How to Quantify Luteolin in Commercial Products
AUG 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luteolin Quantification Background and Objectives
Luteolin, a flavonoid compound found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal plants, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential health benefits. The history of luteolin research dates back to the early 20th century, but intensive scientific investigation began in the 1990s when researchers started exploring its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. The evolution of analytical techniques for quantifying luteolin has paralleled advancements in chromatography, spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry technologies.
The current technological landscape for luteolin quantification encompasses various methodologies, including High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC), Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS), and spectrophotometric techniques. Each method offers distinct advantages and limitations in terms of sensitivity, specificity, cost, and throughput. The progression from traditional wet chemistry methods to sophisticated instrumental analyses represents a significant technological advancement in this field.
Market demands for accurate luteolin quantification have surged with the growing consumer interest in natural health products and functional foods. Nutraceutical companies, pharmaceutical manufacturers, and food producers increasingly require reliable methods to verify the luteolin content in their products for quality control, regulatory compliance, and marketing claims. This demand is further amplified by the expanding body of scientific literature suggesting luteolin's therapeutic potential.
The primary technical objectives for luteolin quantification include developing methods that are: (1) highly sensitive and specific for detecting luteolin in complex matrices; (2) reproducible across different laboratories and instruments; (3) cost-effective for routine quality control applications; (4) capable of distinguishing luteolin from structurally similar flavonoids; and (5) suitable for high-throughput analysis in commercial settings.
Challenges in luteolin quantification stem from its chemical properties, including limited solubility, susceptibility to degradation, and structural similarities with other flavonoids. Additionally, the diverse nature of commercial products containing luteolin—ranging from plant extracts and dietary supplements to functional beverages and cosmetics—necessitates versatile analytical approaches adaptable to various matrices.
Future technological trends in this field are likely to focus on miniaturization of analytical systems, development of rapid screening methods, implementation of green chemistry principles, and integration of artificial intelligence for data analysis and method optimization. The convergence of these trends aims to establish standardized protocols that balance analytical rigor with practical applicability in commercial environments.
The current technological landscape for luteolin quantification encompasses various methodologies, including High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC), Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS), and spectrophotometric techniques. Each method offers distinct advantages and limitations in terms of sensitivity, specificity, cost, and throughput. The progression from traditional wet chemistry methods to sophisticated instrumental analyses represents a significant technological advancement in this field.
Market demands for accurate luteolin quantification have surged with the growing consumer interest in natural health products and functional foods. Nutraceutical companies, pharmaceutical manufacturers, and food producers increasingly require reliable methods to verify the luteolin content in their products for quality control, regulatory compliance, and marketing claims. This demand is further amplified by the expanding body of scientific literature suggesting luteolin's therapeutic potential.
The primary technical objectives for luteolin quantification include developing methods that are: (1) highly sensitive and specific for detecting luteolin in complex matrices; (2) reproducible across different laboratories and instruments; (3) cost-effective for routine quality control applications; (4) capable of distinguishing luteolin from structurally similar flavonoids; and (5) suitable for high-throughput analysis in commercial settings.
Challenges in luteolin quantification stem from its chemical properties, including limited solubility, susceptibility to degradation, and structural similarities with other flavonoids. Additionally, the diverse nature of commercial products containing luteolin—ranging from plant extracts and dietary supplements to functional beverages and cosmetics—necessitates versatile analytical approaches adaptable to various matrices.
Future technological trends in this field are likely to focus on miniaturization of analytical systems, development of rapid screening methods, implementation of green chemistry principles, and integration of artificial intelligence for data analysis and method optimization. The convergence of these trends aims to establish standardized protocols that balance analytical rigor with practical applicability in commercial environments.
Market Demand Analysis for Luteolin Testing Methods
The global market for luteolin testing methods is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health benefits associated with flavonoids and the expanding nutraceutical industry. Current market estimates value the global flavonoid testing market at approximately 5.2 billion USD, with luteolin testing representing a rapidly growing segment within this category. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for luteolin-specific testing methods is projected at 8.7% through 2028, outpacing many other analytical testing segments.
Primary market demand stems from three key sectors: pharmaceutical companies developing luteolin-based therapeutics, nutraceutical manufacturers incorporating luteolin into supplements, and food producers marketing products with enhanced luteolin content. These industries require reliable, cost-effective, and efficient quantification methods to ensure product quality, regulatory compliance, and substantiation of health claims.
Regulatory factors significantly influence market demand for luteolin testing. The FDA, EFSA, and other global regulatory bodies have implemented increasingly stringent requirements for natural product characterization, creating substantial demand for validated analytical methods. Additionally, the growing number of health claims related to luteolin's anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potential anti-cancer properties necessitates accurate quantification to support marketing claims.
Consumer trends are equally important in driving market growth. The shift toward preventative healthcare and natural remedies has increased consumer interest in flavonoid-rich products. Market research indicates that 64% of consumers actively seek products with verified bioactive compounds, creating downstream demand for manufacturers to implement robust testing protocols.
Regional analysis reveals that North America currently dominates the luteolin testing market with 38% market share, followed by Europe (31%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth rate due to the region's traditional use of luteolin-rich botanicals and rapidly expanding nutraceutical manufacturing base.
The competitive landscape for luteolin testing services is fragmented, with specialized analytical laboratories, equipment manufacturers, and in-house testing facilities all competing for market share. Price sensitivity varies by sector, with pharmaceutical applications prioritizing precision over cost, while food manufacturers seek more economical high-throughput solutions.
Future market growth will likely be driven by technological advancements enabling faster, more sensitive detection methods, increased regulatory scrutiny of health claims, and growing consumer demand for transparency regarding bioactive compound content in commercial products.
Primary market demand stems from three key sectors: pharmaceutical companies developing luteolin-based therapeutics, nutraceutical manufacturers incorporating luteolin into supplements, and food producers marketing products with enhanced luteolin content. These industries require reliable, cost-effective, and efficient quantification methods to ensure product quality, regulatory compliance, and substantiation of health claims.
Regulatory factors significantly influence market demand for luteolin testing. The FDA, EFSA, and other global regulatory bodies have implemented increasingly stringent requirements for natural product characterization, creating substantial demand for validated analytical methods. Additionally, the growing number of health claims related to luteolin's anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potential anti-cancer properties necessitates accurate quantification to support marketing claims.
Consumer trends are equally important in driving market growth. The shift toward preventative healthcare and natural remedies has increased consumer interest in flavonoid-rich products. Market research indicates that 64% of consumers actively seek products with verified bioactive compounds, creating downstream demand for manufacturers to implement robust testing protocols.
Regional analysis reveals that North America currently dominates the luteolin testing market with 38% market share, followed by Europe (31%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth rate due to the region's traditional use of luteolin-rich botanicals and rapidly expanding nutraceutical manufacturing base.
The competitive landscape for luteolin testing services is fragmented, with specialized analytical laboratories, equipment manufacturers, and in-house testing facilities all competing for market share. Price sensitivity varies by sector, with pharmaceutical applications prioritizing precision over cost, while food manufacturers seek more economical high-throughput solutions.
Future market growth will likely be driven by technological advancements enabling faster, more sensitive detection methods, increased regulatory scrutiny of health claims, and growing consumer demand for transparency regarding bioactive compound content in commercial products.
Current Analytical Techniques and Limitations
The quantification of luteolin in commercial products currently relies on several analytical techniques, each with specific advantages and limitations. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) remains the gold standard method, offering excellent separation capabilities and reliability. When coupled with various detection systems such as UV-Vis, diode array detection (DAD), or mass spectrometry (MS), HPLC provides sensitive and specific quantification of luteolin even in complex matrices. However, HPLC methods typically require extensive sample preparation, considerable analysis time, and expensive instrumentation.
Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) has emerged as an advancement over traditional HPLC, offering faster analysis times, improved resolution, and reduced solvent consumption. Despite these advantages, the high pressure systems required for UHPLC demand specialized equipment that may not be accessible to all laboratories, particularly in smaller commercial settings or quality control environments with limited resources.
Spectrophotometric methods, including UV-Vis spectroscopy, represent simpler and more cost-effective approaches for luteolin quantification. These techniques are based on the characteristic absorption of luteolin at specific wavelengths. While accessible and rapid, spectrophotometric methods often lack specificity in complex matrices where multiple flavonoids may exhibit overlapping absorption spectra, leading to potential overestimation of luteolin content.
Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) offers a relatively simple and cost-effective screening tool for luteolin identification. When combined with densitometric analysis, TLC can provide semi-quantitative results. However, TLC generally lacks the precision and sensitivity required for accurate quantification in products with low luteolin concentrations.
Capillary Electrophoresis (CE) has demonstrated potential for luteolin analysis, offering high separation efficiency with minimal sample requirements. Despite these advantages, CE methods often struggle with reproducibility issues and lower sensitivity compared to HPLC-based techniques, limiting their widespread adoption in commercial settings.
Immunoassay techniques, including Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), provide highly specific detection of luteolin through antibody-antigen interactions. While offering excellent specificity and potential for high-throughput screening, the development of specific antibodies for luteolin remains challenging, and cross-reactivity with structurally similar flavonoids can compromise accuracy.
A significant limitation across all current analytical methods is the lack of standardized protocols specifically optimized for diverse commercial product matrices. Variations in extraction procedures, mobile phase compositions, and detection parameters across different studies make direct comparison of results problematic. Additionally, matrix effects from complex commercial formulations often interfere with accurate quantification, necessitating extensive method validation for each product type.
Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) has emerged as an advancement over traditional HPLC, offering faster analysis times, improved resolution, and reduced solvent consumption. Despite these advantages, the high pressure systems required for UHPLC demand specialized equipment that may not be accessible to all laboratories, particularly in smaller commercial settings or quality control environments with limited resources.
Spectrophotometric methods, including UV-Vis spectroscopy, represent simpler and more cost-effective approaches for luteolin quantification. These techniques are based on the characteristic absorption of luteolin at specific wavelengths. While accessible and rapid, spectrophotometric methods often lack specificity in complex matrices where multiple flavonoids may exhibit overlapping absorption spectra, leading to potential overestimation of luteolin content.
Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) offers a relatively simple and cost-effective screening tool for luteolin identification. When combined with densitometric analysis, TLC can provide semi-quantitative results. However, TLC generally lacks the precision and sensitivity required for accurate quantification in products with low luteolin concentrations.
Capillary Electrophoresis (CE) has demonstrated potential for luteolin analysis, offering high separation efficiency with minimal sample requirements. Despite these advantages, CE methods often struggle with reproducibility issues and lower sensitivity compared to HPLC-based techniques, limiting their widespread adoption in commercial settings.
Immunoassay techniques, including Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), provide highly specific detection of luteolin through antibody-antigen interactions. While offering excellent specificity and potential for high-throughput screening, the development of specific antibodies for luteolin remains challenging, and cross-reactivity with structurally similar flavonoids can compromise accuracy.
A significant limitation across all current analytical methods is the lack of standardized protocols specifically optimized for diverse commercial product matrices. Variations in extraction procedures, mobile phase compositions, and detection parameters across different studies make direct comparison of results problematic. Additionally, matrix effects from complex commercial formulations often interfere with accurate quantification, necessitating extensive method validation for each product type.
Established Protocols for Luteolin Quantification
01 HPLC methods for luteolin quantification
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) techniques are widely used for the quantitative analysis of luteolin in various samples. These methods typically involve sample preparation through extraction, followed by chromatographic separation and detection. HPLC methods offer high sensitivity and specificity for luteolin quantification, allowing for accurate determination of luteolin content in plant extracts, pharmaceutical formulations, and biological samples.- HPLC methods for luteolin quantification: High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is widely used for the quantification of luteolin in various samples. These methods typically involve sample preparation, chromatographic separation, and detection using UV or other detectors. The techniques allow for precise measurement of luteolin content in plant extracts, pharmaceutical formulations, and biological samples with high sensitivity and reproducibility.
- Spectroscopic methods for luteolin determination: Various spectroscopic techniques are employed for the quantification of luteolin, including UV-visible spectrophotometry, fluorescence spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry. These methods are based on the characteristic absorption or emission properties of luteolin and can be used for rapid screening and quantification in different matrices. Spectroscopic approaches often require less sample preparation than chromatographic methods and can be suitable for high-throughput analysis.
- Extraction and sample preparation techniques: Efficient extraction and sample preparation techniques are crucial for accurate luteolin quantification. Methods include solvent extraction, ultrasonic-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, and solid-phase extraction. These techniques aim to maximize luteolin recovery from complex matrices while minimizing interference from other compounds. Optimization of extraction parameters such as solvent type, temperature, and time is essential for reliable quantification results.
- Bioanalytical methods for luteolin in biological samples: Specialized bioanalytical methods have been developed for the quantification of luteolin in biological samples such as plasma, urine, and tissues. These methods address challenges related to low concentrations, matrix effects, and metabolic transformations. Techniques often combine selective extraction procedures with sensitive detection methods to achieve accurate quantification of luteolin and its metabolites in biological matrices, which is essential for pharmacokinetic and bioavailability studies.
- Standardization and quality control of luteolin-containing products: Methods for standardization and quality control of luteolin-containing products involve establishing reference standards, validation protocols, and stability-indicating assays. These approaches ensure consistent luteolin content in herbal preparations, dietary supplements, and pharmaceutical formulations. Quality control methods typically include multiple analytical techniques to verify identity, purity, and quantity of luteolin, supporting product efficacy and safety claims.
02 Spectroscopic methods for luteolin determination
Spectroscopic techniques, including UV-visible spectrophotometry and fluorescence spectroscopy, provide alternative approaches for luteolin quantification. These methods are based on the characteristic absorption or emission properties of luteolin. Spectroscopic methods are often simpler and faster than chromatographic techniques, making them suitable for routine analysis and quality control of luteolin-containing products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Extraction and sample preparation techniques
Various extraction methods are employed to isolate luteolin from complex matrices prior to quantification. These include solvent extraction, ultrasonic-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, and supercritical fluid extraction. The choice of extraction method significantly impacts the recovery and purity of luteolin, which in turn affects the accuracy of quantification. Optimization of extraction parameters such as solvent type, temperature, and extraction time is crucial for efficient luteolin isolation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Mass spectrometry-based quantification
Mass spectrometry (MS), often coupled with liquid chromatography (LC-MS), provides highly sensitive and selective methods for luteolin quantification. These techniques allow for the detection and quantification of luteolin at very low concentrations in complex matrices. MS-based methods are particularly valuable for the analysis of luteolin in biological samples such as plasma, urine, and tissues, where the compound may be present in trace amounts.Expand Specific Solutions05 Standardization and quality control methods
Standardized protocols for luteolin quantification are essential for quality control of herbal medicines, dietary supplements, and pharmaceutical products containing this flavonoid. These methods involve the use of reference standards, validation procedures, and statistical analysis to ensure accuracy and reproducibility. Quality control approaches include the development of certified reference materials, proficiency testing, and inter-laboratory comparison studies to harmonize luteolin quantification across different laboratories and analytical platforms.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Flavonoid Analysis
The luteolin quantification market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by health supplement and pharmaceutical applications. Market size is expanding due to rising consumer interest in natural bioactive compounds. Technologically, the field is moderately mature with established HPLC and spectrophotometric methods, though innovations in precision and efficiency continue. Leading players include Chenguang Biotech Group, a global leader in plant extracts; Merck Patent GmbH, providing analytical standards and methods; Kemin Industries with expertise in natural ingredients; and Katra Phytochem specializing in carotenoid extraction. Academic institutions like Zhejiang University and Louisiana State University contribute significant research advancements, while pharmaceutical companies such as Laurus Labs and Shandong Danhong are developing applications for therapeutic markets.
Chenguang Biotech Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Chenguang Biotech has developed a comprehensive luteolin quantification approach combining High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with diode array detection (DAD) for commercial products. Their method utilizes a C18 reverse-phase column with a mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile and 0.1% phosphoric acid in water. The company has optimized gradient elution parameters to achieve separation of luteolin from other flavonoids in complex matrices. They've established a validated protocol with linearity in the range of 0.5-100 μg/mL, with detection limits as low as 0.1 μg/mL. For sample preparation, they employ ultrasonic-assisted extraction with methanol or ethanol, followed by filtration and concentration steps. This method has been successfully applied to quantify luteolin in their commercial plant extracts, dietary supplements, and functional food ingredients with recovery rates exceeding 95%.
Strengths: High sensitivity and specificity for luteolin detection in complex matrices; validated protocol with excellent linearity and low detection limits; applicable across multiple product categories. Weaknesses: Requires sophisticated laboratory equipment; time-consuming sample preparation process; may require additional steps for highly complex matrices.
Merck Patent GmbH
Technical Solution: Merck Patent GmbH has pioneered an advanced luteolin quantification system utilizing Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS). Their method employs a BEH C18 column (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 μm) with gradient elution using water and acetonitrile, both containing 0.1% formic acid. The MS/MS detection operates in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode, tracking specific luteolin fragment ions (m/z 287→153, 287→135) for quantification. This approach achieves exceptional sensitivity with limits of detection below 0.05 ng/mL in various matrices. For sample preparation, Merck utilizes QuEChERS (Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged, and Safe) methodology, incorporating dispersive solid-phase extraction (d-SPE) cleanup to minimize matrix effects. The method has been validated according to ICH guidelines, demonstrating linearity (r² > 0.999) across a concentration range of 0.1-1000 ng/mL with intra- and inter-day precision below 3% RSD.
Strengths: Exceptional sensitivity and selectivity through MS/MS detection; minimal matrix interference due to advanced sample cleanup; high-throughput capability with short analysis times; comprehensive validation meeting international standards. Weaknesses: Requires expensive instrumentation and specialized operator training; higher operational costs compared to simpler methods; may be excessive for routine quality control of products with high luteolin content.
Critical Analytical Methods and Validation Studies
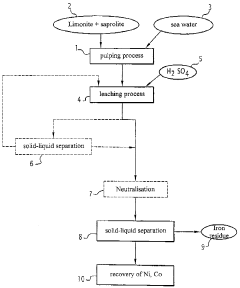
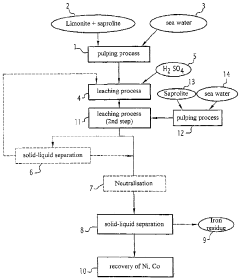
Process for the hydrometallurgical treatment of a lateritic nickel/cobalt ore and process for producing nickel and/or cobalt intermediate concentrates or commercial products using it
PatentInactiveAU2011218755B9
Innovation
- A process that combines limonite and saprolite ores in a pulp with an iron-precipitating agent, leached with sulphuric acid at atmospheric pressure, followed by neutralization and solid-liquid separation to produce nickel and cobalt intermediate concentrates, eliminating the need for separate fraction separation and high-pressure equipment.
Regulatory Standards for Flavonoid Content Claims
The regulatory landscape for flavonoid content claims, particularly for luteolin, varies significantly across global markets, creating challenges for commercial product manufacturers. In the United States, the FDA does not establish specific thresholds for flavonoid content claims, but requires that any claims be truthful, not misleading, and substantiated by scientific evidence. Manufacturers making structure/function claims about luteolin must include a disclaimer that the statement has not been evaluated by the FDA.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) maintains stricter standards, requiring robust scientific evidence for health claims related to flavonoids. For luteolin specifically, no approved health claims currently exist in the EU regulatory framework, limiting marketing possibilities despite the compound's potential health benefits. Manufacturers must adhere to the Novel Food Regulation if luteolin is used at levels significantly higher than those traditionally found in food.
In Asia, particularly Japan and China, regulatory frameworks for flavonoid claims are evolving rapidly. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system allows certain health claims for functional ingredients, including flavonoids, but requires substantial clinical evidence. China's regulatory system has recently implemented more stringent requirements for functional food claims through the State Administration for Market Regulation.
Quantification methodologies for luteolin content must align with internationally recognized standards to support regulatory compliance. The Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) International and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provide validated methods that are generally accepted by regulatory bodies worldwide. These methods typically specify sample preparation procedures, analytical techniques, and acceptable limits of detection and quantification.
Manufacturers seeking to make content claims must implement quality control systems that ensure batch-to-batch consistency in luteolin levels. This includes regular testing using validated methods and maintaining comprehensive documentation of analytical results. Third-party verification through accredited laboratories is increasingly becoming an industry standard practice to enhance credibility of content claims.
The trend toward global harmonization of standards for bioactive compounds is gaining momentum, with initiatives like the CODEX Alimentarius Commission working to establish international guidelines for flavonoid content claims. These efforts aim to reduce regulatory barriers while maintaining consumer protection through science-based standards for quantification and labeling.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) maintains stricter standards, requiring robust scientific evidence for health claims related to flavonoids. For luteolin specifically, no approved health claims currently exist in the EU regulatory framework, limiting marketing possibilities despite the compound's potential health benefits. Manufacturers must adhere to the Novel Food Regulation if luteolin is used at levels significantly higher than those traditionally found in food.
In Asia, particularly Japan and China, regulatory frameworks for flavonoid claims are evolving rapidly. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system allows certain health claims for functional ingredients, including flavonoids, but requires substantial clinical evidence. China's regulatory system has recently implemented more stringent requirements for functional food claims through the State Administration for Market Regulation.
Quantification methodologies for luteolin content must align with internationally recognized standards to support regulatory compliance. The Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) International and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provide validated methods that are generally accepted by regulatory bodies worldwide. These methods typically specify sample preparation procedures, analytical techniques, and acceptable limits of detection and quantification.
Manufacturers seeking to make content claims must implement quality control systems that ensure batch-to-batch consistency in luteolin levels. This includes regular testing using validated methods and maintaining comprehensive documentation of analytical results. Third-party verification through accredited laboratories is increasingly becoming an industry standard practice to enhance credibility of content claims.
The trend toward global harmonization of standards for bioactive compounds is gaining momentum, with initiatives like the CODEX Alimentarius Commission working to establish international guidelines for flavonoid content claims. These efforts aim to reduce regulatory barriers while maintaining consumer protection through science-based standards for quantification and labeling.
Method Transferability and Scale-up Considerations
Method transferability is a critical consideration when developing analytical procedures for luteolin quantification in commercial products. Laboratory-scale methods must be designed with scalability in mind to ensure consistent results across different equipment, personnel, and production volumes. When transferring methods between laboratories or scaling up for industrial applications, several key factors require careful attention. Robustness testing should be conducted to verify that the analytical method maintains accuracy and precision under varying conditions, including different instrument models, reagent sources, and environmental parameters.
Column selection presents particular challenges during method transfer, as different manufacturers' columns may exhibit subtle variations in stationary phase characteristics despite identical specifications. Method validation protocols should include tests with columns from multiple vendors to ensure transferability. Additionally, the availability and cost of specialized columns must be evaluated when considering large-scale implementation.
Sample preparation procedures require standardization to minimize variability during scale-up. Techniques that are feasible for small batches in research settings may become impractical or cost-prohibitive at industrial scale. Automation compatibility should be assessed early in method development to facilitate seamless transition to high-throughput environments. Extraction methods that utilize green solvents and reduced solvent volumes are increasingly preferred for large-scale applications due to environmental and economic considerations.
Instrument calibration protocols must be harmonized across different laboratories and production facilities. Reference standards for luteolin should be sourced from reliable suppliers with certificates of analysis to ensure consistency. The establishment of system suitability tests with appropriate acceptance criteria helps maintain method performance during routine use and transfer between different analytical platforms.
Data processing and interpretation represent another critical aspect of method transferability. Standardized calculation methods, integration parameters, and reporting formats should be established to ensure consistent results interpretation regardless of the analyst or laboratory. Modern analytical data systems with built-in method transfer tools can facilitate this process by automatically adjusting parameters to account for differences in instrument response characteristics.
Regulatory considerations must guide the development of transferable methods, particularly for commercial products subject to quality control requirements. Methods intended for transfer should be developed with pharmacopeial guidelines in mind, incorporating appropriate validation parameters such as specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, and robustness. Documentation practices, including detailed standard operating procedures and method validation reports, are essential for successful technology transfer between research, development, and quality control laboratories.
Column selection presents particular challenges during method transfer, as different manufacturers' columns may exhibit subtle variations in stationary phase characteristics despite identical specifications. Method validation protocols should include tests with columns from multiple vendors to ensure transferability. Additionally, the availability and cost of specialized columns must be evaluated when considering large-scale implementation.
Sample preparation procedures require standardization to minimize variability during scale-up. Techniques that are feasible for small batches in research settings may become impractical or cost-prohibitive at industrial scale. Automation compatibility should be assessed early in method development to facilitate seamless transition to high-throughput environments. Extraction methods that utilize green solvents and reduced solvent volumes are increasingly preferred for large-scale applications due to environmental and economic considerations.
Instrument calibration protocols must be harmonized across different laboratories and production facilities. Reference standards for luteolin should be sourced from reliable suppliers with certificates of analysis to ensure consistency. The establishment of system suitability tests with appropriate acceptance criteria helps maintain method performance during routine use and transfer between different analytical platforms.
Data processing and interpretation represent another critical aspect of method transferability. Standardized calculation methods, integration parameters, and reporting formats should be established to ensure consistent results interpretation regardless of the analyst or laboratory. Modern analytical data systems with built-in method transfer tools can facilitate this process by automatically adjusting parameters to account for differences in instrument response characteristics.
Regulatory considerations must guide the development of transferable methods, particularly for commercial products subject to quality control requirements. Methods intended for transfer should be developed with pharmacopeial guidelines in mind, incorporating appropriate validation parameters such as specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, and robustness. Documentation practices, including detailed standard operating procedures and method validation reports, are essential for successful technology transfer between research, development, and quality control laboratories.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!