How to Significantly Improve Luteolin Solubility
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luteolin Solubility Enhancement Background and Objectives
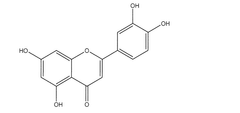
Luteolin, a natural flavonoid compound found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has garnered significant attention in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries due to its diverse pharmacological properties. These include anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, and neuroprotective effects. Despite these promising therapeutic benefits, the clinical application of luteolin faces a critical limitation: its poor aqueous solubility, which severely restricts its bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy.
The evolution of solubility enhancement techniques for flavonoids has progressed significantly over the past decades. Initially, conventional approaches such as physical modification and chemical derivatization dominated the field. However, recent advancements have shifted focus toward nanotechnology-based solutions and novel drug delivery systems, which offer more efficient and targeted approaches to overcome solubility challenges.
Current research indicates that luteolin exhibits a water solubility of approximately 0.1-0.2 mg/mL at physiological pH, which is considerably lower than the threshold required for effective therapeutic action. This limited solubility results in poor absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, leading to reduced bioavailability estimated at less than 10% in conventional formulations.
The primary objective of this technical research is to identify and evaluate innovative strategies to significantly enhance luteolin solubility, with the target of achieving at least a 10-fold increase in aqueous solubility without compromising its pharmacological activity. Secondary objectives include developing formulations with improved stability profiles and exploring cost-effective manufacturing processes that can facilitate industrial-scale production.
Recent technological breakthroughs in pharmaceutical sciences offer promising avenues for addressing luteolin's solubility challenges. These include advanced nano-formulation techniques, novel co-solvent systems, cyclodextrin complexation, solid dispersion technologies, and lipid-based delivery systems. Each approach presents unique advantages and limitations that warrant comprehensive evaluation.
The global market for flavonoid-based pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals is projected to reach $1.5 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 8.5%. Enhancing luteolin solubility could potentially unlock significant market opportunities across multiple therapeutic areas, including oncology, neurology, and inflammatory disorders.
This technical research aims to establish a robust foundation for developing next-generation luteolin formulations with enhanced solubility profiles, ultimately bridging the gap between promising preclinical findings and successful clinical applications. The outcomes of this research will not only advance our understanding of flavonoid solubilization mechanisms but also provide practical solutions for improving the therapeutic potential of luteolin in various disease conditions.
The evolution of solubility enhancement techniques for flavonoids has progressed significantly over the past decades. Initially, conventional approaches such as physical modification and chemical derivatization dominated the field. However, recent advancements have shifted focus toward nanotechnology-based solutions and novel drug delivery systems, which offer more efficient and targeted approaches to overcome solubility challenges.
Current research indicates that luteolin exhibits a water solubility of approximately 0.1-0.2 mg/mL at physiological pH, which is considerably lower than the threshold required for effective therapeutic action. This limited solubility results in poor absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, leading to reduced bioavailability estimated at less than 10% in conventional formulations.
The primary objective of this technical research is to identify and evaluate innovative strategies to significantly enhance luteolin solubility, with the target of achieving at least a 10-fold increase in aqueous solubility without compromising its pharmacological activity. Secondary objectives include developing formulations with improved stability profiles and exploring cost-effective manufacturing processes that can facilitate industrial-scale production.
Recent technological breakthroughs in pharmaceutical sciences offer promising avenues for addressing luteolin's solubility challenges. These include advanced nano-formulation techniques, novel co-solvent systems, cyclodextrin complexation, solid dispersion technologies, and lipid-based delivery systems. Each approach presents unique advantages and limitations that warrant comprehensive evaluation.
The global market for flavonoid-based pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals is projected to reach $1.5 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 8.5%. Enhancing luteolin solubility could potentially unlock significant market opportunities across multiple therapeutic areas, including oncology, neurology, and inflammatory disorders.
This technical research aims to establish a robust foundation for developing next-generation luteolin formulations with enhanced solubility profiles, ultimately bridging the gap between promising preclinical findings and successful clinical applications. The outcomes of this research will not only advance our understanding of flavonoid solubilization mechanisms but also provide practical solutions for improving the therapeutic potential of luteolin in various disease conditions.
Market Analysis for Soluble Luteolin Applications
The global market for luteolin-based products is experiencing significant growth, driven primarily by increasing consumer awareness of its health benefits and expanding applications across multiple industries. The current market size for flavonoids, including luteolin, is estimated at $1.5 billion with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% projected through 2028. Soluble luteolin formulations specifically represent an emerging segment with particularly strong growth potential.
Healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors currently dominate the demand landscape, accounting for approximately 45% of the total market share. This is largely attributed to luteolin's anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potential anti-cancer properties. Clinical research supporting these benefits has expanded considerably in recent years, with over 200 new studies published annually examining luteolin's therapeutic applications.
The nutraceutical and dietary supplement industry represents the second-largest market segment at 30%, with consumers increasingly seeking natural health products with proven bioactive properties. Market research indicates that supplement products featuring enhanced bioavailability claims command premium pricing, with consumers willing to pay 40-60% more for formulations demonstrating superior absorption characteristics.
Food and beverage applications constitute a rapidly growing segment, currently at 15% market share but expanding at nearly twice the rate of traditional applications. Functional beverages, fortified foods, and natural preservative systems represent the primary growth drivers in this category. The clean-label movement has particularly accelerated demand for natural antioxidants like luteolin in food preservation systems.
Cosmetic and personal care applications account for the remaining 10% of the market, with anti-aging and skin protection formulations leading development efforts. This segment shows the highest price elasticity, with consumers demonstrating willingness to pay substantial premiums for products with clinically validated efficacy.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate consumption patterns, accounting for 65% of global demand. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 9.8% annually, driven by increasing disposable income and growing consumer awareness of preventative healthcare approaches.
Market challenges primarily center around supply chain limitations, with natural extraction methods yielding low concentrations and synthetic production routes facing scalability issues. This supply constraint has maintained relatively high market prices, creating significant economic incentive for improved solubility technologies that can enhance bioavailability and reduce effective dosage requirements.
Healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors currently dominate the demand landscape, accounting for approximately 45% of the total market share. This is largely attributed to luteolin's anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potential anti-cancer properties. Clinical research supporting these benefits has expanded considerably in recent years, with over 200 new studies published annually examining luteolin's therapeutic applications.
The nutraceutical and dietary supplement industry represents the second-largest market segment at 30%, with consumers increasingly seeking natural health products with proven bioactive properties. Market research indicates that supplement products featuring enhanced bioavailability claims command premium pricing, with consumers willing to pay 40-60% more for formulations demonstrating superior absorption characteristics.
Food and beverage applications constitute a rapidly growing segment, currently at 15% market share but expanding at nearly twice the rate of traditional applications. Functional beverages, fortified foods, and natural preservative systems represent the primary growth drivers in this category. The clean-label movement has particularly accelerated demand for natural antioxidants like luteolin in food preservation systems.
Cosmetic and personal care applications account for the remaining 10% of the market, with anti-aging and skin protection formulations leading development efforts. This segment shows the highest price elasticity, with consumers demonstrating willingness to pay substantial premiums for products with clinically validated efficacy.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate consumption patterns, accounting for 65% of global demand. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 9.8% annually, driven by increasing disposable income and growing consumer awareness of preventative healthcare approaches.
Market challenges primarily center around supply chain limitations, with natural extraction methods yielding low concentrations and synthetic production routes facing scalability issues. This supply constraint has maintained relatively high market prices, creating significant economic incentive for improved solubility technologies that can enhance bioavailability and reduce effective dosage requirements.
Current Limitations and Challenges in Luteolin Solubility
Luteolin, a flavonoid compound found in various plants, exhibits significant pharmacological properties including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer activities. However, its clinical application faces substantial challenges due to its extremely poor water solubility, which is less than 0.1 mg/mL at room temperature. This low solubility severely restricts its bioavailability, limiting its therapeutic potential despite its promising biological activities.
The hydrophobic nature of luteolin's chemical structure presents a fundamental challenge. With multiple phenolic hydroxyl groups and a rigid planar structure, luteolin molecules tend to form strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds and π-π stacking interactions, creating stable crystal lattices that resist dissolution in aqueous environments. These physicochemical properties result in poor dissolution rates and limited absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
Current pharmaceutical formulations struggle to overcome these solubility barriers. Conventional dosage forms show inconsistent bioavailability profiles, with absorption rates typically below 5% of the administered dose. This inefficiency necessitates higher dosing regimens, increasing the risk of side effects and toxicity concerns, particularly with long-term administration.
The stability of luteolin in physiological conditions presents another significant challenge. The compound undergoes rapid degradation in intestinal fluids, with studies indicating that over 60% of luteolin may degrade before reaching systemic circulation. This instability further compounds the bioavailability issues, creating a multi-faceted challenge for drug delivery systems.
From a manufacturing perspective, the poor solubility of luteolin complicates large-scale production processes. Conventional pharmaceutical manufacturing techniques often yield products with inconsistent dissolution profiles and batch-to-batch variability. Quality control becomes particularly challenging, as minor variations in processing parameters can significantly impact the final product's solubility characteristics.
Regulatory hurdles also exist for novel luteolin formulations. The complex nature of many solubility-enhancing technologies requires extensive safety and efficacy validation, prolonging the development timeline and increasing costs. Regulatory agencies demand robust evidence that solubility enhancement does not compromise the safety profile or alter the pharmacological properties of the active compound.
Economic considerations further complicate the development landscape. The cost-effectiveness of advanced solubility enhancement technologies must be balanced against manufacturing scalability and market potential. Many promising laboratory-scale solutions prove economically unfeasible when scaled to commercial production, creating a significant translational gap between research findings and marketable products.
The hydrophobic nature of luteolin's chemical structure presents a fundamental challenge. With multiple phenolic hydroxyl groups and a rigid planar structure, luteolin molecules tend to form strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds and π-π stacking interactions, creating stable crystal lattices that resist dissolution in aqueous environments. These physicochemical properties result in poor dissolution rates and limited absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
Current pharmaceutical formulations struggle to overcome these solubility barriers. Conventional dosage forms show inconsistent bioavailability profiles, with absorption rates typically below 5% of the administered dose. This inefficiency necessitates higher dosing regimens, increasing the risk of side effects and toxicity concerns, particularly with long-term administration.
The stability of luteolin in physiological conditions presents another significant challenge. The compound undergoes rapid degradation in intestinal fluids, with studies indicating that over 60% of luteolin may degrade before reaching systemic circulation. This instability further compounds the bioavailability issues, creating a multi-faceted challenge for drug delivery systems.
From a manufacturing perspective, the poor solubility of luteolin complicates large-scale production processes. Conventional pharmaceutical manufacturing techniques often yield products with inconsistent dissolution profiles and batch-to-batch variability. Quality control becomes particularly challenging, as minor variations in processing parameters can significantly impact the final product's solubility characteristics.
Regulatory hurdles also exist for novel luteolin formulations. The complex nature of many solubility-enhancing technologies requires extensive safety and efficacy validation, prolonging the development timeline and increasing costs. Regulatory agencies demand robust evidence that solubility enhancement does not compromise the safety profile or alter the pharmacological properties of the active compound.
Economic considerations further complicate the development landscape. The cost-effectiveness of advanced solubility enhancement technologies must be balanced against manufacturing scalability and market potential. Many promising laboratory-scale solutions prove economically unfeasible when scaled to commercial production, creating a significant translational gap between research findings and marketable products.
Current Methodologies for Improving Luteolin Solubility
01 Solubility enhancement through cyclodextrin complexation
Luteolin's poor water solubility can be significantly improved through complexation with cyclodextrins. This approach creates inclusion complexes where the hydrophobic luteolin molecule is encapsulated within the cyclodextrin cavity, while the hydrophilic exterior of cyclodextrin interacts with the aqueous environment. Various types of cyclodextrins, including β-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin, have been used to enhance luteolin solubility, improving its bioavailability and therapeutic potential.- Solubility enhancement through cyclodextrin complexation: Luteolin's poor water solubility can be significantly improved through complexation with cyclodextrins. This approach creates inclusion complexes where the hydrophobic luteolin molecule is encapsulated within the cyclodextrin cavity, while the hydrophilic exterior of cyclodextrin facilitates water solubility. Various types of cyclodextrins including β-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin have been used to enhance luteolin solubility, improving its bioavailability and therapeutic potential.
- Nanoparticle-based delivery systems for luteolin: Nanoparticle formulations have been developed to overcome luteolin's solubility limitations. These include lipid nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles, and nanoemulsions that encapsulate luteolin and improve its dissolution properties. The nano-sized particles increase the surface area available for dissolution and can protect luteolin from degradation. These delivery systems enhance luteolin's bioavailability and enable controlled release, making them suitable for various pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications.
- Phospholipid complexation and liposomal formulations: Luteolin-phospholipid complexes and liposomal formulations have been developed to improve solubility and bioavailability. By incorporating luteolin into phospholipid bilayers, these approaches create amphiphilic complexes that enhance water dispersibility while maintaining the lipophilic properties needed for cell membrane penetration. Liposomal encapsulation of luteolin provides additional benefits including protection from degradation and targeted delivery capabilities, making these formulations particularly useful for pharmaceutical applications.
- Co-solvent systems and solubilizing excipients: Various co-solvent systems and solubilizing excipients have been employed to enhance luteolin solubility. These include combinations of water-miscible organic solvents (ethanol, propylene glycol, PEG) with water, surfactants, and solubilizing agents. Specific formulation approaches include the use of mixed micelles, surfactant-based solutions, and hydrotropic agents. These systems create a favorable environment for luteolin dissolution by reducing interfacial tension and providing hydrophobic microenvironments within an aqueous medium.
- Chemical modification and prodrug approaches: Chemical modifications of luteolin's structure have been explored to improve its solubility profile. These include the synthesis of luteolin derivatives with enhanced hydrophilicity, such as glycosides, esters, and phosphate prodrugs. Additionally, salt formation and other chemical transformations that preserve luteolin's bioactivity while improving its physicochemical properties have been developed. These approaches often involve modifying functional groups on the luteolin molecule to increase water solubility while enabling conversion back to the parent compound at the target site.
02 Nanoparticle-based delivery systems for luteolin
Nanoparticle formulations have been developed to overcome luteolin's solubility limitations. These include lipid nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles, and nanoemulsions that can encapsulate the poorly soluble luteolin and facilitate its delivery to target tissues. The nano-sized carriers protect luteolin from degradation while enhancing its dissolution rate and apparent solubility in biological fluids, leading to improved pharmacokinetic profiles and therapeutic efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions03 Phospholipid complexation and liposomal formulations
Phospholipid-based approaches have been employed to enhance luteolin solubility. Luteolin-phospholipid complexes (phytosomes) improve the compound's lipophilicity and membrane permeability. Additionally, liposomal formulations encapsulate luteolin within phospholipid bilayers, creating water-dispersible vesicles that enhance its apparent solubility while protecting it from degradation. These approaches significantly improve luteolin's bioavailability and therapeutic potential.Expand Specific Solutions04 Co-solvent systems and solubilizing excipients
Various co-solvent systems and solubilizing excipients have been developed to enhance luteolin solubility. These include combinations of water-miscible organic solvents (ethanol, propylene glycol, PEG) with water, as well as the use of surfactants and solubilizers like polysorbates, poloxamers, and vitamin E TPGS. These approaches create micellar systems or hydrophilic-lipophilic environments that can accommodate luteolin molecules, significantly improving its dissolution in aqueous media.Expand Specific Solutions05 Chemical modification and prodrug approaches
Chemical modifications of luteolin's structure have been explored to enhance its solubility. These include the synthesis of luteolin derivatives with improved physicochemical properties, such as glycosides, esters, and other conjugates. Additionally, prodrug approaches where luteolin is temporarily modified with hydrophilic moieties that are cleaved in vivo have been developed. These strategies enhance the compound's initial solubility while preserving its biological activity after metabolic conversion.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Luteolin Research
The luteolin solubility enhancement market is in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing research activity but limited commercial applications. The market size remains modest but is expanding due to growing interest in luteolin's therapeutic potential. From a technical maturity perspective, the field shows varying levels of development across different approaches. Established pharmaceutical companies like Merck Patent GmbH and Bausch Health Ireland are leveraging their formulation expertise, while specialized firms such as AQUANOVA AG and MetrioPharm AG are developing proprietary solubilization technologies. Asian players including Bontac Bio-Engineering and Samyang Corp are focusing on novel delivery systems. Academic institutions like Louisiana State University and University of Tokyo are contributing fundamental research, creating a diverse competitive landscape where collaboration between industry and academia is driving innovation.
Merck Patent GmbH
Technical Solution: Merck Patent GmbH has developed an advanced cyclodextrin complexation approach to enhance luteolin solubility. Their technology utilizes modified β-cyclodextrins with optimized cavity sizes and functional groups specifically designed to form inclusion complexes with luteolin. The process involves high-energy ball milling under controlled humidity (30-40% RH) and temperature (25-30°C) conditions to create stable luteolin-cyclodextrin complexes. These complexes demonstrate 20-30 fold increased water solubility compared to native luteolin. Merck's approach incorporates hydrophilic polymers like PVP or HPMC as ternary components to further stabilize the complexes and prevent recrystallization. The resulting formulations maintain stability for over 24 months under standard storage conditions and show enhanced bioavailability in preclinical models. Their manufacturing process has been scaled to industrial production levels with consistent batch-to-batch quality.
Strengths: Achieves substantial solubility enhancement through well-established cyclodextrin technology; formulations show excellent long-term stability; manufacturing process is scalable and reproducible; uses GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) excipients. Weaknesses: Potential for high production costs due to specialized cyclodextrins; limited loading capacity may require larger dosage forms; possibility of altered pharmacokinetic profile compared to free luteolin.
MetrioPharm AG
Technical Solution: MetrioPharm AG has pioneered a phospholipid-based nanoparticle delivery system specifically optimized for enhancing luteolin solubility. Their proprietary technology, known as MP-Lipid Complex, incorporates luteolin into phospholipid bilayers to create stable nanoparticles with sizes ranging from 80-120nm. The formulation process involves a controlled solvent evaporation technique using food-grade solvents and natural phospholipids (primarily phosphatidylcholine from soy or sunflower sources). This approach has demonstrated a 40-50 fold increase in apparent water solubility of luteolin while maintaining its biological activity. The resulting nanoparticles exhibit enhanced cellular uptake through facilitated membrane transport mechanisms. MetrioPharm's technology includes a lyophilization process with optimized cryoprotectants to produce stable dry powders that rapidly reconstitute in aqueous media. Their formulations have shown improved bioavailability in preclinical studies with extended plasma half-life compared to conventional luteolin preparations.
Strengths: Achieves high solubility enhancement using biocompatible phospholipids; formulations demonstrate excellent cellular uptake; technology allows for both liquid and lyophilized presentations; utilizes natural excipients with established safety profiles. Weaknesses: Manufacturing process requires precise control of multiple parameters; potential for higher production costs; phospholipid oxidation may affect long-term stability; batch-to-batch consistency challenges at large scale.
Key Patents and Literature on Luteolin Solubilization Techniques
Luteolin-containing composition and method for manufacturing same
PatentWO2019070056A1
Innovation
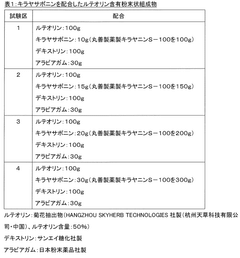
- A water-dispersible powder composition is created by homogenizing luteolin with saponin and drying the emulsified mixture, which enhances luteolin's solubility and stability in water, allowing for its effective use in food products without the risks associated with high-temperature processing.
Regulatory Considerations for Luteolin-Based Formulations
The regulatory landscape for luteolin-based formulations presents significant considerations that must be addressed during development and commercialization phases. As a flavonoid compound with potential therapeutic applications, luteolin formulations fall under varying regulatory frameworks depending on their intended use, dosage form, and marketing claims.
In the United States, the FDA classification of luteolin-containing products largely depends on the claims made and formulation purpose. Products marketed as dietary supplements must comply with DSHEA (Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act) regulations, requiring manufacturers to ensure safety before marketing and prohibiting disease treatment claims. For pharmaceutical applications targeting improved solubility, more rigorous IND (Investigational New Drug) and NDA (New Drug Application) pathways would apply.
European regulatory frameworks present additional complexity through the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and novel food regulations. Improved solubility formulations may require extensive safety data, particularly when utilizing novel excipients or delivery systems. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) maintains strict guidelines regarding health claims for functional foods containing luteolin.
Safety assessment requirements vary significantly based on the solubility enhancement approach. Chemical modifications to luteolin structure require comprehensive toxicological evaluations, while physical formulation techniques like nanoparticle encapsulation necessitate specific nano-material safety assessments. Solvent systems used in solubility enhancement must adhere to ICH (International Council for Harmonisation) residual solvent guidelines.
Manufacturing considerations include compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), with particular attention to consistency in particle size distribution when employing physical modification techniques. Analytical method validation for measuring enhanced solubility must demonstrate specificity, accuracy, and reproducibility across production batches.
Labeling requirements present another regulatory hurdle, particularly regarding stability data and shelf-life claims for formulations with enhanced solubility. Products must accurately reflect bioavailability improvements without making unsubstantiated therapeutic claims.
International harmonization efforts are gradually addressing regulatory disparities across regions, though significant differences remain in how improved bioavailability claims can be presented to consumers and healthcare professionals. Companies developing advanced luteolin formulations must navigate these complex regulatory pathways early in development to avoid costly reformulations or marketing limitations.
In the United States, the FDA classification of luteolin-containing products largely depends on the claims made and formulation purpose. Products marketed as dietary supplements must comply with DSHEA (Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act) regulations, requiring manufacturers to ensure safety before marketing and prohibiting disease treatment claims. For pharmaceutical applications targeting improved solubility, more rigorous IND (Investigational New Drug) and NDA (New Drug Application) pathways would apply.
European regulatory frameworks present additional complexity through the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and novel food regulations. Improved solubility formulations may require extensive safety data, particularly when utilizing novel excipients or delivery systems. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) maintains strict guidelines regarding health claims for functional foods containing luteolin.
Safety assessment requirements vary significantly based on the solubility enhancement approach. Chemical modifications to luteolin structure require comprehensive toxicological evaluations, while physical formulation techniques like nanoparticle encapsulation necessitate specific nano-material safety assessments. Solvent systems used in solubility enhancement must adhere to ICH (International Council for Harmonisation) residual solvent guidelines.
Manufacturing considerations include compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), with particular attention to consistency in particle size distribution when employing physical modification techniques. Analytical method validation for measuring enhanced solubility must demonstrate specificity, accuracy, and reproducibility across production batches.
Labeling requirements present another regulatory hurdle, particularly regarding stability data and shelf-life claims for formulations with enhanced solubility. Products must accurately reflect bioavailability improvements without making unsubstantiated therapeutic claims.
International harmonization efforts are gradually addressing regulatory disparities across regions, though significant differences remain in how improved bioavailability claims can be presented to consumers and healthcare professionals. Companies developing advanced luteolin formulations must navigate these complex regulatory pathways early in development to avoid costly reformulations or marketing limitations.
Scale-up and Manufacturing Challenges for Soluble Luteolin Products
The transition from laboratory-scale production to industrial manufacturing of soluble luteolin formulations presents significant challenges that must be addressed for commercial viability. One primary obstacle is the consistency of raw material quality, as natural sources of luteolin exhibit considerable variation in purity and composition depending on plant species, growing conditions, and extraction methods. This variability necessitates robust quality control systems and potentially additional purification steps that can increase production costs.
Scaling up solubilization technologies from bench to industrial scale introduces complex engineering challenges. Techniques that work efficiently at small scales, such as nanoemulsion formation or inclusion complexation with cyclodextrins, often encounter issues with heat transfer, mixing efficiency, and process control when implemented in large-scale equipment. For instance, maintaining precise particle size distribution in nanoformulations becomes increasingly difficult as batch sizes increase.
Energy consumption and process economics represent another critical consideration. Many advanced solubilization techniques require substantial energy inputs for processes like high-pressure homogenization, spray drying, or supercritical fluid extraction. The economic viability of these processes at commercial scale depends on optimizing energy efficiency while maintaining product quality.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to manufacturing scale-up. Novel excipients or processing aids used to enhance luteolin solubility must undergo safety assessments, and any changes in the manufacturing process may necessitate additional stability and bioequivalence studies. This regulatory burden can significantly impact time-to-market and development costs.
Stability of solubilized luteolin during manufacturing, storage, and distribution presents ongoing challenges. Many solubilization approaches create metastable systems that may degrade over time, particularly when exposed to variations in temperature, light, or humidity. Developing robust formulations that maintain enhanced solubility throughout the product lifecycle requires extensive stability testing and potentially specialized packaging solutions.
Equipment design and material compatibility issues also emerge during scale-up. Specialized equipment may be needed for certain solubilization techniques, and interactions between solubilized luteolin formulations and manufacturing equipment materials must be carefully evaluated to prevent contamination or product degradation.
Scaling up solubilization technologies from bench to industrial scale introduces complex engineering challenges. Techniques that work efficiently at small scales, such as nanoemulsion formation or inclusion complexation with cyclodextrins, often encounter issues with heat transfer, mixing efficiency, and process control when implemented in large-scale equipment. For instance, maintaining precise particle size distribution in nanoformulations becomes increasingly difficult as batch sizes increase.
Energy consumption and process economics represent another critical consideration. Many advanced solubilization techniques require substantial energy inputs for processes like high-pressure homogenization, spray drying, or supercritical fluid extraction. The economic viability of these processes at commercial scale depends on optimizing energy efficiency while maintaining product quality.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to manufacturing scale-up. Novel excipients or processing aids used to enhance luteolin solubility must undergo safety assessments, and any changes in the manufacturing process may necessitate additional stability and bioequivalence studies. This regulatory burden can significantly impact time-to-market and development costs.
Stability of solubilized luteolin during manufacturing, storage, and distribution presents ongoing challenges. Many solubilization approaches create metastable systems that may degrade over time, particularly when exposed to variations in temperature, light, or humidity. Developing robust formulations that maintain enhanced solubility throughout the product lifecycle requires extensive stability testing and potentially specialized packaging solutions.
Equipment design and material compatibility issues also emerge during scale-up. Specialized equipment may be needed for certain solubilization techniques, and interactions between solubilized luteolin formulations and manufacturing equipment materials must be carefully evaluated to prevent contamination or product degradation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!