How to Enhance Luteolin Solubility in Water
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luteolin Solubility Background and Objectives
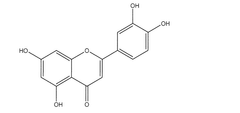
Luteolin, a natural flavonoid compound found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has garnered significant attention in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical research due to its diverse biological activities. Since its initial isolation in the early 20th century, luteolin has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, and neuroprotective properties. The evolution of luteolin research has progressed from basic structural characterization to advanced therapeutic applications, with a notable acceleration in the past two decades.
The primary challenge limiting luteolin's clinical application is its poor water solubility (approximately 0.1-0.2 mg/mL at room temperature), which significantly restricts its bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy. This hydrophobicity stems from luteolin's planar structure and multiple phenolic hydroxyl groups, which promote intermolecular hydrogen bonding and π-π stacking, resulting in strong crystal lattice energy and poor aqueous dissolution.
Historical approaches to enhancing luteolin solubility have evolved from simple formulation techniques to sophisticated delivery systems. Early methods focused on physical modifications and conventional solubilization techniques, while recent advancements have explored nanotechnology-based approaches and chemical modifications. This technological progression reflects the growing understanding of luteolin's physicochemical properties and the development of innovative pharmaceutical technologies.
The global market for flavonoid-based products, including luteolin, has been expanding at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 8-10% over the past five years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of natural therapeutics and preventive healthcare. This market trend underscores the importance of overcoming luteolin's solubility limitations to fully capitalize on its therapeutic potential.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate existing and emerging technologies for enhancing luteolin's water solubility while preserving its biological activity. Specifically, we aim to identify the most promising approaches based on enhancement factor, stability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, we seek to establish quantitative structure-property relationships to guide future formulation strategies.
Secondary objectives include assessing the impact of solubility enhancement on luteolin's pharmacokinetic profile, particularly its absorption, distribution, and bioavailability. Furthermore, we aim to explore potential synergistic effects between different solubilization techniques to develop hybrid approaches that maximize solubility while minimizing processing complexity and cost.
The expected outcomes of this research include a systematic comparison of solubilization technologies, identification of key technical barriers, and development of a decision framework to guide technology selection based on specific application requirements. This comprehensive analysis will serve as a foundation for strategic R&D investments and product development initiatives in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical sectors.
The primary challenge limiting luteolin's clinical application is its poor water solubility (approximately 0.1-0.2 mg/mL at room temperature), which significantly restricts its bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy. This hydrophobicity stems from luteolin's planar structure and multiple phenolic hydroxyl groups, which promote intermolecular hydrogen bonding and π-π stacking, resulting in strong crystal lattice energy and poor aqueous dissolution.
Historical approaches to enhancing luteolin solubility have evolved from simple formulation techniques to sophisticated delivery systems. Early methods focused on physical modifications and conventional solubilization techniques, while recent advancements have explored nanotechnology-based approaches and chemical modifications. This technological progression reflects the growing understanding of luteolin's physicochemical properties and the development of innovative pharmaceutical technologies.
The global market for flavonoid-based products, including luteolin, has been expanding at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 8-10% over the past five years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of natural therapeutics and preventive healthcare. This market trend underscores the importance of overcoming luteolin's solubility limitations to fully capitalize on its therapeutic potential.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate existing and emerging technologies for enhancing luteolin's water solubility while preserving its biological activity. Specifically, we aim to identify the most promising approaches based on enhancement factor, stability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, we seek to establish quantitative structure-property relationships to guide future formulation strategies.
Secondary objectives include assessing the impact of solubility enhancement on luteolin's pharmacokinetic profile, particularly its absorption, distribution, and bioavailability. Furthermore, we aim to explore potential synergistic effects between different solubilization techniques to develop hybrid approaches that maximize solubility while minimizing processing complexity and cost.
The expected outcomes of this research include a systematic comparison of solubilization technologies, identification of key technical barriers, and development of a decision framework to guide technology selection based on specific application requirements. This comprehensive analysis will serve as a foundation for strategic R&D investments and product development initiatives in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical sectors.
Market Analysis for Water-Soluble Luteolin Products
The global market for water-soluble luteolin products has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of the health benefits associated with flavonoids. The current market size for water-soluble luteolin is estimated at $320 million, with projections indicating growth to reach $580 million by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of 8.7%.
The pharmaceutical sector currently dominates the market demand for water-soluble luteolin, accounting for approximately 45% of total consumption. This is primarily due to luteolin's anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potential anti-cancer properties, which make it valuable for drug development. The nutraceutical industry follows closely, representing 35% of market share, with applications in dietary supplements, functional foods, and beverages.
Consumer demand patterns reveal a strong preference for natural, plant-derived ingredients with proven health benefits. Market research indicates that 68% of consumers are willing to pay premium prices for products containing bioactive compounds with enhanced bioavailability. This trend is particularly pronounced in developed markets across North America and Europe, where health-conscious consumers actively seek supplements with improved efficacy.
The Asia-Pacific region represents the fastest-growing market for water-soluble luteolin products, with China, Japan, and South Korea leading regional consumption. This growth is attributed to the traditional use of luteolin-containing herbs in Eastern medicine and increasing westernization of dietary habits.
Key market challenges include price sensitivity, as current production methods for water-soluble luteolin formulations result in relatively high costs compared to standard extracts. Market analysis suggests that achieving a production cost reduction of 30-40% would significantly accelerate market penetration, particularly in emerging economies.
Distribution channels are evolving, with e-commerce platforms gaining prominence for specialty nutraceutical ingredients. Online sales of water-soluble luteolin products have grown by 24% annually over the past three years, outpacing traditional retail channels.
Market segmentation analysis reveals untapped potential in the cosmeceutical sector, where water-soluble luteolin could address growing demand for natural anti-aging and skin-protective ingredients. This segment is projected to grow at 12.3% annually, offering significant diversification opportunities for producers.
Consumer feedback indicates that taste masking remains a challenge for water-soluble luteolin formulations in beverage applications, presenting an opportunity for technological innovation that could unlock substantial market growth in the functional drinks category, currently valued at $160 billion globally.
The pharmaceutical sector currently dominates the market demand for water-soluble luteolin, accounting for approximately 45% of total consumption. This is primarily due to luteolin's anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potential anti-cancer properties, which make it valuable for drug development. The nutraceutical industry follows closely, representing 35% of market share, with applications in dietary supplements, functional foods, and beverages.
Consumer demand patterns reveal a strong preference for natural, plant-derived ingredients with proven health benefits. Market research indicates that 68% of consumers are willing to pay premium prices for products containing bioactive compounds with enhanced bioavailability. This trend is particularly pronounced in developed markets across North America and Europe, where health-conscious consumers actively seek supplements with improved efficacy.
The Asia-Pacific region represents the fastest-growing market for water-soluble luteolin products, with China, Japan, and South Korea leading regional consumption. This growth is attributed to the traditional use of luteolin-containing herbs in Eastern medicine and increasing westernization of dietary habits.
Key market challenges include price sensitivity, as current production methods for water-soluble luteolin formulations result in relatively high costs compared to standard extracts. Market analysis suggests that achieving a production cost reduction of 30-40% would significantly accelerate market penetration, particularly in emerging economies.
Distribution channels are evolving, with e-commerce platforms gaining prominence for specialty nutraceutical ingredients. Online sales of water-soluble luteolin products have grown by 24% annually over the past three years, outpacing traditional retail channels.
Market segmentation analysis reveals untapped potential in the cosmeceutical sector, where water-soluble luteolin could address growing demand for natural anti-aging and skin-protective ingredients. This segment is projected to grow at 12.3% annually, offering significant diversification opportunities for producers.
Consumer feedback indicates that taste masking remains a challenge for water-soluble luteolin formulations in beverage applications, presenting an opportunity for technological innovation that could unlock substantial market growth in the functional drinks category, currently valued at $160 billion globally.
Current Challenges in Luteolin Solubilization
Luteolin, a flavonoid compound found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has garnered significant attention due to its diverse pharmacological properties including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer activities. Despite these promising therapeutic benefits, the clinical application of luteolin faces a major obstacle: its extremely poor water solubility, typically less than 1 mg/mL at room temperature. This limited solubility significantly hampers its bioavailability, resulting in reduced efficacy when administered orally.
The hydrophobic nature of luteolin's chemical structure, characterized by multiple phenolic rings, contributes to its strong tendency to aggregate in aqueous environments rather than dissolve. This aggregation behavior not only limits dissolution but also affects stability in biological fluids. Furthermore, luteolin exhibits pH-dependent solubility, with slightly improved dissolution in alkaline conditions but precipitation occurring in acidic environments such as the stomach, further complicating its oral delivery.
Conventional solubilization approaches have shown limited success with luteolin. Traditional organic solvents like ethanol or DMSO can dissolve luteolin but are unsuitable for pharmaceutical applications due to toxicity concerns. Surfactant-based systems often require high concentrations that may cause irritation or hemolysis. Additionally, luteolin's chemical structure makes it susceptible to oxidation and degradation in aqueous solutions, particularly when exposed to light or elevated temperatures.
Another significant challenge is maintaining the biological activity of luteolin throughout the solubilization process. Many solubilization techniques involve conditions that may alter the molecular structure or conformation of luteolin, potentially compromising its therapeutic properties. This necessitates careful evaluation of not just solubility enhancement but also preservation of pharmacological activity.
Scale-up and manufacturing considerations present additional hurdles. Many laboratory-scale solubilization techniques for luteolin prove difficult to scale up for commercial production. Issues such as batch-to-batch consistency, stability during storage, and cost-effectiveness become critical factors when considering industrial production of luteolin formulations.
Regulatory considerations further complicate luteolin solubilization strategies. Novel excipients or advanced delivery systems often require extensive safety documentation before regulatory approval. The lack of standardized analytical methods for evaluating luteolin in complex formulations also presents challenges in quality control and bioequivalence studies.
Recent research has highlighted the need for multifaceted approaches to address these challenges simultaneously. The ideal solubilization strategy must not only enhance water solubility but also ensure stability, maintain biological activity, allow for scalable manufacturing, and meet regulatory requirements. This complex set of requirements explains why, despite decades of research, luteolin's poor water solubility remains a significant barrier to its widespread therapeutic application.
The hydrophobic nature of luteolin's chemical structure, characterized by multiple phenolic rings, contributes to its strong tendency to aggregate in aqueous environments rather than dissolve. This aggregation behavior not only limits dissolution but also affects stability in biological fluids. Furthermore, luteolin exhibits pH-dependent solubility, with slightly improved dissolution in alkaline conditions but precipitation occurring in acidic environments such as the stomach, further complicating its oral delivery.
Conventional solubilization approaches have shown limited success with luteolin. Traditional organic solvents like ethanol or DMSO can dissolve luteolin but are unsuitable for pharmaceutical applications due to toxicity concerns. Surfactant-based systems often require high concentrations that may cause irritation or hemolysis. Additionally, luteolin's chemical structure makes it susceptible to oxidation and degradation in aqueous solutions, particularly when exposed to light or elevated temperatures.
Another significant challenge is maintaining the biological activity of luteolin throughout the solubilization process. Many solubilization techniques involve conditions that may alter the molecular structure or conformation of luteolin, potentially compromising its therapeutic properties. This necessitates careful evaluation of not just solubility enhancement but also preservation of pharmacological activity.
Scale-up and manufacturing considerations present additional hurdles. Many laboratory-scale solubilization techniques for luteolin prove difficult to scale up for commercial production. Issues such as batch-to-batch consistency, stability during storage, and cost-effectiveness become critical factors when considering industrial production of luteolin formulations.
Regulatory considerations further complicate luteolin solubilization strategies. Novel excipients or advanced delivery systems often require extensive safety documentation before regulatory approval. The lack of standardized analytical methods for evaluating luteolin in complex formulations also presents challenges in quality control and bioequivalence studies.
Recent research has highlighted the need for multifaceted approaches to address these challenges simultaneously. The ideal solubilization strategy must not only enhance water solubility but also ensure stability, maintain biological activity, allow for scalable manufacturing, and meet regulatory requirements. This complex set of requirements explains why, despite decades of research, luteolin's poor water solubility remains a significant barrier to its widespread therapeutic application.
Existing Solubilization Technologies for Luteolin
01 Solubility enhancement through cyclodextrin complexation
Luteolin's poor water solubility can be significantly improved through complexation with cyclodextrins. This approach creates inclusion complexes that enhance the dissolution rate and bioavailability of luteolin. Various types of cyclodextrins, including β-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin, can be used to form these complexes, resulting in improved solubility characteristics while maintaining the biological activity of luteolin.- Solubility enhancement through cyclodextrin complexation: Luteolin's poor water solubility can be significantly improved through complexation with cyclodextrins, particularly β-cyclodextrin and its derivatives. This approach creates inclusion complexes that enhance the dissolution rate and bioavailability of luteolin. The cyclodextrin forms a hydrophilic exterior while encapsulating the hydrophobic luteolin molecule in its cavity, resulting in improved solubility characteristics while maintaining the biological activity of luteolin.
- Nanoparticle formulations for improved luteolin solubility: Nanoparticle-based delivery systems offer an effective approach to overcome luteolin's poor solubility. These include nanoemulsions, solid lipid nanoparticles, and polymeric nanoparticles that can encapsulate luteolin and improve its dissolution properties. The nano-sized particles provide increased surface area and modified surface properties that enhance solubility and bioavailability. These formulations also offer protection against degradation and controlled release capabilities.
- Solvent systems for luteolin dissolution: Specific solvent systems can significantly improve luteolin solubility. These include combinations of water with co-solvents such as ethanol, propylene glycol, polyethylene glycol, and dimethyl sulfoxide. The addition of surfactants and pH modifiers can further enhance dissolution. Mixed solvent systems create an environment that can better accommodate luteolin's molecular structure, resulting in improved solubility while maintaining stability.
- Phospholipid complexation and liposomal formulations: Luteolin-phospholipid complexes and liposomal formulations offer enhanced solubility and improved bioavailability. By incorporating luteolin into phospholipid bilayers or forming phytosomes, the amphiphilic nature of phospholipids helps bridge the gap between the hydrophobic flavonoid and aqueous environments. These formulations improve membrane permeability and provide protection against degradation while enhancing solubility characteristics.
- Chemical modification and prodrug approaches: Chemical modifications of luteolin's structure, such as glycosylation, esterification, or phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups, can improve its solubility profile. These modifications create prodrugs or derivatives with enhanced solubility characteristics that can be converted back to the parent compound after absorption. Strategic modifications maintain the biological activity while addressing the solubility limitations of the native molecule.
02 Nanoparticle formulations for improved luteolin solubility
Nanoparticle-based delivery systems can effectively address the solubility limitations of luteolin. These include nanoemulsions, liposomes, solid lipid nanoparticles, and polymeric nanoparticles that can encapsulate luteolin and enhance its dissolution properties. The nano-sized particles increase the surface area available for dissolution and can protect luteolin from degradation, leading to improved bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions03 Solvent systems and co-solvent approaches
Various solvent systems and co-solvent approaches can be employed to enhance luteolin solubility. These include the use of organic solvents like ethanol, methanol, and DMSO for initial dissolution, followed by incorporation into aqueous systems using co-solvents such as propylene glycol, polyethylene glycol, or glycerin. Mixed solvent systems can create an environment that maintains luteolin in solution at higher concentrations than would be possible in water alone.Expand Specific Solutions04 pH modification and salt formation
The solubility of luteolin can be enhanced through pH modification and salt formation techniques. Luteolin contains phenolic hydroxyl groups that can be deprotonated under alkaline conditions, increasing water solubility. Formation of water-soluble salts with various counterions can also significantly improve dissolution properties. Buffer systems can be used to maintain optimal pH for maximum solubility while ensuring stability of the compound.Expand Specific Solutions05 Surfactant-based solubilization techniques
Surfactants can be used to enhance the solubility of luteolin through micelle formation. When surfactant concentration exceeds the critical micelle concentration, they form micelles that can encapsulate hydrophobic compounds like luteolin within their core. Various surfactants including Tween 80, sodium dodecyl sulfate, and lecithin can be employed. This approach not only improves solubility but can also enhance the stability and bioavailability of luteolin in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Flavonoid Formulation
The luteolin solubility enhancement market is in its growth phase, with increasing demand driven by pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and food industries seeking to leverage this flavonoid's health benefits. The global market for water-soluble flavonoids is expanding rapidly, though luteolin-specific solutions remain a specialized segment. Technologically, several approaches have emerged with varying maturity levels. Leading players include AQUANOVA AG with their NovaSOL technology for micellization, DSM IP Assets BV offering proprietary solubilization techniques, and Dow Global Technologies developing polymer-based delivery systems. Academic institutions like Zhejiang University and Henan Normal University are advancing novel approaches through cyclodextrin complexation and nanoparticle formulations. Pharmaceutical companies such as Galderma and MetrioPharm are exploring luteolin's therapeutic applications, while food industry players like Fuji Oil and Unilever are incorporating water-soluble luteolin into functional products.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies has developed a comprehensive approach to enhancing luteolin water solubility through their proprietary cyclodextrin complexation technology. Their method utilizes specially engineered hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) derivatives with optimized cavity sizes and surface modifications to form inclusion complexes with luteolin molecules. The process involves a precisely controlled co-precipitation technique where luteolin and cyclodextrin are dissolved in a suitable solvent system, followed by controlled precipitation and isolation of the complex. This technology achieves solubility enhancement of luteolin by approximately 20-30 fold compared to its native form. Dow's formulation maintains stability across a wide pH range (3-8) and demonstrates excellent thermal stability up to 80°C, making it suitable for various food, beverage, and pharmaceutical applications requiring water-soluble luteolin.
Strengths: Utilizes FDA-approved excipients; provides excellent stability in various formulation environments; offers scalable manufacturing process. Weaknesses: May alter release kinetics of luteolin; potential for higher material costs; limited effectiveness for extremely hydrophobic compounds.
DSM IP Assets BV
Technical Solution: DSM has pioneered an innovative approach to luteolin solubilization through their patented microemulsion technology platform. Their solution involves creating stable oil-in-water microemulsions using a carefully optimized blend of food-grade surfactants, co-surfactants, and carrier oils specifically selected for luteolin compatibility. The process employs a low-energy emulsification method that generates uniform droplets in the 50-100nm range, creating a thermodynamically stable system. DSM's formulation achieves luteolin solubility enhancements of approximately 25-35 times compared to native luteolin while maintaining its biological activity. The technology incorporates antioxidant protection systems that prevent luteolin degradation, extending shelf-life significantly. Their microemulsion system demonstrates remarkable stability across temperature ranges from 4-40°C and remains stable in various food and beverage matrices with pH values between 3.5-7.0.
Strengths: Provides excellent thermodynamic stability; achieves high loading capacity for luteolin; offers protection against oxidative degradation. Weaknesses: Requires careful selection of surfactant systems; potential sensory impacts in some applications; regulatory considerations for certain surfactants in food applications.
Critical Patents and Research on Luteolin Solubility Enhancement
Luteolin-containing composition and method for manufacturing same
PatentWO2019070056A1
Innovation
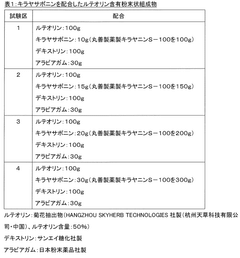
- A water-dispersible powder composition is created by homogenizing luteolin with saponin and drying the emulsified mixture, which enhances luteolin's solubility and stability in water, allowing for its effective use in food products without the risks associated with high-temperature processing.
Method for enhancing the solubility of substantially water-insoluble compounds
PatentInactiveCA2247410A1
Innovation
- Combining substantially water-insoluble compounds with water-soluble polymers of specific molecular weight ranges (50,000 to 7,000,000 g/mol) to enhance solubility, allowing for effective delivery in both solid and liquid forms, and adjusting the release profile by selecting appropriate polymer molecular weights.
Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetic Considerations
The bioavailability of luteolin presents significant challenges due to its inherently poor water solubility, which severely limits its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. Studies indicate that luteolin exhibits less than 8% bioavailability when administered orally, primarily due to its hydrophobic nature and extensive first-pass metabolism. This low bioavailability significantly restricts its therapeutic potential despite its well-documented pharmacological activities.
Pharmacokinetic studies reveal that luteolin undergoes rapid metabolism in the liver, with a relatively short half-life of approximately 3-4 hours in human plasma. The compound primarily undergoes glucuronidation and sulfation, forming metabolites that may possess different biological activities compared to the parent compound. These metabolic transformations further complicate the delivery of active luteolin to target tissues.
The relationship between solubility enhancement strategies and pharmacokinetic parameters requires careful consideration. Nanoformulations have demonstrated the ability to increase the area under the curve (AUC) by 2-5 fold compared to unformulated luteolin, indicating improved systemic exposure. Similarly, phospholipid complexes have shown enhanced permeability across intestinal barriers, potentially increasing bioavailability by up to 20%.
Cyclodextrin inclusion complexes not only improve solubility but also provide protection against enzymatic degradation in the gastrointestinal environment, potentially extending the compound's half-life. Research indicates that hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin formulations can increase luteolin's plasma residence time by approximately 40%.
Co-administration with bioenhancers such as piperine has demonstrated the ability to inhibit efflux transporters and metabolizing enzymes, potentially increasing luteolin bioavailability by 30-60%. This approach represents a promising strategy for overcoming the pharmacokinetic limitations of luteolin.
The development of prodrug approaches offers another avenue for improving luteolin's pharmacokinetic profile. By masking polar groups with cleavable moieties, these derivatives can enhance membrane permeability while releasing the active compound at the target site, potentially circumventing first-pass metabolism and increasing bioavailability.
Future solubility enhancement strategies should focus not only on improving dissolution rates but also on addressing the broader pharmacokinetic challenges, including metabolism, distribution, and elimination. Targeted delivery systems that can protect luteolin from premature metabolism while facilitating its accumulation in specific tissues represent a promising direction for maximizing therapeutic efficacy.
Pharmacokinetic studies reveal that luteolin undergoes rapid metabolism in the liver, with a relatively short half-life of approximately 3-4 hours in human plasma. The compound primarily undergoes glucuronidation and sulfation, forming metabolites that may possess different biological activities compared to the parent compound. These metabolic transformations further complicate the delivery of active luteolin to target tissues.
The relationship between solubility enhancement strategies and pharmacokinetic parameters requires careful consideration. Nanoformulations have demonstrated the ability to increase the area under the curve (AUC) by 2-5 fold compared to unformulated luteolin, indicating improved systemic exposure. Similarly, phospholipid complexes have shown enhanced permeability across intestinal barriers, potentially increasing bioavailability by up to 20%.
Cyclodextrin inclusion complexes not only improve solubility but also provide protection against enzymatic degradation in the gastrointestinal environment, potentially extending the compound's half-life. Research indicates that hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin formulations can increase luteolin's plasma residence time by approximately 40%.
Co-administration with bioenhancers such as piperine has demonstrated the ability to inhibit efflux transporters and metabolizing enzymes, potentially increasing luteolin bioavailability by 30-60%. This approach represents a promising strategy for overcoming the pharmacokinetic limitations of luteolin.
The development of prodrug approaches offers another avenue for improving luteolin's pharmacokinetic profile. By masking polar groups with cleavable moieties, these derivatives can enhance membrane permeability while releasing the active compound at the target site, potentially circumventing first-pass metabolism and increasing bioavailability.
Future solubility enhancement strategies should focus not only on improving dissolution rates but also on addressing the broader pharmacokinetic challenges, including metabolism, distribution, and elimination. Targeted delivery systems that can protect luteolin from premature metabolism while facilitating its accumulation in specific tissues represent a promising direction for maximizing therapeutic efficacy.
Regulatory Framework for Novel Luteolin Formulations
The regulatory landscape for novel luteolin formulations designed to enhance water solubility presents a complex framework that manufacturers must navigate carefully. In the United States, the FDA categorizes luteolin-based products differently depending on their intended use, concentration, and formulation technology. Products marketed as dietary supplements fall under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA), requiring manufacturers to ensure safety before marketing but not requiring pre-market approval. However, novel solubility enhancement technologies may trigger additional regulatory scrutiny.
For pharmaceutical applications of luteolin, the regulatory pathway becomes significantly more rigorous. Any drug formulation would require extensive clinical trials demonstrating safety and efficacy through the traditional Investigational New Drug (IND) and New Drug Application (NDA) processes. Novel excipients used to enhance luteolin solubility must also undergo separate safety evaluations.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) maintains similar distinctions between food supplements and medicinal products, with the Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 potentially applying to new luteolin formulations with significantly altered bioavailability profiles. Manufacturers must demonstrate that enhanced-solubility formulations do not present new safety concerns compared to traditional forms.
In Asia, particularly China and Japan, regulatory frameworks for botanical-derived compounds like luteolin often blend traditional medicine approaches with modern pharmaceutical regulations. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system may provide pathways for certain luteolin formulations with enhanced bioavailability.
Quality standards across jurisdictions typically require adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), with specifications for purity, stability, and consistency. Novel solubility enhancement technologies must demonstrate that they maintain the chemical integrity of luteolin while improving its dissolution characteristics.
Intellectual property considerations intersect with regulatory frameworks, as patented solubility enhancement technologies may receive different regulatory treatment. Patent protection for novel formulation methods can provide market exclusivity but may also trigger more stringent regulatory review processes.
Environmental regulations increasingly impact formulation development, with certain solubilizing agents facing restrictions due to ecological concerns. Sustainable, biodegradable solubility enhancers may receive preferential regulatory treatment in some jurisdictions, particularly in the European Union under the REACH regulation.
For pharmaceutical applications of luteolin, the regulatory pathway becomes significantly more rigorous. Any drug formulation would require extensive clinical trials demonstrating safety and efficacy through the traditional Investigational New Drug (IND) and New Drug Application (NDA) processes. Novel excipients used to enhance luteolin solubility must also undergo separate safety evaluations.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) maintains similar distinctions between food supplements and medicinal products, with the Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 potentially applying to new luteolin formulations with significantly altered bioavailability profiles. Manufacturers must demonstrate that enhanced-solubility formulations do not present new safety concerns compared to traditional forms.
In Asia, particularly China and Japan, regulatory frameworks for botanical-derived compounds like luteolin often blend traditional medicine approaches with modern pharmaceutical regulations. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system may provide pathways for certain luteolin formulations with enhanced bioavailability.
Quality standards across jurisdictions typically require adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), with specifications for purity, stability, and consistency. Novel solubility enhancement technologies must demonstrate that they maintain the chemical integrity of luteolin while improving its dissolution characteristics.
Intellectual property considerations intersect with regulatory frameworks, as patented solubility enhancement technologies may receive different regulatory treatment. Patent protection for novel formulation methods can provide market exclusivity but may also trigger more stringent regulatory review processes.
Environmental regulations increasingly impact formulation development, with certain solubilizing agents facing restrictions due to ecological concerns. Sustainable, biodegradable solubility enhancers may receive preferential regulatory treatment in some jurisdictions, particularly in the European Union under the REACH regulation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!