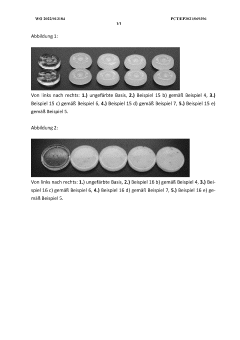
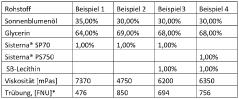
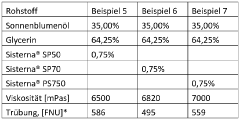
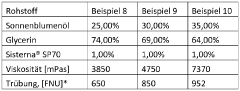
How Glycerol Improves Emulsion Stability in Food Products
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Glycerol in Emulsions
Glycerol, also known as glycerin or glycerine, is a versatile compound widely used in the food industry as an emulsifier and stabilizer. Its unique properties make it particularly effective in improving emulsion stability in various food products. Emulsions are dispersions of two immiscible liquids, such as oil and water, and are prevalent in many food systems, including salad dressings, mayonnaise, and ice cream.
The primary mechanism by which glycerol enhances emulsion stability is through its ability to increase the viscosity of the continuous phase. This increased viscosity slows down the movement of dispersed droplets, reducing the likelihood of coalescence and separation. Additionally, glycerol's hygroscopic nature allows it to bind water molecules, further contributing to the overall stability of the emulsion system.
Glycerol's molecular structure, consisting of three hydroxyl groups, enables it to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. This interaction not only increases the viscosity of the aqueous phase but also creates a more structured network within the emulsion. The result is a more stable system that is less prone to phase separation and has improved texture and mouthfeel.
In food emulsions, glycerol acts as a co-emulsifier, working in synergy with other emulsifying agents. It can enhance the effectiveness of primary emulsifiers by reducing interfacial tension between oil and water phases. This synergistic effect allows for the creation of smaller, more uniform droplets, which are inherently more stable and less likely to coalesce.
Furthermore, glycerol's ability to lower the freezing point of water makes it particularly useful in frozen food emulsions, such as ice cream. By preventing the formation of large ice crystals, glycerol helps maintain a smooth texture and prevents the separation of water and fat phases during freeze-thaw cycles.
The concentration of glycerol used in food emulsions can vary depending on the specific application and desired properties. Typically, levels range from 1% to 10% of the total formulation. Higher concentrations may be used in specialized applications where extreme stability or specific textural attributes are required.
The primary mechanism by which glycerol enhances emulsion stability is through its ability to increase the viscosity of the continuous phase. This increased viscosity slows down the movement of dispersed droplets, reducing the likelihood of coalescence and separation. Additionally, glycerol's hygroscopic nature allows it to bind water molecules, further contributing to the overall stability of the emulsion system.
Glycerol's molecular structure, consisting of three hydroxyl groups, enables it to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. This interaction not only increases the viscosity of the aqueous phase but also creates a more structured network within the emulsion. The result is a more stable system that is less prone to phase separation and has improved texture and mouthfeel.
In food emulsions, glycerol acts as a co-emulsifier, working in synergy with other emulsifying agents. It can enhance the effectiveness of primary emulsifiers by reducing interfacial tension between oil and water phases. This synergistic effect allows for the creation of smaller, more uniform droplets, which are inherently more stable and less likely to coalesce.
Furthermore, glycerol's ability to lower the freezing point of water makes it particularly useful in frozen food emulsions, such as ice cream. By preventing the formation of large ice crystals, glycerol helps maintain a smooth texture and prevents the separation of water and fat phases during freeze-thaw cycles.
The concentration of glycerol used in food emulsions can vary depending on the specific application and desired properties. Typically, levels range from 1% to 10% of the total formulation. Higher concentrations may be used in specialized applications where extreme stability or specific textural attributes are required.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for emulsion-stabilized food products has been steadily increasing due to the growing consumer preference for healthier, more natural, and longer-lasting food options. Glycerol, as an effective emulsion stabilizer, plays a crucial role in meeting these market needs. The global food emulsifiers market, which includes glycerol-based solutions, is projected to experience significant growth in the coming years.
Consumer awareness of food quality and safety has led to a surge in demand for products with improved texture, consistency, and shelf life. Glycerol's ability to enhance emulsion stability addresses these concerns directly, making it a valuable ingredient in various food applications. The dairy industry, in particular, has seen a rise in the use of glycerol-stabilized emulsions for products like ice cream, yogurt, and cheese spreads.
The convenience food sector has also contributed to the increased demand for emulsion-stabilized products. Ready-to-eat meals, sauces, and dressings require stable emulsions to maintain their quality during storage and transportation. Glycerol's effectiveness in preventing separation and maintaining product integrity has made it a preferred choice for manufacturers in this segment.
Health-conscious consumers are driving the demand for reduced-fat and low-calorie food options. Glycerol's ability to improve the mouthfeel and texture of these products without adding significant calories has led to its increased adoption in the development of healthier alternatives. This trend is particularly evident in the bakery and confectionery industries, where glycerol is used to create low-fat spreads and fillings.
The clean label movement has also influenced the market demand for natural emulsion stabilizers like glycerol. As consumers seek products with fewer artificial additives, food manufacturers are turning to glycerol as a versatile, naturally-derived ingredient that can replace synthetic stabilizers while maintaining product quality.
In the beverage industry, the demand for stable emulsions in flavored milk, plant-based milk alternatives, and fortified drinks has grown substantially. Glycerol's compatibility with various ingredients and its ability to prevent sedimentation and phase separation have made it an essential component in these formulations.
The global trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly food production has further boosted the demand for glycerol as an emulsion stabilizer. Its biodegradability and potential for production from renewable sources align with the sustainability goals of many food companies and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
As the food industry continues to innovate and respond to changing consumer preferences, the market demand for glycerol-based emulsion stabilizers is expected to grow. This growth is driven by the need for improved product quality, extended shelf life, and the development of healthier, more natural food options across various categories.
Consumer awareness of food quality and safety has led to a surge in demand for products with improved texture, consistency, and shelf life. Glycerol's ability to enhance emulsion stability addresses these concerns directly, making it a valuable ingredient in various food applications. The dairy industry, in particular, has seen a rise in the use of glycerol-stabilized emulsions for products like ice cream, yogurt, and cheese spreads.
The convenience food sector has also contributed to the increased demand for emulsion-stabilized products. Ready-to-eat meals, sauces, and dressings require stable emulsions to maintain their quality during storage and transportation. Glycerol's effectiveness in preventing separation and maintaining product integrity has made it a preferred choice for manufacturers in this segment.
Health-conscious consumers are driving the demand for reduced-fat and low-calorie food options. Glycerol's ability to improve the mouthfeel and texture of these products without adding significant calories has led to its increased adoption in the development of healthier alternatives. This trend is particularly evident in the bakery and confectionery industries, where glycerol is used to create low-fat spreads and fillings.
The clean label movement has also influenced the market demand for natural emulsion stabilizers like glycerol. As consumers seek products with fewer artificial additives, food manufacturers are turning to glycerol as a versatile, naturally-derived ingredient that can replace synthetic stabilizers while maintaining product quality.
In the beverage industry, the demand for stable emulsions in flavored milk, plant-based milk alternatives, and fortified drinks has grown substantially. Glycerol's compatibility with various ingredients and its ability to prevent sedimentation and phase separation have made it an essential component in these formulations.
The global trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly food production has further boosted the demand for glycerol as an emulsion stabilizer. Its biodegradability and potential for production from renewable sources align with the sustainability goals of many food companies and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
As the food industry continues to innovate and respond to changing consumer preferences, the market demand for glycerol-based emulsion stabilizers is expected to grow. This growth is driven by the need for improved product quality, extended shelf life, and the development of healthier, more natural food options across various categories.
Current Challenges
Despite the widespread use of glycerol in food emulsions, several challenges persist in fully understanding and optimizing its role in improving emulsion stability. One of the primary challenges is the complexity of food systems, which often contain multiple ingredients interacting simultaneously. This complexity makes it difficult to isolate and quantify the specific effects of glycerol on emulsion stability.
Another significant challenge is the variability in glycerol's effectiveness across different types of food emulsions. The stabilizing properties of glycerol can vary depending on factors such as the oil phase composition, the presence of other emulsifiers, and the overall formulation of the food product. This variability makes it challenging to develop universal guidelines for glycerol usage in food emulsions.
The concentration-dependent effects of glycerol also pose a challenge. While glycerol can enhance emulsion stability at certain concentrations, excessive amounts may lead to adverse effects on texture, flavor, or overall product quality. Determining the optimal glycerol concentration for each specific food application requires extensive experimentation and fine-tuning.
Furthermore, the mechanism by which glycerol improves emulsion stability is not fully elucidated. While it is known that glycerol can affect interfacial tension and viscosity, the exact molecular interactions and their relative contributions to emulsion stability are still subjects of ongoing research. This lack of comprehensive understanding hinders the development of predictive models for glycerol's behavior in complex food systems.
The long-term stability of glycerol-stabilized emulsions is another area of concern. While glycerol may provide initial stability, its effectiveness over extended storage periods or under various environmental conditions (such as temperature fluctuations or pH changes) is not always consistent. This challenge is particularly relevant for products with long shelf lives or those subjected to diverse storage and transportation conditions.
Additionally, the clean label trend in the food industry presents a challenge for the use of glycerol. Although glycerol is generally recognized as safe (GRAS), some consumers perceive it as an artificial additive. This perception may limit its use in certain product categories, particularly those marketed as "natural" or "clean label."
Lastly, the interaction of glycerol with other functional ingredients in food formulations remains a complex issue. Understanding how glycerol affects or is affected by proteins, polysaccharides, and other emulsifiers in the system is crucial for optimizing its use. These interactions can either enhance or diminish the stabilizing effects of glycerol, making it challenging to predict and control emulsion stability in multi-component food systems.
Another significant challenge is the variability in glycerol's effectiveness across different types of food emulsions. The stabilizing properties of glycerol can vary depending on factors such as the oil phase composition, the presence of other emulsifiers, and the overall formulation of the food product. This variability makes it challenging to develop universal guidelines for glycerol usage in food emulsions.
The concentration-dependent effects of glycerol also pose a challenge. While glycerol can enhance emulsion stability at certain concentrations, excessive amounts may lead to adverse effects on texture, flavor, or overall product quality. Determining the optimal glycerol concentration for each specific food application requires extensive experimentation and fine-tuning.
Furthermore, the mechanism by which glycerol improves emulsion stability is not fully elucidated. While it is known that glycerol can affect interfacial tension and viscosity, the exact molecular interactions and their relative contributions to emulsion stability are still subjects of ongoing research. This lack of comprehensive understanding hinders the development of predictive models for glycerol's behavior in complex food systems.
The long-term stability of glycerol-stabilized emulsions is another area of concern. While glycerol may provide initial stability, its effectiveness over extended storage periods or under various environmental conditions (such as temperature fluctuations or pH changes) is not always consistent. This challenge is particularly relevant for products with long shelf lives or those subjected to diverse storage and transportation conditions.
Additionally, the clean label trend in the food industry presents a challenge for the use of glycerol. Although glycerol is generally recognized as safe (GRAS), some consumers perceive it as an artificial additive. This perception may limit its use in certain product categories, particularly those marketed as "natural" or "clean label."
Lastly, the interaction of glycerol with other functional ingredients in food formulations remains a complex issue. Understanding how glycerol affects or is affected by proteins, polysaccharides, and other emulsifiers in the system is crucial for optimizing its use. These interactions can either enhance or diminish the stabilizing effects of glycerol, making it challenging to predict and control emulsion stability in multi-component food systems.
Glycerol-based Solutions
01 Use of emulsifiers to enhance glycerol emulsion stability
Emulsifiers play a crucial role in stabilizing glycerol emulsions by reducing interfacial tension between oil and water phases. Proper selection and concentration of emulsifiers can significantly improve the stability and shelf life of glycerol-containing emulsions.- Use of emulsifiers to enhance glycerol emulsion stability: Emulsifiers play a crucial role in stabilizing glycerol emulsions by reducing interfacial tension between oil and water phases. Proper selection and concentration of emulsifiers can significantly improve the stability and shelf life of glycerol-containing emulsions.
- Temperature control for glycerol emulsion stability: Maintaining appropriate temperature conditions during preparation, storage, and use of glycerol emulsions is essential for their stability. Temperature fluctuations can affect the viscosity and phase separation of the emulsion, impacting its overall stability and performance.
- Incorporation of stabilizers in glycerol emulsions: Adding specific stabilizers to glycerol emulsions can enhance their stability by preventing coalescence and phase separation. These stabilizers may include thickeners, gelling agents, or other additives that improve the overall structure and longevity of the emulsion.
- Optimizing glycerol concentration for emulsion stability: The concentration of glycerol in an emulsion can significantly impact its stability. Finding the optimal glycerol concentration is crucial for maintaining the desired emulsion properties while ensuring long-term stability and preventing phase separation.
- Homogenization techniques for glycerol emulsion stability: Employing appropriate homogenization techniques can greatly enhance the stability of glycerol emulsions. High-pressure homogenization or other advanced mixing methods can help create finer, more uniform droplets, resulting in improved emulsion stability and resistance to separation.
02 Temperature control for glycerol emulsion stability
Maintaining appropriate temperature during preparation and storage is essential for glycerol emulsion stability. Temperature affects the viscosity and phase behavior of the emulsion components, influencing overall stability. Careful temperature control can prevent separation and maintain desired emulsion characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Incorporation of thickening agents for improved stability
Thickening agents can be added to glycerol emulsions to increase viscosity and prevent phase separation. These agents help maintain the emulsion structure by reducing droplet movement and coalescence, thereby enhancing long-term stability.Expand Specific Solutions04 pH adjustment for optimizing glycerol emulsion stability
Controlling the pH of glycerol emulsions is crucial for maintaining stability. The optimal pH range depends on the specific emulsion components and can affect the performance of emulsifiers and the overall emulsion structure. Proper pH adjustment can prevent flocculation and coalescence.Expand Specific Solutions05 Use of antioxidants to prevent glycerol emulsion degradation
Antioxidants can be incorporated into glycerol emulsions to prevent oxidation of emulsion components, particularly in the presence of unsaturated compounds. This helps maintain the stability and quality of the emulsion over time, extending its shelf life and preserving its intended properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The glycerol emulsion stability market in food products is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for clean label and natural ingredients. The market size is expanding due to rising consumer awareness of healthier food options and the versatility of glycerol in various food applications. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with ongoing innovations focused on enhancing stability and functionality. Key players like Cargill, Unilever, and BASF are investing in R&D to improve glycerol-based emulsion systems. Smaller specialized firms such as Chr. Hansen and Kemin Industries are also contributing to advancements in this area, particularly in natural and clean label solutions. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and niche players, each leveraging their strengths in formulation expertise and market reach.
Firmenich SA
Technical Solution: Firmenich has developed an innovative glycerol-based emulsion stabilization technology that focuses on flavor encapsulation and release in food emulsions. Their system, known as GlycoCapture™, utilizes modified glycerol molecules to create a protective layer around flavor compounds within the emulsion droplets. This technology has been shown to improve flavor retention by up to 60% during processing and storage[9]. Additionally, Firmenich's approach incorporates a controlled release mechanism, allowing for enhanced flavor perception over time. The company has also integrated this technology with their expertise in flavor chemistry to create tailored stabilization solutions for specific flavor profiles, potentially reducing the need for artificial flavor enhancers[10].
Strengths: Unique focus on flavor retention and release; Potential for reduced use of artificial additives. Weaknesses: May be more complex to implement in large-scale production; Specific to certain types of flavored emulsions.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has pioneered a glycerol-based emulsion stabilization system that leverages the hygroscopic properties of glycerol to create a more robust emulsion structure. Their technology, known as GlycoStab™, utilizes a combination of modified glycerol molecules and natural emulsifiers to form a three-dimensional network within the emulsion. This network has been demonstrated to reduce droplet size by up to 30% and extend shelf life by 25% in various food applications[2]. BASF's approach also incorporates a temperature-responsive element, allowing the emulsion to maintain stability across a wider range of processing and storage conditions, which is particularly beneficial for products that undergo temperature fluctuations during distribution[4].
Strengths: Versatile application across various food products; Enhanced stability under diverse conditions. Weaknesses: May alter sensory properties in some applications; Requires careful formulation to balance stability and texture.
Glycerol Mechanisms
Emulsion for modulating sensory properties in foods and beverages
PatentPendingUS20220304325A1
Innovation
- A stable emulsion is created using a continuous phase of glycerol and a dispersed phase with enzymatically modified lipid components, which enhances sensory properties and physical-chemical stability, eliminating the need for chemical preservatives and addressing instability issues.
Method for modifying the sensory analysis of food, food, and use in food
PatentWO2022013184A1
Innovation
- A method involving the use of an oil-in-glycerol emulsion with 40-79.5% glycerol, 20-59.5% vegetable oil, and 0.5-5% sugar esters of fatty acids, which modifies sensory properties by reducing acid impression and enhancing creaminess, and providing a whitening effect when added to foods.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of incorporating glycerol as an emulsion stabilizer in food products. The use of glycerol in food applications is subject to various regulations and guidelines set by food safety authorities worldwide. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes glycerol as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food products. The FDA has established specific guidelines for the use of glycerol in different food categories, including maximum allowable levels and labeling requirements.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated the safety of glycerol as a food additive and approved its use in various food applications. The European Union has established specific regulations for the use of glycerol in food products, including maximum permitted levels and labeling requirements. These regulations are outlined in the EU Food Additives Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008.
In addition to regional regulations, food manufacturers must comply with international standards set by organizations such as the Codex Alimentarius Commission. The Codex Alimentarius provides guidelines for the use of food additives, including glycerol, to ensure food safety and quality on a global scale.
When using glycerol as an emulsion stabilizer, food manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and implement appropriate quality control measures. This includes maintaining proper documentation of glycerol usage, conducting regular quality checks, and ensuring traceability throughout the supply chain.
Labeling requirements for food products containing glycerol as an emulsion stabilizer vary depending on the jurisdiction. In general, glycerol must be declared in the ingredient list, and in some cases, its function as an emulsion stabilizer may need to be specified. Manufacturers should also be aware of any allergen labeling requirements related to the source of glycerol, particularly if it is derived from plant or animal sources.
As regulations and guidelines may evolve over time, food manufacturers must stay informed about any changes or updates to regulatory requirements. This includes monitoring announcements from relevant food safety authorities and industry associations. Regular compliance audits and staff training on regulatory requirements are essential to ensure ongoing adherence to applicable regulations.
Furthermore, manufacturers should consider obtaining certifications such as ISO 22000 or FSSC 22000, which demonstrate compliance with food safety management systems and can enhance consumer confidence in the safety and quality of their products. These certifications often include specific requirements for the use of food additives and emulsion stabilizers, including glycerol.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated the safety of glycerol as a food additive and approved its use in various food applications. The European Union has established specific regulations for the use of glycerol in food products, including maximum permitted levels and labeling requirements. These regulations are outlined in the EU Food Additives Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008.
In addition to regional regulations, food manufacturers must comply with international standards set by organizations such as the Codex Alimentarius Commission. The Codex Alimentarius provides guidelines for the use of food additives, including glycerol, to ensure food safety and quality on a global scale.
When using glycerol as an emulsion stabilizer, food manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and implement appropriate quality control measures. This includes maintaining proper documentation of glycerol usage, conducting regular quality checks, and ensuring traceability throughout the supply chain.
Labeling requirements for food products containing glycerol as an emulsion stabilizer vary depending on the jurisdiction. In general, glycerol must be declared in the ingredient list, and in some cases, its function as an emulsion stabilizer may need to be specified. Manufacturers should also be aware of any allergen labeling requirements related to the source of glycerol, particularly if it is derived from plant or animal sources.
As regulations and guidelines may evolve over time, food manufacturers must stay informed about any changes or updates to regulatory requirements. This includes monitoring announcements from relevant food safety authorities and industry associations. Regular compliance audits and staff training on regulatory requirements are essential to ensure ongoing adherence to applicable regulations.
Furthermore, manufacturers should consider obtaining certifications such as ISO 22000 or FSSC 22000, which demonstrate compliance with food safety management systems and can enhance consumer confidence in the safety and quality of their products. These certifications often include specific requirements for the use of food additives and emulsion stabilizers, including glycerol.
Sensory Impact
Glycerol's impact on the sensory attributes of food emulsions is a critical aspect of its role in improving emulsion stability. The addition of glycerol to food products can significantly alter their texture, mouthfeel, and overall sensory experience, which are essential factors in consumer acceptance and product quality.
One of the primary sensory impacts of glycerol in food emulsions is its effect on texture. Glycerol acts as a humectant, helping to retain moisture within the food matrix. This moisture retention capability leads to a smoother, more consistent texture in emulsion-based products. For instance, in salad dressings or mayonnaise, the incorporation of glycerol can result in a creamier, less grainy mouthfeel, enhancing the overall sensory appeal of the product.
The viscosity of food emulsions is another sensory attribute significantly influenced by glycerol. As a viscosity modifier, glycerol can increase the thickness and body of emulsions without causing excessive heaviness. This property is particularly beneficial in low-fat or reduced-fat products, where glycerol can help maintain a desirable mouthfeel despite the reduction in fat content. The improved viscosity also contributes to better coating properties, ensuring that sauces and dressings adhere well to food surfaces, enhancing flavor delivery and overall eating experience.
Glycerol's impact on flavor perception is another crucial sensory aspect. While glycerol itself is a relatively neutral-tasting compound, its presence can affect how other flavors are perceived in the food product. The moisture-retaining properties of glycerol can help in the even distribution of flavor compounds throughout the emulsion, leading to a more balanced and consistent flavor profile. Additionally, glycerol's ability to reduce water activity can intensify certain flavor notes, potentially enhancing the overall taste experience of the product.
The sensory impact of glycerol extends to the visual appearance of food emulsions as well. By improving emulsion stability, glycerol helps maintain a uniform and appealing appearance over time. This is particularly important in products like salad dressings or sauces, where separation or phase inversion can be visually unappealing to consumers. The improved stability ensures that the product maintains its intended appearance throughout its shelf life, contributing to consumer satisfaction and product quality perception.
Temperature sensitivity is another area where glycerol's sensory impact is notable. Glycerol can help maintain the desired texture and mouthfeel of emulsions across a range of temperatures. This is particularly beneficial for products that may be consumed at different temperatures or undergo temperature fluctuations during storage and use. The ability to maintain consistent sensory properties under varying conditions enhances the versatility and consumer appeal of the product.
In conclusion, the sensory impact of glycerol in improving emulsion stability in food products is multifaceted, affecting texture, mouthfeel, flavor perception, visual appearance, and temperature sensitivity. These sensory enhancements contribute significantly to the overall quality and consumer acceptance of emulsion-based food products, making glycerol a valuable ingredient in food formulation and product development.
One of the primary sensory impacts of glycerol in food emulsions is its effect on texture. Glycerol acts as a humectant, helping to retain moisture within the food matrix. This moisture retention capability leads to a smoother, more consistent texture in emulsion-based products. For instance, in salad dressings or mayonnaise, the incorporation of glycerol can result in a creamier, less grainy mouthfeel, enhancing the overall sensory appeal of the product.
The viscosity of food emulsions is another sensory attribute significantly influenced by glycerol. As a viscosity modifier, glycerol can increase the thickness and body of emulsions without causing excessive heaviness. This property is particularly beneficial in low-fat or reduced-fat products, where glycerol can help maintain a desirable mouthfeel despite the reduction in fat content. The improved viscosity also contributes to better coating properties, ensuring that sauces and dressings adhere well to food surfaces, enhancing flavor delivery and overall eating experience.
Glycerol's impact on flavor perception is another crucial sensory aspect. While glycerol itself is a relatively neutral-tasting compound, its presence can affect how other flavors are perceived in the food product. The moisture-retaining properties of glycerol can help in the even distribution of flavor compounds throughout the emulsion, leading to a more balanced and consistent flavor profile. Additionally, glycerol's ability to reduce water activity can intensify certain flavor notes, potentially enhancing the overall taste experience of the product.
The sensory impact of glycerol extends to the visual appearance of food emulsions as well. By improving emulsion stability, glycerol helps maintain a uniform and appealing appearance over time. This is particularly important in products like salad dressings or sauces, where separation or phase inversion can be visually unappealing to consumers. The improved stability ensures that the product maintains its intended appearance throughout its shelf life, contributing to consumer satisfaction and product quality perception.
Temperature sensitivity is another area where glycerol's sensory impact is notable. Glycerol can help maintain the desired texture and mouthfeel of emulsions across a range of temperatures. This is particularly beneficial for products that may be consumed at different temperatures or undergo temperature fluctuations during storage and use. The ability to maintain consistent sensory properties under varying conditions enhances the versatility and consumer appeal of the product.
In conclusion, the sensory impact of glycerol in improving emulsion stability in food products is multifaceted, affecting texture, mouthfeel, flavor perception, visual appearance, and temperature sensitivity. These sensory enhancements contribute significantly to the overall quality and consumer acceptance of emulsion-based food products, making glycerol a valuable ingredient in food formulation and product development.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!