to its integration into various mythologies and folklore, such as the theory that Amanita muscaria may have inspired the iconic red-and-white spotted mushrooms in popular culture.
In more recent times, scientific interest in muscimol has grown significantly. Researchers have begun to explore its potential therapeutic applications, particularly in the field of neuroscience. Studies have investigated muscimol's effects on the GABA neurotransmitter system, which plays a crucial role in regulating neuronal excitability in the central nervous system.
The objectives of current research on muscimol consumption traditions are multifaceted. One primary goal is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the historical and cultural contexts in which muscimol has been used. This includes documenting traditional preparation methods, consumption rituals, and the social and spiritual significance attributed to the experience across different cultures.
Another important research objective is to investigate the pharmacological properties of muscimol and its potential medical applications. This includes studying its effects on brain function, exploring its possible use in treating neurological disorders, and assessing its safety profile for potential therapeutic use.
Furthermore, researchers aim to examine the ecological and environmental factors that influence the production of muscimol in Amanita muscaria and related species. This includes studying the mushroom's lifecycle, habitat requirements, and the impact of climate change on its distribution and chemical composition.
Lastly, there is a growing interest in exploring the intersection of traditional knowledge and modern scientific understanding. Researchers seek to bridge the gap between ancient wisdom and contemporary medical practices, potentially uncovering new insights that could benefit both fields of study.
Cultural Significance and Demand Analysis
The cultural significance of muscimol consumption has deep roots in various indigenous traditions, particularly among certain Siberian and North American tribes. This psychoactive compound, found primarily in Amanita muscaria mushrooms, has played a central role in shamanic practices, spiritual rituals, and traditional medicine for centuries. The demand for muscimol-related cultural experiences and products has seen a resurgence in recent years, driven by a growing interest in ethnobotany, alternative healing practices, and the exploration of consciousness.
In traditional Siberian cultures, the use of Amanita muscaria has been closely tied to spiritual and medicinal practices. Shamans have long utilized the mushroom's psychoactive properties to induce altered states of consciousness, facilitating communication with the spirit world and gaining insights into healing and divination. This cultural heritage has attracted increasing attention from researchers, anthropologists, and spiritual seekers, contributing to a rising demand for authentic experiences and knowledge related to muscimol consumption.
The market for muscimol-related products and services has expanded beyond traditional cultural boundaries. There is a growing interest in the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol, particularly in the fields of mental health and neurology. This has led to an increase in research initiatives and clinical trials exploring the compound's effects on conditions such as anxiety, depression, and neurodegenerative disorders. The pharmaceutical industry has shown interest in developing muscimol-based medications, potentially opening up new market opportunities.
The wellness and alternative medicine sectors have also contributed to the rising demand for muscimol-related products. As consumers increasingly seek natural and holistic approaches to health and well-being, there has been a surge in interest in traditional plant medicines and their potential benefits. This trend has created a niche market for muscimol-containing supplements, tinctures, and other preparations, often marketed as natural remedies for stress relief, cognitive enhancement, and spiritual growth.
However, the cultural and market demand for muscimol-related products and experiences is not without challenges. Regulatory issues surrounding the legality and safety of Amanita muscaria and its derivatives vary widely across different jurisdictions, impacting the accessibility and marketability of related products. Additionally, there are concerns about the potential for misuse and the importance of preserving the cultural integrity of traditional practices involving muscimol consumption.
As the interest in muscimol continues to grow, there is an increasing need for education and responsible use guidelines. This has created opportunities for workshops, retreats, and educational programs focused on the cultural significance, safe use, and potential benefits of muscimol-containing substances. These initiatives aim to bridge the gap between traditional knowledge and modern applications, catering to a diverse audience of spiritual seekers, health enthusiasts, and curious individuals.
In traditional Siberian cultures, the use of Amanita muscaria has been closely tied to spiritual and medicinal practices. Shamans have long utilized the mushroom's psychoactive properties to induce altered states of consciousness, facilitating communication with the spirit world and gaining insights into healing and divination. This cultural heritage has attracted increasing attention from researchers, anthropologists, and spiritual seekers, contributing to a rising demand for authentic experiences and knowledge related to muscimol consumption.
The market for muscimol-related products and services has expanded beyond traditional cultural boundaries. There is a growing interest in the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol, particularly in the fields of mental health and neurology. This has led to an increase in research initiatives and clinical trials exploring the compound's effects on conditions such as anxiety, depression, and neurodegenerative disorders. The pharmaceutical industry has shown interest in developing muscimol-based medications, potentially opening up new market opportunities.
The wellness and alternative medicine sectors have also contributed to the rising demand for muscimol-related products. As consumers increasingly seek natural and holistic approaches to health and well-being, there has been a surge in interest in traditional plant medicines and their potential benefits. This trend has created a niche market for muscimol-containing supplements, tinctures, and other preparations, often marketed as natural remedies for stress relief, cognitive enhancement, and spiritual growth.
However, the cultural and market demand for muscimol-related products and experiences is not without challenges. Regulatory issues surrounding the legality and safety of Amanita muscaria and its derivatives vary widely across different jurisdictions, impacting the accessibility and marketability of related products. Additionally, there are concerns about the potential for misuse and the importance of preserving the cultural integrity of traditional practices involving muscimol consumption.
As the interest in muscimol continues to grow, there is an increasing need for education and responsible use guidelines. This has created opportunities for workshops, retreats, and educational programs focused on the cultural significance, safe use, and potential benefits of muscimol-containing substances. These initiatives aim to bridge the gap between traditional knowledge and modern applications, catering to a diverse audience of spiritual seekers, health enthusiasts, and curious individuals.
Current State and Challenges in Muscimol Research
The current state of muscimol research is characterized by a growing interest in its cultural and traditional uses, particularly in indigenous communities. Muscimol, the primary psychoactive compound found in Amanita muscaria mushrooms, has been utilized in various cultural practices for centuries. However, scientific understanding of its effects and potential applications remains limited.
Recent studies have focused on the ethnobotanical aspects of muscimol consumption, documenting traditional preparation methods and ritualistic uses across different cultures. Researchers have identified several indigenous groups in Siberia, North America, and parts of Europe that have historically incorporated Amanita muscaria into their spiritual and medicinal practices.
One of the main challenges in muscimol research is the legal status of the compound and its source mushrooms. In many countries, Amanita muscaria is classified as a controlled substance, limiting access for scientific study. This legal ambiguity has hindered comprehensive clinical trials and large-scale research efforts.
Another significant challenge is the standardization of muscimol extraction and dosage. Traditional preparation methods vary widely, making it difficult to establish consistent protocols for scientific investigation. Researchers are working to develop reliable extraction techniques and quantification methods to ensure reproducibility in studies.
The pharmacological effects of muscimol on the human brain are still not fully understood. While it is known to act as a potent GABA agonist, its complex interactions with other neurotransmitter systems require further exploration. This gap in knowledge presents both a challenge and an opportunity for neuroscientists and pharmacologists.
Safety concerns surrounding muscimol consumption pose another hurdle for researchers. The potential for adverse reactions, particularly when combined with other substances or in individuals with pre-existing health conditions, necessitates careful consideration in study designs and ethical approvals.
Interdisciplinary collaboration has emerged as a crucial aspect of advancing muscimol research. Anthropologists, chemists, neuroscientists, and medical professionals are increasingly working together to bridge the gap between traditional knowledge and modern scientific inquiry.
The development of synthetic analogues of muscimol has opened new avenues for research. These compounds allow for more controlled studies of muscimol's effects without the variability associated with natural sources. However, questions remain about how closely these analogues mimic the full spectrum of effects observed in traditional use.
As interest in psychedelic-assisted therapies grows, there is increasing curiosity about muscimol's potential therapeutic applications. Preliminary studies suggest possible benefits in treating anxiety, depression, and addiction, but rigorous clinical trials are still lacking.
Recent studies have focused on the ethnobotanical aspects of muscimol consumption, documenting traditional preparation methods and ritualistic uses across different cultures. Researchers have identified several indigenous groups in Siberia, North America, and parts of Europe that have historically incorporated Amanita muscaria into their spiritual and medicinal practices.
One of the main challenges in muscimol research is the legal status of the compound and its source mushrooms. In many countries, Amanita muscaria is classified as a controlled substance, limiting access for scientific study. This legal ambiguity has hindered comprehensive clinical trials and large-scale research efforts.
Another significant challenge is the standardization of muscimol extraction and dosage. Traditional preparation methods vary widely, making it difficult to establish consistent protocols for scientific investigation. Researchers are working to develop reliable extraction techniques and quantification methods to ensure reproducibility in studies.
The pharmacological effects of muscimol on the human brain are still not fully understood. While it is known to act as a potent GABA agonist, its complex interactions with other neurotransmitter systems require further exploration. This gap in knowledge presents both a challenge and an opportunity for neuroscientists and pharmacologists.
Safety concerns surrounding muscimol consumption pose another hurdle for researchers. The potential for adverse reactions, particularly when combined with other substances or in individuals with pre-existing health conditions, necessitates careful consideration in study designs and ethical approvals.
Interdisciplinary collaboration has emerged as a crucial aspect of advancing muscimol research. Anthropologists, chemists, neuroscientists, and medical professionals are increasingly working together to bridge the gap between traditional knowledge and modern scientific inquiry.
The development of synthetic analogues of muscimol has opened new avenues for research. These compounds allow for more controlled studies of muscimol's effects without the variability associated with natural sources. However, questions remain about how closely these analogues mimic the full spectrum of effects observed in traditional use.
As interest in psychedelic-assisted therapies grows, there is increasing curiosity about muscimol's potential therapeutic applications. Preliminary studies suggest possible benefits in treating anxiety, depression, and addiction, but rigorous clinical trials are still lacking.
Existing Methodologies for Studying Muscimol Traditions
01 Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol
Muscimol is used in various pharmaceutical compositions for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. These formulations may include controlled release preparations, combinations with other active ingredients, or novel delivery methods to enhance efficacy and reduce side effects.- Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol: Muscimol is used in various pharmaceutical compositions for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. These formulations may include specific dosage forms, delivery methods, and combinations with other active ingredients to enhance therapeutic effects or reduce side effects.
- Muscimol derivatives and analogs: Research focuses on developing muscimol derivatives and analogs with improved pharmacological properties. These modified compounds may have enhanced bioavailability, selectivity, or reduced side effects compared to the parent compound.
- Use of muscimol in neurodegenerative disease treatment: Muscimol and related compounds are investigated for their potential in treating neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's disease. The research explores their neuroprotective properties and ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems.
- Muscimol in anxiety and mood disorder treatments: Studies investigate the use of muscimol and its derivatives in treating anxiety disorders, depression, and other mood-related conditions. The research focuses on their GABA-ergic properties and potential for modulating neural circuits involved in emotional regulation.
- Novel delivery systems for muscimol: Development of innovative delivery systems for muscimol to improve its therapeutic efficacy and reduce side effects. These may include nanoparticle formulations, transdermal patches, or targeted delivery methods to enhance brain penetration and control release kinetics.
02 Muscimol derivatives and analogs
Research focuses on developing muscimol derivatives and analogs with improved pharmacological properties. These modified compounds aim to enhance therapeutic effects, reduce side effects, or improve bioavailability compared to the parent compound.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of muscimol in neurostimulation therapies
Muscimol is explored in combination with neurostimulation techniques for treating various neurological conditions. This approach may involve direct application of muscimol to specific brain regions or its use in conjunction with electrical or magnetic stimulation methods.Expand Specific Solutions04 Muscimol in addiction treatment
Muscimol and its derivatives are investigated for their potential in treating addiction disorders. Research focuses on their ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems involved in addiction pathways, potentially offering new therapeutic strategies for substance abuse disorders.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery systems for muscimol
Innovative delivery systems are being developed to improve the administration and efficacy of muscimol. These may include nanoparticle formulations, transdermal patches, or other advanced drug delivery technologies designed to enhance bioavailability and target specific areas of the body or brain.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Researchers and Institutions in Ethnobotany
The research on cultural traditions centered on muscimol consumption is in an emerging stage, with a growing market driven by increasing interest in traditional practices and potential therapeutic applications. The global market for muscimol-related products is still relatively small but shows promising growth potential. Technologically, the field is in its early stages of development, with companies like Psyched Wellness Ltd. and MycoTechnology, Inc. leading the way in exploring muscimol's properties and applications. Established pharmaceutical companies such as ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. are also showing interest, potentially accelerating research and development in this area. The involvement of academic institutions like the Max Planck Society and the University of Leicester suggests a growing scientific focus on muscimol, which could lead to significant advancements in understanding its cultural and medicinal roles.
Psyched Wellness Ltd.
Technical Solution: Psyched Wellness Ltd. is pioneering research on muscimol, the psychoactive compound found in Amanita muscaria mushrooms. Their approach involves developing a proprietary extraction and purification process to create standardized muscimol extracts[1]. The company is focusing on the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol, particularly in areas such as stress reduction, promoting restful sleep, and supporting cognitive function[2]. They are conducting preclinical studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy of muscimol-based products, with plans to develop nutraceuticals and potentially pharmaceutical-grade formulations[3].
Strengths: Specialized focus on muscimol research, proprietary extraction technology, potential for novel therapeutic applications. Weaknesses: Early stage of research, regulatory challenges for psychoactive compounds, limited clinical data on muscimol's long-term effects.
Max Planck Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Wissenschaften eV
Technical Solution: The Max Planck Society, while not a commercial entity, is at the forefront of basic research that includes studies on psychoactive compounds like muscimol. Their neuroscience institutes are investigating the molecular mechanisms of GABA receptor activation, which is directly relevant to muscimol's effects[6]. Researchers are using advanced imaging techniques and electrophysiology to understand how compounds like muscimol modulate neural circuits[7]. This fundamental research is crucial for understanding the potential therapeutic applications and cultural significance of muscimol-containing plants.
Strengths: World-class research facilities, multidisciplinary approach, potential for groundbreaking discoveries. Weaknesses: Focus on basic research rather than product development, longer timeline for practical applications.
Core Ethnographic Studies on Muscimol Consumption
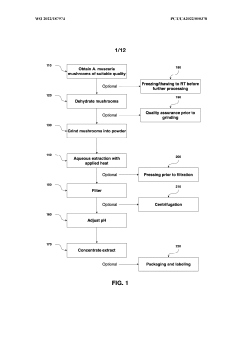
Processes for Extracting Muscimol from Amanita Muscaria
PatentPendingUS20240165180A1
Innovation
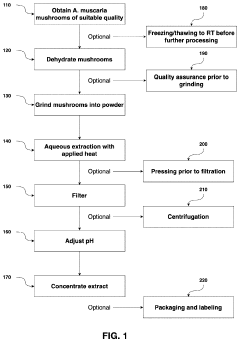
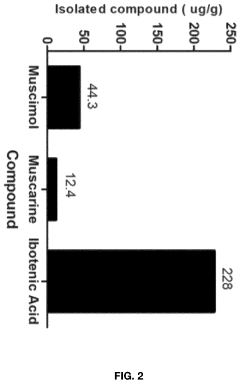
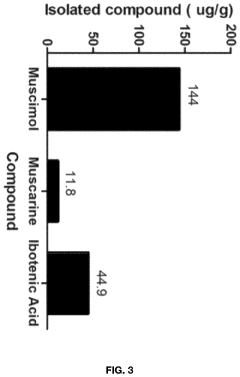
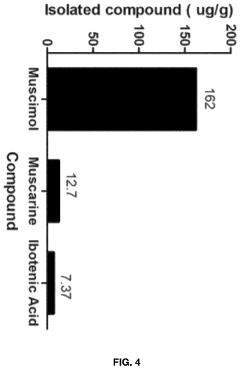
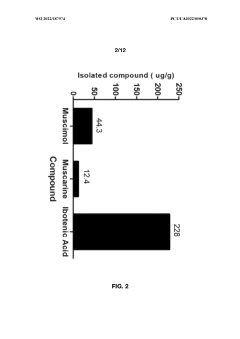
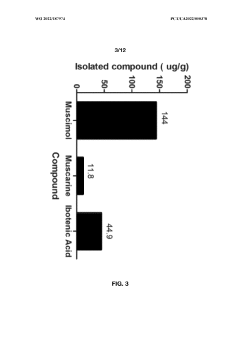
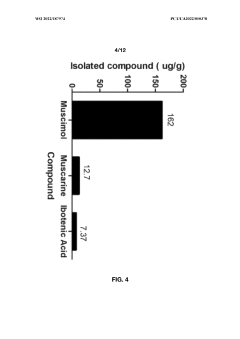
- Aqueous extraction of Amanita muscaria biomass is performed with heat, followed by pH reduction between 2.0 to 4.0 and concentration through distillation or refluxing, which decreases ibotenic acid content and increases muscimol content, resulting in a muscimol-rich extract with enhanced purity.
Processes for extracting muscimol from amanita muscaria
PatentWO2022187974A1
Innovation
- Aqueous extraction methods involving heat, pH reduction, and concentration techniques such as distillation and refluxing are employed to decrease ibotenic acid content and increase muscimol content in the extract, including steps like grinding the mushroom biomass, filtering, and acidification to facilitate decarboxylation of ibotenic acid to muscimol.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The legal and ethical considerations surrounding muscimol consumption are complex and multifaceted, requiring careful examination from various perspectives. Historically, the use of muscimol-containing substances has been deeply rooted in cultural and religious practices of certain indigenous communities. However, modern legal frameworks often classify these substances as controlled or prohibited, creating a tension between traditional practices and contemporary regulations.
From a legal standpoint, the status of muscimol varies significantly across jurisdictions. In many countries, muscimol and its source, Amanita muscaria mushrooms, are classified as controlled substances due to their psychoactive properties. This classification poses challenges for research, as obtaining permits and adhering to strict protocols becomes necessary for scientific investigations. Researchers must navigate a complex regulatory landscape to conduct studies on muscimol consumption traditions.
Ethically, the study of muscimol-related cultural practices raises important questions about cultural preservation, indigenous rights, and the balance between scientific inquiry and respect for traditional knowledge. Researchers must consider the potential impact of their work on communities that have long-standing relationships with these substances. Obtaining informed consent and ensuring community involvement in research design and implementation are crucial ethical considerations.
The principle of cultural relativism also comes into play when examining muscimol consumption traditions. What may be considered a sacred or medicinal practice in one culture could be viewed as substance abuse in another. This dichotomy necessitates a nuanced approach that acknowledges diverse cultural perspectives while also addressing potential health and safety concerns.
Furthermore, the commercialization and potential exploitation of traditional knowledge related to muscimol use present additional ethical challenges. Researchers and policymakers must grapple with questions of intellectual property rights, benefit-sharing, and the protection of indigenous cultural heritage. Ensuring that research outcomes do not lead to the appropriation or misuse of traditional practices is paramount.
As research in this field progresses, it is essential to develop ethical guidelines that respect cultural traditions while adhering to scientific standards and legal requirements. Collaborative approaches involving researchers, indigenous communities, legal experts, and policymakers can help strike a balance between scientific inquiry and cultural sensitivity. Such collaborations can also contribute to the development of more nuanced legal frameworks that accommodate traditional practices within appropriate safeguards.
From a legal standpoint, the status of muscimol varies significantly across jurisdictions. In many countries, muscimol and its source, Amanita muscaria mushrooms, are classified as controlled substances due to their psychoactive properties. This classification poses challenges for research, as obtaining permits and adhering to strict protocols becomes necessary for scientific investigations. Researchers must navigate a complex regulatory landscape to conduct studies on muscimol consumption traditions.
Ethically, the study of muscimol-related cultural practices raises important questions about cultural preservation, indigenous rights, and the balance between scientific inquiry and respect for traditional knowledge. Researchers must consider the potential impact of their work on communities that have long-standing relationships with these substances. Obtaining informed consent and ensuring community involvement in research design and implementation are crucial ethical considerations.
The principle of cultural relativism also comes into play when examining muscimol consumption traditions. What may be considered a sacred or medicinal practice in one culture could be viewed as substance abuse in another. This dichotomy necessitates a nuanced approach that acknowledges diverse cultural perspectives while also addressing potential health and safety concerns.
Furthermore, the commercialization and potential exploitation of traditional knowledge related to muscimol use present additional ethical challenges. Researchers and policymakers must grapple with questions of intellectual property rights, benefit-sharing, and the protection of indigenous cultural heritage. Ensuring that research outcomes do not lead to the appropriation or misuse of traditional practices is paramount.
As research in this field progresses, it is essential to develop ethical guidelines that respect cultural traditions while adhering to scientific standards and legal requirements. Collaborative approaches involving researchers, indigenous communities, legal experts, and policymakers can help strike a balance between scientific inquiry and cultural sensitivity. Such collaborations can also contribute to the development of more nuanced legal frameworks that accommodate traditional practices within appropriate safeguards.
Cross-Cultural Comparative Analysis
The cross-cultural comparative analysis of muscimol consumption traditions reveals fascinating insights into the diverse cultural practices and beliefs surrounding this psychoactive compound. Across various societies, muscimol, primarily derived from Amanita muscaria mushrooms, has played significant roles in religious, medicinal, and social contexts.
In Siberian shamanic traditions, particularly among the Koryak people, muscimol consumption has been a central element of spiritual practices for centuries. Shamans utilize the mushroom's psychoactive properties to induce altered states of consciousness, facilitating communication with the spirit world and divination. The ritualistic use of muscimol in these cultures is deeply intertwined with their cosmology and understanding of the natural world.
Contrastingly, in some Nordic and Baltic cultures, muscimol consumption has been associated with berserker warriors. Historical accounts suggest that these fierce fighters may have consumed Amanita muscaria to induce a trance-like state of fearlessness and heightened strength before battle. This usage highlights the diverse applications of muscimol across different cultural contexts.
In Central American cultures, particularly among certain indigenous groups, muscimol-containing mushrooms have been used in healing rituals and as a means of accessing divine wisdom. The consumption is often accompanied by elaborate ceremonies and guided by experienced shamans or healers, emphasizing the sacred nature of the practice.
Interestingly, the cultural attitudes towards muscimol consumption vary significantly. While some societies revere it as a sacred substance, others view it with caution or outright prohibition. This disparity in perception is often rooted in historical, religious, and social factors unique to each culture.
The methods of preparation and consumption also differ across cultures. Some traditions involve drying and smoking the mushrooms, while others prepare them as teas or incorporate them into food. These variations in preparation techniques can affect the potency and effects of muscimol, contributing to the diverse experiences reported across cultures.
It is noteworthy that the legal status and social acceptance of muscimol consumption vary widely across different regions. While some cultures have preserved their traditional practices, others have seen a decline due to legal restrictions or changing social norms. This dynamic interplay between tradition and modern legislation presents an interesting area for further anthropological and legal research.
In Siberian shamanic traditions, particularly among the Koryak people, muscimol consumption has been a central element of spiritual practices for centuries. Shamans utilize the mushroom's psychoactive properties to induce altered states of consciousness, facilitating communication with the spirit world and divination. The ritualistic use of muscimol in these cultures is deeply intertwined with their cosmology and understanding of the natural world.
Contrastingly, in some Nordic and Baltic cultures, muscimol consumption has been associated with berserker warriors. Historical accounts suggest that these fierce fighters may have consumed Amanita muscaria to induce a trance-like state of fearlessness and heightened strength before battle. This usage highlights the diverse applications of muscimol across different cultural contexts.
In Central American cultures, particularly among certain indigenous groups, muscimol-containing mushrooms have been used in healing rituals and as a means of accessing divine wisdom. The consumption is often accompanied by elaborate ceremonies and guided by experienced shamans or healers, emphasizing the sacred nature of the practice.
Interestingly, the cultural attitudes towards muscimol consumption vary significantly. While some societies revere it as a sacred substance, others view it with caution or outright prohibition. This disparity in perception is often rooted in historical, religious, and social factors unique to each culture.
The methods of preparation and consumption also differ across cultures. Some traditions involve drying and smoking the mushrooms, while others prepare them as teas or incorporate them into food. These variations in preparation techniques can affect the potency and effects of muscimol, contributing to the diverse experiences reported across cultures.
It is noteworthy that the legal status and social acceptance of muscimol consumption vary widely across different regions. While some cultures have preserved their traditional practices, others have seen a decline due to legal restrictions or changing social norms. This dynamic interplay between tradition and modern legislation presents an interesting area for further anthropological and legal research.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!