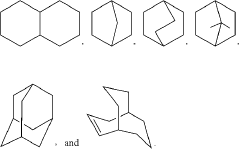
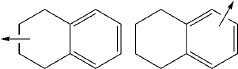
How Tautomerization Influences Drug Metabolite Formation?
JUL 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Tautomerization in Drug Metabolism: Background and Objectives
Tautomerization is a fundamental chemical process that plays a crucial role in drug metabolism. This phenomenon involves the rapid interconversion between structural isomers, known as tautomers, which can significantly influence the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of drugs. The study of tautomerization in drug metabolism has gained increasing attention in recent years due to its profound impact on drug efficacy, toxicity, and overall therapeutic outcomes.
The historical context of tautomerization research dates back to the late 19th century when chemists first observed the dynamic equilibrium between different molecular structures. However, its relevance to drug metabolism was not fully appreciated until the advent of modern analytical techniques and computational methods in the latter half of the 20th century. This technological progress has enabled researchers to delve deeper into the intricacies of tautomeric transformations and their implications for drug design and development.
In the pharmaceutical industry, understanding tautomerization is critical for predicting drug behavior in biological systems. Tautomeric shifts can alter a drug's physicochemical properties, including solubility, lipophilicity, and binding affinity to target proteins. These changes can, in turn, affect the drug's absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) profile, ultimately impacting its therapeutic efficacy and potential side effects.
The primary objective of studying tautomerization in drug metabolism is to enhance the rational design of pharmaceutical compounds. By elucidating the tautomeric preferences of drug molecules under physiological conditions, researchers aim to optimize drug candidates for improved stability, bioavailability, and target specificity. Additionally, understanding tautomerization can help predict potential metabolic pathways and identify metabolites that may contribute to drug activity or toxicity.
Recent technological advancements have propelled the field forward, with high-resolution spectroscopic techniques, advanced chromatography methods, and sophisticated computational modeling tools enabling more accurate characterization of tautomeric equilibria. These developments have paved the way for a more comprehensive understanding of how tautomerization influences drug metabolite formation and, consequently, drug efficacy and safety.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to face challenges in developing new, effective therapies, the study of tautomerization in drug metabolism remains a critical area of research. Future directions in this field are likely to focus on integrating tautomerization considerations into early-stage drug discovery processes, developing predictive models for tautomeric behavior in complex biological environments, and exploring the potential of tautomerization as a strategy for designing novel prodrugs and improving existing medications.
The historical context of tautomerization research dates back to the late 19th century when chemists first observed the dynamic equilibrium between different molecular structures. However, its relevance to drug metabolism was not fully appreciated until the advent of modern analytical techniques and computational methods in the latter half of the 20th century. This technological progress has enabled researchers to delve deeper into the intricacies of tautomeric transformations and their implications for drug design and development.
In the pharmaceutical industry, understanding tautomerization is critical for predicting drug behavior in biological systems. Tautomeric shifts can alter a drug's physicochemical properties, including solubility, lipophilicity, and binding affinity to target proteins. These changes can, in turn, affect the drug's absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) profile, ultimately impacting its therapeutic efficacy and potential side effects.
The primary objective of studying tautomerization in drug metabolism is to enhance the rational design of pharmaceutical compounds. By elucidating the tautomeric preferences of drug molecules under physiological conditions, researchers aim to optimize drug candidates for improved stability, bioavailability, and target specificity. Additionally, understanding tautomerization can help predict potential metabolic pathways and identify metabolites that may contribute to drug activity or toxicity.
Recent technological advancements have propelled the field forward, with high-resolution spectroscopic techniques, advanced chromatography methods, and sophisticated computational modeling tools enabling more accurate characterization of tautomeric equilibria. These developments have paved the way for a more comprehensive understanding of how tautomerization influences drug metabolite formation and, consequently, drug efficacy and safety.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to face challenges in developing new, effective therapies, the study of tautomerization in drug metabolism remains a critical area of research. Future directions in this field are likely to focus on integrating tautomerization considerations into early-stage drug discovery processes, developing predictive models for tautomeric behavior in complex biological environments, and exploring the potential of tautomerization as a strategy for designing novel prodrugs and improving existing medications.
Market Demand for Improved Drug Metabolism Prediction
The pharmaceutical industry is experiencing a growing demand for improved drug metabolism prediction methods, particularly those that account for tautomerization effects. This demand is driven by several factors, including the increasing complexity of drug candidates, the need for more accurate toxicity assessments, and the desire to reduce late-stage failures in drug development.
Tautomerization, a process where a molecule can exist in multiple structural isomers that readily interconvert, plays a crucial role in drug metabolism. It can significantly affect a drug's bioavailability, efficacy, and safety profile. As such, there is a pressing need for tools and methodologies that can accurately predict how tautomerization influences drug metabolite formation.
The market for improved drug metabolism prediction is expanding rapidly. Pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in computational methods and in silico tools that can model tautomerization effects on drug metabolism. This investment is driven by the potential to reduce the time and cost associated with drug discovery and development processes.
Furthermore, regulatory agencies are increasingly emphasizing the importance of understanding drug metabolism, including the impact of tautomerization, in safety assessments. This regulatory focus has created additional market pressure for more sophisticated prediction tools.
The demand for improved prediction methods extends beyond traditional pharmaceutical companies. Contract research organizations (CROs) specializing in drug metabolism studies are also seeking advanced tools to enhance their service offerings. Additionally, academic institutions and research centers are contributing to the development of new prediction methodologies, further fueling market growth.
There is also a growing interest in personalized medicine, which requires a deeper understanding of how individual genetic variations affect drug metabolism. Tautomerization-aware prediction tools are becoming essential in this context, as they can help identify potential metabolic differences among patient populations.
The market is not limited to small molecule drugs. As biologics and other complex therapeutics gain prominence, there is an increasing need for prediction tools that can handle these more intricate molecular structures and their potential tautomeric forms.
In conclusion, the market demand for improved drug metabolism prediction, particularly concerning tautomerization effects, is robust and multifaceted. It spans across various sectors of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, driven by the need for more efficient drug development processes, enhanced safety assessments, and the pursuit of personalized medicine approaches.
Tautomerization, a process where a molecule can exist in multiple structural isomers that readily interconvert, plays a crucial role in drug metabolism. It can significantly affect a drug's bioavailability, efficacy, and safety profile. As such, there is a pressing need for tools and methodologies that can accurately predict how tautomerization influences drug metabolite formation.
The market for improved drug metabolism prediction is expanding rapidly. Pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in computational methods and in silico tools that can model tautomerization effects on drug metabolism. This investment is driven by the potential to reduce the time and cost associated with drug discovery and development processes.
Furthermore, regulatory agencies are increasingly emphasizing the importance of understanding drug metabolism, including the impact of tautomerization, in safety assessments. This regulatory focus has created additional market pressure for more sophisticated prediction tools.
The demand for improved prediction methods extends beyond traditional pharmaceutical companies. Contract research organizations (CROs) specializing in drug metabolism studies are also seeking advanced tools to enhance their service offerings. Additionally, academic institutions and research centers are contributing to the development of new prediction methodologies, further fueling market growth.
There is also a growing interest in personalized medicine, which requires a deeper understanding of how individual genetic variations affect drug metabolism. Tautomerization-aware prediction tools are becoming essential in this context, as they can help identify potential metabolic differences among patient populations.
The market is not limited to small molecule drugs. As biologics and other complex therapeutics gain prominence, there is an increasing need for prediction tools that can handle these more intricate molecular structures and their potential tautomeric forms.
In conclusion, the market demand for improved drug metabolism prediction, particularly concerning tautomerization effects, is robust and multifaceted. It spans across various sectors of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, driven by the need for more efficient drug development processes, enhanced safety assessments, and the pursuit of personalized medicine approaches.
Current Challenges in Tautomer-Mediated Metabolite Formation
The field of tautomer-mediated metabolite formation in drug metabolism faces several significant challenges that hinder our understanding and prediction capabilities. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of tautomeric equilibria in biological systems. The dynamic nature of tautomerization, influenced by factors such as pH, temperature, and solvent effects, makes it difficult to accurately determine which tautomeric form predominates in vivo.
Another challenge lies in the limitations of current analytical techniques. While advanced spectroscopic methods have improved our ability to detect and characterize tautomers, they often fall short when dealing with rapid interconversions or low-abundance species. This gap in detection capabilities can lead to incomplete metabolite profiles and potentially overlooked drug-related toxicities.
The prediction of tautomer-specific metabolism poses a significant hurdle for computational approaches. Existing in silico models struggle to account for the subtle structural changes associated with tautomerization and their impact on enzyme-substrate interactions. This limitation affects the accuracy of metabolite prediction tools and complicates drug design efforts aimed at optimizing metabolic stability.
Furthermore, the lack of standardized protocols for incorporating tautomerization into drug metabolism studies creates inconsistencies across research and regulatory frameworks. This absence of unified approaches hampers the systematic evaluation of tautomer-related effects and impedes the development of comprehensive guidelines for drug development and safety assessment.
The interplay between tautomerization and drug-drug interactions presents another layer of complexity. Tautomeric shifts can alter a compound's ability to inhibit or induce metabolic enzymes, potentially leading to unexpected pharmacokinetic profiles when drugs are co-administered. Current methods for predicting and managing these interactions often overlook the role of tautomerization, resulting in potential safety risks.
Lastly, the challenge of integrating tautomer considerations into high-throughput screening and lead optimization processes remains significant. The additional computational and experimental resources required to account for tautomeric forms can slow down drug discovery pipelines and increase development costs. Striking a balance between thoroughness and efficiency in addressing tautomerization during early-stage drug development continues to be a point of contention in the pharmaceutical industry.
Another challenge lies in the limitations of current analytical techniques. While advanced spectroscopic methods have improved our ability to detect and characterize tautomers, they often fall short when dealing with rapid interconversions or low-abundance species. This gap in detection capabilities can lead to incomplete metabolite profiles and potentially overlooked drug-related toxicities.
The prediction of tautomer-specific metabolism poses a significant hurdle for computational approaches. Existing in silico models struggle to account for the subtle structural changes associated with tautomerization and their impact on enzyme-substrate interactions. This limitation affects the accuracy of metabolite prediction tools and complicates drug design efforts aimed at optimizing metabolic stability.
Furthermore, the lack of standardized protocols for incorporating tautomerization into drug metabolism studies creates inconsistencies across research and regulatory frameworks. This absence of unified approaches hampers the systematic evaluation of tautomer-related effects and impedes the development of comprehensive guidelines for drug development and safety assessment.
The interplay between tautomerization and drug-drug interactions presents another layer of complexity. Tautomeric shifts can alter a compound's ability to inhibit or induce metabolic enzymes, potentially leading to unexpected pharmacokinetic profiles when drugs are co-administered. Current methods for predicting and managing these interactions often overlook the role of tautomerization, resulting in potential safety risks.
Lastly, the challenge of integrating tautomer considerations into high-throughput screening and lead optimization processes remains significant. The additional computational and experimental resources required to account for tautomeric forms can slow down drug discovery pipelines and increase development costs. Striking a balance between thoroughness and efficiency in addressing tautomerization during early-stage drug development continues to be a point of contention in the pharmaceutical industry.
Existing Approaches to Predict Tautomer-Influenced Metabolites
01 Tautomerization in drug metabolism
Tautomerization plays a crucial role in drug metabolism, affecting the formation of drug metabolites. This process involves the interconversion between structural isomers, which can significantly impact the pharmacological properties and metabolic fate of drugs. Understanding tautomerization is essential for predicting drug metabolism and potential drug-drug interactions.- Tautomerization in drug metabolism: Tautomerization plays a crucial role in drug metabolism, affecting the formation of drug metabolites. This process involves the interconversion of structural isomers, which can significantly impact the pharmacological properties and metabolic pathways of drugs. Understanding tautomerization is essential for predicting drug behavior and potential metabolite formation in the body.
- Analytical methods for detecting tautomeric metabolites: Various analytical techniques are employed to detect and characterize tautomeric drug metabolites. These methods include mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and chromatographic techniques. Advanced analytical approaches help researchers identify and quantify tautomeric forms of drug metabolites, providing crucial information for drug development and safety assessment.
- Computational modeling of tautomerization in drug metabolism: Computational methods are increasingly used to predict and model tautomerization in drug metabolism. These in silico approaches employ quantum mechanical calculations, molecular dynamics simulations, and machine learning algorithms to forecast potential tautomeric forms of drug molecules and their metabolites. Such predictive tools aid in the early stages of drug discovery and development.
- Impact of tautomerization on drug-target interactions: Tautomerization can significantly influence drug-target interactions, affecting the binding affinity and specificity of drugs to their molecular targets. The interconversion between tautomeric forms may alter the electronic properties and three-dimensional structure of drug molecules, potentially modifying their interaction with receptors, enzymes, or other biological targets. This phenomenon has important implications for drug efficacy and side effects.
- Tautomerization-induced toxicity in drug metabolism: Tautomerization during drug metabolism can sometimes lead to the formation of toxic metabolites. The interconversion between tautomeric forms may result in reactive intermediates or metabolites with increased toxicity compared to the parent drug. Understanding and predicting such tautomerization-induced toxicity is crucial for drug safety assessment and the development of safer pharmaceutical compounds.
02 Analytical methods for detecting tautomeric metabolites
Various analytical techniques are employed to detect and characterize tautomeric drug metabolites. These methods may include mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and chromatographic techniques. Advanced analytical approaches help researchers identify and quantify tautomeric forms of drug metabolites, providing valuable insights into drug metabolism pathways.Expand Specific Solutions03 Computational modeling of tautomerization in drug metabolism
Computational methods are utilized to predict and model tautomerization processes in drug metabolism. These in silico approaches help researchers understand the energetics and kinetics of tautomeric interconversions, allowing for more accurate predictions of drug metabolite formation. Such models can aid in drug design and optimization by anticipating potential metabolic issues early in the development process.Expand Specific Solutions04 Impact of tautomerization on drug-target interactions
Tautomerization can significantly affect drug-target interactions by altering the structural and electronic properties of drug molecules. This process may lead to changes in binding affinity, selectivity, and overall efficacy of drugs. Understanding the tautomeric behavior of drugs is crucial for optimizing their interactions with target proteins and predicting potential off-target effects.Expand Specific Solutions05 Tautomerization-induced toxicity in drug metabolism
Tautomerization during drug metabolism can potentially lead to the formation of toxic metabolites. This process may result in unexpected chemical reactivity or altered interactions with biological systems, potentially causing adverse effects. Identifying and characterizing tautomeric metabolites that may contribute to drug toxicity is crucial for ensuring drug safety and efficacy in pharmaceutical development.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Tautomerization and Drug Metabolism Research
The field of drug metabolite formation through tautomerization is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global pharmaceutical industry's focus on drug metabolism and safety has driven research in this area, with the market expected to expand significantly in the coming years. Technologically, the field is progressing rapidly, with companies like Auspex Pharmaceuticals, Janssen Pharmaceutica, and Merck & Co. leading innovation. These firms are developing sophisticated methods to predict and control tautomerization in drug design, enhancing drug efficacy and safety profiles. Academic institutions such as China Pharmaceutical University and Université Laval are also contributing to the field's advancement through fundamental research and collaborations with industry partners.
Janssen Pharmaceutica NV
Technical Solution: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV has developed a multi-faceted strategy to investigate tautomerization's role in drug metabolite formation. Their approach integrates in silico modeling, in vitro assays, and in vivo studies to provide a holistic understanding of tautomeric effects. Janssen employs machine learning algorithms trained on extensive datasets to predict tautomeric propensities and their potential impact on metabolic pathways[4]. They have also developed novel NMR techniques to study tautomeric interconversion rates in physiologically relevant conditions, providing crucial kinetic data for metabolite prediction[5]. Furthermore, Janssen has pioneered the use of isotope-labeled compounds to track tautomer-specific metabolite formation in preclinical animal models, offering unique insights into the in vivo relevance of tautomerization in drug metabolism[6].
Strengths: Integrated approach spanning in silico to in vivo studies; innovative use of isotope labeling for in vivo tracking. Weaknesses: Complexity of translating multi-system data into actionable insights for drug development; potential limitations in scaling isotope labeling studies to larger compound sets.
Merck & Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Merck & Co., Inc. has developed a comprehensive approach to studying tautomerization's influence on drug metabolite formation. They utilize advanced computational methods, including quantum mechanical calculations and molecular dynamics simulations, to predict tautomeric equilibria and their impact on drug metabolism[1]. Their research focuses on identifying key tautomeric forms that may lead to unexpected metabolites or altered pharmacokinetics. Merck has also implemented high-throughput screening techniques to experimentally validate computational predictions, allowing for rapid assessment of tautomerization effects across large compound libraries[2]. Additionally, they have developed specialized mass spectrometry methods to detect and quantify tautomeric species in biological samples, providing crucial insights into the in vivo relevance of tautomerization in drug metabolism[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining computational and experimental methods; extensive resources for high-throughput screening and advanced analytics. Weaknesses: Potential overreliance on computational predictions; challenges in translating in vitro findings to in vivo relevance.
Core Innovations in Tautomerization-Aware Drug Design
Inhibitors of anoctamin 6 protein and uses thereof
PatentInactiveUS20230080054A1
Innovation
- Development of specific compounds represented by Formula (I), (II), (III), (IV), and (V) that can inhibit ANO6 activity, which are administered to effectively treat or prevent ANO6-related diseases by modulating ion channel and phospholipid scrambling functions.
Competitive substrate inhibition to increase drug bioavailability
PatentWO2007133476A2
Innovation
- Administering a competitive inhibitor that competes with the drug for metabolizing enzymes, such as bioflavonoids, to reduce presystemic metabolism and enhance systemic bioavailability by co-administering them orally with the drug.
Regulatory Considerations for Tautomer-Related Drug Development
Regulatory considerations play a crucial role in the development of drugs involving tautomers. Tautomerization, the process by which a compound can exist in multiple structural forms, presents unique challenges for drug developers and regulatory agencies alike. The dynamic nature of tautomers can significantly impact drug metabolism, efficacy, and safety profiles, necessitating careful attention throughout the drug development process.
One of the primary regulatory concerns is the accurate identification and characterization of all relevant tautomeric forms of a drug candidate. Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA and EMA, require comprehensive data on the physicochemical properties, stability, and interconversion rates of tautomers. This information is essential for assessing the potential impact on drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties.
In the context of drug metabolite formation, regulatory bodies emphasize the importance of understanding how tautomerization may influence the generation of metabolites. Developers must demonstrate a thorough understanding of the metabolic pathways and potential metabolites arising from different tautomeric forms. This includes identifying any unique metabolites that may be formed due to tautomerization and assessing their safety profiles.
The selection of the most appropriate tautomeric form for drug development is another critical regulatory consideration. Developers must provide a strong scientific rationale for their choice, supported by data on stability, bioavailability, and efficacy. Regulatory agencies may require additional studies to evaluate the potential for interconversion between tautomers in vivo and its impact on drug performance.
From a quality control perspective, regulatory guidelines emphasize the need for robust analytical methods capable of detecting and quantifying different tautomeric forms. These methods must be validated to ensure accurate characterization of the drug substance and product throughout the manufacturing process and shelf life. Stability studies should account for potential tautomeric interconversions under various storage conditions.
Regulatory submissions for tautomer-related drugs often require more extensive documentation compared to traditional single-form compounds. This includes detailed information on tautomer characterization, interconversion kinetics, and the potential impact on drug-drug interactions. Developers may need to provide data from specialized studies designed to address tautomer-specific concerns.
In the realm of intellectual property, regulatory considerations extend to patent protection strategies for tautomeric drugs. Developers must navigate the complexities of patenting multiple tautomeric forms while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements for drug approval. This often involves a delicate balance between maximizing patent protection and meeting regulatory expectations for drug characterization and quality control.
One of the primary regulatory concerns is the accurate identification and characterization of all relevant tautomeric forms of a drug candidate. Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA and EMA, require comprehensive data on the physicochemical properties, stability, and interconversion rates of tautomers. This information is essential for assessing the potential impact on drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties.
In the context of drug metabolite formation, regulatory bodies emphasize the importance of understanding how tautomerization may influence the generation of metabolites. Developers must demonstrate a thorough understanding of the metabolic pathways and potential metabolites arising from different tautomeric forms. This includes identifying any unique metabolites that may be formed due to tautomerization and assessing their safety profiles.
The selection of the most appropriate tautomeric form for drug development is another critical regulatory consideration. Developers must provide a strong scientific rationale for their choice, supported by data on stability, bioavailability, and efficacy. Regulatory agencies may require additional studies to evaluate the potential for interconversion between tautomers in vivo and its impact on drug performance.
From a quality control perspective, regulatory guidelines emphasize the need for robust analytical methods capable of detecting and quantifying different tautomeric forms. These methods must be validated to ensure accurate characterization of the drug substance and product throughout the manufacturing process and shelf life. Stability studies should account for potential tautomeric interconversions under various storage conditions.
Regulatory submissions for tautomer-related drugs often require more extensive documentation compared to traditional single-form compounds. This includes detailed information on tautomer characterization, interconversion kinetics, and the potential impact on drug-drug interactions. Developers may need to provide data from specialized studies designed to address tautomer-specific concerns.
In the realm of intellectual property, regulatory considerations extend to patent protection strategies for tautomeric drugs. Developers must navigate the complexities of patenting multiple tautomeric forms while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements for drug approval. This often involves a delicate balance between maximizing patent protection and meeting regulatory expectations for drug characterization and quality control.
In Silico Tools for Tautomerization Analysis in Drug Discovery
In silico tools for tautomerization analysis have become indispensable in modern drug discovery processes, offering efficient and cost-effective methods to predict and analyze tautomeric forms of drug candidates. These computational approaches leverage advanced algorithms and chemical databases to simulate tautomerization phenomena, providing valuable insights into potential metabolite formation.
One of the primary categories of in silico tools for tautomerization analysis is structure-based prediction software. These programs utilize molecular mechanics and quantum mechanical calculations to evaluate the energetics and stability of different tautomeric forms. By considering factors such as bond lengths, angles, and electronic distributions, these tools can generate comprehensive lists of possible tautomers for a given compound.
Another crucial class of in silico tools focuses on rule-based tautomer generation. These systems employ predefined chemical rules and heuristics to identify potential tautomeric transformations. By applying these rules systematically, they can rapidly generate and enumerate tautomers, even for complex molecular structures. This approach is particularly useful for high-throughput screening of large compound libraries.
Machine learning-based tautomerization prediction tools have gained significant traction in recent years. These models are trained on extensive datasets of known tautomeric pairs and can learn intricate patterns and relationships between molecular structures and their tautomeric behaviors. Deep learning architectures, such as graph neural networks, have shown promising results in accurately predicting tautomeric equilibria and relative stabilities.
Quantum chemical methods, while computationally intensive, offer the highest level of accuracy in tautomerization analysis. Ab initio and density functional theory (DFT) calculations can provide detailed insights into the electronic structures and energetics of tautomers. These methods are particularly valuable for studying complex tautomeric systems or when experimental data is limited.
Integration of tautomerization analysis tools with other in silico drug discovery platforms has greatly enhanced their utility. By combining tautomer prediction with ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion) modeling and toxicity prediction software, researchers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of how tautomerization may influence drug metabolism and overall pharmacokinetic properties.
As the field of computational chemistry continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in the accuracy and efficiency of in silico tautomerization analysis tools. The integration of artificial intelligence and big data approaches is likely to yield more sophisticated predictive models, enabling researchers to better navigate the complex landscape of drug metabolite formation influenced by tautomerization.
One of the primary categories of in silico tools for tautomerization analysis is structure-based prediction software. These programs utilize molecular mechanics and quantum mechanical calculations to evaluate the energetics and stability of different tautomeric forms. By considering factors such as bond lengths, angles, and electronic distributions, these tools can generate comprehensive lists of possible tautomers for a given compound.
Another crucial class of in silico tools focuses on rule-based tautomer generation. These systems employ predefined chemical rules and heuristics to identify potential tautomeric transformations. By applying these rules systematically, they can rapidly generate and enumerate tautomers, even for complex molecular structures. This approach is particularly useful for high-throughput screening of large compound libraries.
Machine learning-based tautomerization prediction tools have gained significant traction in recent years. These models are trained on extensive datasets of known tautomeric pairs and can learn intricate patterns and relationships between molecular structures and their tautomeric behaviors. Deep learning architectures, such as graph neural networks, have shown promising results in accurately predicting tautomeric equilibria and relative stabilities.
Quantum chemical methods, while computationally intensive, offer the highest level of accuracy in tautomerization analysis. Ab initio and density functional theory (DFT) calculations can provide detailed insights into the electronic structures and energetics of tautomers. These methods are particularly valuable for studying complex tautomeric systems or when experimental data is limited.
Integration of tautomerization analysis tools with other in silico drug discovery platforms has greatly enhanced their utility. By combining tautomer prediction with ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion) modeling and toxicity prediction software, researchers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of how tautomerization may influence drug metabolism and overall pharmacokinetic properties.
As the field of computational chemistry continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in the accuracy and efficiency of in silico tautomerization analysis tools. The integration of artificial intelligence and big data approaches is likely to yield more sophisticated predictive models, enabling researchers to better navigate the complex landscape of drug metabolite formation influenced by tautomerization.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!