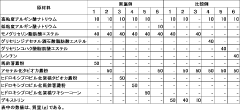
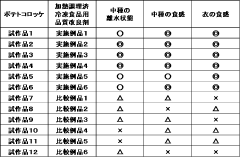
How Glycerol Enhances Quality of Freeze-Dried Foods
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Glycerol in Freeze-Drying: Background and Objectives
Freeze-drying, also known as lyophilization, is a sophisticated preservation technique that has revolutionized the food industry. This process involves removing water from food products through sublimation, resulting in lightweight, shelf-stable items that retain much of their original flavor, texture, and nutritional value. The use of glycerol in freeze-drying has emerged as a significant area of interest due to its potential to enhance the quality of freeze-dried foods.
The history of freeze-drying dates back to the 15th century, with the Inca civilization using primitive freeze-drying techniques to preserve potatoes. However, modern freeze-drying technology was developed during World War II for preserving blood plasma and penicillin. Since then, the technique has been refined and applied to various industries, including food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards improving the quality of freeze-dried products, particularly in terms of texture, rehydration properties, and overall sensory attributes. This is where glycerol, a simple polyol compound, has gained attention. Glycerol, also known as glycerin, is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid widely used in the food industry as a humectant, sweetener, and solvent.
The primary objective of incorporating glycerol in freeze-drying processes is to enhance the quality of the final product. Glycerol acts as a cryoprotectant, helping to maintain the structural integrity of food products during the freeze-drying process. It also influences the glass transition temperature of the food matrix, which is crucial for preserving the product's stability during storage.
Furthermore, glycerol's hygroscopic nature can potentially improve the rehydration properties of freeze-dried foods, addressing one of the main challenges in this preservation method. By enhancing water retention and distribution within the food matrix, glycerol may contribute to a more desirable texture and mouthfeel upon reconstitution.
The technological evolution in this field is driven by the growing demand for high-quality, convenient, and nutritious food products with extended shelf life. As consumers become more health-conscious and seek natural ingredients, the use of glycerol, a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) substance, aligns well with these market trends.
Understanding the mechanisms by which glycerol enhances the quality of freeze-dried foods is crucial for optimizing processing parameters and developing innovative formulations. This research area intersects food science, physical chemistry, and materials science, requiring a multidisciplinary approach to fully elucidate the complex interactions between glycerol, food components, and the freeze-drying process.
The history of freeze-drying dates back to the 15th century, with the Inca civilization using primitive freeze-drying techniques to preserve potatoes. However, modern freeze-drying technology was developed during World War II for preserving blood plasma and penicillin. Since then, the technique has been refined and applied to various industries, including food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards improving the quality of freeze-dried products, particularly in terms of texture, rehydration properties, and overall sensory attributes. This is where glycerol, a simple polyol compound, has gained attention. Glycerol, also known as glycerin, is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid widely used in the food industry as a humectant, sweetener, and solvent.
The primary objective of incorporating glycerol in freeze-drying processes is to enhance the quality of the final product. Glycerol acts as a cryoprotectant, helping to maintain the structural integrity of food products during the freeze-drying process. It also influences the glass transition temperature of the food matrix, which is crucial for preserving the product's stability during storage.
Furthermore, glycerol's hygroscopic nature can potentially improve the rehydration properties of freeze-dried foods, addressing one of the main challenges in this preservation method. By enhancing water retention and distribution within the food matrix, glycerol may contribute to a more desirable texture and mouthfeel upon reconstitution.
The technological evolution in this field is driven by the growing demand for high-quality, convenient, and nutritious food products with extended shelf life. As consumers become more health-conscious and seek natural ingredients, the use of glycerol, a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) substance, aligns well with these market trends.
Understanding the mechanisms by which glycerol enhances the quality of freeze-dried foods is crucial for optimizing processing parameters and developing innovative formulations. This research area intersects food science, physical chemistry, and materials science, requiring a multidisciplinary approach to fully elucidate the complex interactions between glycerol, food components, and the freeze-drying process.
Market Analysis for Enhanced Freeze-Dried Products
The market for enhanced freeze-dried products has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for convenient, long-lasting, and nutritious food options. The incorporation of glycerol in freeze-dried foods has opened up new opportunities for product innovation and market expansion.
The global freeze-dried food market is experiencing robust growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising popularity of convenience foods, increasing awareness of food preservation techniques, and the growing demand for lightweight, shelf-stable products in various sectors, including outdoor recreation, emergency preparedness, and military applications.
The use of glycerol as a quality enhancer in freeze-dried foods has created a niche market segment within the broader freeze-dried food industry. This segment is expected to grow at an even faster rate than the overall market, as consumers become more aware of the benefits of glycerol-enhanced products, such as improved texture, flavor retention, and extended shelf life.
Key market drivers for glycerol-enhanced freeze-dried products include the growing health-conscious consumer base, increasing disposable incomes in developing countries, and the expanding application of freeze-dried foods in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, as consumers have shown increased interest in long-lasting, nutritious food options for home storage and emergency preparedness.
The market for glycerol-enhanced freeze-dried products is segmented by product type, distribution channel, and geography. Product types include fruits, vegetables, meats, dairy products, and ready-to-eat meals. Among these, fruits and vegetables hold the largest market share due to their widespread use in snacks, breakfast cereals, and instant soups.
Distribution channels for these products include supermarkets/hypermarkets, specialty stores, online retail, and others. Online retail has emerged as the fastest-growing distribution channel, driven by the increasing popularity of e-commerce and the convenience it offers to consumers.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for glycerol-enhanced freeze-dried products, owing to high consumer awareness, advanced food processing technologies, and well-established distribution networks. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, fueled by changing dietary habits, increasing urbanization, and rising disposable incomes in countries like China and India.
The global freeze-dried food market is experiencing robust growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising popularity of convenience foods, increasing awareness of food preservation techniques, and the growing demand for lightweight, shelf-stable products in various sectors, including outdoor recreation, emergency preparedness, and military applications.
The use of glycerol as a quality enhancer in freeze-dried foods has created a niche market segment within the broader freeze-dried food industry. This segment is expected to grow at an even faster rate than the overall market, as consumers become more aware of the benefits of glycerol-enhanced products, such as improved texture, flavor retention, and extended shelf life.
Key market drivers for glycerol-enhanced freeze-dried products include the growing health-conscious consumer base, increasing disposable incomes in developing countries, and the expanding application of freeze-dried foods in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, as consumers have shown increased interest in long-lasting, nutritious food options for home storage and emergency preparedness.
The market for glycerol-enhanced freeze-dried products is segmented by product type, distribution channel, and geography. Product types include fruits, vegetables, meats, dairy products, and ready-to-eat meals. Among these, fruits and vegetables hold the largest market share due to their widespread use in snacks, breakfast cereals, and instant soups.
Distribution channels for these products include supermarkets/hypermarkets, specialty stores, online retail, and others. Online retail has emerged as the fastest-growing distribution channel, driven by the increasing popularity of e-commerce and the convenience it offers to consumers.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for glycerol-enhanced freeze-dried products, owing to high consumer awareness, advanced food processing technologies, and well-established distribution networks. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, fueled by changing dietary habits, increasing urbanization, and rising disposable incomes in countries like China and India.
Current Challenges in Freeze-Drying Technology
Freeze-drying technology, while widely used in food preservation, still faces several significant challenges that impact product quality and process efficiency. One of the primary issues is the long processing time required, which can lead to increased production costs and reduced throughput. The extended exposure to low temperatures and vacuum conditions can also result in structural damage to food products, affecting their texture and rehydration properties.
Another major challenge is the energy-intensive nature of the freeze-drying process. The need for maintaining low temperatures and high vacuum conditions contributes to substantial energy consumption, raising concerns about sustainability and operational costs. This energy demand also presents difficulties in scaling up production to meet increasing market demands while maintaining economic viability.
Product quality inconsistencies remain a persistent issue in freeze-drying technology. Variations in moisture content across the product batch can lead to differences in shelf life and organoleptic properties. Additionally, the loss of volatile compounds during the drying process can result in diminished flavor and aroma profiles, potentially reducing consumer acceptance of freeze-dried foods.
The collapse of food structure during freeze-drying is another critical challenge. This phenomenon occurs when the product temperature exceeds its collapse temperature, leading to a loss of porous structure and reduced rehydration capacity. Preventing collapse while optimizing drying rates requires precise control of process parameters, which can be technically demanding and may limit the range of products suitable for freeze-drying.
Microbial safety concerns also persist in freeze-dried foods. While the low moisture content generally inhibits microbial growth, certain pathogens can survive the freeze-drying process and remain viable in the final product. Ensuring complete inactivation of microorganisms without compromising product quality presents an ongoing challenge for food manufacturers.
The development of novel formulations and processing techniques to address these challenges is an active area of research. The use of cryoprotectants, such as glycerol, has shown promise in improving product quality and process efficiency. However, optimizing the incorporation of these additives while maintaining the nutritional and sensory attributes of the original food product remains a complex task requiring further investigation and technological advancements.
Another major challenge is the energy-intensive nature of the freeze-drying process. The need for maintaining low temperatures and high vacuum conditions contributes to substantial energy consumption, raising concerns about sustainability and operational costs. This energy demand also presents difficulties in scaling up production to meet increasing market demands while maintaining economic viability.
Product quality inconsistencies remain a persistent issue in freeze-drying technology. Variations in moisture content across the product batch can lead to differences in shelf life and organoleptic properties. Additionally, the loss of volatile compounds during the drying process can result in diminished flavor and aroma profiles, potentially reducing consumer acceptance of freeze-dried foods.
The collapse of food structure during freeze-drying is another critical challenge. This phenomenon occurs when the product temperature exceeds its collapse temperature, leading to a loss of porous structure and reduced rehydration capacity. Preventing collapse while optimizing drying rates requires precise control of process parameters, which can be technically demanding and may limit the range of products suitable for freeze-drying.
Microbial safety concerns also persist in freeze-dried foods. While the low moisture content generally inhibits microbial growth, certain pathogens can survive the freeze-drying process and remain viable in the final product. Ensuring complete inactivation of microorganisms without compromising product quality presents an ongoing challenge for food manufacturers.
The development of novel formulations and processing techniques to address these challenges is an active area of research. The use of cryoprotectants, such as glycerol, has shown promise in improving product quality and process efficiency. However, optimizing the incorporation of these additives while maintaining the nutritional and sensory attributes of the original food product remains a complex task requiring further investigation and technological advancements.
Glycerol-Based Solutions in Freeze-Drying
01 Purification methods for glycerol
Various purification techniques are employed to improve glycerol quality, including distillation, ion exchange, and membrane filtration. These methods help remove impurities and increase the purity of glycerol, making it suitable for use in different industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics.- Purification methods for glycerol: Various purification techniques are employed to improve glycerol quality, including distillation, ion exchange, and membrane filtration. These methods help remove impurities and increase the purity of glycerol, making it suitable for use in different industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics.
- Quality assessment and control of glycerol: Implementing quality control measures and assessment techniques is crucial for ensuring high-quality glycerol. This includes monitoring parameters such as purity, color, odor, and moisture content. Advanced analytical methods and standardized testing procedures are used to maintain consistent glycerol quality across batches.
- Glycerol production from renewable sources: Producing high-quality glycerol from renewable sources, such as biodiesel byproducts or fermentation processes, is an emerging trend. This approach focuses on developing sustainable production methods while maintaining or improving glycerol quality, addressing environmental concerns and meeting industry standards.
- Glycerol derivatives and modifications: Developing glycerol derivatives and modifications to enhance its properties and applications is an important aspect of glycerol quality improvement. This includes chemical modifications, polymerization, and the creation of glycerol-based compounds with specific characteristics tailored for various industrial uses.
- Storage and handling of high-quality glycerol: Proper storage and handling techniques are essential for maintaining glycerol quality. This involves using appropriate containers, controlling temperature and humidity, preventing contamination, and implementing best practices for transportation and long-term storage to preserve the glycerol's purity and properties.
02 Quality assessment and control of glycerol
Implementing quality control measures and assessment techniques is crucial for ensuring high-quality glycerol. This includes monitoring parameters such as purity, color, odor, and moisture content. Advanced analytical methods like gas chromatography and spectroscopy are used to detect and quantify impurities, ensuring the glycerol meets industry standards.Expand Specific Solutions03 Glycerol production from renewable sources
Producing high-quality glycerol from renewable sources, such as biodiesel byproducts or fermentation processes, is an emerging trend. These methods focus on optimizing production conditions and developing efficient purification steps to obtain glycerol with improved quality and sustainability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Glycerol quality enhancement for specific applications
Tailoring glycerol quality for specific applications involves modifying its properties or adding specific additives. This can include adjusting pH, viscosity, or incorporating stabilizers to enhance its performance in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovative technologies for glycerol quality improvement
Emerging technologies are being developed to enhance glycerol quality, including novel catalytic processes, advanced separation techniques, and biotechnological approaches. These innovations aim to produce higher purity glycerol more efficiently and cost-effectively, addressing the growing demand for high-quality glycerol in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Freeze-Drying Industry
The freeze-dried food industry is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for convenient, long-lasting food products. The market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the use of glycerol to enhance freeze-dried food quality is at a relatively mature stage, with ongoing research and development efforts. Key players like Nestlé, Cargill, and Ajinomoto are actively involved in advancing freeze-drying technologies. Smaller specialized companies such as ICS Solutions and Renewable Alternatives are also contributing to innovations in this field. Academic institutions like Jiangnan University and the University of California are conducting research to further improve freeze-drying processes and product quality.
Kao Corp.
Technical Solution: Kao Corporation has developed an innovative approach to using glycerol in freeze-dried foods, focusing on its application in personal care and beauty-oriented nutritional products. Their method involves incorporating glycerol into a proprietary emulsion system before freeze-drying, which helps to improve the stability and bioavailability of functional ingredients such as collagen and vitamins[13]. Kao's research has shown that glycerol acts as a protective agent for these sensitive compounds during the freeze-drying process, preserving their efficacy in the final product[15]. The company has also explored the use of glycerol in combination with other humectants to create freeze-dried beauty supplements with improved texture and dissolution properties[17]. Kao's technology allows for the production of freeze-dried functional foods that maintain their nutritional and cosmetic benefits while offering convenient consumption options.
Strengths: Enhanced stability and bioavailability of functional ingredients, improved texture and dissolution of beauty supplements. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in application to traditional food products, may require specific marketing strategies to target beauty-conscious consumers.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Technical Solution: Nestlé has developed a proprietary freeze-drying process that incorporates glycerol to enhance the quality of freeze-dried foods. Their method involves pre-treating food materials with a glycerol solution before freeze-drying, which helps to maintain the cellular structure and prevent collapse during the drying process[1]. This results in improved texture, flavor retention, and rehydration properties of the final product. Nestlé's research has shown that glycerol acts as a cryoprotectant, reducing ice crystal formation and protecting sensitive food components during freezing and subsequent drying[3]. The company has also optimized the glycerol concentration and freeze-drying parameters to achieve the best balance between product quality and process efficiency[5].
Strengths: Improved product quality, better texture and flavor retention, enhanced rehydration properties. Weaknesses: Potential increase in production costs, need for careful control of glycerol levels to avoid excessive sweetness or texture changes.
Glycerol's Mechanism in Quality Enhancement
Method for preparing heterogenetic corneal material
PatentActiveUS20160251617A1
Innovation
- A method involving the preparation of heterogenetic corneal materials using a sequence of steps including eyeball washing, sterilization, cell inactivation, virus inactivation, crosslinking with glycerol and crosslinking agents like EDC and NHS, and gentle crosslinking to maintain the three-dimensional collagen structure, reducing immunogenicity and degradation, and preserving transparency.
Quality improver for cooked frozen food, cooked frozen food and method for producing the frozen food
PatentActiveJP2016182077A
Innovation
- A quality improver comprising sodium alginate, monoglycerin fatty acid ester, and starch is kneaded into the food material, which is then cooked and frozen, to maintain texture during natural thawing.
Food Safety Regulations for Freeze-Dried Products
Food safety regulations for freeze-dried products are crucial to ensure consumer health and maintain product quality. These regulations encompass various aspects of production, packaging, storage, and distribution. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the safety of freeze-dried foods, while in Europe, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) sets the standards.
One of the primary concerns in freeze-dried food safety is the prevention of microbial growth. Although the freeze-drying process significantly reduces water activity, which inhibits bacterial growth, proper handling and storage are still essential. Regulations typically require manufacturers to implement Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) systems to identify and control potential food safety hazards throughout the production process.
Packaging regulations for freeze-dried foods are designed to maintain product integrity and prevent contamination. Manufacturers must use materials that are food-grade and provide an adequate barrier against moisture and oxygen. Vacuum-sealed packaging is often required to extend shelf life and preserve nutritional quality. Labeling regulations mandate clear information on ingredients, allergens, nutritional content, and storage instructions.
Temperature control during storage and transportation is another critical aspect of freeze-dried food safety regulations. While these products are generally stable at room temperature, extreme heat or humidity can compromise their quality and safety. Regulations often specify temperature ranges for storage and distribution to maintain product integrity.
Hygiene standards in production facilities are strictly regulated to prevent contamination. This includes requirements for regular cleaning and sanitization of equipment, proper employee hygiene practices, and pest control measures. Many regulations also mandate the use of food-grade materials in all equipment that comes into contact with the product.
Quality control measures are an integral part of freeze-dried food safety regulations. Manufacturers are required to conduct regular testing for microbial contamination, moisture content, and other quality parameters. Batch testing and record-keeping are often mandatory to ensure traceability in case of safety issues.
Regulations also address the use of additives in freeze-dried foods. While glycerol is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA, its use must comply with specific guidelines. Manufacturers must ensure that any additives used, including glycerol, do not compromise food safety or quality.
International trade of freeze-dried foods is subject to additional regulations. Products must meet the safety standards of both the exporting and importing countries. This often involves obtaining certifications and undergoing inspections to ensure compliance with international food safety standards.
One of the primary concerns in freeze-dried food safety is the prevention of microbial growth. Although the freeze-drying process significantly reduces water activity, which inhibits bacterial growth, proper handling and storage are still essential. Regulations typically require manufacturers to implement Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) systems to identify and control potential food safety hazards throughout the production process.
Packaging regulations for freeze-dried foods are designed to maintain product integrity and prevent contamination. Manufacturers must use materials that are food-grade and provide an adequate barrier against moisture and oxygen. Vacuum-sealed packaging is often required to extend shelf life and preserve nutritional quality. Labeling regulations mandate clear information on ingredients, allergens, nutritional content, and storage instructions.
Temperature control during storage and transportation is another critical aspect of freeze-dried food safety regulations. While these products are generally stable at room temperature, extreme heat or humidity can compromise their quality and safety. Regulations often specify temperature ranges for storage and distribution to maintain product integrity.
Hygiene standards in production facilities are strictly regulated to prevent contamination. This includes requirements for regular cleaning and sanitization of equipment, proper employee hygiene practices, and pest control measures. Many regulations also mandate the use of food-grade materials in all equipment that comes into contact with the product.
Quality control measures are an integral part of freeze-dried food safety regulations. Manufacturers are required to conduct regular testing for microbial contamination, moisture content, and other quality parameters. Batch testing and record-keeping are often mandatory to ensure traceability in case of safety issues.
Regulations also address the use of additives in freeze-dried foods. While glycerol is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA, its use must comply with specific guidelines. Manufacturers must ensure that any additives used, including glycerol, do not compromise food safety or quality.
International trade of freeze-dried foods is subject to additional regulations. Products must meet the safety standards of both the exporting and importing countries. This often involves obtaining certifications and undergoing inspections to ensure compliance with international food safety standards.
Sustainability in Freeze-Drying Processes
Sustainability in freeze-drying processes has become a critical focus in the food industry, particularly in relation to the use of glycerol as a quality enhancer. As the demand for freeze-dried foods continues to grow, it is essential to address the environmental impact of these processes and explore sustainable alternatives.
The freeze-drying industry has traditionally been energy-intensive, consuming significant amounts of electricity and water. However, recent advancements in technology and process optimization have led to more sustainable practices. The incorporation of glycerol in freeze-drying processes not only improves product quality but also contributes to sustainability efforts.
One of the primary sustainability benefits of using glycerol in freeze-drying is the reduction in energy consumption. Glycerol acts as a cryoprotectant, lowering the freezing point of water in food products. This allows for more efficient freeze-drying at higher temperatures, reducing the energy required for the process. Studies have shown that glycerol-enhanced freeze-drying can reduce energy consumption by up to 20% compared to traditional methods.
Water conservation is another crucial aspect of sustainability in freeze-drying processes. Glycerol's hygroscopic properties help retain moisture in the final product, reducing the amount of water that needs to be removed during the drying process. This not only improves the texture and rehydration properties of freeze-dried foods but also decreases the overall water usage in the production cycle.
The use of glycerol also extends the shelf life of freeze-dried products, contributing to sustainability by reducing food waste. Improved stability and moisture retention in glycerol-enhanced freeze-dried foods mean that these products can be stored for longer periods without compromising quality. This extended shelf life reduces the likelihood of spoilage and waste throughout the supply chain.
Furthermore, glycerol itself is a sustainable ingredient, often derived from renewable sources such as vegetable oils or as a byproduct of biodiesel production. The integration of this eco-friendly compound into freeze-drying processes aligns with the growing demand for sustainable food production methods.
Innovations in freeze-drying equipment have also contributed to improved sustainability. Modern freeze-dryers are designed with energy-efficient components, such as improved insulation and heat recovery systems. When combined with glycerol-enhanced processes, these technological advancements significantly reduce the carbon footprint of freeze-dried food production.
As the food industry continues to prioritize sustainability, the role of glycerol in enhancing both quality and eco-friendliness of freeze-dried foods is likely to expand. Future research may focus on optimizing glycerol concentrations and exploring synergistic effects with other natural cryoprotectants to further improve the sustainability of freeze-drying processes.
The freeze-drying industry has traditionally been energy-intensive, consuming significant amounts of electricity and water. However, recent advancements in technology and process optimization have led to more sustainable practices. The incorporation of glycerol in freeze-drying processes not only improves product quality but also contributes to sustainability efforts.
One of the primary sustainability benefits of using glycerol in freeze-drying is the reduction in energy consumption. Glycerol acts as a cryoprotectant, lowering the freezing point of water in food products. This allows for more efficient freeze-drying at higher temperatures, reducing the energy required for the process. Studies have shown that glycerol-enhanced freeze-drying can reduce energy consumption by up to 20% compared to traditional methods.
Water conservation is another crucial aspect of sustainability in freeze-drying processes. Glycerol's hygroscopic properties help retain moisture in the final product, reducing the amount of water that needs to be removed during the drying process. This not only improves the texture and rehydration properties of freeze-dried foods but also decreases the overall water usage in the production cycle.
The use of glycerol also extends the shelf life of freeze-dried products, contributing to sustainability by reducing food waste. Improved stability and moisture retention in glycerol-enhanced freeze-dried foods mean that these products can be stored for longer periods without compromising quality. This extended shelf life reduces the likelihood of spoilage and waste throughout the supply chain.
Furthermore, glycerol itself is a sustainable ingredient, often derived from renewable sources such as vegetable oils or as a byproduct of biodiesel production. The integration of this eco-friendly compound into freeze-drying processes aligns with the growing demand for sustainable food production methods.
Innovations in freeze-drying equipment have also contributed to improved sustainability. Modern freeze-dryers are designed with energy-efficient components, such as improved insulation and heat recovery systems. When combined with glycerol-enhanced processes, these technological advancements significantly reduce the carbon footprint of freeze-dried food production.
As the food industry continues to prioritize sustainability, the role of glycerol in enhancing both quality and eco-friendliness of freeze-dried foods is likely to expand. Future research may focus on optimizing glycerol concentrations and exploring synergistic effects with other natural cryoprotectants to further improve the sustainability of freeze-drying processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!