How laryngoscope handle design affects clinician ergonomics.
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Laryngoscope Evolution
The evolution of the laryngoscope has been a journey of continuous innovation, driven by the need to improve clinician ergonomics and patient outcomes. The earliest laryngoscopes, developed in the early 19th century, were simple, straight-bladed instruments that provided limited visibility and required significant skill to manipulate. These early designs often led to clinician fatigue and potential injury due to the awkward positioning required during intubation procedures.
As medical understanding and technology advanced, the Macintosh laryngoscope, introduced in the 1940s, marked a significant milestone. Its curved blade design allowed for easier lifting of the epiglottis and improved visualization of the vocal cords. This innovation reduced the physical strain on clinicians during intubation, but still required considerable force and dexterity to use effectively.
The late 20th century saw the introduction of fiber-optic laryngoscopes, which revolutionized the field by providing enhanced illumination and visualization. These devices incorporated light sources directly into the blade, eliminating the need for separate light attachments and improving the clinician's line of sight. The improved visibility reduced the need for extreme neck extension and minimized the risk of dental trauma to patients.
In recent years, video laryngoscopes have emerged as a game-changing technology. These devices integrate miniature cameras into the blade tip, projecting a magnified view of the airway onto an external screen. This innovation has significantly reduced the physical strain on clinicians by allowing them to maintain a more natural posture during intubation. The improved visualization has also led to higher success rates and reduced procedure times, particularly in difficult airway scenarios.
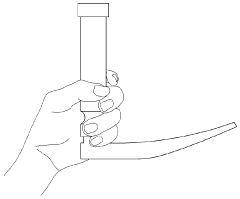
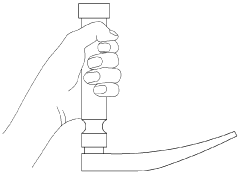
Ergonomic considerations have become increasingly central to laryngoscope design. Modern handles are crafted with materials and shapes that provide better grip and control, reducing hand fatigue during prolonged use. Some designs now incorporate adjustable angles between the handle and blade, allowing clinicians to customize the device to their preferred working position.
The integration of disposable components has addressed infection control concerns while also contributing to improved ergonomics. Lightweight, single-use blades and handles reduce the overall weight of the device, minimizing strain on the clinician's hands and wrists during procedures.
As we look to the future, emerging technologies such as augmented reality and artificial intelligence are poised to further revolutionize laryngoscope design. These advancements promise to provide real-time guidance, automated airway assessment, and even more intuitive ergonomic interfaces, potentially reducing the physical and cognitive load on clinicians during intubation procedures.
As medical understanding and technology advanced, the Macintosh laryngoscope, introduced in the 1940s, marked a significant milestone. Its curved blade design allowed for easier lifting of the epiglottis and improved visualization of the vocal cords. This innovation reduced the physical strain on clinicians during intubation, but still required considerable force and dexterity to use effectively.
The late 20th century saw the introduction of fiber-optic laryngoscopes, which revolutionized the field by providing enhanced illumination and visualization. These devices incorporated light sources directly into the blade, eliminating the need for separate light attachments and improving the clinician's line of sight. The improved visibility reduced the need for extreme neck extension and minimized the risk of dental trauma to patients.
In recent years, video laryngoscopes have emerged as a game-changing technology. These devices integrate miniature cameras into the blade tip, projecting a magnified view of the airway onto an external screen. This innovation has significantly reduced the physical strain on clinicians by allowing them to maintain a more natural posture during intubation. The improved visualization has also led to higher success rates and reduced procedure times, particularly in difficult airway scenarios.
Ergonomic considerations have become increasingly central to laryngoscope design. Modern handles are crafted with materials and shapes that provide better grip and control, reducing hand fatigue during prolonged use. Some designs now incorporate adjustable angles between the handle and blade, allowing clinicians to customize the device to their preferred working position.
The integration of disposable components has addressed infection control concerns while also contributing to improved ergonomics. Lightweight, single-use blades and handles reduce the overall weight of the device, minimizing strain on the clinician's hands and wrists during procedures.
As we look to the future, emerging technologies such as augmented reality and artificial intelligence are poised to further revolutionize laryngoscope design. These advancements promise to provide real-time guidance, automated airway assessment, and even more intuitive ergonomic interfaces, potentially reducing the physical and cognitive load on clinicians during intubation procedures.
Ergonomic Market Demand
The ergonomic market demand for improved laryngoscope handle designs has been steadily increasing in recent years. This trend is driven by the growing awareness of the importance of clinician comfort and safety during intubation procedures. Healthcare providers and institutions are recognizing that ergonomically designed laryngoscopes can significantly reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and improve overall performance during critical airway management tasks.
The market for ergonomic laryngoscopes is expanding globally, with North America and Europe leading in adoption rates. This growth is fueled by stringent workplace safety regulations and a heightened focus on healthcare worker well-being. Developing regions, such as Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are also showing increased interest in ergonomic medical devices, presenting new market opportunities for manufacturers.
One of the key drivers of market demand is the rising incidence of work-related musculoskeletal disorders among anesthesiologists and emergency medicine physicians. Studies have shown that traditional laryngoscope designs can lead to wrist strain, hand fatigue, and poor posture during prolonged use. This has created a strong demand for handles that offer improved grip, reduced weight, and better balance to minimize physical stress on clinicians.
The aging healthcare workforce in many developed countries is another factor contributing to the demand for ergonomic laryngoscopes. As experienced clinicians continue to work into their later years, there is a greater need for tools that can accommodate age-related changes in dexterity and strength. This demographic shift is pushing manufacturers to innovate and develop more user-friendly handle designs.
Healthcare institutions are increasingly prioritizing ergonomic equipment as part of their risk management and quality improvement strategies. This institutional-level demand is driving bulk purchases of ergonomically designed laryngoscopes, further stimulating market growth. Additionally, the focus on patient safety and successful first-attempt intubations is aligning with the benefits offered by ergonomic handle designs, which can improve clinician performance and reduce procedure-related complications.
The market is also seeing a trend towards customizable handle designs that can be adjusted to fit individual clinician preferences. This personalization aspect is becoming a key selling point for manufacturers and is expected to drive further innovation in the sector. As the healthcare industry continues to emphasize evidence-based practices, there is a growing demand for laryngoscope handles that have been scientifically validated for their ergonomic benefits.
In conclusion, the ergonomic market demand for laryngoscope handles is robust and multifaceted, driven by clinical needs, regulatory pressures, and a broader focus on healthcare worker well-being. As this market continues to evolve, it presents significant opportunities for innovation and growth in the medical device industry.
The market for ergonomic laryngoscopes is expanding globally, with North America and Europe leading in adoption rates. This growth is fueled by stringent workplace safety regulations and a heightened focus on healthcare worker well-being. Developing regions, such as Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are also showing increased interest in ergonomic medical devices, presenting new market opportunities for manufacturers.
One of the key drivers of market demand is the rising incidence of work-related musculoskeletal disorders among anesthesiologists and emergency medicine physicians. Studies have shown that traditional laryngoscope designs can lead to wrist strain, hand fatigue, and poor posture during prolonged use. This has created a strong demand for handles that offer improved grip, reduced weight, and better balance to minimize physical stress on clinicians.
The aging healthcare workforce in many developed countries is another factor contributing to the demand for ergonomic laryngoscopes. As experienced clinicians continue to work into their later years, there is a greater need for tools that can accommodate age-related changes in dexterity and strength. This demographic shift is pushing manufacturers to innovate and develop more user-friendly handle designs.
Healthcare institutions are increasingly prioritizing ergonomic equipment as part of their risk management and quality improvement strategies. This institutional-level demand is driving bulk purchases of ergonomically designed laryngoscopes, further stimulating market growth. Additionally, the focus on patient safety and successful first-attempt intubations is aligning with the benefits offered by ergonomic handle designs, which can improve clinician performance and reduce procedure-related complications.
The market is also seeing a trend towards customizable handle designs that can be adjusted to fit individual clinician preferences. This personalization aspect is becoming a key selling point for manufacturers and is expected to drive further innovation in the sector. As the healthcare industry continues to emphasize evidence-based practices, there is a growing demand for laryngoscope handles that have been scientifically validated for their ergonomic benefits.
In conclusion, the ergonomic market demand for laryngoscope handles is robust and multifaceted, driven by clinical needs, regulatory pressures, and a broader focus on healthcare worker well-being. As this market continues to evolve, it presents significant opportunities for innovation and growth in the medical device industry.
Handle Design Challenges
Laryngoscope handle design presents several significant challenges that directly impact clinician ergonomics and, consequently, the effectiveness of intubation procedures. One of the primary challenges is achieving an optimal balance between handle size and weight. A handle that is too large or heavy can lead to fatigue and reduced control during prolonged procedures, while one that is too small may not provide adequate grip and stability.
The shape of the handle is another critical factor. Traditional cylindrical designs may not conform well to the natural contours of the hand, leading to increased muscle strain and potential discomfort during use. Ergonomic designs that incorporate curved or contoured surfaces to match hand anatomy are being explored, but finding a universal solution that accommodates various hand sizes and gripping preferences remains challenging.
Material selection for handle construction also poses difficulties. While metal handles offer durability and can be easily sterilized, they may become slippery when exposed to bodily fluids or when used with gloves. Conversely, rubberized or textured materials that enhance grip can be more challenging to clean and may degrade over time with repeated sterilization processes.
The integration of advanced features into the handle, such as video displays or control buttons for video laryngoscopes, introduces additional ergonomic considerations. These features must be positioned for easy access without compromising the overall grip and balance of the device. The challenge lies in incorporating these elements without significantly altering the familiar form factor that clinicians are accustomed to.
Another design challenge is addressing the variability in user technique and preference. Different clinicians may have distinct ways of holding and manipulating the laryngoscope, making it difficult to create a one-size-fits-all solution. Designers must consider how to accommodate various grip styles while still maintaining optimal ergonomics for the majority of users.
The need for single-use disposable handles in certain clinical settings introduces further complications. These handles must balance cost-effectiveness with ergonomic performance, often leading to compromises in design and material quality. Ensuring that disposable handles provide comparable ergonomic benefits to their reusable counterparts without significantly increasing healthcare costs is an ongoing challenge.
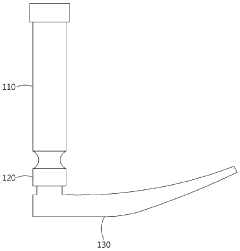
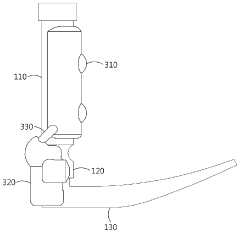
Lastly, the handle design must also consider the interface with the laryngoscope blade. The connection mechanism needs to be secure and easy to operate while not interfering with the overall ergonomics of the handle. Achieving a seamless integration between handle and blade design is crucial for optimal performance and user comfort during intubation procedures.
The shape of the handle is another critical factor. Traditional cylindrical designs may not conform well to the natural contours of the hand, leading to increased muscle strain and potential discomfort during use. Ergonomic designs that incorporate curved or contoured surfaces to match hand anatomy are being explored, but finding a universal solution that accommodates various hand sizes and gripping preferences remains challenging.
Material selection for handle construction also poses difficulties. While metal handles offer durability and can be easily sterilized, they may become slippery when exposed to bodily fluids or when used with gloves. Conversely, rubberized or textured materials that enhance grip can be more challenging to clean and may degrade over time with repeated sterilization processes.
The integration of advanced features into the handle, such as video displays or control buttons for video laryngoscopes, introduces additional ergonomic considerations. These features must be positioned for easy access without compromising the overall grip and balance of the device. The challenge lies in incorporating these elements without significantly altering the familiar form factor that clinicians are accustomed to.
Another design challenge is addressing the variability in user technique and preference. Different clinicians may have distinct ways of holding and manipulating the laryngoscope, making it difficult to create a one-size-fits-all solution. Designers must consider how to accommodate various grip styles while still maintaining optimal ergonomics for the majority of users.
The need for single-use disposable handles in certain clinical settings introduces further complications. These handles must balance cost-effectiveness with ergonomic performance, often leading to compromises in design and material quality. Ensuring that disposable handles provide comparable ergonomic benefits to their reusable counterparts without significantly increasing healthcare costs is an ongoing challenge.
Lastly, the handle design must also consider the interface with the laryngoscope blade. The connection mechanism needs to be secure and easy to operate while not interfering with the overall ergonomics of the handle. Achieving a seamless integration between handle and blade design is crucial for optimal performance and user comfort during intubation procedures.
Current Handle Solutions
01 Ergonomic handle design for improved grip and control
Laryngoscope handles are designed with ergonomic features to enhance grip and control during use. These designs may include contoured shapes, textured surfaces, or adjustable components to accommodate different hand sizes and preferences. The improved ergonomics aim to reduce hand fatigue and increase precision during intubation procedures.- Ergonomic handle design for improved grip and control: Laryngoscope handles are designed with ergonomic features to enhance grip and control during use. These designs may include contoured shapes, textured surfaces, or adjustable components to accommodate different hand sizes and preferences. The improved ergonomics aim to reduce hand fatigue and increase precision during intubation procedures.
- Adjustable handle configurations for user comfort: Some laryngoscope handles feature adjustable configurations to enhance user comfort. These may include telescoping handles, rotatable components, or interchangeable grip options. The ability to customize the handle position and orientation allows healthcare professionals to maintain optimal ergonomics during various intubation scenarios.
- Integration of electronic components for enhanced functionality: Modern laryngoscope handles often incorporate electronic components to improve functionality. These may include LED lights, video displays, or sensors for monitoring vital signs. The integration of these components is designed to maintain ergonomic comfort while providing additional features to assist in intubation procedures.
- Lightweight materials for reduced user fatigue: Laryngoscope handles are increasingly manufactured using lightweight materials to reduce user fatigue during prolonged use. These materials may include advanced polymers or lightweight metals that maintain durability while minimizing the overall weight of the device. The reduced weight contributes to improved ergonomics and ease of handling.
- Modular handle designs for versatility: Some laryngoscope handles feature modular designs that allow for easy customization and maintenance. These designs may include interchangeable components, detachable grips, or adaptable connectors for various blade types. The modular approach enhances ergonomics by allowing users to configure the handle to their specific preferences and requirements.
02 Adjustable handle configurations for versatility
Some laryngoscope handles feature adjustable configurations, allowing users to modify the handle position or angle. This adaptability enables healthcare professionals to customize the device for optimal comfort and performance in various clinical scenarios. Adjustable handles may incorporate pivoting mechanisms or interchangeable components.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of advanced functionalities in the handle
Modern laryngoscope handles often integrate advanced functionalities to enhance usability and performance. These may include built-in light sources, video cameras, or display screens for improved visualization during intubation. The integration of these features is designed to maintain ergonomic comfort while providing additional clinical benefits.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lightweight and balanced handle construction
Laryngoscope handles are engineered to be lightweight and well-balanced to reduce user fatigue during prolonged use. The use of advanced materials and optimized weight distribution contributes to improved ergonomics and maneuverability. This design approach aims to enhance the overall user experience and procedural efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Modular handle designs for customization
Some laryngoscope handles feature modular designs that allow for customization and easy maintenance. These designs may include interchangeable components, such as grip sections or battery compartments, enabling users to tailor the handle to their specific needs or preferences. Modular designs also facilitate easier cleaning and component replacement.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Laryngoscope Makers
The laryngoscope handle design market is in a mature stage, with established players like Karl Storz SE & Co. KG and Ambu A/S dominating the industry. The global market size for laryngoscopes is estimated to be around $200-250 million annually, with steady growth projected. Technological advancements focus on improving ergonomics and reducing clinician fatigue, with companies like Zhejiang Youyi Medical Equipment Co Ltd and Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. introducing innovative designs. The competition is intense, with both traditional medical device manufacturers and newer entrants like Neurent Medical Ltd. vying for market share. Overall, the industry is characterized by incremental innovations aimed at enhancing user experience and patient outcomes.
Boston Scientific Medical Device Ltd.
Technical Solution: Boston Scientific has developed the Bronchoflex™ video bronchoscope, which, while primarily designed for bronchoscopy, incorporates ergonomic principles that can be applied to laryngoscope design. The device features a lightweight, ergonomically designed control body that allows for single-handed operation. This design reduces hand fatigue and improves maneuverability during procedures. The Bronchoflex™ also includes an adjustable LCD monitor that can be positioned for optimal viewing, reducing neck strain for the clinician[10][12]. While not specifically a laryngoscope, the ergonomic principles applied in this design demonstrate Boston Scientific's focus on improving clinician comfort and efficiency in endoscopic procedures[11].
Strengths: Lightweight design, single-handed operation capability, and adjustable viewing monitor. Weaknesses: Not specifically designed for laryngoscopy, may require adaptation for direct laryngeal examination.
Karl Storz SE & Co. KG
Technical Solution: Karl Storz has developed the C-MAC® video laryngoscope system, which features an ergonomically designed handle with a low profile blade. The handle incorporates a high-resolution camera and LED light source, providing an optimal view of the airway. The design allows for a more natural hand position, reducing wrist strain during intubation procedures. The system also includes a portable monitor that can be positioned for optimal viewing, further enhancing ergonomics for the clinician[1][3]. Karl Storz has also introduced the C-MAC® S video laryngoscope, which features a single-use blade design, addressing hygiene concerns while maintaining ergonomic benefits[5].
Strengths: Advanced imaging technology, ergonomic handle design, and versatile blade options. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to traditional laryngoscopes, potential for technical issues in electronic components.
Ergonomic Patent Analysis
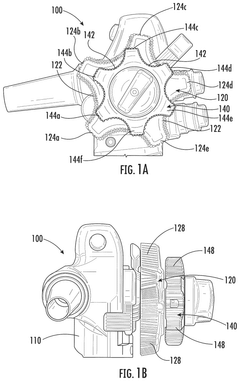
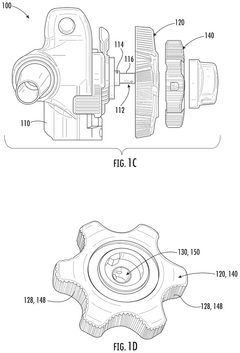
Knobs for endoscopes with improved usability and ergonomics
PatentPendingUS20250085735A1
Innovation
- The design includes a control handle with first and second control knobs, where the first knob is larger and has a greater outer dimension than the second, both with textured gripping surfaces and varying lever arm lengths to reduce torque requirements and improve ergonomics, allowing for easier manipulation of the endoscope.
Assisting handle for medical applicances and laryngoscopes using the same
PatentInactiveKR1020180118382A
Innovation
- An auxiliary handle with a grip portion that includes ergonomic design features like protrusions and shock-absorbing materials, allowing users to hold the blade and connection parts alongside the handle, customizable in size and shape to fit individual hand sizes and shapes, enhancing grip stability and comfort.
Clinical Usage Patterns
Laryngoscope handle design significantly influences clinical usage patterns and ergonomics for healthcare professionals. The traditional rigid, straight handle design has been the standard for decades, but it often leads to suboptimal positioning and strain for clinicians during intubation procedures.
In typical clinical scenarios, practitioners must adopt awkward postures to align the laryngoscope blade with the patient's airway. This often results in excessive wrist extension and ulnar deviation, particularly when intubating patients in hospital beds or on operating tables. Such positioning can lead to fatigue and potential repetitive strain injuries over time.
Recent ergonomic studies have shown that angled or articulating handle designs can improve clinician comfort and reduce physical strain during intubation. These designs allow for a more natural wrist position and better leverage, especially in challenging airway scenarios. As a result, there has been a gradual shift towards adopting these ergonomic handle designs in many clinical settings.
The frequency and duration of laryngoscope use vary significantly across different medical specialties. Anesthesiologists and emergency medicine physicians tend to perform intubations more frequently, sometimes multiple times per shift. In contrast, other specialists may only occasionally need to use a laryngoscope. This variation in usage patterns underscores the importance of handle designs that can accommodate a wide range of user preferences and physical attributes.
Training and familiarity also play crucial roles in clinical usage patterns. Many clinicians develop habits and techniques based on their initial training with traditional handle designs. Introducing new ergonomic designs often requires a period of adaptation and retraining to fully realize the benefits. Some institutions have implemented simulation-based training programs to help clinicians transition to newer, more ergonomic handle designs.
The impact of handle design on clinical efficiency and patient outcomes is an area of ongoing research. Some studies suggest that ergonomic designs may lead to faster intubation times and improved first-attempt success rates, particularly in difficult airway cases. However, more comprehensive data is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of handle design on clinical performance and patient safety.
In typical clinical scenarios, practitioners must adopt awkward postures to align the laryngoscope blade with the patient's airway. This often results in excessive wrist extension and ulnar deviation, particularly when intubating patients in hospital beds or on operating tables. Such positioning can lead to fatigue and potential repetitive strain injuries over time.
Recent ergonomic studies have shown that angled or articulating handle designs can improve clinician comfort and reduce physical strain during intubation. These designs allow for a more natural wrist position and better leverage, especially in challenging airway scenarios. As a result, there has been a gradual shift towards adopting these ergonomic handle designs in many clinical settings.
The frequency and duration of laryngoscope use vary significantly across different medical specialties. Anesthesiologists and emergency medicine physicians tend to perform intubations more frequently, sometimes multiple times per shift. In contrast, other specialists may only occasionally need to use a laryngoscope. This variation in usage patterns underscores the importance of handle designs that can accommodate a wide range of user preferences and physical attributes.
Training and familiarity also play crucial roles in clinical usage patterns. Many clinicians develop habits and techniques based on their initial training with traditional handle designs. Introducing new ergonomic designs often requires a period of adaptation and retraining to fully realize the benefits. Some institutions have implemented simulation-based training programs to help clinicians transition to newer, more ergonomic handle designs.
The impact of handle design on clinical efficiency and patient outcomes is an area of ongoing research. Some studies suggest that ergonomic designs may lead to faster intubation times and improved first-attempt success rates, particularly in difficult airway cases. However, more comprehensive data is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of handle design on clinical performance and patient safety.
Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory landscape surrounding laryngoscope handle design is complex and multifaceted, involving various agencies and standards that aim to ensure patient safety and clinician well-being. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating medical devices, including laryngoscopes. The FDA classifies laryngoscopes as Class I medical devices, which are subject to general controls but typically exempt from premarket notification requirements.
However, manufacturers must still adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and register their establishments with the FDA. The agency also requires reporting of adverse events related to device use, which can inform future regulatory decisions and design improvements. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for workplace ergonomics that indirectly influence laryngoscope handle design.
International standards also play a significant role in shaping laryngoscope handle design. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed specific standards, such as ISO 7376:2020, which outlines requirements for laryngoscopes and handles. These standards address aspects like dimensions, materials, and performance characteristics, which can impact ergonomics.
In the European Union, laryngoscopes fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into full effect in May 2021. The MDR places a stronger emphasis on clinical evidence and post-market surveillance, potentially driving manufacturers to focus more on ergonomic considerations in their designs. Compliance with these regulations often requires manufacturers to conduct usability studies and risk assessments, which can highlight ergonomic issues and lead to design improvements.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the importance of human factors and ergonomics in medical device design. The FDA has issued guidance documents on applying human factors and usability engineering to medical devices, which can influence laryngoscope handle design. These guidelines emphasize the need for user-centered design processes and thorough usability testing to minimize use-related hazards.
As awareness of clinician ergonomics grows, there is potential for more specific regulations or standards focused on the ergonomic aspects of medical devices like laryngoscopes. This could lead to more stringent requirements for handle designs that minimize physical strain and improve user comfort during procedures. Manufacturers may need to provide more comprehensive ergonomic data and user studies as part of their regulatory submissions in the future.
However, manufacturers must still adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and register their establishments with the FDA. The agency also requires reporting of adverse events related to device use, which can inform future regulatory decisions and design improvements. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for workplace ergonomics that indirectly influence laryngoscope handle design.
International standards also play a significant role in shaping laryngoscope handle design. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed specific standards, such as ISO 7376:2020, which outlines requirements for laryngoscopes and handles. These standards address aspects like dimensions, materials, and performance characteristics, which can impact ergonomics.
In the European Union, laryngoscopes fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into full effect in May 2021. The MDR places a stronger emphasis on clinical evidence and post-market surveillance, potentially driving manufacturers to focus more on ergonomic considerations in their designs. Compliance with these regulations often requires manufacturers to conduct usability studies and risk assessments, which can highlight ergonomic issues and lead to design improvements.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the importance of human factors and ergonomics in medical device design. The FDA has issued guidance documents on applying human factors and usability engineering to medical devices, which can influence laryngoscope handle design. These guidelines emphasize the need for user-centered design processes and thorough usability testing to minimize use-related hazards.
As awareness of clinician ergonomics grows, there is potential for more specific regulations or standards focused on the ergonomic aspects of medical devices like laryngoscopes. This could lead to more stringent requirements for handle designs that minimize physical strain and improve user comfort during procedures. Manufacturers may need to provide more comprehensive ergonomic data and user studies as part of their regulatory submissions in the future.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!