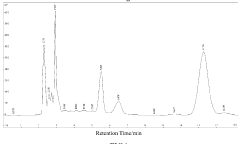
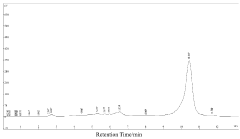
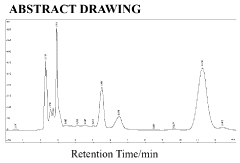
How to Quantify Luteolin in Herbal Extracts
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luteolin Quantification Background and Objectives
Luteolin, a flavonoid compound found in various medicinal plants and herbs, has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its potential therapeutic properties. The quantification of luteolin in herbal extracts represents a critical area of research that bridges analytical chemistry, pharmacognosy, and pharmaceutical development. Historically, the analysis of bioactive compounds in medicinal plants has evolved from rudimentary chemical tests to sophisticated instrumental methods, with luteolin quantification following this trajectory.
The evolution of luteolin quantification techniques has progressed through several distinct phases. Early methods relied on colorimetric assays and thin-layer chromatography, which provided only semi-quantitative results. The introduction of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) in the 1970s marked a significant advancement, enabling more precise quantification. Recent decades have witnessed the integration of mass spectrometry and other detection techniques, further enhancing sensitivity and specificity.
Current technological trends in luteolin quantification focus on developing more efficient, accurate, and cost-effective analytical methods. These include the optimization of extraction procedures, the development of green analytical chemistry approaches, and the application of advanced separation techniques such as ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC). Additionally, there is growing interest in portable and rapid analysis systems that can provide on-site quantification capabilities.
The primary objectives of luteolin quantification research encompass several dimensions. First, establishing standardized and validated analytical methods that ensure reproducibility and reliability across different laboratories. Second, developing techniques capable of detecting and quantifying luteolin at increasingly lower concentrations, particularly relevant for herbs with naturally low luteolin content. Third, creating methods that can differentiate between luteolin and structurally similar flavonoids, addressing the challenge of selectivity.
Furthermore, there is a pressing need for techniques that can effectively handle the complex matrices of herbal extracts, which often contain numerous interfering compounds. This complexity necessitates sophisticated sample preparation strategies and detection methods. The ultimate goal is to develop comprehensive analytical approaches that not only quantify luteolin but also provide information about its bioavailability and stability in various formulations.
The significance of accurate luteolin quantification extends beyond academic research to practical applications in quality control of herbal medicines, dietary supplements, and functional foods. As regulatory requirements for natural products become more stringent globally, reliable quantification methods become essential for ensuring product consistency, efficacy, and safety. This technical landscape sets the stage for exploring innovative solutions to the challenges of luteolin quantification in diverse herbal matrices.
The evolution of luteolin quantification techniques has progressed through several distinct phases. Early methods relied on colorimetric assays and thin-layer chromatography, which provided only semi-quantitative results. The introduction of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) in the 1970s marked a significant advancement, enabling more precise quantification. Recent decades have witnessed the integration of mass spectrometry and other detection techniques, further enhancing sensitivity and specificity.
Current technological trends in luteolin quantification focus on developing more efficient, accurate, and cost-effective analytical methods. These include the optimization of extraction procedures, the development of green analytical chemistry approaches, and the application of advanced separation techniques such as ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC). Additionally, there is growing interest in portable and rapid analysis systems that can provide on-site quantification capabilities.
The primary objectives of luteolin quantification research encompass several dimensions. First, establishing standardized and validated analytical methods that ensure reproducibility and reliability across different laboratories. Second, developing techniques capable of detecting and quantifying luteolin at increasingly lower concentrations, particularly relevant for herbs with naturally low luteolin content. Third, creating methods that can differentiate between luteolin and structurally similar flavonoids, addressing the challenge of selectivity.
Furthermore, there is a pressing need for techniques that can effectively handle the complex matrices of herbal extracts, which often contain numerous interfering compounds. This complexity necessitates sophisticated sample preparation strategies and detection methods. The ultimate goal is to develop comprehensive analytical approaches that not only quantify luteolin but also provide information about its bioavailability and stability in various formulations.
The significance of accurate luteolin quantification extends beyond academic research to practical applications in quality control of herbal medicines, dietary supplements, and functional foods. As regulatory requirements for natural products become more stringent globally, reliable quantification methods become essential for ensuring product consistency, efficacy, and safety. This technical landscape sets the stage for exploring innovative solutions to the challenges of luteolin quantification in diverse herbal matrices.
Market Demand Analysis for Luteolin Extraction Methods
The global market for luteolin extraction methods is experiencing significant growth, driven primarily by increasing consumer awareness of natural health products and the expanding applications of luteolin in pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic industries. Current market estimates value the global flavonoid market, of which luteolin is a key component, at approximately 1.5 billion USD with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% projected through 2027.
The pharmaceutical sector represents the largest demand segment for luteolin quantification methods, accounting for roughly 40% of the market share. This is largely attributed to luteolin's demonstrated anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potential anti-cancer properties, which have sparked extensive research into its therapeutic applications. Clinical trials investigating luteolin's efficacy in treating various conditions have increased by 35% over the past five years.
Nutraceutical and dietary supplement manufacturers constitute the second-largest market segment, with particular growth observed in Asia-Pacific regions where traditional herbal medicine maintains strong cultural relevance. Countries like China, India, and Japan are experiencing annual growth rates of 9-11% in luteolin-containing supplement sales, significantly outpacing global averages.
The cosmetic industry has emerged as the fastest-growing sector for luteolin applications, with a CAGR exceeding 8.5%. This growth is driven by increasing consumer preference for natural ingredients and luteolin's skin-protective and anti-aging properties. Premium cosmetic brands have begun highlighting luteolin content as a key selling point in their marketing campaigns.
Market analysis reveals a clear trend toward more precise, reliable, and cost-effective quantification methods. End-users are increasingly demanding standardized testing protocols that can accurately determine luteolin content in complex herbal matrices. This demand is particularly pronounced among quality control laboratories and contract research organizations that require high-throughput screening capabilities.
Regulatory developments are significantly influencing market dynamics. The implementation of stricter quality control standards by agencies such as the FDA and EMA has created substantial demand for validated analytical methods. Additionally, the growing popularity of product certification programs like USP, EP, and various organic certifications necessitates reliable quantification methods to verify label claims.
Regional market analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently lead in terms of advanced luteolin quantification technology adoption, while Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market due to its extensive traditional medicine industry and rapidly developing pharmaceutical sector. The Middle East and Africa remain relatively untapped markets with significant growth potential as awareness of herbal medicine benefits increases.
The pharmaceutical sector represents the largest demand segment for luteolin quantification methods, accounting for roughly 40% of the market share. This is largely attributed to luteolin's demonstrated anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potential anti-cancer properties, which have sparked extensive research into its therapeutic applications. Clinical trials investigating luteolin's efficacy in treating various conditions have increased by 35% over the past five years.
Nutraceutical and dietary supplement manufacturers constitute the second-largest market segment, with particular growth observed in Asia-Pacific regions where traditional herbal medicine maintains strong cultural relevance. Countries like China, India, and Japan are experiencing annual growth rates of 9-11% in luteolin-containing supplement sales, significantly outpacing global averages.
The cosmetic industry has emerged as the fastest-growing sector for luteolin applications, with a CAGR exceeding 8.5%. This growth is driven by increasing consumer preference for natural ingredients and luteolin's skin-protective and anti-aging properties. Premium cosmetic brands have begun highlighting luteolin content as a key selling point in their marketing campaigns.
Market analysis reveals a clear trend toward more precise, reliable, and cost-effective quantification methods. End-users are increasingly demanding standardized testing protocols that can accurately determine luteolin content in complex herbal matrices. This demand is particularly pronounced among quality control laboratories and contract research organizations that require high-throughput screening capabilities.
Regulatory developments are significantly influencing market dynamics. The implementation of stricter quality control standards by agencies such as the FDA and EMA has created substantial demand for validated analytical methods. Additionally, the growing popularity of product certification programs like USP, EP, and various organic certifications necessitates reliable quantification methods to verify label claims.
Regional market analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently lead in terms of advanced luteolin quantification technology adoption, while Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market due to its extensive traditional medicine industry and rapidly developing pharmaceutical sector. The Middle East and Africa remain relatively untapped markets with significant growth potential as awareness of herbal medicine benefits increases.
Current Analytical Techniques and Challenges
The quantification of luteolin in herbal extracts currently employs several analytical techniques, each with distinct advantages and limitations. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) remains the gold standard, offering excellent separation capabilities and reliable quantification. HPLC coupled with various detection methods such as UV-Vis spectrophotometry, diode array detection (DAD), and mass spectrometry (MS) provides versatile approaches for luteolin analysis. UV-Vis detection typically monitors luteolin at wavelengths between 340-350 nm, while MS detection offers enhanced sensitivity and specificity through molecular weight and fragmentation pattern identification.
Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) has emerged as an advancement over traditional HPLC, utilizing smaller particle size columns (sub-2μm) and higher pressures to achieve faster analysis times, improved resolution, and reduced solvent consumption. This technique has proven particularly valuable for complex herbal matrices where multiple flavonoids coexist.
Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) and its advanced version, High-Performance TLC (HPTLC), offer simpler, more cost-effective alternatives for luteolin quantification. While less precise than HPLC methods, these techniques provide adequate screening capabilities and are particularly useful in resource-limited settings or for rapid preliminary analyses.
Spectroscopic methods including UV-Vis spectrophotometry and fluorescence spectroscopy provide direct measurement options but suffer from limited specificity in complex herbal matrices. These methods often require additional sample preparation steps to minimize interference from other plant constituents.
Despite these advances, significant challenges persist in luteolin quantification. The complex nature of herbal extracts presents a primary obstacle, as numerous structurally similar flavonoids and other phytochemicals can interfere with accurate detection. Matrix effects from various plant components frequently complicate analysis, necessitating extensive sample preparation procedures.
Standardization issues represent another major challenge, with different extraction methods, solvents, and analytical conditions yielding variable results across laboratories. The lack of universally accepted reference standards for luteolin quantification further complicates cross-study comparisons and method validation.
Sample preparation remains a critical bottleneck, requiring time-consuming extraction, purification, and concentration steps to isolate luteolin from complex matrices. The stability of luteolin during these processes presents additional concerns, as oxidation and degradation can occur, leading to underestimation of actual content.
Sensitivity limitations affect many current methods, particularly when analyzing samples with low luteolin concentrations. This challenge becomes especially pronounced when working with dilute extracts or when regulatory or quality control specifications demand detection at trace levels.
Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) has emerged as an advancement over traditional HPLC, utilizing smaller particle size columns (sub-2μm) and higher pressures to achieve faster analysis times, improved resolution, and reduced solvent consumption. This technique has proven particularly valuable for complex herbal matrices where multiple flavonoids coexist.
Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) and its advanced version, High-Performance TLC (HPTLC), offer simpler, more cost-effective alternatives for luteolin quantification. While less precise than HPLC methods, these techniques provide adequate screening capabilities and are particularly useful in resource-limited settings or for rapid preliminary analyses.
Spectroscopic methods including UV-Vis spectrophotometry and fluorescence spectroscopy provide direct measurement options but suffer from limited specificity in complex herbal matrices. These methods often require additional sample preparation steps to minimize interference from other plant constituents.
Despite these advances, significant challenges persist in luteolin quantification. The complex nature of herbal extracts presents a primary obstacle, as numerous structurally similar flavonoids and other phytochemicals can interfere with accurate detection. Matrix effects from various plant components frequently complicate analysis, necessitating extensive sample preparation procedures.
Standardization issues represent another major challenge, with different extraction methods, solvents, and analytical conditions yielding variable results across laboratories. The lack of universally accepted reference standards for luteolin quantification further complicates cross-study comparisons and method validation.
Sample preparation remains a critical bottleneck, requiring time-consuming extraction, purification, and concentration steps to isolate luteolin from complex matrices. The stability of luteolin during these processes presents additional concerns, as oxidation and degradation can occur, leading to underestimation of actual content.
Sensitivity limitations affect many current methods, particularly when analyzing samples with low luteolin concentrations. This challenge becomes especially pronounced when working with dilute extracts or when regulatory or quality control specifications demand detection at trace levels.
Established Protocols for Luteolin Quantification
01 Chromatographic methods for luteolin quantification
Various chromatographic techniques are employed for accurate quantification of luteolin in different samples. These methods include high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC), and liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC-MS). These techniques offer high sensitivity and specificity for luteolin detection, allowing for precise quantification even in complex matrices. The methods typically involve sample preparation, chromatographic separation, and detection using appropriate detectors to ensure quantification accuracy.- Chromatographic methods for luteolin quantification: Various chromatographic techniques are employed for accurate quantification of luteolin in different samples. These methods include high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC), and liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC-MS). These techniques provide high sensitivity and specificity for luteolin detection, allowing for precise quantification even in complex matrices. The methods typically involve sample preparation steps such as extraction, filtration, and concentration before analysis.
- Spectroscopic techniques for luteolin measurement: Spectroscopic methods offer alternative approaches for luteolin quantification with varying degrees of accuracy. These include UV-visible spectrophotometry, fluorescence spectroscopy, and infrared spectroscopy. These techniques are often less expensive and faster than chromatographic methods, though they may offer lower specificity in complex samples. Calibration curves using pure luteolin standards are typically employed to ensure quantification accuracy, and various mathematical models may be applied to improve the reliability of measurements.
- Biosensor and immunoassay-based quantification: Novel biosensor and immunoassay technologies have been developed for rapid and sensitive luteolin quantification. These methods utilize specific biological recognition elements such as antibodies, aptamers, or enzymes that selectively bind to luteolin. The binding events are then converted into measurable signals through various transduction mechanisms. These approaches offer advantages in terms of portability, speed, and potential for point-of-use applications, though validation against established chromatographic methods is typically required to ensure accuracy.
- Sample preparation techniques for improved accuracy: Effective sample preparation is crucial for accurate luteolin quantification. Various extraction methods, including solid-phase extraction, liquid-liquid extraction, and ultrasonic-assisted extraction, have been developed to isolate luteolin from complex matrices. Clean-up procedures to remove interfering compounds may include filtration, centrifugation, and the use of specific sorbents. These preparation techniques significantly impact the final quantification accuracy by improving recovery rates and reducing matrix effects that could otherwise lead to over- or under-estimation of luteolin content.
- Validation and standardization of quantification methods: Ensuring the accuracy of luteolin quantification requires rigorous validation and standardization protocols. This includes determining method parameters such as linearity, precision, accuracy, limit of detection, limit of quantification, and robustness. Reference standards and certified reference materials are used to calibrate instruments and validate methods. Inter-laboratory comparison studies help establish method reliability across different settings. Statistical approaches for data analysis and uncertainty estimation are also essential components of ensuring quantification accuracy.
02 Spectroscopic techniques for luteolin analysis
Spectroscopic methods provide alternative approaches for luteolin quantification with varying degrees of accuracy. These techniques include UV-visible spectrophotometry, fluorescence spectroscopy, and infrared spectroscopy. While these methods may be less specific than chromatographic techniques, they offer advantages in terms of speed, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. The accuracy of spectroscopic methods can be enhanced through appropriate calibration procedures and the use of reference standards to establish reliable quantification protocols.Expand Specific Solutions03 Biosensor-based methods for luteolin detection
Innovative biosensor technologies have been developed for the quantification of luteolin with improved accuracy and sensitivity. These biosensors utilize various biological recognition elements such as enzymes, antibodies, or aptamers coupled with transduction mechanisms to generate measurable signals proportional to luteolin concentration. The integration of nanomaterials and advanced signal processing algorithms enhances the performance of these biosensors, allowing for rapid and accurate quantification of luteolin in diverse sample types.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sample preparation techniques affecting quantification accuracy
The accuracy of luteolin quantification is significantly influenced by sample preparation methods. Various extraction techniques, including solvent extraction, ultrasonic-assisted extraction, and microwave-assisted extraction, impact the recovery and stability of luteolin. Purification steps such as solid-phase extraction and liquid-liquid partitioning help remove interfering compounds that could affect quantification accuracy. Standardized sample preparation protocols are essential to ensure reproducible and accurate results in luteolin analysis across different laboratories and sample matrices.Expand Specific Solutions05 Validation and quality control for luteolin quantification methods
Ensuring the accuracy of luteolin quantification requires comprehensive method validation and quality control procedures. This includes determining parameters such as linearity, precision, accuracy, limit of detection, limit of quantification, and robustness. The use of certified reference materials, internal standards, and participation in proficiency testing programs helps establish method reliability. Statistical approaches for data analysis and uncertainty estimation contribute to the overall assessment of quantification accuracy, enabling researchers to report results with appropriate confidence levels.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Phytochemical Analysis
The quantification of luteolin in herbal extracts is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market demand driven by pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications. The global market is expanding as companies recognize luteolin's therapeutic potential, though standardized quantification methods are still evolving. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with established HPLC and spectrophotometric techniques, but innovations in precision and efficiency continue. Key players include pharmaceutical companies like Jiangsu Kanion Pharmaceutical and Shijiazhuang Yiling Pharmaceutical focusing on traditional medicine applications, while Chenguang Biotech Group and OmniActive Health Technologies lead in extract standardization. Academic institutions such as Louisiana State University and Nanyang Technological University contribute significant research advancements in analytical methodologies.
Jiangsu Kanion Sunshine Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
Technical Solution: Jiangsu Kanion Sunshine Pharmaceutical has developed a dual-platform approach for luteolin quantification combining HPLC-UV with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) techniques. Their HPLC method utilizes C18 columns with gradient elution of acetonitrile and phosphoric acid buffer, optimized for various Chinese medicinal herbs. The company has created proprietary monoclonal antibodies against luteolin for their ELISA platform, enabling high-throughput screening with 96-well plate formats. Their technology includes specialized extraction protocols using ultrasonic-assisted extraction with optimized solvent systems (70% ethanol) and temperature conditions. The method incorporates internal standardization and has been validated with linearity ranges of 0.2-50 μg/mL for HPLC and 0.05-10 μg/mL for ELISA, with detection limits of 0.05 μg/mL and 0.01 μg/mL respectively.
Strengths: Dual-platform approach provides both precise quantification (HPLC) and high-throughput screening (ELISA), good sensitivity with low detection limits, and validated protocols for multiple Chinese medicinal herbs. Weaknesses: ELISA method may have cross-reactivity issues with structurally similar flavonoids, requires development and production of specific antibodies, and has a narrower linear range than chromatographic methods.
Chenguang Biotech Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Chenguang Biotech has developed a comprehensive luteolin quantification platform utilizing High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) coupled with Diode Array Detection (DAD) and Mass Spectrometry (MS). Their approach involves optimized extraction protocols using ultrasonic-assisted extraction with methanol-water mixtures at controlled temperatures and durations. The company has established validated methods for luteolin quantification in various plant matrices including Chrysanthemum, Lonicera japonica, and Artemisia annua. Their technology incorporates internal standardization with reference compounds and has demonstrated linearity in the range of 0.5-100 μg/mL with detection limits as low as 0.1 μg/mL. Chenguang's method includes hydrolysis steps to convert luteolin glycosides to aglycones for total luteolin determination, enabling comprehensive profiling of both free and bound forms.
Strengths: High precision with reported RSD values <2%, comprehensive detection of both free luteolin and glycoside forms, and established validation protocols across multiple herbal matrices. Weaknesses: Requires sophisticated laboratory equipment, relatively time-consuming sample preparation procedures, and potential matrix interference issues when analyzing complex herbal extracts.
Critical Technologies in Flavonoid Detection
Method for preparing high-purity luteolin by ferrous salt
PatentActiveZA202202840A
Innovation
- A method involving the direct addition of ferrous salts to a peanut shell alcohol aqueous extracting solution to form a complex with luteolin, followed by centrifugation, dissolution in an acidic environment, and extraction with ethyl acetate, simplifying the process and achieving high-purity luteolin through recrystallization.
Quality Control Standards for Herbal Extracts
Quality control standards for herbal extracts containing luteolin are essential for ensuring product consistency, safety, and efficacy. These standards typically encompass several critical parameters that manufacturers must adhere to throughout the production process.
The identification and quantification of luteolin in herbal extracts require well-established analytical methods that meet international regulatory requirements. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) coupled with UV detection represents the gold standard for luteolin quantification, with specifications typically requiring a minimum purity of 95% for the reference standard and clearly defined system suitability parameters.
Acceptable limits for luteolin content must be established based on pharmacopoeial standards, with typical specifications ranging from 0.5% to 5% depending on the plant source. These limits should account for natural variation while ensuring therapeutic efficacy. The European Pharmacopoeia and United States Pharmacopeia provide specific monographs for several luteolin-containing herbs, establishing benchmark standards for the industry.
Validation protocols for analytical methods must demonstrate specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, and robustness according to ICH Q2(R1) guidelines. For luteolin quantification, the validation should specifically address potential interference from structurally similar flavonoids and matrix effects from complex herbal extracts.
Stability testing requirements for luteolin-containing extracts typically mandate accelerated and long-term studies under controlled temperature and humidity conditions. These tests should monitor potential degradation of luteolin over time, with acceptance criteria generally allowing no more than 5-10% reduction from the labeled content throughout the product's shelf life.
Manufacturing controls must include in-process testing at critical points, with particular attention to extraction parameters that affect luteolin yield and purity. Standardized extraction procedures, solvent specifications, and temperature controls are essential components of these manufacturing standards.
Certificate of Analysis (CoA) requirements should include quantitative results for luteolin content, related compounds, residual solvents, heavy metals, and microbial limits. Modern standards increasingly require advanced analytical techniques such as LC-MS/MS for confirmation of identity and purity, especially for premium grade extracts.
Regulatory compliance frameworks vary globally, with the most stringent requirements found in pharmaceutical-grade herbal extracts. The European Medicines Agency (EMA), FDA, and various national pharmacopoeias have established specific guidelines for herbal medicinal products that manufacturers must navigate to ensure market access.
The identification and quantification of luteolin in herbal extracts require well-established analytical methods that meet international regulatory requirements. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) coupled with UV detection represents the gold standard for luteolin quantification, with specifications typically requiring a minimum purity of 95% for the reference standard and clearly defined system suitability parameters.
Acceptable limits for luteolin content must be established based on pharmacopoeial standards, with typical specifications ranging from 0.5% to 5% depending on the plant source. These limits should account for natural variation while ensuring therapeutic efficacy. The European Pharmacopoeia and United States Pharmacopeia provide specific monographs for several luteolin-containing herbs, establishing benchmark standards for the industry.
Validation protocols for analytical methods must demonstrate specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, and robustness according to ICH Q2(R1) guidelines. For luteolin quantification, the validation should specifically address potential interference from structurally similar flavonoids and matrix effects from complex herbal extracts.
Stability testing requirements for luteolin-containing extracts typically mandate accelerated and long-term studies under controlled temperature and humidity conditions. These tests should monitor potential degradation of luteolin over time, with acceptance criteria generally allowing no more than 5-10% reduction from the labeled content throughout the product's shelf life.
Manufacturing controls must include in-process testing at critical points, with particular attention to extraction parameters that affect luteolin yield and purity. Standardized extraction procedures, solvent specifications, and temperature controls are essential components of these manufacturing standards.
Certificate of Analysis (CoA) requirements should include quantitative results for luteolin content, related compounds, residual solvents, heavy metals, and microbial limits. Modern standards increasingly require advanced analytical techniques such as LC-MS/MS for confirmation of identity and purity, especially for premium grade extracts.
Regulatory compliance frameworks vary globally, with the most stringent requirements found in pharmaceutical-grade herbal extracts. The European Medicines Agency (EMA), FDA, and various national pharmacopoeias have established specific guidelines for herbal medicinal products that manufacturers must navigate to ensure market access.
Regulatory Compliance in Natural Product Analysis
The regulatory landscape for natural product analysis, particularly for compounds like luteolin in herbal extracts, is complex and constantly evolving. Manufacturers and researchers must navigate a web of international, national, and industry-specific regulations that govern the identification, quantification, and quality control of bioactive compounds in herbal products.
In the United States, the FDA's current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs) for dietary supplements (21 CFR Part 111) establish requirements for identity, purity, strength, and composition testing. These regulations mandate validated analytical methods for quantifying bioactive compounds like luteolin, with specific documentation requirements for method validation parameters including accuracy, precision, specificity, and linearity.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides more detailed guidelines through its "Quality of Herbal Medicinal Products/Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products" framework. These guidelines specifically address the challenges of standardizing herbal extracts and require comprehensive characterization of marker compounds such as luteolin, with validated quantification methods that demonstrate robustness across different batches.
International harmonization efforts through organizations like the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) have established quality guidelines (Q2(R1)) for analytical method validation that apply to natural product analysis. These guidelines provide a standardized approach to method validation parameters that must be considered when developing quantification methods for luteolin.
Pharmacopoeial standards, including those from the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.), and Chinese Pharmacopoeia, contain specific monographs for many herbal materials that include luteolin-containing plants. These monographs often specify accepted analytical methods and reference standards for quantification, creating legally enforceable quality standards in many jurisdictions.
Emerging regulations increasingly focus on the traceability and sustainability of natural products. The Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit-sharing requires proper documentation of the origin of biological resources, affecting research and development activities involving herbal extracts. This adds another layer of compliance requirements for organizations working with luteolin-containing plants.
Laboratory accreditation standards, particularly ISO/IEC 17025, establish technical requirements for testing laboratories performing luteolin quantification. Compliance with these standards ensures that analytical results are reliable, reproducible, and internationally recognized, which is crucial for global trade in herbal products containing luteolin.
In the United States, the FDA's current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs) for dietary supplements (21 CFR Part 111) establish requirements for identity, purity, strength, and composition testing. These regulations mandate validated analytical methods for quantifying bioactive compounds like luteolin, with specific documentation requirements for method validation parameters including accuracy, precision, specificity, and linearity.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides more detailed guidelines through its "Quality of Herbal Medicinal Products/Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products" framework. These guidelines specifically address the challenges of standardizing herbal extracts and require comprehensive characterization of marker compounds such as luteolin, with validated quantification methods that demonstrate robustness across different batches.
International harmonization efforts through organizations like the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) have established quality guidelines (Q2(R1)) for analytical method validation that apply to natural product analysis. These guidelines provide a standardized approach to method validation parameters that must be considered when developing quantification methods for luteolin.
Pharmacopoeial standards, including those from the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.), and Chinese Pharmacopoeia, contain specific monographs for many herbal materials that include luteolin-containing plants. These monographs often specify accepted analytical methods and reference standards for quantification, creating legally enforceable quality standards in many jurisdictions.
Emerging regulations increasingly focus on the traceability and sustainability of natural products. The Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit-sharing requires proper documentation of the origin of biological resources, affecting research and development activities involving herbal extracts. This adds another layer of compliance requirements for organizations working with luteolin-containing plants.
Laboratory accreditation standards, particularly ISO/IEC 17025, establish technical requirements for testing laboratories performing luteolin quantification. Compliance with these standards ensures that analytical results are reliable, reproducible, and internationally recognized, which is crucial for global trade in herbal products containing luteolin.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!